diff options
| author | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2024-04-27 11:08:07 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2024-04-27 11:08:07 +0000 |
| commit | c69cb8cc094cc916adbc516b09e944cd3d137c01 (patch) | |
| tree | f2878ec41fb6d0e3613906c6722fc02b934eeb80 /docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md | |
| parent | Initial commit. (diff) | |
| download | netdata-c69cb8cc094cc916adbc516b09e944cd3d137c01.tar.xz netdata-c69cb8cc094cc916adbc516b09e944cd3d137c01.zip | |
Adding upstream version 1.29.3.upstream/1.29.3upstream
Signed-off-by: Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org>
Diffstat (limited to 'docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md | 147 |
1 files changed, 147 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md b/docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000..f37dadc --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md @@ -0,0 +1,147 @@ +<!-- +title: "Monitor and visualize anomalies with Netdata (part 2)" +description: "Using unsupervised anomaly detection and machine learning, get notified " +image: /img/seo/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.png +author: "Joel Hans" +author_title: "Editorial Director, Technical & Educational Resources" +author_img: "/img/authors/joel-hans.jpg" +custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/guides/monitor/visualize-monitor-anomalies.md +--> + +# Monitor and visualize anomalies with Netdata (part 2) + +Welcome to part 2 of our series of guides on using _unsupervised anomaly detection_ to detect issues with your systems, +containers, and applications using the open-source Netdata Agent. For an introduction to detecting anomalies and +monitoring associated metrics, see [part 1](/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md), which covers prerequisites and +configuration basics. + +With anomaly detection in the Netdata Agent set up, you will now want to visualize and monitor which charts have +anomalous data, when, and where to look next. + +> 💡 In certain cases, the anomalies collector doesn't start immediately after restarting the Netdata Agent. If this +> happens, you won't see the dashboard section or the relevant [charts](#visualize-anomalies-in-charts) right away. Wait +> a minute or two, refresh, and look again. If the anomalies charts and alarms are still not present, investigate the +> error log with `less /var/log/netdata/error.log | grep anomalies`. + +## Test anomaly detection + +Time to see the Netdata Agent's unsupervised anomaly detection in action. To trigger anomalies on the Nginx web server, +use `ab`, otherwise known as [Apache Bench](https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/programs/ab.html). Despite its name, it +works just as well with Nginx web servers. Install it on Ubuntu/Debian systems with `sudo apt install apache2-utils`. + +> 💡 If you haven't followed the guide's example of using Nginx, an easy way to test anomaly detection on your node is +> to use the `stress-ng` command, which is available on most Linux distributions. Run `stress-ng --cpu 0` to create CPU +> stress or `stress-ng --vm 0` for RAM stress. Each test will cause some "collateral damage," in that you may see CPU +> utilization rise when running the RAM test, and vice versa. + +The following test creates a minimum of 10,000,000 requests for Nginx to handle, with a maximum of 10 at any given time, +with a run time of 60 seconds. If your system can handle those 10,000,000 in less than 60 seconds, `ab` will keep +sending requests until the timer runs out. + +```bash +ab -k -c 10 -t 60 -n 10000000 http://127.0.0.1/ +``` + +Let's see how Netdata detects this anomalous behavior and propagates information to you through preconfigured alarms and +dashboards that automatically organize anomaly detection metrics into meaningful charts to help you begin root cause +analysis (RCA). + +## Monitor anomalies with alarms + +The anomalies collector creates two "classes" of alarms for each chart captured by the `charts_regex` setting. All these +alarms are preconfigured based on your [configuration in +`anomalies.conf`](/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md#configure-the-anomalies-collector). With the `charts_regex` +and `charts_to_exclude` settings from [part 1](/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md) of this guide series, the +Netdata Agent creates 32 alarms driven by unsupervised anomaly detection. + +The first class triggers warning alarms when the average anomaly probability for a given chart has stayed above 50% for +at least the last two minutes. + +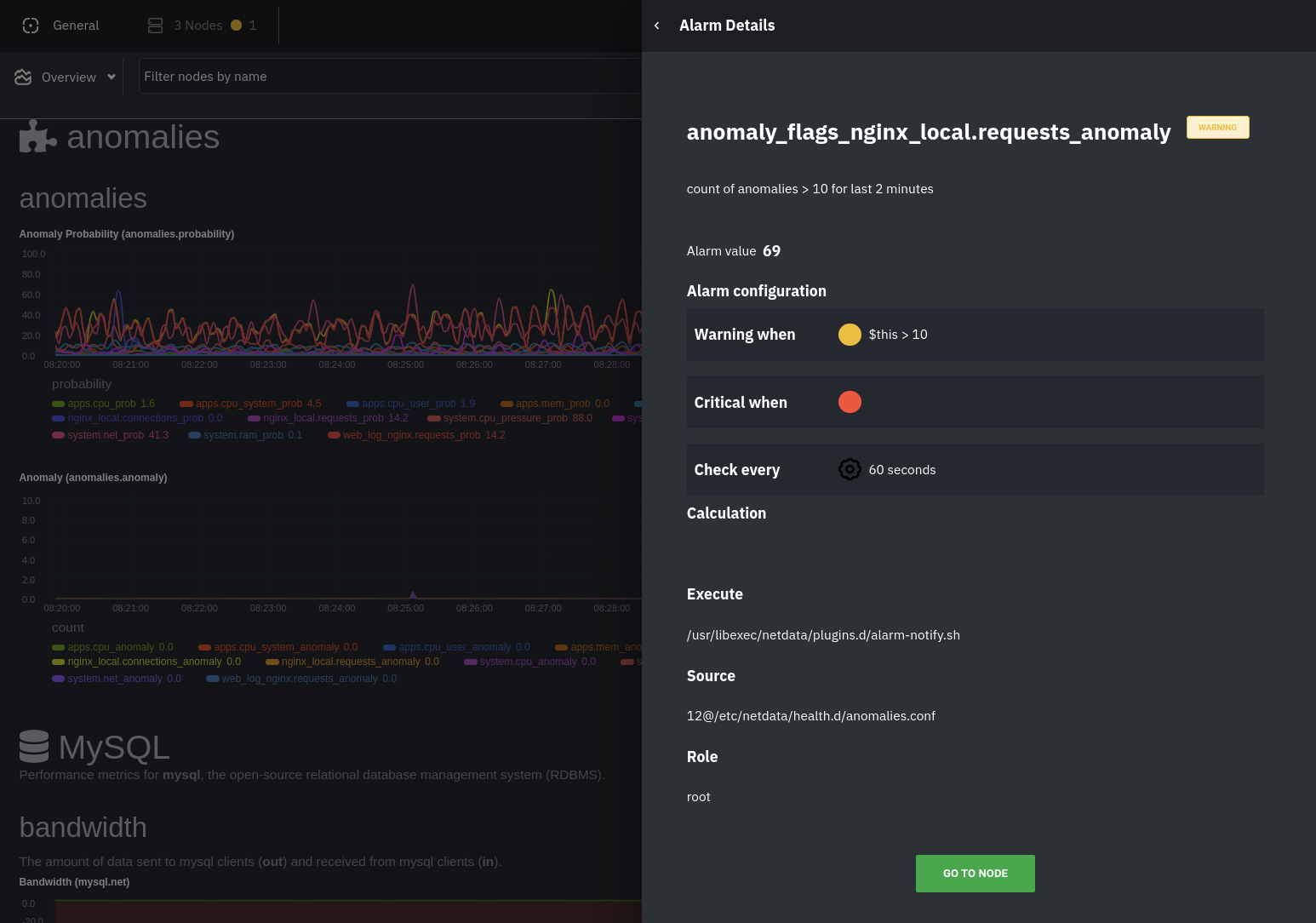 + +The second class triggers warning alarms when the number of anomalies in the last two minutes hits 10 or higher. + +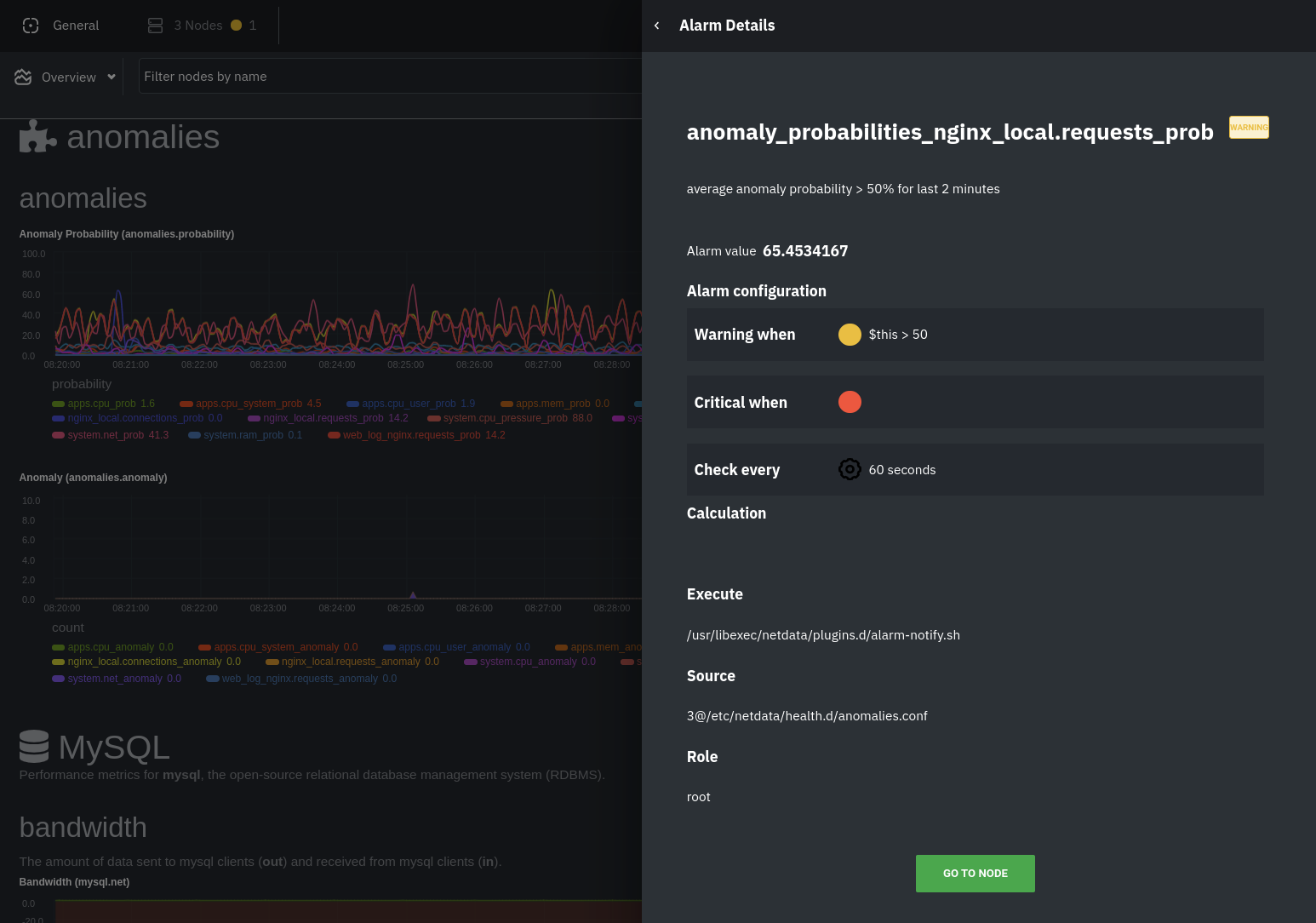 + +If you see either of these alarms in Netdata Cloud, the local Agent dashboard, or on your preferred notification +platform, it's a safe bet that the node's current metrics have deviated from normal. That doesn't necessarily mean +there's a full-blown incident, depending on what application/service you're using anomaly detection on, but it's worth +further investigation. + +As you use the anomalies collector, you may find that the default settings provide too many or too few genuine alarms. +In this case, [configure the alarm](/docs/monitor/configure-alarms.md) with `sudo ./edit-config +health.d/anomalies.conf`. Take a look at the `lookup` line syntax in the [health +reference](/health/REFERENCE.md#alarm-line-lookup) to understand how the anomalies collector automatically creates +alarms for any dimension on the `anomalies_local.probability` and `anomalies_local.anomaly` charts. + +## Visualize anomalies in charts + +In either [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud) or the local Agent dashboard at `http://NODE:19999`, click on the +**Anomalies** [section](/web/gui/README.md#sections) to see the pair of anomaly detection charts, which are +preconfigured to visualize per-second anomaly metrics based on your [configuration in +`anomalies.conf`](/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md#configure-the-anomalies-collector). + +These charts have the contexts `anomalies.probability` and `anomalies.anomaly`. Together, these charts +create meaningful visualizations for immediately recognizing not only that something is going wrong on your node, but +give context as to where to look next. + +The `anomalies_local.probability` chart shows the probability that the latest observed data is anomalous, based on the +trained model. The `anomalies_local.anomaly` chart visualizes 0→1 predictions based on whether the latest observed +data is anomalous based on the trained model. Both charts share the same dimensions, which you configured via +`charts_regex` and `charts_to_exclude` in [part 1](/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md). + +In other words, the `probability` chart shows the amplitude of the anomaly, whereas the `anomaly` chart provides quick +yes/no context. + +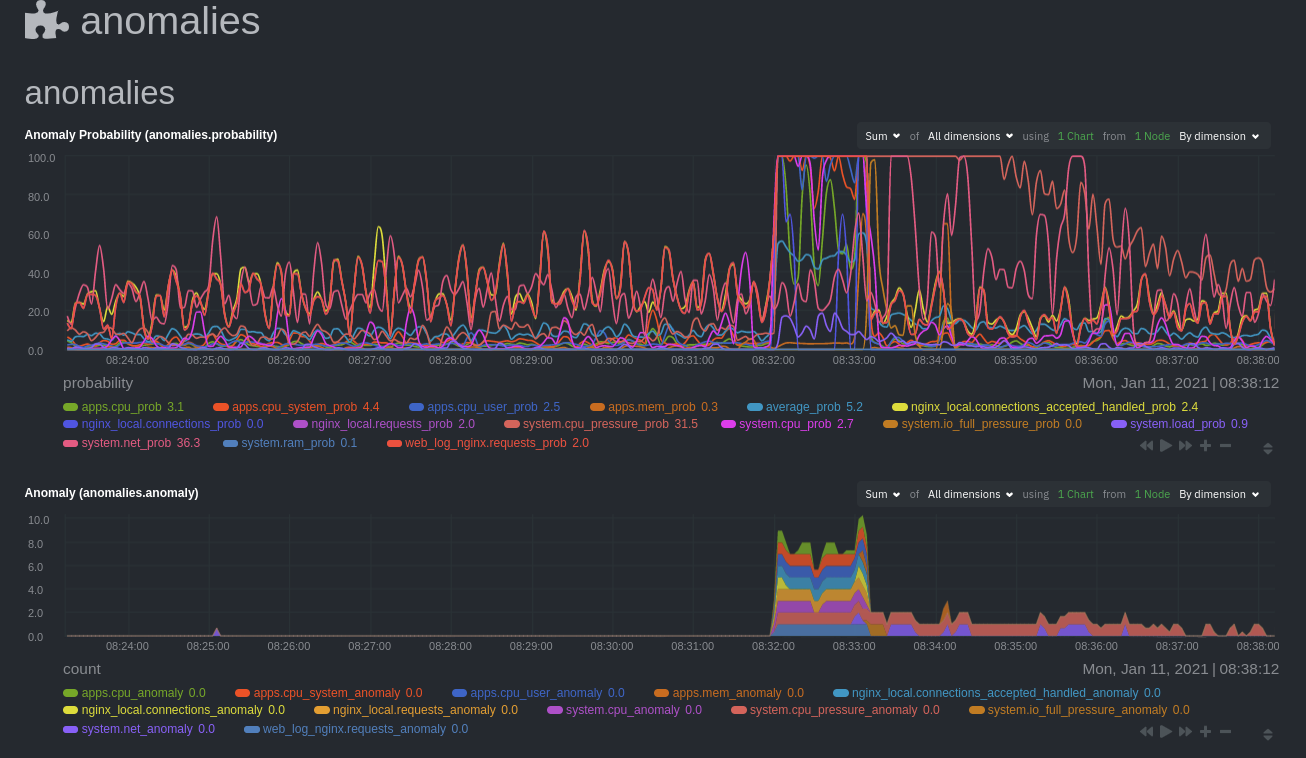 + +Before `08:32:00`, both charts show little in the way of verified anomalies. Based on the metrics the anomalies +collector has trained on, a certain percentage of anomaly probability score is normal, as seen in the +`web_log_nginx_requests_prob` dimension and a few others. What you're looking for is large deviations from the "noise" +in the `anomalies.probability` chart, or any increments to the `anomalies.anomaly` chart. + +Unsurprisingly, the stress test that began at `08:32:00` caused significant changes to these charts. The three +dimensions that immediately shot to 100% anomaly probability, and remained there during the test, were +`web_log_nginx.requests_prob`, `nginx_local.connections_accepted_handled_prob`, and `system.cpu_pressure_prob`. + +## Build an anomaly detection dashboard + +[Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud) features a drag-and-drop [dashboard +editor](/docs/visualize/create-dashboards.md) that helps you create entirely new dashboards with charts targeted for +your specific applications. + +For example, here's a dashboard designed for visualizing anomalies present in an Nginx web server, including +documentation about why the dashboard exists and where to look next based on what you're seeing: + +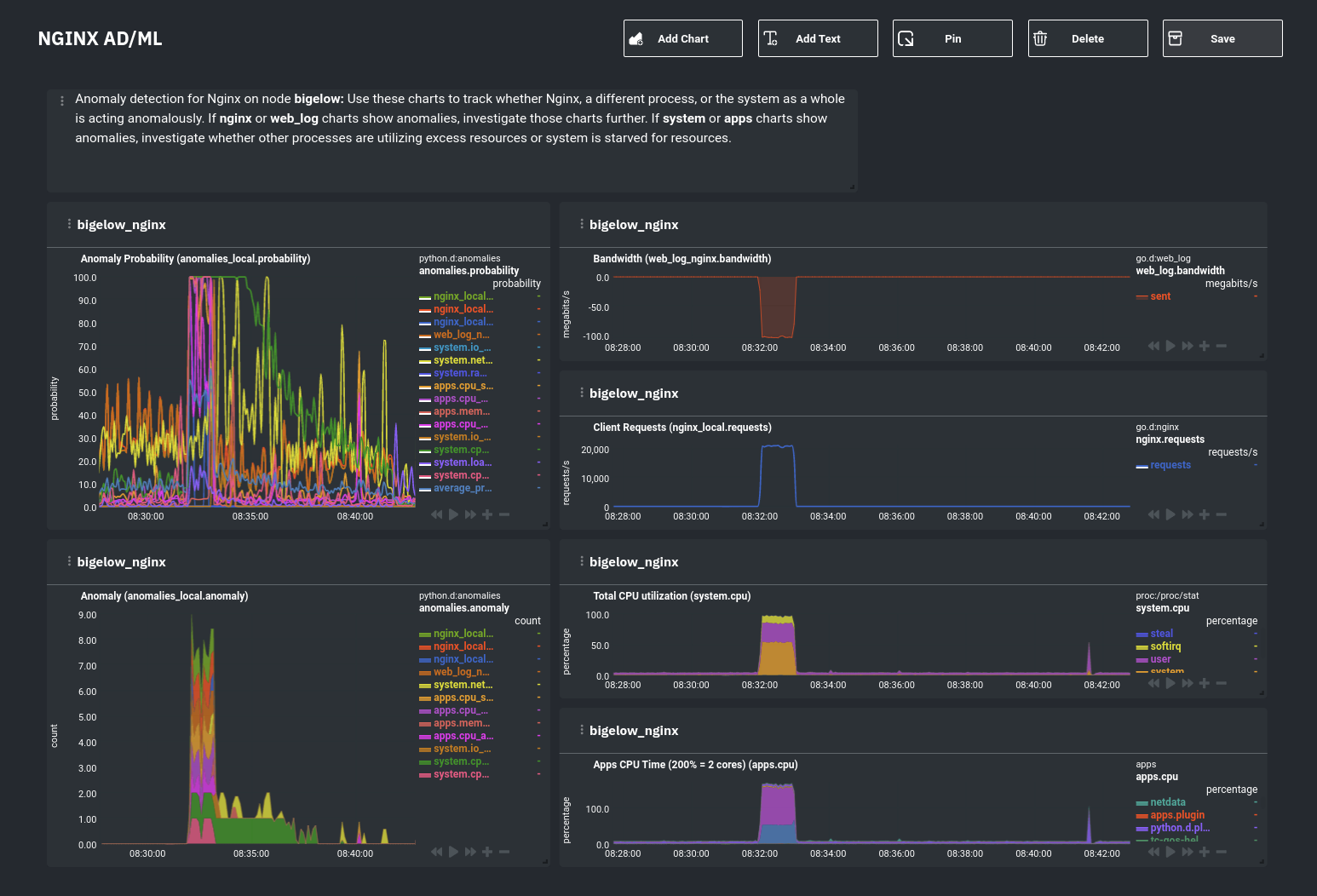 + +Use the anomaly charts for instant visual identification of potential anomalies, and then Nginx-specific charts, in the +right column, to validate whether the probability and anomaly counters are showing a valid incident worth further +investigation using [Metric Correlations](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations) to narrow +the dashboard into only the charts relevant to what you're seeing from the anomalies collector. + +## What's next? + +Between this guide and [part 1](/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md), which covered setup and configuration, you +now have a fundamental understanding of how unsupervised anomaly detection in Netdata works, from root cause to alarms +to preconfigured or custom dashboards. + +We'd love to hear your feedback on the anomalies collector. Hop over to the [community +forum](https://community.netdata.cloud/t/anomalies-collector-feedback-megathread/767), and let us know if you're already getting value from +unsupervised anomaly detection, or would like to see something added to it. You might even post a custom configuration +that works well for monitoring some other popular application, like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Redis, or anything else we +[support through collectors](/collectors/COLLECTORS.md). + +In part 3 of this series on unsupervised anomaly detection using Netdata, we'll create a custom model to apply +unsupervised anomaly detection to an entire mission-critical application. Stay tuned! + +### Related reference documentation + +- [Netdata Agent · Anomalies collector](/collectors/python.d.plugin/anomalies/README.md) +- [Netdata Cloud · Build new dashboards](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards) + +[](<>) |
