diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md | 238 |
1 files changed, 0 insertions, 238 deletions
diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md b/docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md deleted file mode 100644 index 2289c71c9..000000000 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,238 +0,0 @@ -import { OneLineInstallWget } from '@site/src/components/OneLineInstall/' - -# LAMP stack monitoring with Netdata - -Set up robust LAMP stack monitoring (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) in a few minutes using Netdata. - -The LAMP stack is the "hello world" for deploying dynamic web applications. It's fast, flexible, and reliable, which -means a developer or sysadmin won't go far in their career without interacting with the stack and its services. - -_LAMP_ is an acronym of the core services that make up the web application: **L**inux, **A**pache, **M**ySQL, and -**P**HP. - -- [Linux](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux) is the operating system running the whole stack. -- [Apache](https://httpd.apache.org/) is a web server that responds to HTTP requests from users and returns web pages. -- [MySQL](https://www.mysql.com/) is a database that stores and returns information based on queries from the web - application. -- [PHP](https://www.php.net/) is a scripting language used to query the MySQL database and build new pages. - -LAMP stacks are the foundation for tons of end-user applications, with [Wordpress](https://wordpress.org/) being the -most popular. - -## Challenge - -You've already deployed a LAMP stack, either in testing or production. You want to monitor every service's performance -and availability to ensure the best possible experience for your end-users. You might also be particularly interested in -using a free, open-source monitoring tool. - -Depending on your monitoring experience, you may not even know what metrics you're looking for, much less how to build -dashboards using a query language. You need a robust monitoring experience that has the metrics you need without a ton -of required setup. - -## Solution - -In this tutorial, you'll set up robust LAMP stack monitoring with Netdata in just a few minutes. When you're done, -you'll have one dashboard to monitor every part of your web application, including each essential LAMP stack service. - -This dashboard updates every second with new metrics, and pairs those metrics up with preconfigured alerts to keep you -informed of any errors or odd behavior. - -## What you need to get started - -To follow this tutorial, you need: - -- A physical or virtual Linux system, which we'll call a _node_. -- A functional LAMP stack. There's plenty of tutorials for installing a LAMP stack, like [this - one](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-linux-apache-mysql-php-lamp-stack-ubuntu-18-04) - from Digital Ocean. -- Optionally, a [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-up?cloudRoute=/spaces) account, which you can use to view - metrics from multiple nodes in one dashboard, and a whole lot more, for free. - -## Install the Netdata Agent - -If you don't have the free, open-source Netdata monitoring agent installed on your node yet, get started with a [single -kickstart command](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md): - -<OneLineInstallWget/> - -The Netdata Agent is now collecting metrics from your node every second. You don't need to jump into the dashboard yet, -but if you're curious, open your favorite browser and navigate to `http://localhost:19999` or `http://NODE:19999`, -replacing `NODE` with the hostname or IP address of your system. - -## Enable hardware and Linux system monitoring - -There's nothing you need to do to enable [system monitoring](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/system-metrics.md) and Linux monitoring with -the Netdata Agent, which autodetects metrics from CPUs, memory, disks, networking devices, and Linux processes like -systemd without any configuration. If you're using containers, Netdata automatically collects resource utilization -metrics from each using the [cgroups data collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md). - -## Enable Apache monitoring - -Let's begin by configuring Apache to work with Netdata's [Apache data -collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/apache/README.md). - -Actually, there's nothing for you to do to enable Apache monitoring with Netdata. - -Apache comes with `mod_status` enabled by default these days, and Netdata is smart enough to look for metrics at that -endpoint without you configuring it. Netdata is already collecting [`mod_status` -metrics](https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/mod_status.html), which is just _part_ of your web server monitoring. - -## Enable web log monitoring - -The Netdata Agent also comes with a [web log -collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/weblog/README.md), which reads Apache's access -log file, processes each line, and converts them into per-second metrics. On Debian systems, it reads the file at -`/var/log/apache2/access.log`. - -At installation, the Netdata Agent adds itself to the [`adm` -group](https://wiki.debian.org/SystemGroups#Groups_without_an_associated_user), which gives the `netdata` process the -right privileges to read Apache's log files. In other words, you don't need to do anything to enable Apache web log -monitoring. - -## Enable MySQL monitoring - -Because your MySQL database is password-protected, you do need to tell MySQL to allow the `netdata` user to connect to -without a password. Netdata's [MySQL data -collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/mysql/README.md) collects metrics in _read-only_ -mode, without being able to alter or affect operations in any way. - -First, log into the MySQL shell. Then, run the following three commands, one at a time: - -```mysql -CREATE USER 'netdata'@'localhost'; -GRANT USAGE, REPLICATION CLIENT, PROCESS ON *.* TO 'netdata'@'localhost'; -FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -``` - -Run `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate alternative for your -system](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/start-stop-restart.md), to collect dozens of metrics every second for robust MySQL monitoring. - -## Enable PHP monitoring - -Unlike Apache or MySQL, PHP isn't a service that you can monitor directly, unless you instrument a PHP-based application -with [StatsD](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/collectors/statsd.plugin/README.md). - -However, if you use [PHP-FPM](https://php-fpm.org/) in your LAMP stack, you can monitor that process with our [PHP-FPM -data collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/phpfpm/README.md). - -Open your PHP-FPM configuration for editing, replacing `7.4` with your version of PHP: - -```bash -sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf -``` - -> Not sure what version of PHP you're using? Run `php -v`. - -Find the line that reads `;pm.status_path = /status` and remove the `;` so it looks like this: - -```conf -pm.status_path = /status -``` - -Next, add a new `/status` endpoint to Apache. Open the Apache configuration file you're using for your LAMP stack. - -```bash -sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/your_lamp_stack.conf -``` - -Add the following to the end of the file, again replacing `7.4` with your version of PHP: - -```apache -ProxyPass "/status" "unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost" -``` - -Save and close the file. Finally, restart the PHP-FPM, Apache, and Netdata processes. - -```bash -sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm.service -sudo systemctl restart apache2 -sudo systemctl restart netdata -``` - -As the Netdata Agent starts up again, it automatically connects to the new `127.0.0.1/status` page and collects -per-second PHP-FPM metrics to get you started with PHP monitoring. - -## View LAMP stack metrics - -If the Netdata Agent isn't already open in your browser, open a new tab and navigate to `http://localhost:19999` or -`http://NODE:19999`, replacing `NODE` with the hostname or IP address of your system. - -> If you [signed up](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-up?cloudRoute=/spaces) for Netdata Cloud earlier, you can also view -> the exact same LAMP stack metrics there, plus additional features, like drag-and-drop custom dashboards. Be sure to -> [connecting your node](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/claim/README.md) to start streaming metrics to your browser through Netdata Cloud. - -Netdata automatically organizes all metrics and charts onto a single page for easy navigation. Peek at gauges to see -overall system performance, then scroll down to see more. Click-and-drag with your mouse to pan _all_ charts back and -forth through different time intervals, or hold `SHIFT` and use the scrollwheel (or two-finger scroll) to zoom in and -out. Check out our doc on [interacting with charts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) for all the details. - -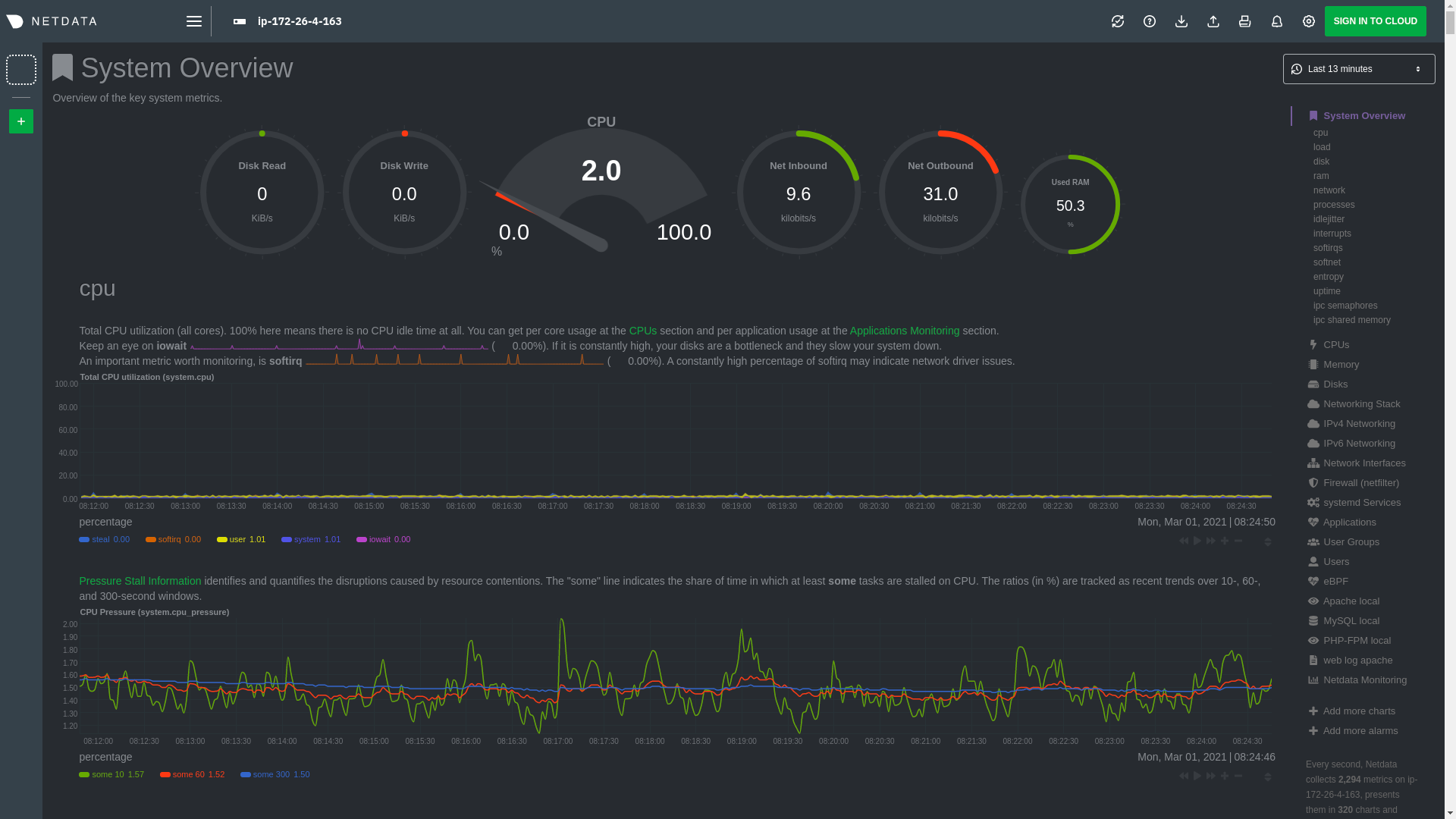 - -The **System Overview** section, which you can also see in the right-hand menu, contains key hardware monitoring charts, -including CPU utilization, memory page faults, network monitoring, and much more. The **Applications** section shows you -exactly which Linux processes are using the most system resources. - -Next, let's check out LAMP-specific metrics. You should see four relevant sections: **Apache local**, **MySQL local**, -**PHP-FPM local**, and **web log apache**. Click on any of these to see metrics from each service in your LAMP stack. - -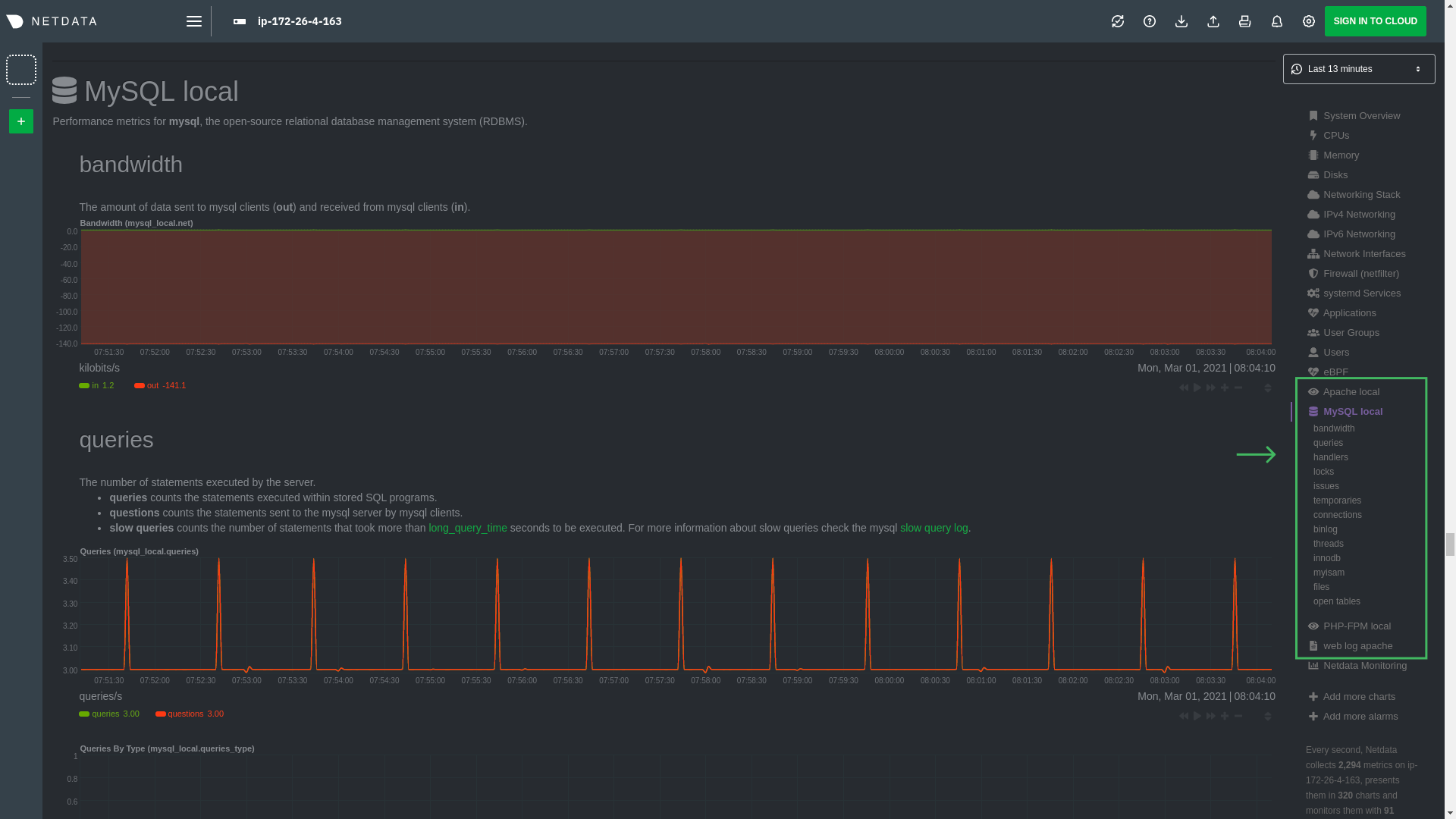 - -### Key LAMP stack monitoring charts - -Here's a quick reference for what charts you might want to focus on after setting up Netdata. - -| Chart name / context | Type | Why? | -|-------------------------------------------------------|---------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| System Load Average (`system.load`) | Hardware monitoring | A good baseline load average is `0.7`, while `1` (on a 1-core system, `2` on a 2-core system, and so on) means resources are "perfectly" utilized. Higher load indicates a bottleneck somewhere in your system. | -| System RAM (`system.ram`) | Hardware monitoring | Look at the `free` dimension. If that drops to `0`, your system will use swap memory and slow down. | -| Uptime (`apache_local.uptime`) | Apache monitoring | This chart should always be "climbing," indicating a continuous uptime. Investigate any drops back to `0`. | -| Requests By Type (`web_log_apache.requests_by_type`) | Apache monitoring | Check for increases in the `error` or `bad` dimensions, which could indicate users arriving at broken pages or PHP returning errors. | -| Queries (`mysql_local.queries`) | MySQL monitoring | Queries is the total number of queries (queries per second, QPS). Check this chart for sudden spikes or drops, which indicate either increases in traffic/demand or bottlenecks in hardware performance. | -| Active Connections (`mysql_local.connections_active`) | MySQL monitoring | If the `active` dimension nears the `limit`, your MySQL database will bottleneck responses. | -| Performance (phpfpm_local.performance) | PHP monitoring | The `slow requests` dimension lets you know if any requests exceed the configured `request_slowlog_timeout`. If so, users might be having a less-than-ideal experience. | - -## Get alerts for LAMP stack errors - -The Netdata Agent comes with hundreds of pre-configured alerts to help you keep tabs on your system, including 19 alerts -designed for smarter LAMP stack monitoring. - -Click the 🔔 icon in the top navigation to [see active alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md). The **Active** tabs -shows any alerts currently triggered, while the **All** tab displays a list of _every_ pre-configured alert. The - -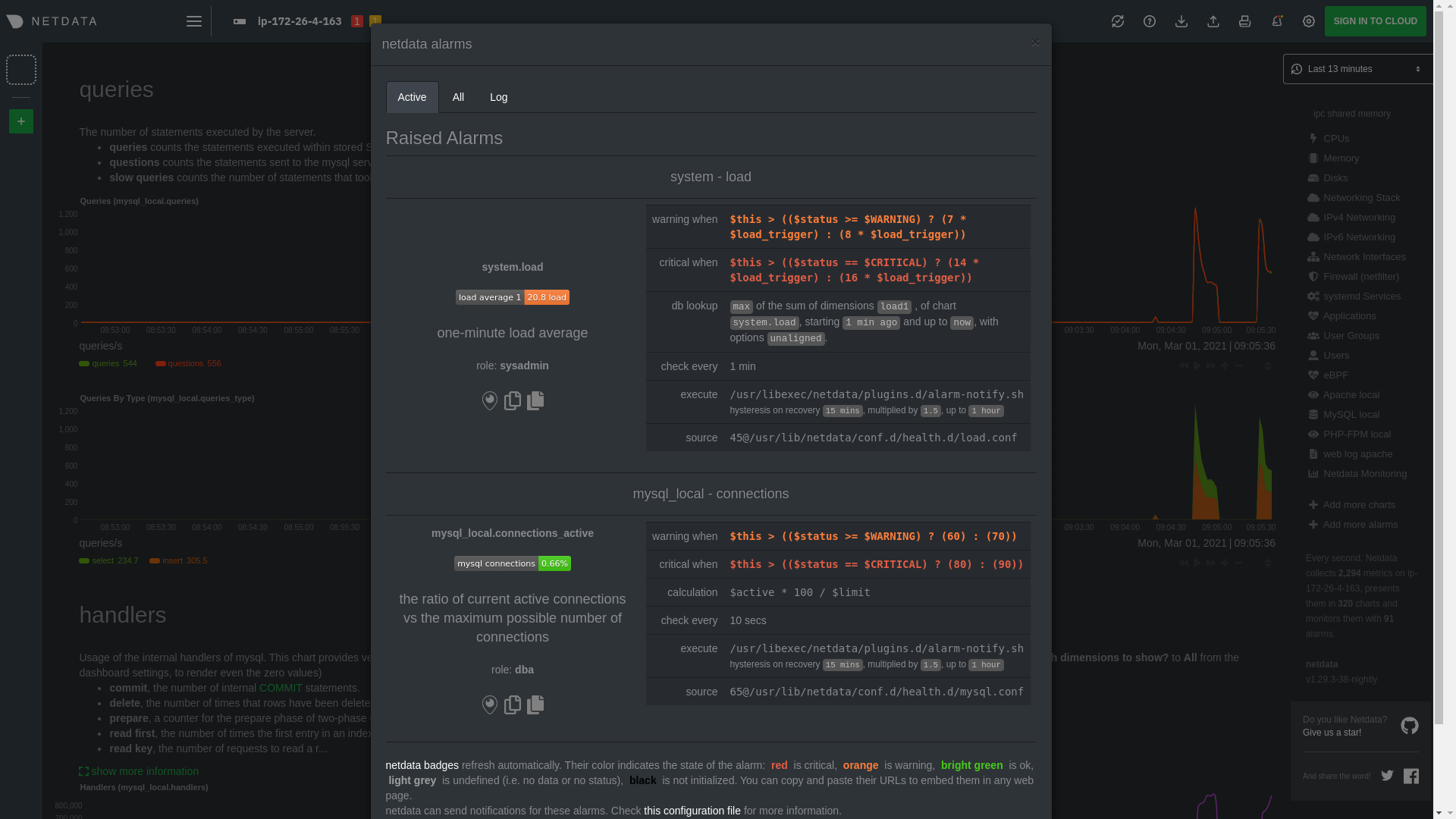 - -[Tweak alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/health/REFERENCE.md) based on your infrastructure monitoring needs, and to see these alerts -in other places, like your inbox or a Slack channel, [enable a notification -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md). - -## What's next? - -You've now set up robust monitoring for your entire LAMP stack: Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP (-FPM, to be exact). These -metrics will help you keep tabs on the performance and availability of your web application and all its essential -services. The per-second metrics granularity means you have the most accurate information possible for troubleshooting -any LAMP-related issues. - -Another powerful way to monitor the availability of a LAMP stack is the [`httpcheck` -collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/httpcheck/README.md), which pings a web server at -a regular interval and tells you whether if and how quickly it's responding. The `response_match` option also lets you -monitor when the web server's response isn't what you expect it to be, which might happen if PHP-FPM crashes, for -example. - -The best way to use the `httpcheck` collector is from a separate node from the one running your LAMP stack, which is why -we're not covering it here, but it _does_ work in a single-node setup. Just don't expect it to tell you if your whole -node crashed. - -If you're planning on managing more than one node, or want to take advantage of advanced features, like finding the -source of issues faster with [Metric Correlations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md), -[sign up](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-up?cloudRoute=/spaces) for a free Netdata Cloud account. - -### Related reference documentation - -- [Netdata Agent · Get started](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · Apache data collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/apache/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · Web log collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/weblog/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · MySQL data collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/mysql/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · PHP-FPM data collector](https://github.com/netdata/go.d.plugin/blob/master/modules/phpfpm/README.md) - |
