diff options
| author | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2021-03-31 12:58:11 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2021-03-31 12:58:11 +0000 |
| commit | f99c4526d94d3e04124c5c48ab4a3da6ca53a458 (patch) | |
| tree | a2ed8860030cc49f492b09b3222d593c65619800 /packaging/installer/methods | |
| parent | Adding upstream version 1.29.3. (diff) | |
| download | netdata-f99c4526d94d3e04124c5c48ab4a3da6ca53a458.tar.xz netdata-f99c4526d94d3e04124c5c48ab4a3da6ca53a458.zip | |
Adding upstream version 1.30.0.upstream/1.30.0
Signed-off-by: Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org>
Diffstat (limited to 'packaging/installer/methods')
| -rw-r--r-- | packaging/installer/methods/kickstart-64.md | 2 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md | 2 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md | 231 |
3 files changed, 107 insertions, 128 deletions
diff --git a/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart-64.md b/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart-64.md index 120cc9e11..dbb0cd464 100644 --- a/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart-64.md +++ b/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart-64.md @@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ To use `md5sum` to verify the integrity of the `kickstart-static64.sh` script yo command above, run the following: ```bash -[ "047c86a7c8905955bee39b6980a28e30" = "$(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart-static64.sh | md5sum | cut -d ' ' -f 1)" ] && echo "OK, VALID" || echo "FAILED, INVALID" +[ "33ed36d80c7db0e501b68c4c0c3ceb02" = "$(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart-static64.sh | md5sum | cut -d ' ' -f 1)" ] && echo "OK, VALID" || echo "FAILED, INVALID" ``` If the script is valid, this command will return `OK, VALID`. diff --git a/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md b/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md index f825f808e..8ad99dc4a 100644 --- a/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md +++ b/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md @@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ To use `md5sum` to verify the integrity of the `kickstart.sh` script you will do run the following: ```bash -[ "8df7a45b2abb336c84507b7c107bcba3" = "$(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh | md5sum | cut -d ' ' -f 1)" ] && echo "OK, VALID" || echo "FAILED, INVALID" +[ "35e92cd3fd8a29621e23962ac5626dfc" = "$(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh | md5sum | cut -d ' ' -f 1)" ] && echo "OK, VALID" || echo "FAILED, INVALID" ``` If the script is valid, this command will return `OK, VALID`. diff --git a/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md b/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md index 3e85928e9..f593765fc 100644 --- a/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md +++ b/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md @@ -1,25 +1,21 @@ <!-- -title: "Install Netdata on a Kubernetes cluster" -description: "Use Netdata's Helm chart to bootstrap a Netdata monitoring and troubleshooting toolkit on your Kubernetes (k8s) cluster." +title: "Deploy Kubernetes monitoring with Netdata" +description: "Deploy Netdata to monitor a Kubernetes cluster to monitor the health, performance, resource utilization, and application metrics of a Kubernetes cluster in real time." custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md --> -# Install Netdata on a Kubernetes cluster +# Deploy Kubernetes monitoring with Netdata This document details how to install Netdata on an existing Kubernetes (k8s) cluster. By following these directions, you -will use Netdata's [Helm chart](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart) to bootstrap a Netdata deployment on your cluster. -The Helm chart installs one parent pod for storing metrics and managing alarm notifications plus an additional child pod -for every node in the cluster. +will use Netdata's [Helm chart](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart) to create a Kubernetes monitoring deployment on +your cluster. -Each child pod will collect metrics from the node it runs on, in addition to [compatible -applications](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#service-discovery-and-supported-services), plus any endpoints covered -by our [generic Prometheus collector](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/agent/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus), -via [service discovery](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery/). Each child pod will also collect -[cgroups](/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md), -[Kubelet](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/agent/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubelet), and -[kube-proxy](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/agent/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubeproxy) metrics from its node. +The Helm chart installs one `parent` pod for storing metrics and managing alarm notifications, plus an additional +`child` pod for every node in the cluster, responsible for collecting metrics from the node, Kubernetes control planes, +pods/containers, and [supported application-specific +metrics](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#service-discovery-and-supported-services). -To install Netdata on a Kubernetes cluster, you need: +To deploy Kubernetes monitoring with Netdata, you need: - A working cluster running Kubernetes v1.9 or newer. - The [kubectl](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/) command line tool, within [one minor version @@ -27,12 +23,6 @@ To install Netdata on a Kubernetes cluster, you need: administrative system. - The [Helm package manager](https://helm.sh/) v3.0.0 or newer on the same administrative system. -The default configuration creates one `parent` pod, installed on one of your cluster's nodes, and a DaemonSet for -additional `child` pods. This DaemonSet ensures that every node in your k8s cluster also runs a `child` pod, including -the node that also runs `parent`. The `child` pods collect metrics and stream the information to the `parent` pod, which -uses two persistent volumes to store metrics and alarms. The `parent` pod also handles alarm notifications and enables -the Netdata dashboard using an ingress controller. - ## Install the Netdata Helm chart We recommend you install the Helm chart using our Helm repository. In the `helm install` command, replace `netdata` with @@ -43,147 +33,125 @@ helm repo add netdata https://netdata.github.io/helmchart/ helm install netdata netdata/netdata ``` -> You can also install the Netdata Helm chart by cloning the -> [repository](https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/netdata/netdata#install-by-cloning-the-repository) and manually -> running Helm against the included chart. - -### Post-installation - Run `kubectl get services` and `kubectl get pods` to confirm that your cluster now runs a `netdata` service, one -`parent` pod, and three `child` pods. +parent pod, and multiple child pods. -You've now installed Netdata on your Kubernetes cluster. See how to [access the Netdata -dashboard](#access-the-netdata-dashboard) to confirm it's working as expected, or see the next section to [configure the -Helm chart](#configure-the-netdata-helm-chart) to suit your cluster's particular setup. +You've now installed Netdata on your Kubernetes cluster. Next, it's time to opt-in and enable the powerful Kubernetes +dashboards available in Netdata Cloud. -## Configure the Netdata Helm chart +## Claim your Kubernetes cluster to Netdata Cloud -Read up on the various configuration options in the [Helm chart -documentation](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#configuration) to see if you need to change any of the options based -on your cluster's setup. +To start [Kubernetes monitoring](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes/), you must first +[claim](/claim/README.md) your Kubernetes cluster to [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud). Claiming securely +connects your Kubernetes cluster to stream metrics data to Netdata Cloud, enabling Kubernetes-specific visualizations +like the health map and time-series composite charts. -To change a setting, use the `--set` or `--values` arguments with `helm install`, for the initial deployment, or `helm upgrade` to upgrade an existing deployment. +First, find your claiming script in Netdata Cloud by clicking on your Space's dropdown, then **Manage your Space**. +Click the **Nodes** tab to reveal the `netdata-claim.sh` script for your Space in Netdata Cloud. You need the `TOKEN` +and `ROOM` values. -```bash -helm install --set a.b.c=xyz netdata netdata/netdata -helm upgrade --set a.b.c=xyz netdata netdata/netdata -``` - -For example, to change the size of the persistent metrics volume on the parent node: +Next, create a file called `override.yml`. ```bash -helm install --set parent.database.volumesize=4Gi netdata netdata/netdata -helm upgrade --set parent.database.volumesize=4Gi netdata netdata/netdata +touch override.yml ``` -### Configure service discovery - -As mentioned in the introduction, Netdata has a [service discovery -plugin](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery/#service-discovery) to identify compatible pods and collect -metrics from the service they run. The Netdata Helm chart installs this service discovery plugin into your k8s cluster. - -Service discovery scans your cluster for pods exposed on certain ports and with certain image names. By default, it -looks for its supported services on the ports they most commonly listen on, and using default image names. Service -discovery currently supports [popular -applications](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#service-discovery-and-supported-services), plus any endpoints covered -by our [generic Prometheus collector](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/agent/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus). - -If you haven't changed listening ports, image names, or other defaults, service discovery should find your pods, create -the proper configurations based on the service that pod runs, and begin monitoring them immediately after deployment. +Paste the following into your `override.yml` file, replacing instances of `ROOM` and `TOKEN` with those from the +claiming script from Netdata Cloud. These settings claim your `parent`/`child` nodes to Netdata Cloud and store more +metrics in the nodes' time-series databases. + +```yaml +parent: + claiming: + enabled: true + token: "TOKEN" + rooms: "ROOM" + +child: + claiming: + enabled: true + token: "TOKEN" + rooms: "ROOM" + configs: + netdata: + data: | + [global] + memory mode = ram + history = 3600 + [health] + enabled = no +``` -However, if you have changed some of these defaults, you need to copy a file from the Netdata Helm chart repository, -make your edits, and pass the changed file to `helm install`/`helm upgrade`. +> ❗ These override settings, along with the Helm chart's defaults, will retain an hour's worth of metrics (`history = +> 3600`, or `3600 seconds`) on each child node. Based on your metrics retention needs, and the resources available on +> your cluster, you may want to increase the `history` setting. -First, copy the file to your administrative system. +Apply these new settings: ```bash -curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/netdata/helmchart/master/charts/netdata/sdconfig/child.yml -o child.yml +helm upgrade -f override.yml netdata netdata/netdata ``` -Edit the new `child.yml` file according to your needs. See the [Helm chart -configuration](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#configuration) and the file itself for details. +The cluster terminates the old pods and creates new ones with the proper persistence and claiming configuration. You'll +see your nodes, containers, and pods appear in Netdata Cloud in a few seconds. -You can then run `helm install`/`helm upgrade` with the `--set-file` argument to use your configured `child.yml` file -instead of the default, changing the path if you copied it elsewhere. +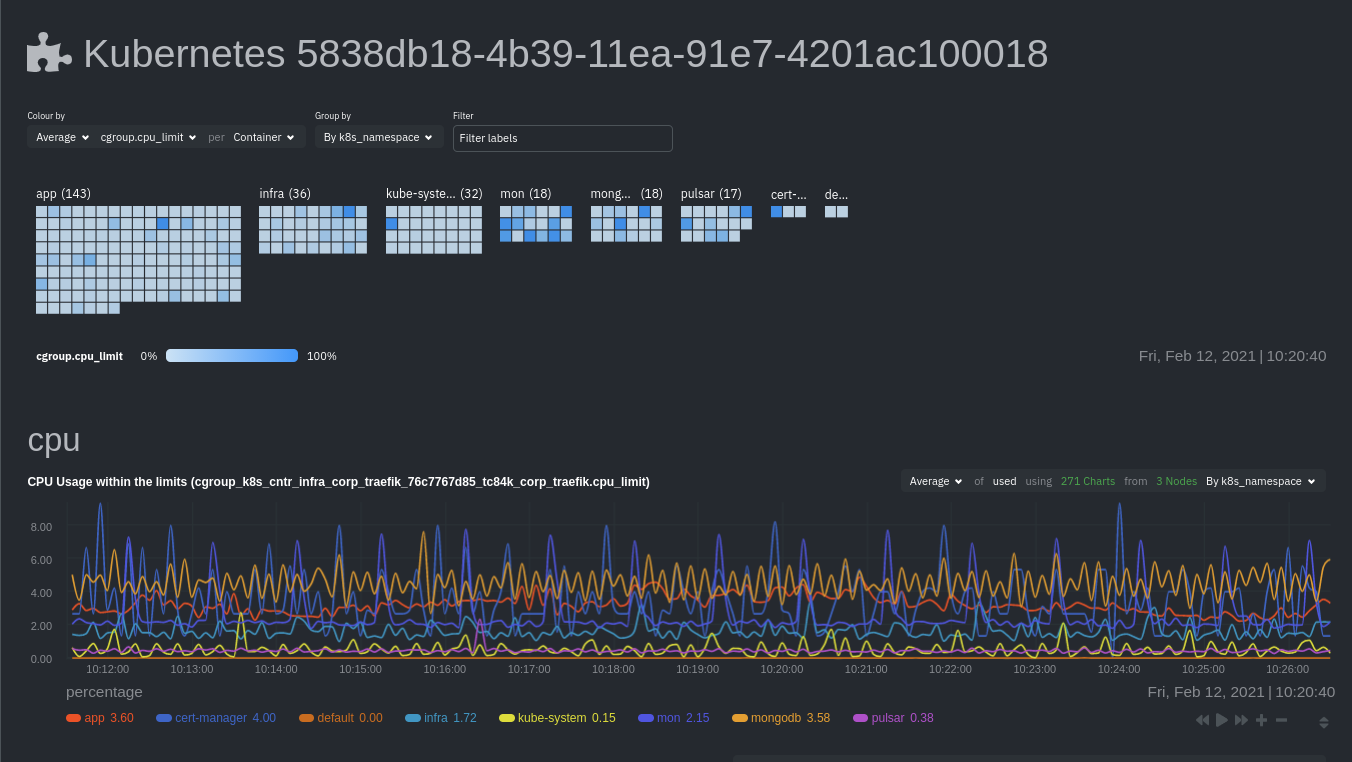 -```bash -helm install --set-file sd.child.configmap.from.value=./child.yml netdata netdata/netdata -helm upgrade --set-file sd.child.configmap.from.value=./child.yml netdata netdata/netdata -``` +If you don't need to configure your Netdata deployment, [skip down](#whats-next) to see how Kubernetes monitoring works +in Netdata, in addition to more guides and resources. -Your configured service discovery is now pushed to your cluster. +## Configure your Netdata monitoring deployment -## Access the Netdata dashboard +Read up on the various configuration options in the [Helm chart +documentation](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#configuration) if you need to tweak your Kubernetes monitoring. -Accessing the Netdata dashboard itself depends on how you set up your k8s cluster and the Netdata Helm chart. If you -installed the Helm chart with the default `service.type=ClusterIP`, you will need to forward a port to the parent pod. +Your first option is to create an `override.yml` file, if you haven't created one already for +[claiming](#claim-your-kubernetes-cluster-to-netdata-cloud), then apply the new configuration to your cluster with `helm +upgrade`. ```bash -kubectl port-forward netdata-parent-0 19999:19999 +helm upgrade -f override.yml netdata netdata/netdata ``` -You can now access the dashboard at `http://CLUSTER:19999`, replacing `CLUSTER` with the IP address or hostname of your -k8s cluster. - -If you set up the Netdata Helm chart with `service.type=LoadBalancer`, you can find the external IP for the load -balancer with `kubectl get services`, under the `EXTERNAL-IP` column. +If you want to change only a single setting, use the `--set` argument with `helm upgrade`. For example, to change the +size of the persistent metrics volume on the parent node: ```bash -kubectl get services -NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE -cockroachdb ClusterIP None <none> 26257/TCP,8080/TCP 46h -cockroachdb-public ClusterIP 10.245.148.233 <none> 26257/TCP,8080/TCP 46h -kubernetes ClusterIP 10.245.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 47h -netdata LoadBalancer 10.245.160.131 203.0.113.0 19999:32231/TCP 74m +helm upgrade --set parent.database.volumesize=4Gi netdata netdata/netdata ``` -In the above example, access the dashboard by navigating to `http://203.0.113.0:19999`. - -## Claim a Kubernetes cluster's parent pod - -You can [claim](/claim/README.md) a cluster's parent Netdata pod to see its real-time metrics alongside any other nodes -you monitor using [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud). +### Configure service discovery -> Netdata Cloud does not currently support claiming child nodes because the Helm chart does not allocate a persistent -> volume for them. +Netdata's [service discovery](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery/#service-discovery), installed as part +of the Helm chart installation, finds what services are running in a cluster's containers and automatically collects +service-level metrics from them. -Ensure persistence is enabled on the parent pod by running the following `helm upgrade` command. +Service discovery supports [popular applications](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#applications) and [Prometheus +endpoints](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#prometheus-endpoints). -```bash -helm upgrade \ - --set parent.database.persistence=true \ - --set parent.alarms.persistence=true \ - netdata netdata/netdata -``` +If your cluster runs services on non-default ports or uses non-default names, you may need to configure service +discovery to start collecting metrics from your services. You have to edit the default ConfigMap that is shipped with +the Helmchart and deploy that to your cluster. -Next, find your claiming script in Netdata Cloud by clicking on your Space's dropdown, then **Manage your Space**. Click -the **Nodes** tab. Netdata Cloud shows a script similar to the following: +First, copy the default file to your administrative system. ```bash -sudo netdata-claim.sh -token=TOKEN -rooms=ROOM1,ROOM2 -url=https://app.netdata.cloud +curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/netdata/helmchart/master/charts/netdata/sdconfig/child.yml -o child.yml ``` -You will need the values of `TOKEN` and `ROOM1,ROOM2` for the command, which sets `parent.claiming.enabled`, -`parent.claiming.token`, and `parent.claiming.rooms` to complete the parent pod claiming process. +Edit the new `child.yml` file according to your needs. See the [Helm chart +configuration](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#configuration) and the file itself for details. -Run the following `helm upgrade` command after replacing `TOKEN` and `ROOM1,ROOM2` with the values found in the claiming -script from Netdata Cloud. The quotations are required. +You can then run `helm upgrade` with the `--set-file` argument to use your configured `child.yml` file instead of the +default, changing the path if you copied it elsewhere. ```bash -helm upgrade \ - --set parent.claiming.enabled=true \ - --set parent.claiming.token="TOKEN" \ - --set parent.claiming.rooms="ROOM1,ROOM2" \ - netdata netdata/netdata +helm upgrade --set-file sd.child.configmap.from.value=./child.yml netdata netdata/netdata ``` -The cluster terminates the old parent pod and creates a new one with the proper claiming configuration. You can see your -parent pod in Netdata Cloud after a few moments. You can now [build new -dashboards](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards) using the parent pod's metrics or run [Metric -Correlations](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations) to troubleshoot anomalies. - - +Now that you pushed an edited ConfigMap to your cluster, service discovery should find and set up metrics collection +from your non-default service. ## Update/reinstall the Netdata Helm chart @@ -194,16 +162,27 @@ with the name of the release, if you changed it upon installation: helm upgrade netdata netdata/netdata ``` +To update Netdata's Helm chart to the latest version, run `helm repo update`, then deploy `upgrade` it`: + +```bash +helm repo update +helm upgrade netdata netdata/netdata +``` + ## What's next? -Read the [monitoring a Kubernetes cluster guide](/docs/guides/monitor/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md) for details on the -various metrics and charts created by the Helm chart and some best practices on real-time troubleshooting using Netdata. +[Start Kubernetes monitoring](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes/) in Netdata Cloud, which +comes with meaningful visualizations out of the box. + +Read our guide, [_Kubernetes monitoring with Netdata: Overview and +visualizations_](/docs/guides/monitor/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md), for a complete walkthrough of Netdata's Kubernetes +monitoring capabilities, including a health map of every container in your infrastructure, aggregated resource +utilization metrics, and application metrics. -Check out our [infrastructure](/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md) for details about additional k8s monitoring features, -and learn more about [configuring the Netdata Agent](/docs/configure/nodes.md) to better understand the settings you -might be interested in changing. +### Related reference documentation -To further configure Netdata for your cluster, see our [Helm chart repository](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart) and -the [service discovery repository](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery/). +- [Netdata Cloud · Kubernetes monitoring](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes/) +- [Netdata Helm chart](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart) +- [Netdata service discovery](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery/) [](<>) |
