diff options
| author | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2024-07-24 09:54:23 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2024-07-24 09:54:44 +0000 |
| commit | 836b47cb7e99a977c5a23b059ca1d0b5065d310e (patch) | |
| tree | 1604da8f482d02effa033c94a84be42bc0c848c3 /src/health/REFERENCE.md | |
| parent | Releasing debian version 1.44.3-2. (diff) | |
| download | netdata-836b47cb7e99a977c5a23b059ca1d0b5065d310e.tar.xz netdata-836b47cb7e99a977c5a23b059ca1d0b5065d310e.zip | |
Merging upstream version 1.46.3.
Signed-off-by: Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org>
Diffstat (limited to 'src/health/REFERENCE.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | src/health/REFERENCE.md | 1106 |
1 files changed, 1106 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/src/health/REFERENCE.md b/src/health/REFERENCE.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..8b0a9177e --- /dev/null +++ b/src/health/REFERENCE.md @@ -0,0 +1,1106 @@ +# Configure alerts + +Netdata's health watchdog is highly configurable, with support for dynamic thresholds, hysteresis, alert templates, and +more. You can tweak any of the existing alerts based on your infrastructure's topology or specific monitoring needs, or +create new entities. + +You can use health alerts in conjunction with any of Netdata's [collectors](/src/collectors/README.md) (see +the [supported collector list](/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md)) to monitor the health of your systems, containers, and +applications in real time. + +While you can see active alerts both on the local dashboard and Netdata Cloud, all health alerts are configured _per +node_ via individual Netdata Agents. If you want to deploy a new alert across your +[infrastructure](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md), you must configure each node with the same health configuration +files. + +## Reload health configuration + +You do not need to restart the Netdata Agent between changes to health configuration files, such as specific health entities. Instead, you can use `netdatacli` and the `reload-health` option to prevent gaps in metrics collection. + +```bash +sudo netdatacli reload-health +``` + +If `netdatacli` doesn't work on your system, send a `SIGUSR2` signal to the daemon, which reloads health configuration without restarting the entire process. + +```bash +killall -USR2 netdata +``` + +## Edit health configuration files + +You can configure the Agent's health watchdog service by editing files in two locations: + +- The `[health]` section in `netdata.conf`. By editing the daemon's behavior, you can disable health monitoring + altogether, run health checks more or less often, and more. See + [daemon configuration](/src/daemon/config/README.md#health-section-options) for a table of + all the available settings, their default values, and what they control. + +- The individual `.conf` files in `health.d/`. These health entity files are organized by the type of metric they are + performing calculations on or their associated collector. You should edit these files using the `edit-config` + script. For example: `sudo ./edit-config health.d/cpu.conf`. + +Navigate to your [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) and +use `edit-config` to make changes to any of these files. + +### Edit individual alerts + +For example, to edit the `cpu.conf` health configuration file, run: + +```bash +sudo ./edit-config health.d/cpu.conf +``` + +Each health configuration file contains one or more health _entities_, which always begin with `alarm:` or `template:`. +For example, here is the first health entity in `health.d/cpu.conf`: + +```yaml + template: 10min_cpu_usage + on: system.cpu + class: Utilization + type: System +component: CPU + lookup: average -10m unaligned of user,system,softirq,irq,guest + units: % + every: 1m + warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (75) : (85)) + crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (85) : (95)) + delay: down 15m multiplier 1.5 max 1h + summary: CPU utilization + info: Average cpu utilization for the last 10 minutes (excluding iowait, nice and steal) + to: sysadmin +``` + +To tune this alert to trigger warning and critical alerts at a lower CPU utilization, change the `warn` and `crit` lines +to the values of your choosing. For example: + +```yaml + warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (60) : (75)) + crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (75) : (85)) +``` + +Save the file and [reload Netdata's health configuration](#reload-health-configuration) to apply your changes. + +## Disable or silence alerts + +Alerts and notifications can be disabled permanently via configuration changes, or temporarily, via the +[health management API](/src/web/api/health/README.md). The +available options are described below. + +### Disable all alerts + +In the `netdata.conf` `[health]` section, set `enabled` to `no`, and restart the agent. + +### Disable some alerts + +In the `netdata.conf` `[health]` section, set `enabled alarms` to a +[simple pattern](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) that +excludes one or more alerts. e.g. `enabled alarms = !oom_kill *` will load all alerts except `oom_kill`. + +You can also [edit the file where the alert is defined](#edit-individual-alerts), comment out its definition, +and [reload Netdata's health configuration](#reload-health-configuration). + +### Silence an individual alert + +You can stop receiving notification for an individual alert by [changing](#edit-individual-alerts) the `to:` line to `silent`. + +```yaml + to: silent +``` + +This action requires that you [reload Netdata's health configuration](#reload-health-configuration). + +### Temporarily disable alerts at runtime + +When you need to frequently disable all or some alerts from triggering during certain times (for instance +when running backups) you can use the +[health management API](/src/web/api/health/README.md). +The API allows you to issue commands to control the health engine's behavior without changing configuration, +or restarting the agent. + +### Temporarily silence notifications at runtime + +If you want health checks to keep running and alerts to keep getting triggered, but notifications to be +suppressed temporarily, you can use the +[health management API](/src/web/api/health/README.md). +The API allows you to issue commands to control the health engine's behavior without changing configuration, +or restarting the agent. + +## Write a new health entity + +While tuning existing alerts may work in some cases, you may need to write entirely new health entities based on how +your systems, containers, and applications work. + +Read the [health entity reference](#health-entity-reference) for a full listing of the format, +syntax, and functionality of health entities. + +To write a new health entity into a new file, navigate to your [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md), +then use `touch` to create a new file in the `health.d/` directory. Use `edit-config` to start editing the file. + +As an example, let's create a `ram-usage.conf` file. + +```bash +sudo touch health.d/ram-usage.conf +sudo ./edit-config health.d/ram-usage.conf +``` + +For example, here is a health entity that triggers a warning alert when a node's RAM usage rises above 80%, and a +critical alert above 90%: + +```yaml + alarm: ram_usage + on: system.ram +lookup: average -1m percentage of used + units: % + every: 1m + warn: $this > 80 + crit: $this > 90 + info: The percentage of RAM being used by the system. +``` + +Let's look into each of the lines to see how they create a working health entity. + +- `alarm`: The name for your new entity. The name needs to follow these requirements: + - Any alphabet letter or number. + - The symbols `.` and `_`. + - Cannot be `chart name`, `dimension name`, `family name`, or `chart variable names`. + +- `on`: Which chart the entity listens to. + +- `lookup`: Which metrics the alert monitors, the duration of time to monitor, and how to process the metrics into a + usable format. + - `average`: Calculate the average of all the metrics collected. + - `-1m`: Use metrics from 1 minute ago until now to calculate that average. + - `percentage`: Clarify that we're calculating a percentage of RAM usage. + - `of used`: Specify which dimension (`used`) on the `system.ram` chart you want to monitor with this entity. + +- `units`: Use percentages rather than absolute units. + +- `every`: How often to perform the `lookup` calculation to decide whether to trigger this alert. + +- `warn`/`crit`: The value at which Netdata should trigger a warning or critical alert. This example uses simple + syntax, but most pre-configured health entities use + [hysteresis](#special-use-of-the-conditional-operator) to avoid superfluous notifications. + +- `info`: A description of the alert, which will appear in the dashboard and notifications. + +In human-readable format: + +> This health entity, named **ram_usage**, watches the **system.ram** chart. It looks up the last **1 minute** of +> metrics from the **used** dimension and calculates the **average** of all those metrics in a **percentage** format, +> using a **% unit**. The entity performs this lookup **every minute**. +> +> If the average RAM usage percentage over the last 1 minute is **more than 80%**, the entity triggers a warning alert. +> If the usage is **more than 90%**, the entity triggers a critical alert. + +When you finish writing this new health entity, [reload Netdata's health configuration](#reload-health-configuration) to +see it live on the local dashboard or Netdata Cloud. + +## Health entity reference + +The following reference contains information about the syntax and options of _health entities_, which Netdata attaches +to charts in order to trigger alerts. + +### Entity types + +There are two entity types: **alarms** and **templates**. They have the same format and feature set—the only difference +is their label. + +**Alerts** are attached to specific charts and use the `alarm` label. + +**Templates** define rules that apply to all charts of a specific context, and use the `template` label. Templates help +you apply one entity to all disks, all network interfaces, all MySQL databases, and so on. + +Alerts have higher precedence and will override templates. +If the `alert` and `template` entities have the same name and are attached to the same chart, Netdata will use `alarm`. + +### Entity format + +Netdata parses the following lines. Beneath the table is an in-depth explanation of each line's purpose and syntax. + +- The `alarm` or `template` line must be the first line of any entity. +- The `on` line is **always required**. +- The `every` line is **required** if not using `lookup`. +- Each entity **must** have at least one of the following lines: `lookup`, `calc`, `warn`, or `crit`. +- A few lines use space-separated lists to define how the entity behaves. You can use `*` as a wildcard or prefix with + `!` for a negative match. Order is important, too! See our [simple patterns docs](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) for + more examples. +- Lines terminated by a `\` are spliced together with the next line. The backslash is removed and the following line is + joined with the current one. No space is inserted, so you may split a line anywhere, even in the middle of a word. + This comes in handy if your `info` line consists of several sentences. + +| line | required | functionality | +|-----------------------------------------------------|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| [`alarm`/`template`](#alert-line-alarm-or-template) | yes | Name of the alert/template. | +| [`on`](#alert-line-on) | yes | The chart this alert should attach to. | +| [`class`](#alert-line-class) | no | The general alert classification. | +| [`type`](#alert-line-type) | no | What area of the system the alert monitors. | +| [`component`](#alert-line-component) | no | Specific component of the type of the alert. | +| [`lookup`](#alert-line-lookup) | yes | The database lookup to find and process metrics for the chart specified through `on`. | +| [`calc`](#alert-line-calc) | yes (see above) | A calculation to apply to the value found via `lookup` or another variable. | +| [`every`](#alert-line-every) | no | The frequency of the alert. | +| [`green`/`red`](#alert-lines-green-and-red) | no | Set the green and red thresholds of a chart. | +| [`warn`/`crit`](#alert-lines-warn-and-crit) | yes (see above) | Expressions evaluating to true or false, and when true, will trigger the alert. | +| [`to`](#alert-line-to) | no | A list of roles to send notifications to. | +| [`exec`](#alert-line-exec) | no | The script to execute when the alert changes status. | +| [`delay`](#alert-line-delay) | no | Optional hysteresis settings to prevent floods of notifications. | +| [`repeat`](#alert-line-repeat) | no | The interval for sending notifications when an alert is in WARNING or CRITICAL mode. | +| [`options`](#alert-line-options) | no | Add an option to not clear alerts. | +| [`host labels`](#alert-line-host-labels) | no | Restrict an alert or template to a list of matching labels present on a host. | +| [`chart labels`](#alert-line-chart-labels) | no | Restrict an alert or template to a list of matching labels present on a chart. | +| [`summary`](#alert-line-summary) | no | A brief description of the alert. | +| [`info`](#alert-line-info) | no | A longer text field that provides more information of this alert | + +The `alarm` or `template` line must be the first line of any entity. + +#### Alert line `alarm` or `template` + +This line starts an alert or template based on the [entity type](#entity-types) you're interested in creating. + +**Alert:** + +```yaml +alarm: NAME +``` + +**Template:** + +```yaml +template: NAME +``` + +`NAME` can be any alpha character, with `.` (period) and `_` (underscore) as the only allowed symbols, but the names +cannot be `chart name`, `dimension name`, `family name`, or `chart variables names`. + +#### Alert line `on` + +This line defines the chart this alert should attach to. + +**Alerts:** + +```yaml +on: CHART +``` + +The value `CHART` should be the unique ID or name of the chart you're interested in, as shown on the dashboard. In the +image below, the unique ID is `system.cpu`. + +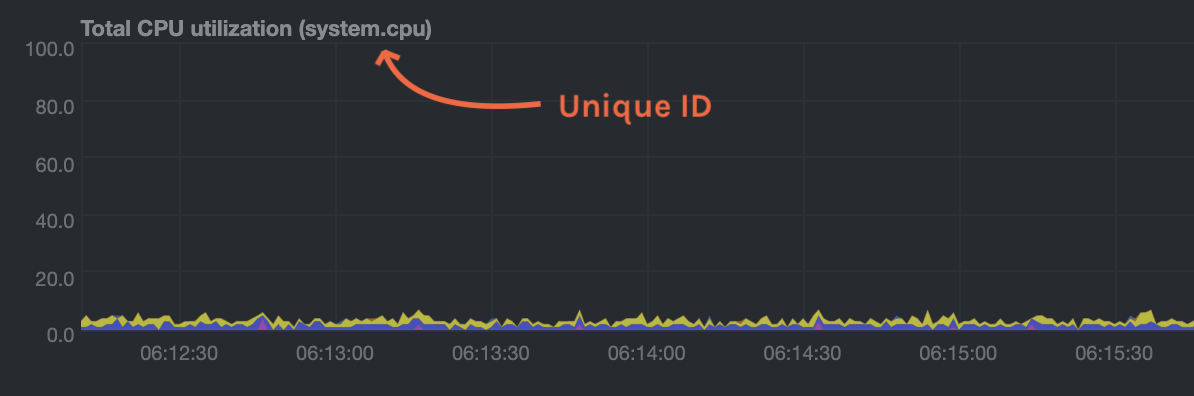 + +**Template:** + +```yaml +on: CONTEXT +``` + +The value `CONTEXT` should be the context you want this template to attach to. + +Need to find the context? Hover over the date on any given chart and look at the tooltip. In the image below, which +shows a disk I/O chart, the tooltip reads: `proc:/proc/diskstats, disk.io`. + +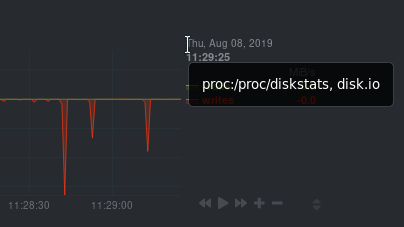 + +You're interested in what comes after the comma: `disk.io`. That's the name of the chart's context. + +If you create a template using the `disk.io` context, it will apply an alert to every disk available on your system. + +#### Alert line `class` + +This indicates the type of error (or general problem area) that the alert or template applies to. For example, `Latency` can be used for alerts that trigger on latency issues on network interfaces, web servers, or database systems. Example: + +```yaml +class: Latency +``` + +<details> +<summary>Netdata's stock alerts use the following `class` attributes by default:</summary> + +| Class | +|-------------| +| Errors | +| Latency | +| Utilization | +| Workload | + +</details> + +`class` will default to `Unknown` if the line is missing from the alert configuration. + +#### Alert line `type` + +Type can be used to indicate the broader area of the system that the alert applies to. For example, under the general `Database` type, you can group together alerts that operate on various database systems, like `MySQL`, `CockroachDB`, `CouchDB` etc. Example: + +```yaml +type: Database +``` + +<details> +<summary>Netdata's stock alerts use the following `type` attributes by default, but feel free to adjust for your own requirements.</summary> + +| Type | Description | +|-----------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Ad Filtering | Services related to Ad Filtering (like pi-hole) | +| Certificates | Certificates monitoring related | +| Cgroups | Alerts for cpu and memory usage of control groups | +| Computing | Alerts for shared computing applications (e.g. boinc) | +| Containers | Container related alerts (e.g. docker instances) | +| Database | Database systems (e.g. MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc) | +| Data Sharing | Used to group together alerts for data sharing applications | +| DHCP | Alerts for dhcp related services | +| DNS | Alerts for dns related services | +| Kubernetes | Alerts for kubernetes nodes monitoring | +| KV Storage | Key-Value pairs services alerts (e.g. memcached) | +| Linux | Services specific to Linux (e.g. systemd) | +| Messaging | Alerts for message passing services (e.g. vernemq) | +| Netdata | Internal Netdata components monitoring | +| Other | When an alert doesn't fit in other types. | +| Power Supply | Alerts from power supply related services (e.g. apcupsd) | +| Search engine | Alerts for search services (e.g. elasticsearch) | +| Storage | Class for alerts dealing with storage services (storage devices typically live under `System`) | +| System | General system alerts (e.g. cpu, network, etc.) | +| Virtual Machine | Virtual Machine software | +| Web Proxy | Web proxy software (e.g. squid) | +| Web Server | Web server software (e.g. Apache, ngnix, etc.) | +| Windows | Alerts for monitor of windows services | + +</details> + +If an alert configuration is missing the `type` line, its value will default to `Unknown`. + +#### Alert line `component` + +Component can be used to narrow down what the previous `type` value specifies for each alert or template. Continuing from the previous example, `component` might include `MySQL`, `CockroachDB`, `MongoDB`, all under the same `Database` type. Example: + +```yaml +component: MySQL +``` + +As with the `class` and `type` line, if `component` is missing from the configuration, its value will default to `Unknown`. + +#### Alert line `lookup` + +This line makes a database lookup to find a value. This result of this lookup is available as `$this`. + +The format is: + +```yaml +lookup: METHOD(GROUPING OPTIONS) AFTER [at BEFORE] [every DURATION] [OPTIONS] [of DIMENSIONS] +``` + +The full [database query API](/src/web/api/queries/README.md) is supported. In short: + +- `METHOD` is one of the available [grouping methods](/src/web/api/queries/README.md#grouping-methods) such as `average`, `min`, `max` etc. + This is required. + + - `GROUPING OPTIONS` are optional and can have the form `CONDITION VALUE`, where `CONDITION` is `!=`, `=`, `<=`, `<`, `>`, `>=` and `VALUE` is a number. The `CONDITION` and `VALUE` are required for `countif`, while `VALUE` is used by `percentile`, `trimmed_mean` and `trimmed_median`. + +- `AFTER` is a relative number of seconds, but it also accepts a single letter for changing + the units, like `-1s` = 1 second in the past, `-1m` = 1 minute in the past, `-1h` = 1 hour + in the past, `-1d` = 1 day in the past. You need a negative number (i.e. how far in the past + to look for the value). **This is required**. + +- `at BEFORE` is by default 0 and is not required. Using this you can define the end of the + lookup. So data will be evaluated between `AFTER` and `BEFORE`. + +- `every DURATION` sets the updated frequency of the lookup (supports single letter units as + above too). + +- `OPTIONS` is a space separated list of `percentage`, `absolute`, `min`, `max`, `average`, `sum`, + `min2max`, `unaligned`, `match-ids`, `match-names`. + + - `percentage` during time-aggregation, calculate the percentage of the selected dimensions over the total of all dimensions. + - `absolute` during time-aggregation, turns all sample values positive before using them. + - `min` after time-aggregation of each dimension, return the minimum of all dimensions. + - `max` after time-aggregation of each dimension, return the maximum of all dimensions. + - `average` after time-aggregation of each dimension, return the average of all dimensions. + - `sum` after time-aggregation of each dimension, return the sum of all dimensions (this is the default). + - `min2max` after time-aggregation of each dimension, return the delta between the min and the max of the dimensions. + - `unaligned` prevents shifting the query window to multiples of the query duration. + - `match-ids` matches the dimensions based on their IDs (the default is enabled, give `match-names` to disable). + - `match-names` matches the dimension based on their names (the default is enabled, give `match-ids` to disable). + +- `of DIMENSIONS` is optional and has to be the last parameter. Dimensions have to be separated + by `,` or `|`. The space characters found in dimensions will be kept as-is (a few dimensions + have spaces in their names). This accepts Netdata simple patterns _(with `words` separated by + `,` or `|` instead of spaces)_ and the `match-ids` and `match-names` options affect the searches + for dimensions. + +The result of the lookup will be available as `$this` and `$NAME` in expressions. +The timestamps of the timeframe evaluated by the database lookup is available as variables +`$after` and `$before` (both are unix timestamps). + +#### Alert line `calc` + +A `calc` is designed to apply some calculation to the values or variables available to the entity. The result of the +calculation will be made available at the `$this` variable, overwriting the value from your `lookup`, to use in warning +and critical expressions. + +When paired with `lookup`, `calc` will perform the calculation just after `lookup` has retrieved a value from Netdata's +database. + +You can use `calc` without `lookup` if you are using [other available variables](#variables). + +The `calc` line uses [expressions](#expressions) for its syntax. + +```yaml +calc: EXPRESSION +``` + +#### Alert line `every` + +Sets the update frequency of this alert. This is the same to the `every DURATION` given +in the `lookup` lines. + +Format: + +```yaml +every: DURATION +``` + +`DURATION` accepts `s` for seconds, `m` is minutes, `h` for hours, `d` for days. + +#### Alert lines `green` and `red` + +Set the green and red thresholds of a chart. Both are available as `$green` and `$red` in expressions. If multiple +alerts define different thresholds, the ones defined by the first alert will be used. Eventually it will be visualized +on the dashboard, so only one set of them is allowed If you need multiple sets of them in different alerts, use +absolute numbers instead of `$red` and `$green`. + +Format: + +```yaml +green: NUMBER +red: NUMBER +``` + +#### Alert lines `warn` and `crit` + +Define the expression that triggers either a warning or critical alert. These are optional, and should evaluate to +either true or false (or zero/non-zero). + +The format uses Netdata's [expressions syntax](#expressions). + +```yaml +warn: EXPRESSION +crit: EXPRESSION +``` + +#### Alert line `to` + +This will be the first script parameter that will be executed when the alert changes its status. Its meaning is left up to +the `exec` script. + +The default `exec` script, `alarm-notify.sh`, uses this field as a space separated list of roles, which are then +consulted to find the exact recipients per notification method. + +Format: + +```yaml +to: ROLE1 ROLE2 ROLE3 ... +``` + +#### Alert line `exec` + +Script to be executed when the alert status changes. + +Format: + +```yaml +exec: SCRIPT +``` + +The default `SCRIPT` is Netdata's `alarm-notify.sh`, which supports all the notifications methods Netdata supports, +including custom hooks. + +#### Alert line `delay` + +This is used to provide optional hysteresis settings for the notifications, to defend against notification floods. These +settings do not affect the actual alert - only the time the `exec` script is executed. + +Format: + +```yaml +delay: [[[up U] [down D] multiplier M] max X] +``` + +- `up U` defines the delay to be applied to a notification for an alert that raised its status + (i.e. CLEAR to WARNING, CLEAR to CRITICAL, WARNING to CRITICAL). For example, `up 10s`, the + notification for this event will be sent 10 seconds after the actual event. This is used in + hope the alert will get back to its previous state within the duration given. The default `U` + is zero. + +- `down D` defines the delay to be applied to a notification for an alert that moves to lower + state (i.e. CRITICAL to WARNING, CRITICAL to CLEAR, WARNING to CLEAR). For example, `down 1m` + will delay the notification by 1 minute. This is used to prevent notifications for flapping + alerts. The default `D` is zero. + +- `multiplier M` multiplies `U` and `D` when an alert changes state, while a notification is + delayed. The default multiplier is `1.0`. + +- `max X` defines the maximum absolute notification delay an alert may get. The default `X` + is `max(U * M, D * M)` (i.e. the max duration of `U` or `D` multiplied once with `M`). + + Example: + + `delay: up 10s down 15m multiplier 2 max 1h` + + The time is `00:00:00` and the status of the alert is CLEAR. + + | time of event | new status | delay | notification will be sent | why | + |---------------|------------|---------------------|---------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------| + | 00:00:01 | WARNING | `up 10s` | 00:00:11 | first state switch | + | 00:00:05 | CLEAR | `down 15m x2` | 00:30:05 | the alert changes state while a notification is delayed, so it was multiplied | + | 00:00:06 | WARNING | `up 10s x2 x2` | 00:00:26 | multiplied twice | + | 00:00:07 | CLEAR | `down 15m x2 x2 x2` | 00:45:07 | multiplied 3 times. | + + So: + + - `U` and `D` are multiplied by `M` every time the alert changes state (any state, not just + their matching one) and a delay is in place. + - All are reset to their defaults when the alert switches state without a delay in place. + +#### Alert line `repeat` + +Defines the interval between repeating notifications for the alerts in CRITICAL or WARNING mode. This will override the +default interval settings inherited from health settings in `netdata.conf`. The default settings for repeating +notifications are `default repeat warning = DURATION` and `default repeat critical = DURATION` which can be found in +health stock configuration, when one of these interval is bigger than 0, Netdata will activate the repeat notification +for `CRITICAL`, `CLEAR` and `WARNING` messages. + +Format: + +```yaml +repeat: [off] [warning DURATION] [critical DURATION] +``` + +- `off`: Turns off the repeating feature for the current alert. This is effective when the default repeat settings has + been enabled in health configuration. +- `warning DURATION`: Defines the interval when the alert is in WARNING state. Use `0s` to turn off the repeating + notification for WARNING mode. +- `critical DURATION`: Defines the interval when the alert is in CRITICAL state. Use `0s` to turn off the repeating + notification for CRITICAL mode. + +#### Alert line `options` + +The only possible value for the `options` line is + +```yaml +options: no-clear-notification +``` + +For some alerts we need compare two time-frames, to detect anomalies. For example, `health.d/httpcheck.conf` has an +alert template called `web_service_slow` that compares the average http call response time over the last 3 minutes, +compared to the average over the last hour. It triggers a warning alert when the average of the last 3 minutes is twice +the average of the last hour. In such cases, it is easy to trigger the alert, but difficult to tell when the alert is +cleared. As time passes, the newest window moves into the older, so the average response time of the last hour will keep +increasing. Eventually, the comparison will find the averages in the two time-frames close enough to clear the alert. +However, the issue was not resolved, it's just a matter of the newer data "polluting" the old. For such alerts, it's a +good idea to tell Netdata to not clear the notification, by using the `no-clear-notification` option. + +#### Alert line `host labels` + +Defines the list of labels present on a host. See our [host labels guide](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/organize-systems-metrics-and-alerts.md) for +an explanation of host labels and how to implement them. + +For example, let's suppose that `netdata.conf` is configured with the following labels: + +```yaml +[host labels] + installed = 20191211 + room = server +``` + +And more labels in `netdata.conf` for workstations: + +```yaml +[host labels] + installed = 201705 + room = workstation +``` + +By defining labels inside of `netdata.conf`, you can now apply labels to alerts. For example, you can add the following +line to any alerts you'd like to apply to hosts that have the label `room = server`. + +```yaml +host labels: room = server +``` + +The `host labels` is a space-separated list that accepts simple patterns. For example, you can create an alert +that will be applied to all hosts installed in the last decade with the following line: + +```yaml +host labels: installed = 201* +``` + +See our [simple patterns docs](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) for more examples. + +#### Alert line `chart labels` + +Similar to host labels, the `chart labels` key can be used to filter if an alert will load or not for a specific chart, based on +whether these chart labels match or not. + +The list of chart labels present on each chart can be obtained from http://localhost:19999/api/v1/charts?all + +For example, each `disk_space` chart defines a chart label called `mount_point` with each instance of this chart having +a value there of which mount point it monitors. + +If you have an e.g. external disk mounted on `/mnt/disk1` and you don't wish any related disk space alerts running for +it (but you do for all other mount points), you can add the following to the alert's configuration: + +```yaml +chart labels: mount_point=!/mnt/disk1 * +``` + +The `chart labels` is a space-separated list that accepts simple patterns. If you use multiple different chart labels, +then the result is an AND between them. i.e. the following: + +```yaml +chart labels: mount_point=/mnt/disk1 device=sda +``` + +Will create the alert if the `mount_point` is `/mnt/disk1` and the `device` is `sda`. Furthermore, if a chart label name +is specified that does not exist in the chart, the chart won't be matched. + +See our [simple patterns docs](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) for more examples. + +#### Alert line `summary` + +The summary field contains a brief title of the alert. It is used as the subject for the notifications, and in +dashboard list of alerts. An example for the `ram_available` alert is: + +```yaml +summary: Available Ram +``` + +summary fields can contain special variables in their text that will be replaced during run-time to provide more specific +alert information. Current variables supported are: + +| variable | description | +|---------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ${family} | Will be replaced by the family instance for the alert (e.g. eth0) | +| ${label:LABEL_NAME} | The variable will be replaced with the value of the chart label | + +For example, a summary field like the following: + +```yaml +summary: 1 minute received traffic overflow for ${label:device} +``` + +Will be rendered on the alert acting on interface `eth0` as: + +```yaml +summary: 1 minute received traffic overflow for eth0 +``` + +> Please note that variable names are case-sensitive. + +#### Alert line `info` + +The info field can contain a small piece of text describing the alert or template. This will be rendered in +notifications and UI elements whenever the specific alert is in focus. An example for the `ram_available` alert is: + +```yaml +info: Percentage of estimated amount of RAM available for userspace processes, without causing swapping +``` + +info fields can contain special variables in their text that will be replaced during run-time to provide more specific +alert information. Current variables supported are: + +| variable | description | +|---------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ${family} | Will be replaced by the family instance for the alert (e.g. eth0) | +| ${label:LABEL_NAME} | The variable will be replaced with the value of the chart label | + +For example, an info field like the following: + +```yaml +info: average inbound utilization for the network interface ${family} over the last minute +``` + +Will be rendered on the alert acting on interface `eth0` as: + +```yaml +info: average inbound utilization for the network interface eth0 over the last minute +``` + +An alert acting on a chart that has a chart label named e.g. `target`, with a value of `https://netdata.cloud/`, +can be enriched as follows: + +```yaml +info: average ratio of HTTP responses with unexpected status over the last 5 minutes for the site ${label:target} +``` + +Will become: + +```yaml +info: average ratio of HTTP responses with unexpected status over the last 5 minutes for the site https://netdata.cloud/ +``` + +> Please note that variable names are case-sensitive. + +## Expressions + +Netdata has an internal infix expression parser under `libnetdata/eval`. This parses expressions and creates an internal +structure that allows fast execution of them. + +These operators are supported `+`, `-`, `*`, `/`, `<`, `==`, `<=`, `<>`, `!=`, `>`, `>=`, `&&`, `||`, `!`, `AND`, `OR`, `NOT`. +Boolean operators result in either `1` (true) or `0` (false). + +The conditional evaluation operator `?` is supported too. Using this operator IF-THEN-ELSE conditional statements can be +specified. The format is: `(condition) ? (true expression) : (false expression)`. So, Netdata will first evaluate the +`condition` and based on the result will either evaluate `true expression` or `false expression`. + +Example: `($this > 0) ? ($avail * 2) : ($used / 2)`. + +Nested such expressions are also supported (i.e. `true expression` and `false expression` can contain conditional +evaluations). + +Expressions also support the `abs()` function. + +Expressions can have variables. Variables start with `$`. Check below for more information. + +There are two special values you can use: + +- `nan`, for example `$this != nan` will check if the variable `this` is available. A variable can be `nan` if the + database lookup failed. All calculations (i.e. addition, multiplication, etc.) with a `nan` result in a `nan`. + +- `inf`, for example `$this != inf` will check if `this` is not infinite. A value or variable can be set to infinite + if divided by zero. All calculations (i.e. addition, multiplication, etc.) with a `inf` result in a `inf`. + +### Special use of the conditional operator + +A common (but not necessarily obvious) use of the conditional evaluation operator is to provide +[hysteresis](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hysteresis) around the critical or warning thresholds. This usage helps to +avoid bogus messages resulting from small variations in the value when it is varying regularly but staying close to the +threshold value, without needing to delay sending messages at all. + +An example of such usage from the default CPU usage alerts bundled with Netdata is: + +```yaml +warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (75) : (85)) +crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (85) : (95)) +``` + +The above say: + +- If the alert is currently a warning, then the threshold for being considered a warning is 75, otherwise it's 85. + +- If the alert is currently critical, then the threshold for being considered critical is 85, otherwise it's 95. + +Which in turn, results in the following behavior: + +- While the value is rising, it will trigger a warning when it exceeds 85, and a critical alert when it exceeds 95. + +- While the value is falling, it will return to a warning state when it goes below 85, and a normal state when it goes + below 75. + +- If the value is constantly varying between 80 and 90, then it will trigger a warning the first time it goes above + 85, but will remain a warning until it goes below 75 (or goes above 85). + +- If the value is constantly varying between 90 and 100, then it will trigger a critical alert the first time it goes + above 95, but will remain a critical alert goes below 85 (at which point it will return to being a warning). + +## Variables + +You can find all the variables that can be used for a given chart, using +`http://NODE:19999/api/v1/alarm_variables?chart=CHART_NAME`, replacing `NODE` with the IP address or hostname for your +Agent dashboard. For example, [variables for the `system.cpu` chart of the +registry](https://registry.my-netdata.io/api/v1/alarm_variables?chart=system.cpu). + +> If you don't know how to find the CHART_NAME, you can read about it [here](/src/web/README.md#charts). + +Netdata supports 3 internal indexes for variables that will be used in health monitoring. + +<details><summary>The variables below can be used in both chart alerts and context templates.</summary> + +Although the `alarm_variables` link shows you variables for a particular chart, the same variables can also be used in +templates for charts belonging to a given [context](/src/web/README.md#contexts). The reason is that all charts of a given +context are essentially identical, with the only difference being the family that identifies a particular hardware or software instance. + +</details> + +- **chart local variables**. All the dimensions of the chart are exposed as local variables. The value of `$this` for + the other configured alerts of the chart also appears, under the name of each configured alert. + + Charts also define a few special variables: + + - `$last_collected_t` is the unix timestamp of the last data collection + - `$collected_total_raw` is the sum of all the dimensions (their last collected values) + - `$update_every` is the update frequency of the chart + - `$green` and `$red` the threshold defined in alerts (these are per chart - the charts inherits them from the first alert that defined them) + + > Chart dimensions define their last calculated (i.e. interpolated) value, exactly as + shown on the charts, but also a variable with their name and suffix `_raw` that resolves + to the last collected value - as collected and another with suffix `_last_collected_t` + that resolves to unix timestamp the dimension was last collected (there may be dimensions + that fail to be collected while others continue normally). + +- **host variables**. All the dimensions of all charts, including all alerts, in fullname. + Fullname is `CHART.VARIABLE`, where `CHART` is either the chart id or the chart name (both + are supported). + +- **special variables** are: + + - `$this`, which is resolved to the value of the current alert. + + - `$status`, which is resolved to the current status of the alert (the current = the last + status, i.e. before the current database lookup and the evaluation of the `calc` line). + This values can be compared with `$REMOVED`, `$UNINITIALIZED`, `$UNDEFINED`, `$CLEAR`, + `$WARNING`, `$CRITICAL`. These values are incremental, e.g. `$status > $CLEAR` works as + expected. + + - `$now`, which is resolved to current unix timestamp. + +## Alert statuses + +Alerts can have the following statuses: + +- `REMOVED` - the alert has been deleted (this happens when a SIGUSR2 is sent to Netdata + to reload health configuration) + +- `UNINITIALIZED` - the alert is not initialized yet + +- `UNDEFINED` - the alert failed to be calculated (i.e. the database lookup failed, + a division by zero occurred, etc.) + +- `CLEAR` - the alert is not armed / raised (i.e. is OK) + +- `WARNING` - the warning expression resulted in true or non-zero + +- `CRITICAL` - the critical expression resulted in true or non-zero + +The external script will be called for all status changes. + +## Example alerts + +Check the `health/health.d/` directory for all alerts shipped with Netdata. + +Here are a few examples: + +### Example 1 - check server alive + +A simple check if an apache server is alive: + +```yaml +template: apache_last_collected_secs + on: apache.requests + calc: $now - $last_collected_t + every: 10s + warn: $this > ( 5 * $update_every) + crit: $this > (10 * $update_every) +``` + +The above checks that Netdata is able to collect data from apache. In detail: + +```yaml +template: apache_last_collected_secs +``` + +The above defines a **template** named `apache_last_collected_secs`. +The name is important since `$apache_last_collected_secs` resolves to the `calc` line. +So, try to give something descriptive. + +```yaml + on: apache.requests +``` + +The above applies the **template** to all charts that have `context = apache.requests` +(i.e. all your apache servers). + +```yaml + calc: $now - $last_collected_t +``` + +- `$now` is a standard variable that resolves to the current timestamp. + +- `$last_collected_t` is the last data collection timestamp of the chart. + So this calculation gives the number of seconds passed since the last data collection. + +```yaml + every: 10s +``` + +The alert will be evaluated every 10 seconds. + +```yaml + warn: $this > ( 5 * $update_every) + crit: $this > (10 * $update_every) +``` + +If these result in non-zero or true, they trigger the alert. + +- `$this` refers to the value of this alert (e.g. the result of the `calc` line). + We could also use `$apache_last_collected_secs`. + +`$update_every` is the update frequency of the chart, in seconds. + +So, the warning condition checks if we have not collected data from apache for 5 +iterations and the critical condition checks for 10 iterations. + +### Example 2 - disk space + +Check if any of the disks is critically low on disk space: + +```yaml +template: disk_full_percent + on: disk.space + calc: $used * 100 / ($avail + $used) + every: 1m + warn: $this > 80 + crit: $this > 95 + repeat: warning 120s critical 10s +``` + +`$used` and `$avail` are the `used` and `avail` chart dimensions as shown on the dashboard. + +So, the `calc` line finds the percentage of used space. `$this` resolves to this percentage. + +This is a repeating alert and if the alert becomes CRITICAL it repeats the notifications every 10 seconds. It also +repeats notifications every 2 minutes if the alert goes into WARNING mode. + +### Example 3 - disk fill rate + +Predict if any disk will run out of space in the near future. + +We do this in 2 steps: + +Calculate the disk fill rate: + +```yaml + template: disk_fill_rate + on: disk.space + lookup: max -1s at -30m unaligned of avail + calc: ($this - $avail) / (30 * 60) + every: 15s +``` + +In the `calc` line: `$this` is the result of the `lookup` line (i.e. the free space 30 minutes +ago) and `$avail` is the current disk free space. So the `calc` line will either have a positive +number of GB/second if the disk is filling up, or a negative number of GB/second if the disk is +freeing up space. + +There is no `warn` or `crit` lines here. So, this template will just do the calculation and +nothing more. + +Predict the hours after which the disk will run out of space: + +```yaml + template: disk_full_after_hours + on: disk.space + calc: $avail / $disk_fill_rate / 3600 + every: 10s + warn: $this > 0 and $this < 48 + crit: $this > 0 and $this < 24 +``` + +The `calc` line estimates the time in hours, we will run out of disk space. Of course, only +positive values are interesting for this check, so the warning and critical conditions check +for positive values and that we have enough free space for 48 and 24 hours respectively. + +Once this alert triggers we will receive an email like this: + + + +### Example 4 - dropped packets + +Check if any network interface is dropping packets: + +```yaml +template: 30min_packet_drops + on: net.drops + lookup: sum -30m unaligned absolute + every: 10s + crit: $this > 0 +``` + +The `lookup` line will calculate the sum of the all dropped packets in the last 30 minutes. + +The `crit` line will issue a critical alert if even a single packet has been dropped. + +Note that the drops chart does not exist if a network interface has never dropped a single packet. +When Netdata detects a dropped packet, it will add the chart, and it will automatically attach this +alert to it. + +### Example 5 - Z-Score based alert + +Derive a "[Z Score](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_score)" based alert on `user` dimension of the `system.cpu` chart: + +```yaml + alarm: cpu_user_mean + on: system.cpu +lookup: mean -60s of user + every: 10s + + alarm: cpu_user_stddev + on: system.cpu +lookup: stddev -60s of user + every: 10s + + alarm: cpu_user_zscore + on: system.cpu +lookup: mean -10s of user + calc: ($this - $cpu_user_mean) / $cpu_user_stddev + every: 10s + warn: $this < -2 or $this > 2 + crit: $this < -3 or $this > 3 +``` + +Since [`z = (x - mean) / stddev`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_score) we create two input alerts, one for `mean` and one for `stddev` and then use them both as inputs in our final `cpu_user_zscore` alert. + +### Example 6 - [Anomaly rate](/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate) based CPU chart alert + +Warning if 5 minute rolling [anomaly rate](/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate) averaged across all CPU dimensions is above 5%, critical if it goes above 20%: + +```yaml +template: ml_5min_cpu_chart + on: system.cpu + lookup: average -5m anomaly-bit of * + calc: $this + units: % + every: 30s + warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (5) : (20)) + crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (20) : (100)) + info: rolling 5min anomaly rate for system.cpu chart +``` + +The `lookup` line will calculate the average anomaly rate across all `system.cpu` dimensions over the last 5 minues. In this case +Netdata will create one alert for the chart. + +### Example 7 - [Anomaly rate](/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate) based node level alert + +Warning if 5 minute rolling [anomaly rate](/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate) averaged across all ML enabled dimensions is above 5%, critical if it goes above 20%: + +```yaml +template: ml_5min_node + on: anomaly_detection.anomaly_rate + lookup: average -5m of anomaly_rate + calc: $this + units: % + every: 30s + warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (5) : (20)) + crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (20) : (100)) + info: rolling 5min anomaly rate for all ML enabled dims +``` + +The `lookup` line will use the `anomaly_rate` dimension of the `anomaly_detection.anomaly_rate` ML chart to calculate the average [node level anomaly rate](/src/ml/README.md#node-anomaly-rate) over the last 5 minutes. + +## Troubleshooting + +You can compile Netdata with [debugging](/src/daemon/README.md#debugging) and then set in `netdata.conf`: + +```yaml +[global] + debug flags = 0x0000000000800000 +``` + +Then check your `/var/log/netdata/debug.log`. It will show you how it works. Important: this will generate a lot of +output in debug.log. + +You can find the context of charts by looking up the chart in either `http://NODE:19999/netdata.conf` or +`http://NODE:19999/api/v1/charts`, replacing `NODE` with the IP address or hostname for your Agent dashboard. + +You can find how Netdata interpreted the expressions by examining the alert at +`http://NODE:19999/api/v1/alarms?all`. For each expression, Netdata will return the expression as given in its +config file, and the same expression with additional parentheses added to indicate the evaluation flow of the +expression. |
