diff options
| author | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2024-04-28 09:25:25 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org> | 2024-04-28 09:25:25 +0000 |
| commit | 7eecd0464223b1bf79351c8f29cb3da5ee31d936 (patch) | |
| tree | 7e5deff77c13c92858808181794568f2d49c6f62 | |
| parent | Initial commit. (diff) | |
| download | spectre-meltdown-checker-upstream.tar.xz spectre-meltdown-checker-upstream.zip | |
Adding upstream version 0.45.upstream/0.45upstream
Signed-off-by: Daniel Baumann <daniel.baumann@progress-linux.org>
| -rw-r--r-- | .github/workflows/check.yml | 73 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | Dockerfile | 7 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | FAQ.md | 143 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | README.md | 180 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | docker-compose.yml | 15 | ||||
| -rwxr-xr-x | spectre-meltdown-checker.sh | 6258 |
6 files changed, 6676 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/.github/workflows/check.yml b/.github/workflows/check.yml new file mode 100644 index 0000000..c928dd5 --- /dev/null +++ b/.github/workflows/check.yml @@ -0,0 +1,73 @@ +name: CI + +on: [push, pull_request] + +jobs: + build: + + runs-on: ubuntu-latest + + steps: + - uses: actions/checkout@v1 + - name: install prerequisites + run: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y shellcheck jq sqlite3 iucode-tool + - name: shellcheck + run: shellcheck -s sh spectre-meltdown-checker.sh + - name: check indentation + run: | + if [ $(grep -cPv "^\t*\S|^$" spectre-meltdown-checker.sh) != 0 ]; then + echo "Badly indented lines found:" + grep -nPv "^\t*\S|^$" spectre-meltdown-checker.sh + exit 1 + else + echo "Indentation seems correct." + fi + - name: check direct execution + run: | + expected=15 + nb=$(sudo ./spectre-meltdown-checker.sh --batch json | jq '.[]|.CVE' | wc -l) + if [ "$nb" -ne "$expected" ]; then + echo "Invalid number of CVEs reported: $nb instead of $expected" + exit 1 + else + echo "OK $nb CVEs reported" + fi + - name: check docker-compose run execution + run: | + expected=15 + docker-compose build + nb=$(docker-compose run --rm spectre-meltdown-checker --batch json | jq '.[]|.CVE' | wc -l) + if [ "$nb" -ne "$expected" ]; then + echo "Invalid number of CVEs reported: $nb instead of $expected" + exit 1 + else + echo "OK $nb CVEs reported" + fi + - name: check docker run execution + run: | + expected=15 + docker build -t spectre-meltdown-checker . + nb=$(docker run --rm --privileged -v /boot:/boot:ro -v /dev/cpu:/dev/cpu:ro -v /lib/modules:/lib/modules:ro spectre-meltdown-checker --batch json | jq '.[]|.CVE' | wc -l) + if [ "$nb" -ne "$expected" ]; then + echo "Invalid number of CVEs reported: $nb instead of $expected" + exit 1 + else + echo "OK $nb CVEs reported" + fi + - name: check fwdb update + run: | + nbtmp1=$(find /tmp 2>/dev/null | wc -l) + ./spectre-meltdown-checker.sh --update-fwdb; ret=$? + if [ "$ret" != 0 ]; then + echo "Non-zero return value: $ret" + exit 1 + fi + nbtmp2=$(find /tmp 2>/dev/null | wc -l) + if [ "$nbtmp1" != "$nbtmp2" ]; then + echo "Left temporary files!" + exit 1 + fi + if ! [ -e ~/.mcedb ]; then + echo "No .mcedb file found after updating fwdb" + exit 1 + fi diff --git a/Dockerfile b/Dockerfile new file mode 100644 index 0000000..93fe602 --- /dev/null +++ b/Dockerfile @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +FROM alpine:3.7 + +RUN apk --update --no-cache add kmod binutils grep perl + +COPY . /check + +ENTRYPOINT ["/check/spectre-meltdown-checker.sh"] @@ -0,0 +1,143 @@ +# Questions + +- [What to expect from this tool?](#what-to-expect-from-this-tool) +- [Why was this script written in the first place?](#why-was-this-script-written-in-the-first-place) +- [Why are those vulnerabilities so different than regular CVEs?](#why-are-those-vulnerabilities-so-different-than-regular-cves) +- [What do "affected", "vulnerable" and "mitigated" mean exactly?](#what-do-affected-vulnerable-and-mitigated-mean-exactly) +- [What are the main design decisions regarding this script?](#what-are-the-main-design-decisions-regarding-this-script) +- [Everything is indicated in `sysfs` now, is this script still useful?](#everything-is-indicated-in-sysfs-now-is-this-script-still-useful) +- [How does this script work?](#how-does-this-script-work) +- [Which BSD OSes are supported?](#which-bsd-oses-are-supported) +- [Why is my OS not supported?](#why-is-my-os-not-supported) +- [The tool says there is an updated microcode for my CPU, but I don't have it!](#the-tool-says-there-is-an-updated-microcode-for-my-cpu-but-i-dont-have-it) +- [The tool says that I need a more up-to-date microcode, but I have the more recent version!](#the-tool-says-that-i-need-a-more-up-to-date-microcode-but-i-have-the-more-recent-version) +- [Which rules are governing the support of a CVE in this tool?](#which-rules-are-governing-the-support-of-a-cve-in-this-tool) + +# Answers + +## What to expect from this tool? + +This tool does its best to determine where your system stands on each of the collectively named [transient execution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transient_execution_CPU_vulnerability) vulnerabilities (also sometimes called "speculative execution" vulnerabilities) that were made public since early 2018. It doesn't attempt to run any kind of exploit, and can't guarantee that your system is secure, but rather helps you verifying if your system is affected, and if it is, checks whether it has the known mitigations in place to avoid being vulnerable. +Some mitigations could also exist in your kernel that this script doesn't know (yet) how to detect, or it might falsely detect mitigations that in the end don't work as expected (for example, on backported or modified kernels). + +Please also note that for Spectre vulnerabilities, all software can possibly be exploited, this tool only verifies that the kernel (which is the core of the system) you're using has the proper protections in place. Verifying all the other software is out of the scope of this tool. As a general measure, ensure you always have the most up to date stable versions of all the software you use, especially for those who are exposed to the world, such as network daemons and browsers. + +This tool has been released in the hope that it'll be useful, but don't use it to jump to definitive conclusions about your security: hardware vulnerabilities are [complex beasts](#why-are-those-vulnerabilities-so-different-than-regular-cves), and collective understanding of each vulnerability is evolving with time. + +## Why was this script written in the first place? + +The first commit of this script is dated *2018-01-07*, only 4 days after the world first heard about the Meltdown and the Spectre attacks. With those attacks disclosure, a _whole new range of vulnerabilities_ that were previously thought to be mostly theoretical and only possible in very controlled environments (labs) - hence of little interest for most except researchers - suddenly became completely mainstream and apparently trivial to conduct on an immensely large number of systems. + +On the few hours and days after that date, the whole industry went crazy. Proper, verified information about these vulnerabilities was incredibly hard to find, because before this, even the CPU vendors never had to deal with managing security vulnerabilities at scale, as software vendors do since decades. There were a lot of FUD, and the apparent silence of the vendors was enough for most to fear the worst. The whole industry had everything to learn about this new type of vulnerabilities. However, most systems administrators had a few simple questions: + +- Am **I** vulnerable? And if yes, +- What do I have to do to mitigate these vulnerabilities on **my** system? + +Unfortunately, answering those questions was very difficult (and still is to some extent), even if the safe answer to the first question was "you probably are". This script was written to try to give simple answers to those simple questions, and was made to evolve as the information about these vulnerabilities became available. On the first few days, there was several new versions published **per day**. + +## Why are those vulnerabilities so different than regular CVEs? + +Those are hardware vulnerabilities, while most of the CVEs we see everyday are software vulnerabilities. A quick comparison would be: + +Software vulnerability: +- Can be fixed? Yes. +- How to fix? Update the software (or uninstall it!) + +Hardware vulnerability: +- Can be fixed? No, only mitigated (or buy new hardware!) +- How to ~~fix~~ mitigate? In the worst case scenario, 5 "layers" need to be updated: the microcode/firmware, the host OS kernel, the hypervisor, the VM OS kernel, and possibly all the software running on the VM. + +A more detailed video explanation is available here: https://youtu.be/2gB9U1EcCss?t=85 + +## What do "affected", "vulnerable" and "mitigated" mean exactly? + +- **Affected** means that your CPU's hardware, as it went out of the factory, is known to be concerned by a specific vulnerability, i.e. the vulnerability applies to your hardware model. Note that it says nothing about whether a given vulnerability can actually be used to exploit your system. However, an unaffected CPU will never be vulnerable, and doesn't need to have mitigations in place. +- **Vulnerable** implies that you're using an **affected** CPU, and means that a given vulnerability can be exploited on your system, because no (or insufficient) mitigations are in place. +- **Mitigated** implies that a previously **vulnerable** system has followed all the steps (updated all the required layers) to ensure a given vulnerability cannot be exploited. About what "layers" mean, see [the previous question](#why-are-those-vulnerabilities-so-different-than-regular-cves). + +## What are the main design decisions regarding this script? + +There are a few rules that govern how this tool is written. + +1) It should be okay to run this script in a production environment. This implies, but is not limited to: + + * 1a. Never modify the system it's running on, and if it needs to e.g. load a kernel module it requires, that wasn't loaded before it was launched, it'll take care to unload it on exit + * 1b. Never attempt to "fix" or "mitigate" any vulnerability, or modify any configuration. It just reports what it thinks is the status of your system. It leaves all decisions to the sysadmin. + * 1c. Never attempt to run any kind of exploit to tell whether a vulnerability is mitigated, because it would violate 1a), could lead to unpredictable system behavior, and might even lead to wrong conclusions, as some PoC must be compiled with specific options and prerequisites, otherwise giving wrong information (especially for Spectre). If you want to run PoCs, do it yourself, but please read carefully about the PoC and the vulnerability. PoCs about a hardware vulnerability are way more complicated and prone to false conclusions than PoCs for software vulnerabilities. + +2) Never look at the kernel version to tell whether it supports mitigation for a given vulnerability. This implies never hardcoding version numbers in the script. This would defeat the purpose: this script should be able to detect mitigations in unknown kernels, with possibly backported or forward-ported patches. Also, don't believe what `sysfs` says, when possible. See the next question about this. + +3) Never look at the microcode version to tell whether it has the proper mechanisms in place to support mitigation for a given vulnerability. This implies never hardcoding version numbers in the script. Instead, look for said mechanisms, as the kernel would do. + +4) When a CPU is not known to be explicitly unaffected by a vulnerability, make the assumption that it is. This strong design choice has it roots in the early speculative execution vulnerability days (see [this answer](#why-was-this-script-written-in-the-first-place)), and is still a good approach as of today. + +## Everything is indicated in `sysfs` now, is this script still useful? + +A lot as changed since 2018. Nowadays, the industry adapted and this range of vulnerabilities is almost "business as usual", as software vulnerabilities are. However, due to their complexity, it's still not as easy as just checking a version number to ensure a vulnerability is closed. + +Granted, we now have a standard way under Linux to check whether our system is affected, vulnerable, mitigated against most of these vulnerabilities. By having a look at the `sysfs` hierarchy, and more precisely the `/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/` folder, one can have a pretty good insight about its system state for each of the listed vulnerabilities. Note that the output can be a little different with some vendors (e.g. Red Hat has some slightly different output than the vanilla kernel for some vulnerabilities), but it's still a gigantic leap forward, given where we were in 2018 when this script was started, and it's very good news. The kernel is the proper place to have this because the kernel knows everything about itself (the mitigations it might have), and the CPU (its model, and microcode features that are exposed). + +However I see a few reasons why this script might still be useful to you, and that's why its development has not halted when the `sysfs` hierarchy came out: + +- A given version of the kernel doesn't have knowledge about the future. To put it in another way: a given version of the kernel only has the understanding of a vulnerability available at the time it was compiled. Let me explain this: when a new vulnerability comes out, new versions of the microcode and kernels are released, with mitigations in place. With such a kernel, a new `sysfs` entry will appear. However, after a few weeks or months, corner cases can be discovered, previously-thought unaffected CPUs can turn out to be affected in the end, and sometimes mitigations can end up being insufficient. Of course, if you're always running the latest kernel version from kernel.org, this issue might be limited for you. The spectre-meltdown-checker script doesn't depend on a kernel's knowledge and understanding of a vulnerability to compute its output. That is, unless you tell it to (using the `--sysfs-only` option). + +- Mitigating a vulnerability completely can sometimes be tricky, and have a lot of complicated prerequisites, depending on your kernel version, CPU vendor, model and even sometimes stepping, CPU microcode, hypervisor support, etc. The script gives a very detailed insight about each of the prerequisites of mitigation for every vulnerability, step by step, hence pointing out what is missing on your system as a whole to completely mitigate an issue. + +- The script can be pointed at a kernel image, and will deep dive into it, telling you if this kernel will mitigate vulnerabilities that might be present on your system. This is a good way to verify before booting a new kernel, that it'll mitigate the vulnerabilities you expect it to, especially if you modified a few config options around these topics. + +- The script will also work regardless of the custom patches that might be integrated in the kernel you're running (or you're pointing it to, in offline mode), and completely ignores the advertised kernel version, to tell whether a given kernel mitigates vulnerabilities. This is especially useful for non-vanilla kernel, where patches might be backported, sometimes silently (this has already happened, too). + +- Educational purposes: the script gives interesting insights about a vulnerability, and how the different parts of the system work together to mitigate it. + +There are probably other reasons, but that are the main ones that come to mind. In the end, of course, only you can tell whether it's useful for your use case ;) + +## How does this script work? + +On one hand, the script gathers information about your CPU, and the features exposed by its microcode. To do this, it uses the low-level CPUID instruction (through the `cpuid` kernel module under Linux, and the `cpucontrol` tool under BSD), and queries to the MSR registers of your CPU (through the `msr` kernel module under Linux, and the `cpucontrol` tool under BSD). + +On another hand, the script looks into the kernel image your system is running on, for clues about the mitigations it supports. Of course, this is very specific for each operating system, even if the implemented mitigation is functionally the same, the actual code is completely specific. As you can imagine, the Linux kernel code has a few in common with a BSD kernel code, for example. Under Linux, the script supports looking into the kernel image, and possibly the System.map and kernel config file, if these are available. Under BSD, it looks into the kernel file only. + +Then, for each vulnerability it knows about, the script decides whether your system is [affected, vulnerable, and mitigated](#what-do-affected-vulnerable-and-mitigated-mean-exactly) against it, using the information it gathered about your hardware and your kernel. + +## Which BSD OSes are supported? + +For the BSD range of operating systems, the script will work as long as the BSD you're using supports `cpuctl` and `linprocfs`. This is not the case for OpenBSD for example. Known BSD flavors having proper support are: FreeBSD, NetBSD, DragonflyBSD. Derivatives of those should also work. To know why other BSDs will likely never be supported, see [why is my OS not supported?](#why-is-my-os-not-supported). + +## Why is my OS not supported? + +This tool only supports Linux, and [some flavors of BSD](#which-bsd-oses-are-supported). Other OSes will most likely never be supported, due to [how this script works](#how-does-this-script-work). It would require implementing these OSes specific way of querying the CPU. It would also require to get documentation (if available) about how this OS mitigates each vulnerability, down to this OS kernel code, and if documentation is not available, reverse-engineer the difference between a known old version of a kernel, and a kernel that mitigates a new vulnerability. This means that all the effort has to be duplicated times the number of supported OSes, as everything is specific, by construction. It also implies having a deep understanding of every OS, which takes years to develop. However, if/when other tools appear for other OSes, that share the same goal of this one, they might be listed here as a convenience. + +## The tool says there is an updated microcode for my CPU, but I don't have it! + +Even if your operating system is fully up to date, the tool might still tell you that there is a more recent microcode version for your CPU. Currently, it uses (and merges) information from two sources: + +- The official [Intel microcode repository](https://github.com/intel/Intel-Linux-Processor-Microcode-Data-Files) +- The awesome platomav's [MCExtractor database](https://github.com/platomav/MCExtractor) for non-Intel CPUs + +Generally, for Intel CPUs it means that Intel does have a more recent version for your CPU, and for other CPUs it means that a more recent version has already been seen in the wild. However, your OS vendor might have chosen not to ship this new version (yet), maybe because it's currently being tested, or for other reasons. This tool can't tell you when or if this will be the case. You should ask your vendor about it. Technically, you can still go and upgrade your microcode yourself, and use this tool to confirm whether you did it successfully. Updating the microcode for you is out of the scope of this tool, as this would violate [rule 1b](#what-are-the-main-design-decisions-regarding-this-script). + +## The tool says that I need a more up-to-date microcode, but I have the more recent version! + +This can happen for a few reasons: + +- Your CPU is no longer supported by the vendor. In that case, new versions of the microcode will never be published, and vulnerabilities requiring microcode features will never be fixed. On most of these vulnerabilities, you'll have no way to mitigate the issue on a vulnerable system, appart from buying a more recent CPU. Sometimes, you might be able to mitigate the issue by disabling a CPU feature instead (often at the cost of speed). When this is the case, the script will list this as one of the possible mitigations for the vulnerability. + +- The vulnerability is recent, and your CPU has not yet received a microcode update for the vendor. Often, these updates come in batches, and it can take several batches to cover all the supported CPUs. + +In both cases, you can contact your vendor to know whether there'll be an update or not, and if yes, when. For Intel, at the time this FAQ entry was written, such guidance was [available here](https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/topics/software-security-guidance/processors-affected-consolidated-product-cpu-model.html). + +## Which rules are governing the support of a CVE in this tool? + +On the early days, it was easy: just Spectre and Meltdown (hence the tool name), because that's all we had. Now that this range of vulnerability is seeing a bunch of newcomers every year, this question is legitimate. + +To stick with this tool's goal, a good indication as to why a CVE should be supported, is when mitigating it requires either kernel modifications, microcode modifications, or both. + +Counter-examples include (non-exhaustive list): + +- [CVE-2019-14615](https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues/340), mitigating this issue is done by updating the Intel driver. This is out of the scope of this tool. +- [CVE-2019-15902](https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues/304), this CVE is due to a bad backport in the stable kernel. If the faulty backport was part of the mitigation of another supported CVE, and this bad backport was detectable (without hardcoding kernel versions, see [rule 2](#why-are-those-vulnerabilities-so-different-than-regular-cves)), it might have been added as a bullet point in the concerned CVE's section in the tool. However, this wasn't the case. +- The "[Take A Way](https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues/344)" vulnerability, AMD said that they believe this is not a new attack, hence there were no microcode and no kernel modification made. As there is nothing to look for, this is out of the scope of this tool. +- [CVE-2020-0550](https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues/347), the vendor thinks this is hardly exploitable in the wild, and as mitigations would be too performance impacting, as a whole the industry decided to not address it. As there is nothing to check for, this is out of the scope of this tool. +- [CVE-2020-0551](https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues/348), the industry decided to not address it, as it is believed mitigations for other CVEs render this attack practically hard to make, Intel just released an updated SDK for SGX to help mitigate the issue, but this is out of the scope of this tool. + +Look for the [information](https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues?q=is%3Aissue+is%3Aopen+label%3Ainformation) tag in the issues list for more examples. diff --git a/README.md b/README.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000..710840b --- /dev/null +++ b/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,180 @@ +Spectre & Meltdown Checker +========================== + +A shell script to assess your system's resilience against the several [transient execution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transient_execution_CPU_vulnerability) CVEs that were published since early 2018, and give you guidance as to how to mitigate them. + +CVE | Name | Aliases +------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------- +[CVE-2017-5753](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-5754) | Bounds Check Bypass | Spectre Variant 1 +[CVE-2017-5715](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-5715) | Branch Target Injection | Spectre Variant 2 +[CVE-2017-5754](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-5754) | Rogue Data Cache Load | Meltdown, Variant 3 +[CVE-2018-3640](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3640) | Rogue System Register Read | Variant 3a +[CVE-2018-3639](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3639) | Speculative Store Bypass | Variant 4 +[CVE-2018-3615](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3615) | L1 Terminal Fault | L1TF, Foreshadow (SGX) +[CVE-2018-3620](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3620) | L1 Terminal Fault | L1TF, Foreshadow-NG (OS) +[CVE-2018-3646](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-3646) | L1 Terminal Fault | L1TF, Foreshadow-NG (VMM) +[CVE-2018-12126](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-12126) | Microarchitectural Store Buffer Data Sampling | MSBDS, Fallout +[CVE-2018-12130](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-12130) | Microarchitectural Fill Buffer Data Sampling | MFBDS, ZombieLoad +[CVE-2018-12127](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-12127) | Microarchitectural Load Port Data Sampling | MLPDS, RIDL +[CVE-2019-11091](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-11091) | Microarchitectural Data Sampling Uncacheable Memory | MDSUM, RIDL +[CVE-2019-11135](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-11135) | TSX asynchronous abort | TAA, ZombieLoad V2 +[CVE-2018-12207](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-12207) | Machine Mheck Exception on Page Size Changes | MCEPSC, No eXcuses, iTLB Multihit +[CVE-2020-0543](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2020-0543) | Special Register Buffer Data Sampling | SRBDS + +Supported operating systems: +- Linux (all versions, flavors and distros) +- FreeBSD, NetBSD, DragonFlyBSD and derivatives (others BSDs are [not supported](FAQ.md#which-bsd-oses-are-supported)) + +For Linux systems, the tool will detect mitigations, including backported non-vanilla patches, regardless of the advertised kernel version number and the distribution (such as Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, openSUSE, Arch, ...), it also works if you've compiled your own kernel. More information [here](FAQ.md#how-does-this-script-work). + +Other operating systems such as MacOS, Windows, ESXi, etc. [will most likely never be supported](FAQ.md#why-is-my-os-not-supported). + +Supported architectures: +- `x86` (32 bits) +- `amd64`/`x86_64` (64 bits) +- `ARM` and `ARM64` +- other architectures will work, but mitigations (if they exist) might not always be detected + +## Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) + +- What is the purpose of this tool? +- Why was it written? +- How can it be useful to me? +- How does it work? +- What can I expect from it? + +All these questions (and more) have detailed answers in the [FAQ](FAQ.md), please have a look! + +## Easy way to run the script + +- Get the latest version of the script using `curl` *or* `wget` + +```bash +curl -L https://meltdown.ovh -o spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +wget https://meltdown.ovh -O spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +``` + +- Inspect the script. You never blindly run scripts you downloaded from the Internet, do you? + +```bash +vim spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +``` + +- When you're ready, run the script as root + +```bash +chmod +x spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +sudo ./spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +``` + +### Run the script in a docker container + +#### With docker-compose + +```shell +docker-compose build +docker-compose run --rm spectre-meltdown-checker +``` + +#### Without docker-compose + +```shell +docker build -t spectre-meltdown-checker . +docker run --rm --privileged -v /boot:/boot:ro -v /dev/cpu:/dev/cpu:ro -v /lib/modules:/lib/modules:ro spectre-meltdown-checker +``` + +## Example of script output + +- Intel Haswell CPU running under Ubuntu 16.04 LTS + + + +- AMD Ryzen running under OpenSUSE Tumbleweed + +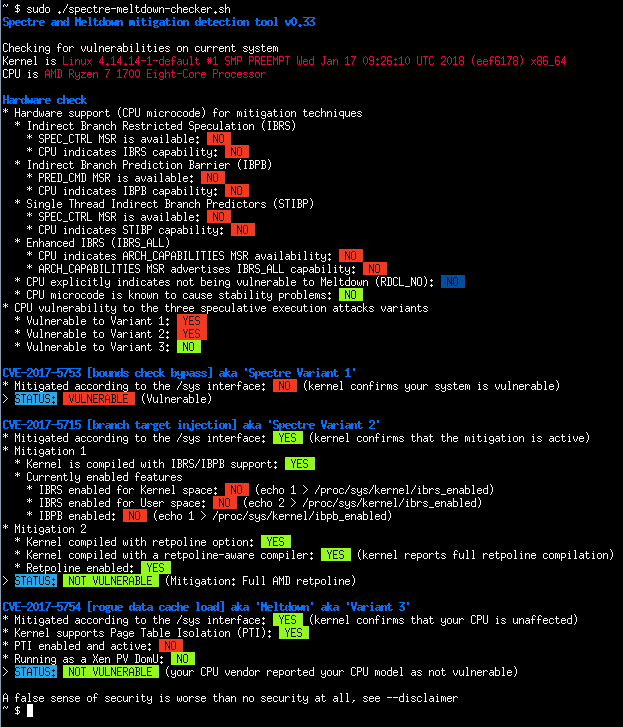 + +- Batch mode (JSON flavor) + + + +## Quick summary of the CVEs + +**CVE-2017-5753** bounds check bypass (Spectre Variant 1) + + - Impact: Kernel & all software + - Mitigation: recompile software *and* kernel with a modified compiler that introduces the LFENCE opcode at the proper positions in the resulting code + - Performance impact of the mitigation: negligible + +**CVE-2017-5715** branch target injection (Spectre Variant 2) + + - Impact: Kernel + - Mitigation 1: new opcode via microcode update that should be used by up to date compilers to protect the BTB (by flushing indirect branch predictors) + - Mitigation 2: introducing "retpoline" into compilers, and recompile software/OS with it + - Performance impact of the mitigation: high for mitigation 1, medium for mitigation 2, depending on your CPU + +**CVE-2017-5754** rogue data cache load (Meltdown) + + - Impact: Kernel + - Mitigation: updated kernel (with PTI/KPTI patches), updating the kernel is enough + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low to medium + +**CVE-2018-3640** rogue system register read (Variant 3a) + + - Impact: TBC + - Mitigation: microcode update only + - Performance impact of the mitigation: negligible + +**CVE-2018-3639** speculative store bypass (Variant 4) + + - Impact: software using JIT (no known exploitation against kernel) + - Mitigation: microcode update + kernel update making possible for affected software to protect itself + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low to medium + +**CVE-2018-3615** l1 terminal fault (Foreshadow-NG SGX) + + - Impact: Kernel & all software (any physical memory address in the system) + - Mitigation: microcode update + - Performance impact of the mitigation: negligible + +**CVE-2018-3620** l1 terminal fault (Foreshadow-NG SMM) + + - Impact: Kernel & System management mode + - Mitigation: updated kernel (with PTE inversion) + - Performance impact of the mitigation: negligible + +**CVE-2018-3646** l1 terminal fault (Foreshadow-NG VMM) + + - Impact: Virtualization software and Virtual Machine Monitors + - Mitigation: disable ept (extended page tables), disable hyper-threading (SMT), or updated kernel (with L1d flush) + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low to significant + +**CVE-2018-12126** [MSBDS] Microarchitectural Store Buffer Data Sampling (Fallout) + +**CVE-2018-12130** [MFBDS] Microarchitectural Fill Buffer Data Sampling (ZombieLoad) + +**CVE-2018-12127** [MLPDS] Microarchitectural Load Port Data Sampling (RIDL) + +**CVE-2019-11091** [MDSUM] Microarchitectural Data Sampling Uncacheable Memory (RIDL) + + - Note: These 4 CVEs are similar and collectively named "MDS" vulnerabilities, the mitigation is identical for all + - Impact: Kernel + - Mitigation: microcode update + kernel update making possible to protect various CPU internal buffers from unprivileged speculative access to data + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low to significant + +**CVE-2019-11135** TSX Asynchronous Abort (TAA, ZombieLoad V2) + + - Impact: Kernel + - Mitigation: microcode update + kernel update making possible to protect various CPU internal buffers from unprivileged speculative access to data + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low to significant + +**CVE-2018-12207** machine check exception on page size changes (No eXcuses, iTLB Multihit) + + - Impact: Virtualization software and Virtual Machine Monitors + - Mitigation: disable hugepages use in hypervisor, or update hypervisor to benefit from mitigation + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low to significant + +**CVE-2020-0543** Special Register Buffer Data Sampling (SRBDS) + + - Impact: Kernel + - Mitigation: microcode update + kernel update helping to protect various CPU internal buffers from unprivileged speculative access to data + - Performance impact of the mitigation: low diff --git a/docker-compose.yml b/docker-compose.yml new file mode 100644 index 0000000..c4024d6 --- /dev/null +++ b/docker-compose.yml @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ +version: '2' + +services: + spectre-meltdown-checker: + build: + context: ./ + dockerfile: ./Dockerfile + image: spectre-meltdown-checker:latest + container_name: spectre-meltdown-checker + privileged: true + network_mode: none + volumes: + - /boot:/boot:ro + - /dev/cpu:/dev/cpu:ro + - /lib/modules:/lib/modules:ro diff --git a/spectre-meltdown-checker.sh b/spectre-meltdown-checker.sh new file mode 100755 index 0000000..10064af --- /dev/null +++ b/spectre-meltdown-checker.sh @@ -0,0 +1,6258 @@ +#! /bin/sh +# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0-only +# vim: set ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 noet: +# +# Spectre & Meltdown checker +# +# Check for the latest version at: +# https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker +# git clone https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker.git +# or wget https://meltdown.ovh -O spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +# or curl -L https://meltdown.ovh -o spectre-meltdown-checker.sh +# +# Stephane Lesimple +# +VERSION='0.45' + +trap 'exit_cleanup' EXIT +trap '_warn "interrupted, cleaning up..."; exit_cleanup; exit 1' INT +exit_cleanup() +{ + # cleanup the temp decompressed config & kernel image + [ -n "${dumped_config:-}" ] && [ -f "$dumped_config" ] && rm -f "$dumped_config" + [ -n "${kerneltmp:-}" ] && [ -f "$kerneltmp" ] && rm -f "$kerneltmp" + [ -n "${kerneltmp2:-}" ] && [ -f "$kerneltmp2" ] && rm -f "$kerneltmp2" + [ -n "${mcedb_tmp:-}" ] && [ -f "$mcedb_tmp" ] && rm -f "$mcedb_tmp" + [ -n "${intel_tmp:-}" ] && [ -d "$intel_tmp" ] && rm -rf "$intel_tmp" + [ "${mounted_debugfs:-}" = 1 ] && umount /sys/kernel/debug 2>/dev/null + [ "${mounted_procfs:-}" = 1 ] && umount "$procfs" 2>/dev/null + [ "${insmod_cpuid:-}" = 1 ] && rmmod cpuid 2>/dev/null + [ "${insmod_msr:-}" = 1 ] && rmmod msr 2>/dev/null + [ "${kldload_cpuctl:-}" = 1 ] && kldunload cpuctl 2>/dev/null + [ "${kldload_vmm:-}" = 1 ] && kldunload vmm 2>/dev/null +} + +# if we were git clone'd, adjust VERSION +if [ -d "$(dirname "$0")/.git" ] && command -v git >/dev/null 2>&1; then + describe=$(git -C "$(dirname "$0")" describe --tags --dirty 2>/dev/null) + [ -n "$describe" ] && VERSION=$(echo "$describe" | sed -e s/^v//) +fi + +show_usage() +{ + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + cat <<EOF + Usage: + Live mode (auto): $(basename $0) [options] + Live mode (manual): $(basename $0) [options] <[--kernel <kimage>] [--config <kconfig>] [--map <mapfile>]> --live + Offline mode: $(basename $0) [options] <[--kernel <kimage>] [--config <kconfig>] [--map <mapfile>]> + + Modes: + Two modes are available. + + First mode is the "live" mode (default), it does its best to find information about the currently running kernel. + To run under this mode, just start the script without any option (you can also use --live explicitly) + + Second mode is the "offline" mode, where you can inspect a non-running kernel. + This mode is automatically enabled when you specify the location of the kernel file, config and System.map files: + + --kernel kernel_file specify a (possibly compressed) Linux or BSD kernel file + --config kernel_config specify a kernel config file (Linux only) + --map kernel_map_file specify a kernel System.map file (Linux only) + + If you want to use live mode while specifying the location of the kernel, config or map file yourself, + you can add --live to the above options, to tell the script to run in live mode instead of the offline mode, + which is enabled by default when at least one file is specified on the command line. + + Options: + --no-color don't use color codes + --verbose, -v increase verbosity level, possibly several times + --explain produce an additional human-readable explanation of actions to take to mitigate a vulnerability + --paranoid require IBPB to deem Variant 2 as mitigated + also require SMT disabled + unconditional L1D flush to deem Foreshadow-NG VMM as mitigated + also require SMT disabled to deem MDS vulnerabilities mitigated + + --no-sysfs don't use the /sys interface even if present [Linux] + --sysfs-only only use the /sys interface, don't run our own checks [Linux] + --coreos special mode for CoreOS (use an ephemeral toolbox to inspect kernel) [Linux] + + --arch-prefix PREFIX specify a prefix for cross-inspecting a kernel of a different arch, for example "aarch64-linux-gnu-", + so that invoked tools will be prefixed with this (i.e. aarch64-linux-gnu-objdump) + --batch text produce machine readable output, this is the default if --batch is specified alone + --batch short produce only one line with the vulnerabilities separated by spaces + --batch json produce JSON output formatted for Puppet, Ansible, Chef... + --batch nrpe produce machine readable output formatted for NRPE + --batch prometheus produce output for consumption by prometheus-node-exporter + + --variant VARIANT specify which variant you'd like to check, by default all variants are checked + VARIANT can be one of 1, 2, 3, 3a, 4, l1tf, msbds, mfbds, mlpds, mdsum, taa, mcepsc, srbds + can be specified multiple times (e.g. --variant 2 --variant 3) + --cve [cve1,cve2,...] specify which CVE you'd like to check, by default all supported CVEs are checked + --hw-only only check for CPU information, don't check for any variant + --no-hw skip CPU information and checks, if you're inspecting a kernel not to be run on this host + --vmm [auto,yes,no] override the detection of the presence of a hypervisor, default: auto + --allow-msr-write allow probing for write-only MSRs, this might produce kernel logs or be blocked by your system + --cpu [#,all] interact with CPUID and MSR of CPU core number #, or all (default: CPU core 0) + --update-fwdb update our local copy of the CPU microcodes versions database (using the awesome + MCExtractor project and the Intel firmwares GitHub repository) + --update-builtin-fwdb same as --update-fwdb but update builtin DB inside the script itself + --dump-mock-data used to mimick a CPU on an other system, mainly used to help debugging this script + + Return codes: + 0 (not vulnerable), 2 (vulnerable), 3 (unknown), 255 (error) + + IMPORTANT: + A false sense of security is worse than no security at all. + Please use the --disclaimer option to understand exactly what this script does. + +EOF +} + +show_disclaimer() +{ + cat <<EOF +Disclaimer: + +This tool does its best to determine whether your system is immune (or has proper mitigations in place) for the +collectively named "speculative execution" vulnerabilities. It doesn't attempt to run any kind of exploit, and can't guarantee +that your system is secure, but rather helps you verifying whether your system has the known correct mitigations in place. +However, some mitigations could also exist in your kernel that this script doesn't know (yet) how to detect, or it might +falsely detect mitigations that in the end don't work as expected (for example, on backported or modified kernels). + +Your system exposure also depends on your CPU. As of now, AMD and ARM processors are marked as immune to some or all of these +vulnerabilities (except some specific ARM models). All Intel processors manufactured since circa 1995 are thought to be vulnerable, +except some specific/old models, such as some early Atoms. Whatever processor one uses, one might seek more information +from the manufacturer of that processor and/or of the device in which it runs. + +The nature of the discovered vulnerabilities being quite new, the landscape of vulnerable processors can be expected +to change over time, which is why this script makes the assumption that all CPUs are vulnerable, except if the manufacturer +explicitly stated otherwise in a verifiable public announcement. + +Please also note that for Spectre vulnerabilities, all software can possibly be exploited, this tool only verifies that the +kernel (which is the core of the system) you're using has the proper protections in place. Verifying all the other software +is out of the scope of this tool. As a general measure, ensure you always have the most up to date stable versions of all +the software you use, especially for those who are exposed to the world, such as network daemons and browsers. + +This tool has been released in the hope that it'll be useful, but don't use it to jump to conclusions about your security. + +EOF +} + +os=$(uname -s) + +# parse options +opt_kernel='' +opt_config='' +opt_map='' +opt_live=-1 +opt_no_color=0 +opt_batch=0 +opt_batch_format='text' +opt_verbose=1 +opt_cve_list='' +opt_cve_all=1 +opt_no_sysfs=0 +opt_sysfs_only=0 +opt_coreos=0 +opt_arch_prefix='' +opt_hw_only=0 +opt_no_hw=0 +opt_vmm=-1 +opt_allow_msr_write=0 +opt_cpu=0 +opt_explain=0 +opt_paranoid=0 +opt_mock=0 + +global_critical=0 +global_unknown=0 +nrpe_vuln='' + +supported_cve_list='CVE-2017-5753 CVE-2017-5715 CVE-2017-5754 CVE-2018-3640 CVE-2018-3639 CVE-2018-3615 CVE-2018-3620 CVE-2018-3646 CVE-2018-12126 CVE-2018-12130 CVE-2018-12127 CVE-2019-11091 CVE-2019-11135 CVE-2018-12207 CVE-2020-0543' + +# find a sane command to print colored messages, we prefer `printf` over `echo` +# because `printf` behavior is more standard across Linux/BSD +# we'll try to avoid using shell builtins that might not take options +echo_cmd_type='echo' +# ignore SC2230 here because `which` ignores builtins while `command -v` doesn't, and +# we don't want builtins here. Even if `which` is not installed, we'll fallback to the +# `echo` builtin anyway, so this is safe. +# shellcheck disable=SC2230 +if command -v printf >/dev/null 2>&1; then + echo_cmd=$(command -v printf) + echo_cmd_type='printf' +elif which echo >/dev/null 2>&1; then + echo_cmd=$(which echo) +else + # maybe the `which` command is broken? + [ -x /bin/echo ] && echo_cmd=/bin/echo + # for Android + [ -x /system/bin/echo ] && echo_cmd=/system/bin/echo +fi +# still empty? fallback to builtin +[ -z "$echo_cmd" ] && echo_cmd='echo' +__echo() +{ + opt="$1" + shift + _msg="$*" + + if [ "$opt_no_color" = 1 ] ; then + # strip ANSI color codes + # some sed versions (i.e. toybox) can't seem to handle + # \033 aka \x1B correctly, so do it for them. + if [ "$echo_cmd_type" = printf ]; then + _interpret_chars='' + else + _interpret_chars='-e' + fi + _ctrlchar=$($echo_cmd $_interpret_chars "\033") + _msg=$($echo_cmd $_interpret_chars "$_msg" | sed -r "s/$_ctrlchar\[([0-9][0-9]?(;[0-9][0-9]?)?)?m//g") + fi + if [ "$echo_cmd_type" = printf ]; then + if [ "$opt" = "-n" ]; then + $echo_cmd "$_msg" + else + $echo_cmd "$_msg\n" + fi + else + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + $echo_cmd $opt -e "$_msg" + fi +} + +_echo() +{ + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge "$1" ]; then + shift + __echo '' "$*" + fi +} + +_echo_nol() +{ + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge "$1" ]; then + shift + __echo -n "$*" + fi +} + +_warn() +{ + _echo 0 "\033[31m$*\033[0m" >&2 +} + +_info() +{ + _echo 1 "$*" +} + +_info_nol() +{ + _echo_nol 1 "$*" +} + +_verbose() +{ + _echo 2 "$*" +} + +_verbose_nol() +{ + _echo_nol 2 "$*" +} + +_debug() +{ + _echo 3 "\033[34m(debug) $*\033[0m" +} + +explain() +{ + if [ "$opt_explain" = 1 ] ; then + _info '' + _info "> \033[41m\033[30mHow to fix:\033[0m $*" + fi +} + +cve2name() +{ + case "$1" in + CVE-2017-5753) echo "Spectre Variant 1, bounds check bypass";; + CVE-2017-5715) echo "Spectre Variant 2, branch target injection";; + CVE-2017-5754) echo "Variant 3, Meltdown, rogue data cache load";; + CVE-2018-3640) echo "Variant 3a, rogue system register read";; + CVE-2018-3639) echo "Variant 4, speculative store bypass";; + CVE-2018-3615) echo "Foreshadow (SGX), L1 terminal fault";; + CVE-2018-3620) echo "Foreshadow-NG (OS), L1 terminal fault";; + CVE-2018-3646) echo "Foreshadow-NG (VMM), L1 terminal fault";; + CVE-2018-12126) echo "Fallout, microarchitectural store buffer data sampling (MSBDS)";; + CVE-2018-12130) echo "ZombieLoad, microarchitectural fill buffer data sampling (MFBDS)";; + CVE-2018-12127) echo "RIDL, microarchitectural load port data sampling (MLPDS)";; + CVE-2019-11091) echo "RIDL, microarchitectural data sampling uncacheable memory (MDSUM)";; + CVE-2019-11135) echo "ZombieLoad V2, TSX Asynchronous Abort (TAA)";; + CVE-2018-12207) echo "No eXcuses, iTLB Multihit, machine check exception on page size changes (MCEPSC)";; + CVE-2020-0543) echo "Special Register Buffer Data Sampling (SRBDS)";; + *) echo "$0: error: invalid CVE '$1' passed to cve2name()" >&2; exit 255;; + esac +} + +is_cpu_affected_cached=0 +_is_cpu_affected_cached() +{ + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + case "$1" in + CVE-2017-5753) return $variant1;; + CVE-2017-5715) return $variant2;; + CVE-2017-5754) return $variant3;; + CVE-2018-3640) return $variant3a;; + CVE-2018-3639) return $variant4;; + CVE-2018-3615) return $variantl1tf_sgx;; + CVE-2018-3620) return $variantl1tf;; + CVE-2018-3646) return $variantl1tf;; + CVE-2018-12126) return $variant_msbds;; + CVE-2018-12130) return $variant_mfbds;; + CVE-2018-12127) return $variant_mlpds;; + CVE-2019-11091) return $variant_mdsum;; + CVE-2019-11135) return $variant_taa;; + CVE-2018-12207) return $variant_itlbmh;; + CVE-2020-0543) return $variant_srbds;; + *) echo "$0: error: invalid variant '$1' passed to is_cpu_affected()" >&2; exit 255;; + esac +} + +is_cpu_affected() +{ + # param: one of the $supported_cve_list items + # returns 0 if affected, 1 if not affected + # (note that in shell, a return of 0 is success) + # by default, everything is affected, we work in a "whitelist" logic here. + # usage: is_cpu_affected CVE-xxxx-yyyy && do something if affected + if [ "$is_cpu_affected_cached" = 1 ]; then + _is_cpu_affected_cached "$1" + return $? + fi + + variant1='' + variant2='' + variant3='' + variant3a='' + variant4='' + variantl1tf='' + variant_msbds='' + variant_mfbds='' + variant_mlpds='' + variant_mdsum='' + variant_taa='' + variant_itlbmh='' + variant_srbds='' + + if is_cpu_mds_free; then + [ -z "$variant_msbds" ] && variant_msbds=immune + [ -z "$variant_mfbds" ] && variant_mfbds=immune + [ -z "$variant_mlpds" ] && variant_mlpds=immune + [ -z "$variant_mdsum" ] && variant_mdsum=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: cpu not affected by Microarchitectural Data Sampling" + fi + + if is_cpu_taa_free; then + [ -z "$variant_taa" ] && variant_taa=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: cpu not affected by TSX Asynhronous Abort" + fi + + if is_cpu_srbds_free; then + [ -z "$variant_srbds" ] && variant_srbds=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: cpu not affected by Special Register Buffer Data Sampling" + fi + + if is_cpu_specex_free; then + variant1=immune + variant2=immune + variant3=immune + variant3a=immune + variant4=immune + variantl1tf=immune + variant_msbds=immune + variant_mfbds=immune + variant_mlpds=immune + variant_mdsum=immune + variant_taa=immune + variant_srbds=immune + elif is_intel; then + # Intel + # https://github.com/crozone/SpectrePoC/issues/1 ^F E5200 => spectre 2 not affected + # https://github.com/paboldin/meltdown-exploit/issues/19 ^F E5200 => meltdown affected + # model name : Pentium(R) Dual-Core CPU E5200 @ 2.50GHz + if echo "$cpu_friendly_name" | grep -qE 'Pentium\(R\) Dual-Core[[:space:]]+CPU[[:space:]]+E[0-9]{4}K?'; then + variant1=vuln + [ -z "$variant2" ] && variant2=immune + variant3=vuln + fi + if [ "$capabilities_rdcl_no" = 1 ]; then + # capability bit for future Intel processor that will explicitly state + # that they're not affected to Meltdown + # this var is set in check_cpu() + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + [ -z "$variantl1tf" ] && variantl1tf=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: RDCL_NO is set so not vuln to meltdown nor l1tf" + fi + if [ "$capabilities_ssb_no" = 1 ]; then + # capability bit for future Intel processor that will explicitly state + # that they're not affected to Variant 4 + # this var is set in check_cpu() + [ -z "$variant4" ] && variant4=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: SSB_NO is set so not vuln to variant4" + fi + if is_cpu_ssb_free; then + [ -z "$variant4" ] && variant4=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: cpu not affected by speculative store bypass so not vuln to variant4" + fi + # variant 3a + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNL" ] || [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNM" ]; then + _debug "is_cpu_affected: xeon phi immune to variant 3a" + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + elif [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_D" ]; then + # https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/security-center/advisory/intel-sa-00115.html + # https://github.com/speed47/spectre-meltdown-checker/issues/310 + # => silvermont CPUs (aka cherry lake for tablets and brawsell for mobile/desktop) don't seem to be affected + # => goldmont ARE affected + _debug "is_cpu_affected: silvermont immune to variant 3a" + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + fi + fi + # L1TF (RDCL_NO already checked above) + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_TABLET" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT_NP" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_PLUS" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_TREMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNM" ]; then + + _debug "is_cpu_affected: intel family 6 but model known to be immune to l1tf" + [ -z "$variantl1tf" ] && variantl1tf=immune + else + _debug "is_cpu_affected: intel family 6 is vuln to l1tf" + variantl1tf=vuln + fi + elif [ "$cpu_family" -lt 6 ]; then + _debug "is_cpu_affected: intel family < 6 is immune to l1tf" + [ -z "$variantl1tf" ] && variantl1tf=immune + fi + elif is_amd || is_hygon; then + # AMD revised their statement about variant2 => affected + # https://www.amd.com/en/corporate/speculative-execution + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + # https://www.amd.com/en/corporate/security-updates + # "We have not identified any AMD x86 products susceptible to the Variant 3a vulnerability in our analysis to-date." + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + if is_cpu_ssb_free; then + [ -z "$variant4" ] && variant4=immune + _debug "is_cpu_affected: cpu not affected by speculative store bypass so not vuln to variant4" + fi + variantl1tf=immune + elif [ "$cpu_vendor" = CAVIUM ]; then + variant3=immune + variant3a=immune + variantl1tf=immune + elif [ "$cpu_vendor" = PHYTIUM ]; then + variant3=immune + variant3a=immune + variantl1tf=immune + elif [ "$cpu_vendor" = ARM ]; then + # ARM + # reference: https://developer.arm.com/support/security-update + # some devices (phones or other) have several ARMs and as such different part numbers, + # an example is "bigLITTLE". we shouldn't rely on the first CPU only, so we check the whole list + i=0 + for cpupart in $cpu_part_list + do + i=$(( i + 1 )) + # do NOT quote $cpu_arch_list below + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + cpuarch=$(echo $cpu_arch_list | awk '{ print $'$i' }') + _debug "checking cpu$i: <$cpupart> <$cpuarch>" + # some kernels report AArch64 instead of 8 + [ "$cpuarch" = "AArch64" ] && cpuarch=8 + if [ -n "$cpupart" ] && [ -n "$cpuarch" ]; then + # Cortex-R7 and Cortex-R8 are real-time and only used in medical devices or such + # I can't find their CPU part number, but it's probably not that useful anyway + # model R7 R8 A8 A9 A12 A15 A17 A57 A72 A73 A75 A76 Neoverse-N1 A77 + # part ? ? c08 c09 c0d c0f c0e d07 d08 d09 d0a d0b d0c d0d + # arch 7? 7? 7 7 7 7 7 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 + # + # Whitelist identified non-affected processors, use vulnerability information from + # https://developer.arm.com/support/arm-security-updates/speculative-processor-vulnerability + # Partnumbers can be found here: + # https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/master/gcc/config/arm/arm-cpus.in + # + # Maintain cumulative check of vulnerabilities - + # if at least one of the cpu is affected, then the system is affected + if [ "$cpuarch" = 7 ] && echo "$cpupart" | grep -q -w -e 0xc08 -e 0xc09 -e 0xc0d -e 0xc0e; then + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + [ -z "$variant4" ] && variant4=immune + _debug "checking cpu$i: armv7 A8/A9/A12/A17 non affected to variants 3, 3a & 4" + elif [ "$cpuarch" = 7 ] && echo "$cpupart" | grep -q -w -e 0xc0f; then + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + variant3a=vuln + [ -z "$variant4" ] && variant4=immune + _debug "checking cpu$i: armv7 A15 non affected to variants 3 & 4" + elif [ "$cpuarch" = 8 ] && echo "$cpupart" | grep -q -w -e 0xd07 -e 0xd08; then + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + variant3a=vuln + variant4=vuln + _debug "checking cpu$i: armv8 A57/A72 non affected to variants 3" + elif [ "$cpuarch" = 8 ] && echo "$cpupart" | grep -q -w -e 0xd09; then + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + variant4=vuln + _debug "checking cpu$i: armv8 A73 non affected to variants 3 & 3a" + elif [ "$cpuarch" = 8 ] && echo "$cpupart" | grep -q -w -e 0xd0a; then + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + variant3=vuln + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + variant4=vuln + _debug "checking cpu$i: armv8 A75 non affected to variant 3a" + elif [ "$cpuarch" = 8 ] && echo "$cpupart" | grep -q -w -e 0xd0b -e 0xd0c -e 0xd0d; then + variant1=vuln + [ -z "$variant2" ] && variant2=immune + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + variant4=vuln + _debug "checking cpu$i: armv8 A76/A77/NeoverseN1 non affected to variant 2, 3 & 3a" + elif [ "$cpuarch" -le 7 ] || { [ "$cpuarch" = 8 ] && [ $(( cpupart )) -lt $(( 0xd07 )) ]; } ; then + [ -z "$variant1" ] && variant1=immune + [ -z "$variant2" ] && variant2=immune + [ -z "$variant3" ] && variant3=immune + [ -z "$variant3a" ] && variant3a=immune + [ -z "$variant4" ] && variant4=immune + _debug "checking cpu$i: arm arch$cpuarch, all immune (v7 or v8 and model < 0xd07)" + else + variant1=vuln + variant2=vuln + variant3=vuln + variant3a=vuln + variant4=vuln + _debug "checking cpu$i: arm unknown arch$cpuarch part$cpupart, considering vuln" + fi + fi + _debug "is_cpu_affected: for cpu$i and so far, we have <$variant1> <$variant2> <$variant3> <$variant3a> <$variant4>" + done + variantl1tf=immune + fi + + # we handle iTLB Multihit here (not linked to is_specex_free) + if is_intel; then + # commit f9aa6b73a407b714c9aac44734eb4045c893c6f7 + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_TABLET" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNM" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_PLUS" ]; then + _debug "is_cpu_affected: intel family 6 but model known to be immune to itlbmh" + [ -z "$variant_itlbmh" ] && variant_itlbmh=immune + else + _debug "is_cpu_affected: intel family 6 is vuln to itlbmh" + variant_itlbmh=vuln + fi + elif [ "$cpu_family" -lt 6 ]; then + _debug "is_cpu_affected: intel family < 6 is immune to itlbmh" + [ -z "$variant_itlbmh" ] && variant_itlbmh=immune + fi + else + _debug "is_cpu_affected: non-intel not affected to itlbmh" + [ -z "$variant_itlbmh" ] && variant_itlbmh=immune + fi + + _debug "is_cpu_affected: temp results are <$variant1> <$variant2> <$variant3> <$variant3a> <$variant4> <$variantl1tf>" + [ "$variant1" = "immune" ] && variant1=1 || variant1=0 + [ "$variant2" = "immune" ] && variant2=1 || variant2=0 + [ "$variant3" = "immune" ] && variant3=1 || variant3=0 + [ "$variant3a" = "immune" ] && variant3a=1 || variant3a=0 + [ "$variant4" = "immune" ] && variant4=1 || variant4=0 + [ "$variantl1tf" = "immune" ] && variantl1tf=1 || variantl1tf=0 + [ "$variant_msbds" = "immune" ] && variant_msbds=1 || variant_msbds=0 + [ "$variant_mfbds" = "immune" ] && variant_mfbds=1 || variant_mfbds=0 + [ "$variant_mlpds" = "immune" ] && variant_mlpds=1 || variant_mlpds=0 + [ "$variant_mdsum" = "immune" ] && variant_mdsum=1 || variant_mdsum=0 + [ "$variant_taa" = "immune" ] && variant_taa=1 || variant_taa=0 + [ "$variant_itlbmh" = "immune" ] && variant_itlbmh=1 || variant_itlbmh=0 + [ "$variant_srbds" = "immune" ] && variant_srbds=1 || variant_srbds=0 + variantl1tf_sgx="$variantl1tf" + # even if we are affected to L1TF, if there's no SGX, we're not affected to the original foreshadow + [ "$cpuid_sgx" = 0 ] && variantl1tf_sgx=1 + _debug "is_cpu_affected: final results are <$variant1> <$variant2> <$variant3> <$variant3a> <$variant4> <$variantl1tf> <$variantl1tf_sgx>" + is_cpu_affected_cached=1 + _is_cpu_affected_cached "$1" + return $? +} + +is_cpu_specex_free() +{ + # return true (0) if the CPU doesn't do speculative execution, false (1) if it does. + # if it's not in the list we know, return false (1). + # source: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c#n882 + # { X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL, X86_FEATURE_ANY }, + # { X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_TABLET, X86_FEATURE_ANY }, + # { X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL_MID, X86_FEATURE_ANY }, + # { X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_MID, X86_FEATURE_ANY }, + # { X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL, X86_FEATURE_ANY }, + # { X86_VENDOR_CENTAUR, 5 }, + # { X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 5 }, + # { X86_VENDOR_NSC, 5 }, + # { X86_VENDOR_ANY, 4 }, + + parse_cpu_details + if is_intel; then + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_TABLET" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_MID" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL" ]; then + return 0 + fi + elif [ "$cpu_family" = 5 ]; then + return 0 + fi + fi + [ "$cpu_family" = 4 ] && return 0 + return 1 +} + +is_cpu_mds_free() +{ + # return true (0) if the CPU isn't affected by microarchitectural data sampling, false (1) if it does. + # if it's not in the list we know, return false (1). + # source: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c + #VULNWL_INTEL(ATOM_GOLDMONT, NO_MDS | NO_L1TF), + #VULNWL_INTEL(ATOM_GOLDMONT_X, NO_MDS | NO_L1TF), + #VULNWL_INTEL(ATOM_GOLDMONT_PLUS, NO_MDS | NO_L1TF), + + #/* AMD Family 0xf - 0x12 */ + #VULNWL_AMD(0x0f, NO_MELTDOWN | NO_SSB | NO_L1TF | NO_MDS), + #VULNWL_AMD(0x10, NO_MELTDOWN | NO_SSB | NO_L1TF | NO_MDS), + #VULNWL_AMD(0x11, NO_MELTDOWN | NO_SSB | NO_L1TF | NO_MDS), + #VULNWL_AMD(0x12, NO_MELTDOWN | NO_SSB | NO_L1TF | NO_MDS), + + #/* FAMILY_ANY must be last, otherwise 0x0f - 0x12 matches won't work */ + #VULNWL_AMD(X86_FAMILY_ANY, NO_MELTDOWN | NO_L1TF | NO_MDS), + #VULNWL_HYGON(X86_FAMILY_ANY, NO_MELTDOWN | NO_L1TF | NO_MDS), + parse_cpu_details + if is_intel; then + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_PLUS" ]; then + return 0 + fi + fi + [ "$capabilities_mds_no" = 1 ] && return 0 + fi + + # official statement from AMD says none of their CPUs are affected + # https://www.amd.com/en/corporate/product-security + # https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/security-whitepaper.pdf + if is_amd; then + return 0 + elif is_hygon; then + return 0 + elif [ "$cpu_vendor" = CAVIUM ]; then + return 0 + elif [ "$cpu_vendor" = PHYTIUM ]; then + return 0 + elif [ "$cpu_vendor" = ARM ]; then + return 0 + fi + + return 1 +} + + +is_cpu_taa_free() +{ + # return true (0) if the CPU isn't affected by tsx asynchronous aborts, false (1) if it does. + # There are three types of processors that do not require additional mitigations. + # 1. CPUs that do not support Intel TSX are not affected. + # 2. CPUs that enumerate IA32_ARCH_CAPABILITIES[TAA_NO] (bit 8)=1 are not affected. + # 3. CPUs that support Intel TSX and do not enumerate IA32_ARCH_CAPABILITIES[MDS_NO] (bit 5)=1 + # do not need additional mitigations beyond what is already required to mitigate MDS. + + if ! is_intel; then + return 0 + # is intel + elif [ "$capabilities_taa_no" = 1 ] || [ "$cpuid_rtm" = 0 ]; then + return 0 + fi + + return 1 +} + +is_cpu_srbds_free() +{ + # return zero (0) if the CPU isn't affected by special register buffer data sampling, one (1) if it is. + # If it's not in the list we know, return one (1). + # source: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c + # + # A processor is affected by SRBDS if its Family_Model and stepping is in the + # following list, with the exception of the listed processors + # exporting MDS_NO while Intel TSX is available yet not enabled. The + # latter class of processors are only affected when Intel TSX is enabled + # by software using TSX_CTRL_MSR otherwise they are not affected. + # + # ============= ============ ======== + # common name Family_Model Stepping + # ============= ============ ======== + # IvyBridge 06_3AH All (INTEL_FAM6_IVYBRIDGE) + # + # Haswell 06_3CH All (INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL) + # Haswell_L 06_45H All (INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_L) + # Haswell_G 06_46H All (INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_G) + # + # Broadwell_G 06_47H All (INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_G) + # Broadwell 06_3DH All (INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL) + # + # Skylake_L 06_4EH All (INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_L) + # Skylake 06_5EH All (INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE) + # + # Kabylake_L 06_8EH <=0xC (MDS_NO) (INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_L) + # + # Kabylake 06_9EH <=0xD (MDS_NO) (INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE) + # ============= ============ ======== + parse_cpu_details + if is_intel; then + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_IVYBRIDGE" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_L" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_G" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_G" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_L" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE" ]; then + return 1 + elif [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_L" ] && [ "$cpu_stepping" -le 12 ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE" ] && [ "$cpu_stepping" -le 13 ]; then + if [ "$capabilities_mds_no" -eq 1 ] && { [ "$cpuid_rtm" -eq 0 ] || [ "$tsx_ctrl_msr_rtm_disable" -eq 1 ] ;} ; then + return 0 + else + return 1 + fi + fi + fi + fi + + return 0 + +} + +is_cpu_ssb_free() +{ + # return true (0) if the CPU isn't affected by speculative store bypass, false (1) if it does. + # if it's not in the list we know, return false (1). + # source1: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c#n945 + # source2: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/tip/tip.git/tree/arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c + # Only list CPUs that speculate but are immune, to avoid duplication of cpus listed in is_cpu_specex_free() + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_X }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_MID }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_CORE_YONAH }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNL }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_INTEL, 6, INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNM }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_AMD, 0x12, }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_AMD, 0x11, }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_AMD, 0x10, }, + #{ X86_VENDOR_AMD, 0xf, }, + parse_cpu_details + if is_intel; then + if [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ]; then + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_D" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_MID" ]; then + return 0 + elif [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_CORE_YONAH" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNL" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = "$INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNM" ]; then + return 0 + fi + fi + fi + if is_amd; then + if [ "$cpu_family" = "18" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_family" = "17" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_family" = "16" ] || \ + [ "$cpu_family" = "15" ]; then + return 0 + fi + fi + if is_hygon; then + return 1 + fi + [ "$cpu_family" = 4 ] && return 0 + return 1 +} + +show_header() +{ + _info "Spectre and Meltdown mitigation detection tool v$VERSION" + _info +} + +[ -z "$HOME" ] && HOME="$(getent passwd "$(whoami)" | cut -d: -f6)" +mcedb_cache="$HOME/.mcedb" +update_fwdb() +{ + show_header + + set -e + + if [ -r "$mcedb_cache" ]; then + previous_dbversion=$(awk '/^# %%% MCEDB / { print $4 }' "$mcedb_cache") + fi + + # first, download the MCE.db from the excellent platomav's MCExtractor project + mcedb_tmp="$(mktemp -t smc-mcedb-XXXXXX)" + mcedb_url='https://github.com/platomav/MCExtractor/raw/master/MCE.db' + _info_nol "Fetching MCE.db from the MCExtractor project... " + if command -v wget >/dev/null 2>&1; then + wget -q "$mcedb_url" -O "$mcedb_tmp"; ret=$? + elif command -v curl >/dev/null 2>&1; then + curl -sL "$mcedb_url" -o "$mcedb_tmp"; ret=$? + elif command -v fetch >/dev/null 2>&1; then + fetch -q "$mcedb_url" -o "$mcedb_tmp"; ret=$? + else + echo ERROR "please install one of \`wget\`, \`curl\` of \`fetch\` programs" + return 1 + fi + if [ "$ret" != 0 ]; then + echo ERROR "error $ret while downloading MCE.db" + return $ret + fi + echo DONE + + # second, get the Intel firmwares from GitHub + intel_tmp="$(mktemp -d -t smc-intelfw-XXXXXX)" + intel_url="https://github.com/intel/Intel-Linux-Processor-Microcode-Data-Files/archive/main.zip" + _info_nol "Fetching Intel firmwares... " + ## https://github.com/intel/Intel-Linux-Processor-Microcode-Data-Files.git + if command -v wget >/dev/null 2>&1; then + wget -q "$intel_url" -O "$intel_tmp/fw.zip"; ret=$? + elif command -v curl >/dev/null 2>&1; then + curl -sL "$intel_url" -o "$intel_tmp/fw.zip"; ret=$? + elif command -v fetch >/dev/null 2>&1; then + fetch -q "$intel_url" -o "$intel_tmp/fw.zip"; ret=$? + else + echo ERROR "please install one of \`wget\`, \`curl\` of \`fetch\` programs" + return 1 + fi + if [ "$ret" != 0 ]; then + echo ERROR "error $ret while downloading Intel firmwares" + return $ret + fi + echo DONE + + # now extract MCEdb contents using sqlite + _info_nol "Extracting MCEdb data... " + if ! command -v sqlite3 >/dev/null 2>&1; then + echo ERROR "please install the \`sqlite3\` program" + return 1 + fi + mcedb_revision=$(sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "select revision from MCE") + if [ -z "$mcedb_revision" ]; then + echo ERROR "downloaded file seems invalid" + return 1 + fi + sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "alter table Intel add column origin text" + sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "update Intel set origin='mce'" + + echo OK "MCExtractor database revision $mcedb_revision" + + # parse Intel firmwares to get their versions + _info_nol "Integrating Intel firmwares data to db... " + if ! command -v unzip >/dev/null 2>&1; then + echo ERROR "please install the \`unzip\` program" + return 1 + fi + ( cd "$intel_tmp" && unzip fw.zip >/dev/null; ) + if ! [ -d "$intel_tmp/Intel-Linux-Processor-Microcode-Data-Files-main/intel-ucode" ]; then + echo ERROR "expected the 'intel-ucode' folder in the downloaded zip file" + return 1 + fi + + if ! command -v iucode_tool >/dev/null 2>&1; then + if ! command -v iucode-tool >/dev/null 2>&1; then + echo ERROR "please install the \`iucode-tool\` program" + return 1 + else + iucode_tool="iucode-tool" + fi + else + iucode_tool="iucode_tool" + fi + # 079/001: sig 0x000106c2, pf_mask 0x01, 2009-04-10, rev 0x0217, size 5120 + # 078/004: sig 0x000106ca, pf_mask 0x10, 2009-08-25, rev 0x0107, size 5120 + $iucode_tool -l "$intel_tmp/Intel-Linux-Processor-Microcode-Data-Files-main/intel-ucode" | grep -wF sig | while read -r _line + do + _line=$( echo "$_line" | tr -d ',') + _cpuid=$( echo "$_line" | awk '{print $3}') + _cpuid=$(( _cpuid )) + _cpuid=$(printf "0x%08X" "$_cpuid") + _date=$( echo "$_line" | awk '{print $6}' | tr -d '-') + _version=$(echo "$_line" | awk '{print $8}') + _version=$(( _version )) + _version=$(printf "0x%08X" "$_version") + _sqlstm="$(printf "INSERT INTO Intel (origin,cpuid,version,yyyymmdd) VALUES (\"%s\",\"%s\",\"%s\",\"%s\");" "intel" "$(printf "%08X" "$_cpuid")" "$(printf "%08X" "$_version")" "$_date")" + sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "$_sqlstm" + done + _intel_timestamp=$(stat -c %Y "$intel_tmp/Intel-Linux-Processor-Microcode-Data-Files-main/license" 2>/dev/null) + if [ -n "$_intel_timestamp" ]; then + # use this date, it matches the last commit date + _intel_latest_date=$(date +%Y%m%d -d @"$_intel_timestamp") + else + echo "Falling back to the latest microcode date" + _intel_latest_date=$(sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "SELECT yyyymmdd from Intel WHERE origin = 'intel' ORDER BY yyyymmdd DESC LIMIT 1;") + fi + echo DONE "(version $_intel_latest_date)" + + dbversion="$mcedb_revision+i$_intel_latest_date" + + if [ "$1" != builtin ] && [ -n "$previous_dbversion" ] && [ "$previous_dbversion" = "v$dbversion" ]; then + echo "We already have this version locally, no update needed" + return 0 + fi + + _info_nol "Building local database... " + { + echo "# Spectre & Meltdown Checker"; + echo "# %%% MCEDB v$dbversion"; + sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "SELECT '# I,0x'||t1.cpuid||',0x'||MAX(t1.version)||','||t1.yyyymmdd FROM Intel AS t1 LEFT OUTER JOIN Intel AS t2 ON t2.cpuid=t1.cpuid AND t2.yyyymmdd > t1.yyyymmdd WHERE t2.yyyymmdd IS NULL GROUP BY t1.cpuid ORDER BY t1.cpuid ASC;" | grep -v '^# .,0x00000000,'; + sqlite3 "$mcedb_tmp" "SELECT '# A,0x'||t1.cpuid||',0x'||MAX(t1.version)||','||t1.yyyymmdd FROM AMD AS t1 LEFT OUTER JOIN AMD AS t2 ON t2.cpuid=t1.cpuid AND t2.yyyymmdd > t1.yyyymmdd WHERE t2.yyyymmdd IS NULL GROUP BY t1.cpuid ORDER BY t1.cpuid ASC;" | grep -v '^# .,0x00000000,'; + } > "$mcedb_cache" + echo DONE "(version $dbversion)" + + if [ "$1" = builtin ]; then + newfile=$(mktemp -t smc-builtin-XXXXXX) + awk '/^# %%% MCEDB / { exit }; { print }' "$0" > "$newfile" + awk '{ if (NR>1) { print } }' "$mcedb_cache" >> "$newfile" + cat "$newfile" > "$0" + rm -f "$newfile" + fi +} + +parse_opt_file() +{ + # parse_opt_file option_name option_value + option_name="$1" + option_value="$2" + if [ -z "$option_value" ]; then + show_header + show_usage + echo "$0: error: --$option_name expects one parameter (a file)" >&2 + exit 1 + elif [ ! -e "$option_value" ]; then + show_header + echo "$0: error: couldn't find file $option_value" >&2 + exit 1 + elif [ ! -f "$option_value" ]; then + show_header + echo "$0: error: $option_value is not a file" >&2 + exit 1 + elif [ ! -r "$option_value" ]; then + show_header + echo "$0: error: couldn't read $option_value (are you root?)" >&2 + exit 1 + fi + echo "$option_value" + exit 0 +} + +while [ -n "${1:-}" ]; do + if [ "$1" = "--kernel" ]; then + opt_kernel=$(parse_opt_file kernel "$2"); ret=$? + [ $ret -ne 0 ] && exit 255 + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--config" ]; then + opt_config=$(parse_opt_file config "$2"); ret=$? + [ $ret -ne 0 ] && exit 255 + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--map" ]; then + opt_map=$(parse_opt_file map "$2"); ret=$? + [ $ret -ne 0 ] && exit 255 + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--arch-prefix" ]; then + opt_arch_prefix="$2" + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--live" ]; then + opt_live=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--no-color" ]; then + opt_no_color=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--no-sysfs" ]; then + opt_no_sysfs=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--sysfs-only" ]; then + opt_sysfs_only=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--coreos" ]; then + opt_coreos=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--coreos-within-toolbox" ]; then + # don't use directly: used internally by --coreos + opt_coreos=0 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--paranoid" ]; then + opt_paranoid=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--hw-only" ]; then + opt_hw_only=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--no-hw" ]; then + opt_no_hw=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--allow-msr-write" ]; then + opt_allow_msr_write=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--cpu" ]; then + opt_cpu=$2 + if [ "$opt_cpu" != all ]; then + if echo "$opt_cpu" | grep -Eq '^[0-9]+'; then + opt_cpu=$(( opt_cpu )) + else + echo "$0: error: --cpu should be an integer or 'all', got '$opt_cpu'" >&2 + exit 255 + fi + fi + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--no-explain" ]; then + # deprecated, kept for compatibility + opt_explain=0 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--update-fwdb" ] || [ "$1" = "--update-mcedb" ]; then + update_fwdb + exit $? + elif [ "$1" = "--update-builtin-fwdb" ] || [ "$1" = "--update-builtin-mcedb" ]; then + update_fwdb builtin + exit $? + elif [ "$1" = "--dump-mock-data" ]; then + opt_mock=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--explain" ]; then + opt_explain=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--batch" ]; then + opt_batch=1 + opt_verbose=0 + opt_no_color=1 + shift + case "$1" in + text|short|nrpe|json|prometheus) opt_batch_format="$1"; shift;; + --*) ;; # allow subsequent flags + '') ;; # allow nothing at all + *) + echo "$0: error: unknown batch format '$1'" >&2 + echo "$0: error: --batch expects a format from: text, nrpe, json" >&2 + exit 255 + ;; + esac + elif [ "$1" = "-v" ] || [ "$1" = "--verbose" ]; then + opt_verbose=$(( opt_verbose + 1 )) + [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ] && opt_mock=1 + shift + elif [ "$1" = "--cve" ]; then + if [ -z "$2" ]; then + echo "$0: error: option --cve expects a parameter, supported CVEs are: $supported_cve_list" >&2 + exit 255 + fi + selected_cve=$(echo "$supported_cve_list" | grep -iwo "$2") + if [ -n "$selected_cve" ]; then + opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list $selected_cve" + opt_cve_all=0 + else + echo "$0: error: unsupported CVE specified ('$2'), supported CVEs are: $supported_cve_list" >&2 + exit 255 + fi + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--vmm" ]; then + if [ -z "$2" ]; then + echo "$0: error: option --vmm (auto, yes, no)" >&2 + exit 255 + fi + case "$2" in + auto) opt_vmm=-1;; + yes) opt_vmm=1;; + no) opt_vmm=0;; + *) echo "$0: error: expected one of (auto, yes, no) to option --vmm instead of '$2'" >&2; exit 255;; + esac + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "--variant" ]; then + if [ -z "$2" ]; then + echo "$0: error: option --variant expects a parameter (1, 2, 3, 3a, 4 or l1tf)" >&2 + exit 255 + fi + case "$2" in + 1) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2017-5753"; opt_cve_all=0;; + 2) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2017-5715"; opt_cve_all=0;; + 3) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2017-5754"; opt_cve_all=0;; + 3a) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-3640"; opt_cve_all=0;; + 4) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-3639"; opt_cve_all=0;; + msbds) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-12126"; opt_cve_all=0;; + mfbds) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-12130"; opt_cve_all=0;; + mlpds) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-12127"; opt_cve_all=0;; + mdsum) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2019-11091"; opt_cve_all=0;; + l1tf) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-3615 CVE-2018-3620 CVE-2018-3646"; opt_cve_all=0;; + taa) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2019-11135"; opt_cve_all=0;; + mcepsc) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2018-12207"; opt_cve_all=0;; + srbds) opt_cve_list="$opt_cve_list CVE-2020-0543"; opt_cve_all=0;; + *) + echo "$0: error: invalid parameter '$2' for --variant, expected either 1, 2, 3, 3a, 4, l1tf, msbds, mfbds, mlpds, mdsum, taa, mcepsc or srbds" >&2; + exit 255 + ;; + esac + shift 2 + elif [ "$1" = "-h" ] || [ "$1" = "--help" ]; then + show_header + show_usage + exit 0 + elif [ "$1" = "--version" ]; then + opt_no_color=1 + show_header + exit 0 + elif [ "$1" = "--disclaimer" ]; then + show_header + show_disclaimer + exit 0 + else + show_header + show_usage + echo "$0: error: unknown option '$1'" + exit 255 + fi +done + +show_header + +if [ "$opt_no_sysfs" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_sysfs_only" = 1 ]; then + _warn "Incompatible options specified (--no-sysfs and --sysfs-only), aborting" + exit 255 +fi + +if [ "$opt_no_hw" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_hw_only" = 1 ]; then + _warn "Incompatible options specified (--no-hw and --hw-only), aborting" + exit 255 +fi + +if [ "$opt_live" = -1 ]; then + if [ -n "$opt_kernel" ] || [ -n "$opt_config" ] || [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + # no --live specified and we have a least one of the kernel/config/map files on the cmdline: offline mode + opt_live=0 + else + opt_live=1 + fi +fi + +# print status function +# param1: color +# param2: message to print +# param3(optional): supplement message to print between () +pstatus() +{ + if [ "$opt_no_color" = 1 ]; then + _info_nol "$2" + else + case "$1" in + red) _col="\033[41m\033[30m";; + green) _col="\033[42m\033[30m";; + yellow) _col="\033[43m\033[30m";; + blue) _col="\033[44m\033[30m";; + *) _col="";; + esac + _info_nol "$_col $2 \033[0m" + fi + [ -n "${3:-}" ] && _info_nol " ($3)" + _info + unset _col +} + +# Print the final status of a vulnerability (incl. batch mode) +# Arguments are: CVE UNK/OK/VULN description +pvulnstatus() +{ + pvulnstatus_last_cve="$1" + if [ "$opt_batch" = 1 ]; then + case "$1" in + CVE-2017-5753) aka="SPECTRE VARIANT 1";; + CVE-2017-5715) aka="SPECTRE VARIANT 2";; + CVE-2017-5754) aka="MELTDOWN";; + CVE-2018-3640) aka="VARIANT 3A";; + CVE-2018-3639) aka="VARIANT 4";; + CVE-2018-3615) aka="L1TF SGX";; + CVE-2018-3620) aka="L1TF OS";; + CVE-2018-3646) aka="L1TF VMM";; + CVE-2018-12126) aka="MSBDS";; + CVE-2018-12130) aka="MFBDS";; + CVE-2018-12127) aka="MLPDS";; + CVE-2019-11091) aka="MDSUM";; + CVE-2019-11135) aka="TAA";; + CVE-2018-12207) aka="ITLBMH";; + CVE-2020-0543) aka="SRBDS";; + *) echo "$0: error: invalid CVE '$1' passed to pvulnstatus()" >&2; exit 255;; + esac + + case "$opt_batch_format" in + text) _echo 0 "$1: $2 ($3)";; + short) short_output="${short_output}$1 ";; + json) + case "$2" in + UNK) is_vuln="null";; + VULN) is_vuln="true";; + OK) is_vuln="false";; + *) echo "$0: error: unknown status '$2' passed to pvulnstatus()" >&2; exit 255;; + esac + [ -z "$json_output" ] && json_output='[' + json_output="${json_output}{\"NAME\":\"$aka\",\"CVE\":\"$1\",\"VULNERABLE\":$is_vuln,\"INFOS\":\"$3\"}," + ;; + + nrpe) [ "$2" = VULN ] && nrpe_vuln="$nrpe_vuln $1";; + prometheus) + prometheus_output="${prometheus_output:+$prometheus_output\n}specex_vuln_status{name=\"$aka\",cve=\"$1\",status=\"$2\",info=\"$3\"} 1" + ;; + *) echo "$0: error: invalid batch format '$opt_batch_format' specified" >&2; exit 255;; + esac + fi + + # always fill global_* vars because we use that do decide the program exit code + case "$2" in + UNK) global_unknown="1";; + VULN) global_critical="1";; + OK) ;; + *) echo "$0: error: unknown status '$2' passed to pvulnstatus()" >&2; exit 255;; + esac + + # display info if we're not in quiet/batch mode + vulnstatus="$2" + shift 2 + _info_nol "> \033[46m\033[30mSTATUS:\033[0m " + : "${final_summary:=}" + case "$vulnstatus" in + UNK) pstatus yellow 'UNKNOWN' "$@"; final_summary="$final_summary \033[43m\033[30m$pvulnstatus_last_cve:??\033[0m";; + VULN) pstatus red 'VULNERABLE' "$@"; final_summary="$final_summary \033[41m\033[30m$pvulnstatus_last_cve:KO\033[0m";; + OK) pstatus green 'NOT VULNERABLE' "$@"; final_summary="$final_summary \033[42m\033[30m$pvulnstatus_last_cve:OK\033[0m";; + *) echo "$0: error: unknown status '$vulnstatus' passed to pvulnstatus()" >&2; exit 255;; + esac +} + + +# The 3 below functions are taken from the extract-linux script, available here: +# https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/scripts/extract-vmlinux +# The functions have been modified for better integration to this script +# The original header of the file has been retained below + +# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- +# extract-vmlinux - Extract uncompressed vmlinux from a kernel image +# +# Inspired from extract-ikconfig +# (c) 2009,2010 Dick Streefland <dick@streefland.net> +# +# (c) 2011 Corentin Chary <corentin.chary@gmail.com> +# +# Licensed under the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2). +# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- + +kernel='' +kernel_err='' +check_kernel() +{ + _file="$1" + _mode="${2:-normal}" + # checking the return code of readelf -h is not enough, we could get + # a damaged ELF file and validate it, check for stderr warnings too + + # the warning "readelf: Warning: [16]: Link field (0) should index a symtab section./" can appear on valid kernels, ignore it + _readelf_warnings=$("${opt_arch_prefix}readelf" -S "$_file" 2>&1 >/dev/null | grep -v 'should index a symtab section' | tr "\n" "/"); ret=$? + _readelf_sections=$("${opt_arch_prefix}readelf" -S "$_file" 2>/dev/null | grep -c -e data -e text -e init) + _kernel_size=$(stat -c %s "$_file" 2>/dev/null || stat -f %z "$_file" 2>/dev/null || echo 10000) + _debug "check_kernel: ret=$? size=$_kernel_size sections=$_readelf_sections warnings=$_readelf_warnings" + if [ "$_mode" = desperate ]; then + if "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$_file" | grep -Eq '^Linux version '; then + _debug "check_kernel (desperate): ... matched!" + if [ "$_readelf_sections" = 0 ] && grep -qF -e armv6 -e armv7 "$_file"; then + _debug "check_kernel (desperate): raw arm binary found, adjusting objdump options" + objdump_options="-D -b binary -marm" + else + objdump_options="-d" + fi + return 0 + else + _debug "check_kernel (desperate): ... invalid" + fi + else + if [ $ret -eq 0 ] && [ -z "$_readelf_warnings" ] && [ "$_readelf_sections" -gt 0 ]; then + if [ "$_kernel_size" -ge 100000 ]; then + _debug "check_kernel: ... file is valid" + objdump_options="-d" + return 0 + else + _debug "check_kernel: ... file seems valid but is too small, ignoring" + fi + else + _debug "check_kernel: ... file is invalid" + fi + fi + return 1 +} + +try_decompress() +{ + # The obscure use of the "tr" filter is to work around older versions of + # "grep" that report the byte offset of the line instead of the pattern. + + # Try to find the header ($1) and decompress from here + _debug "try_decompress: looking for $3 magic in $6" + for pos in $(tr "$1\n$2" "\n$2=" < "$6" | grep -abo "^$2") + do + _debug "try_decompress: magic for $3 found at offset $pos" + if ! command -v "$3" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + if [ "$8" = 1 ]; then + # pass1: if the tool is not installed, just bail out silently + # and hope that the next decompression tool will be, and that + # it'll happen to be the proper one for this kernel + _debug "try_decompress: the '$3' tool is not installed (pass 1), try the next algo" + else + # pass2: if the tool is not installed, populate kernel_err this time + kernel_err="missing '$3' tool, please install it, usually it's in the '$5' package" + _debug "try_decompress: $kernel_err" + fi + return 1 + fi + pos=${pos%%:*} + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + tail -c+$pos "$6" 2>/dev/null | $3 $4 > "$kerneltmp" 2>/dev/null; ret=$? + if [ ! -s "$kerneltmp" ]; then + # don't rely on $ret, sometimes it's != 0 but worked + # (e.g. gunzip ret=2 just means there was trailing garbage) + _debug "try_decompress: decompression with $3 failed (err=$ret)" + elif check_kernel "$kerneltmp" "$7"; then + kernel="$kerneltmp" + _debug "try_decompress: decompressed with $3 successfully!" + return 0 + elif [ "$3" != "cat" ]; then + _debug "try_decompress: decompression with $3 worked but result is not a kernel, trying with an offset" + [ -z "$kerneltmp2" ] && kerneltmp2=$(mktemp -t smc-kernel-XXXXXX) + cat "$kerneltmp" > "$kerneltmp2" + try_decompress '\177ELF' xxy 'cat' '' cat "$kerneltmp2" && return 0 + else + _debug "try_decompress: decompression with $3 worked but result is not a kernel" + fi + done + return 1 +} + +extract_kernel() +{ + [ -n "${1:-}" ] || return 1 + # Prepare temp files: + kerneltmp="$(mktemp -t smc-kernel-XXXXXX)" + + # Initial attempt for uncompressed images or objects: + if check_kernel "$1"; then + _debug "extract_kernel: found kernel is valid, no decompression needed" + cat "$1" > "$kerneltmp" + kernel=$kerneltmp + return 0 + fi + + # That didn't work, so retry after decompression. + for pass in 1 2; do + for mode in normal desperate; do + _debug "extract_kernel: pass $pass $mode mode" + try_decompress '\037\213\010' xy gunzip '' gunzip "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress '\002\041\114\030' xyy 'lz4' '-d -l' liblz4-tool "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress '\3757zXZ\000' abcde unxz '' xz-utils "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress 'BZh' xy bunzip2 '' bzip2 "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress '\135\0\0\0' xxx unlzma '' xz-utils "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress '\211\114\132' xy 'lzop' '-d' lzop "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress '\177ELF' xxy 'cat' '' cat "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + try_decompress '(\265/\375' xxy unzstd '' zstd "$1" "$mode" "$pass" && return 0 + done + done + # kernel_err might already have been populated by try_decompress() if we're missing one of the tools + if [ -z "$kernel_err" ]; then + kernel_err="kernel compression format is unknown or image is invalid" + fi + _verbose "Couldn't extract the kernel image ($kernel_err), accuracy might be reduced" + return 1 +} + +# end of extract-vmlinux functions + +mount_debugfs() +{ + if [ ! -e /sys/kernel/debug/sched_features ]; then + # try to mount the debugfs hierarchy ourselves and remember it to umount afterwards + mount -t debugfs debugfs /sys/kernel/debug 2>/dev/null && mounted_debugfs=1 + fi +} + +load_msr() +{ + # only attempt to do it once even if called multiple times + [ "${load_msr_once:-}" = 1 ] && return + load_msr_once=1 + + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + if ! grep -qw msr "$procfs/modules" 2>/dev/null; then + modprobe msr 2>/dev/null && insmod_msr=1 + _debug "attempted to load module msr, insmod_msr=$insmod_msr" + else + _debug "msr module already loaded" + fi + else + if ! kldstat -q -m cpuctl; then + kldload cpuctl 2>/dev/null && kldload_cpuctl=1 + _debug "attempted to load module cpuctl, kldload_cpuctl=$kldload_cpuctl" + else + _debug "cpuctl module already loaded" + fi + fi +} + +load_cpuid() +{ + # only attempt to do it once even if called multiple times + [ "${load_cpuid_once:-}" = 1 ] && return + load_cpuid_once=1 + + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + if ! grep -qw cpuid "$procfs/modules" 2>/dev/null; then + modprobe cpuid 2>/dev/null && insmod_cpuid=1 + _debug "attempted to load module cpuid, insmod_cpuid=$insmod_cpuid" + else + _debug "cpuid module already loaded" + fi + else + if ! kldstat -q -m cpuctl; then + kldload cpuctl 2>/dev/null && kldload_cpuctl=1 + _debug "attempted to load module cpuctl, kldload_cpuctl=$kldload_cpuctl" + else + _debug "cpuctl module already loaded" + fi + fi +} + +# shellcheck disable=SC2034 +EAX=1; EBX=2; ECX=3; EDX=4; +READ_CPUID_RET_OK=0 +READ_CPUID_RET_KO=1 +READ_CPUID_RET_ERR=2 +read_cpuid() +{ + if [ "$opt_cpu" != all ]; then + # we only have one core to read, do it and return the result + read_cpuid_one_core $opt_cpu "$@" + return $? + fi + + # otherwise we must read all cores + for _core in $(seq 0 "$max_core_id"); do + read_cpuid_one_core "$_core" "$@"; ret=$? + if [ "$_core" = 0 ]; then + # save the result of the first core, for comparison with the others + _first_core_ret=$ret + _first_core_value=$read_cpuid_value + else + # compare first core with the other ones + if [ $_first_core_ret != $ret ] || [ "$_first_core_value" != "$read_cpuid_value" ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="result is not homogeneous between all cores, at least core 0 and $_core differ!" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + fi + done + # if we're here, all cores agree, return the result + return $ret +} + +read_cpuid_one_core() +{ + # on which core to send the CPUID instruction + _core="$1" + # leaf is the value of the eax register when calling the cpuid instruction: + _leaf="$2" + # subleaf is the value of the ecx register when calling the cpuid instruction: + _subleaf="$3" + # eax=1 ebx=2 ecx=3 edx=4: + _register="$4" + # number of bits to shift the register right to, 0-31: + _shift="$5" + # mask to apply as an AND operand to the shifted register value + _mask="$6" + # wanted value (optional), if present we return 0(true) if the obtained value is equal, 1 otherwise: + _wanted="${7:-}" + # in any case, the read value is globally available in $read_cpuid_value + read_cpuid_value='' + read_cpuid_msg='unknown error' + + if [ $# -lt 6 ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="read_cpuid: missing arguments, got only $#, expected at least 6: $*" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + if [ "$_register" -gt 4 ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="read_cpuid: register must be 0-4, got $_register" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + if [ "$_shift" -gt 32 ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="read_cpuid: shift must be 0-31, got $_shift" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + + if [ ! -e /dev/cpu/0/cpuid ] && [ ! -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + # try to load the module ourselves (and remember it so we can rmmod it afterwards) + load_cpuid + fi + + if [ -e /dev/cpu/0/cpuid ]; then + # Linux + if [ ! -r /dev/cpu/0/cpuid ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="Couldn't load cpuid module" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + # on some kernel versions, /dev/cpu/0/cpuid doesn't imply that the cpuid module is loaded, in that case dd returns an error, + # we use that fact to load the module if dd returns an error + if ! dd if=/dev/cpu/0/cpuid bs=16 count=1 >/dev/null 2>&1; then + load_cpuid + fi + # we need _leaf to be converted to decimal for dd + _leaf=$(( _leaf )) + _subleaf=$(( _subleaf )) + _position=$(( _leaf + (_subleaf << 32) )) + # to avoid using iflag=skip_bytes, which doesn't exist on old versions of dd, seek to the closer multiple-of-16 + _ddskip=$(( _position / 16 )) + _odskip=$(( _position - _ddskip * 16 )) + # now read the value + _cpuid=$(dd if="/dev/cpu/$_core/cpuid" bs=16 skip=$_ddskip count=$((_odskip + 1)) 2>/dev/null | od -j $((_odskip * 16)) -A n -t u4) + elif [ -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + # BSD + if [ ! -r /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="Couldn't read cpuid info from cpuctl" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + _cpuid=$(cpucontrol -i "$_leaf","$_subleaf" "/dev/cpuctl$_core" 2>/dev/null | cut -d: -f2-) + # cpuid level 0x4, level_type 0x2: 0x1c004143 0x01c0003f 0x000001ff 0x00000000 + else + read_cpuid_msg="Found no way to read cpuid info" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + + _debug "cpuid: leaf$_leaf subleaf$_subleaf on cpu$_core, eax-ebx-ecx-edx: $_cpuid" + _mockvarname="SMC_MOCK_CPUID_${_leaf}_${_subleaf}" + # shellcheck disable=SC1083 + if [ -n "$(eval echo \${$_mockvarname:-})" ]; then + _cpuid="$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + _debug "read_cpuid: MOCKING enabled for leaf $_leaf subleaf $_subleaf, will return $_cpuid" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPUID_${_leaf}_${_subleaf}='$_cpuid'") + fi + if [ -z "$_cpuid" ]; then + read_cpuid_msg="Failed to get cpuid data" + return $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR + fi + + # get the value of the register we want + _reg=$(echo "$_cpuid" | awk '{print $'"$_register"'}') + # Linux returns it as decimal, BSD as hex, normalize to decimal + _reg=$(( _reg )) + # shellcheck disable=SC2046 + _debug "cpuid: wanted register ($_register) has value $_reg aka "$(printf "%08x" "$_reg") + _reg_shifted=$(( _reg >> _shift )) + # shellcheck disable=SC2046 + _debug "cpuid: shifted value by $_shift is $_reg_shifted aka "$(printf "%x" "$_reg_shifted") + read_cpuid_value=$(( _reg_shifted & _mask )) + # shellcheck disable=SC2046 + _debug "cpuid: after AND $_mask, final value is $read_cpuid_value aka "$(printf "%x" "$read_cpuid_value") + if [ -n "$_wanted" ]; then + _debug "cpuid: wanted $_wanted and got $read_cpuid_value" + if [ "$read_cpuid_value" = "$_wanted" ]; then + return $READ_CPUID_RET_OK + else + return $READ_CPUID_RET_KO + fi + fi + + return $READ_CPUID_RET_OK +} + +dmesg_grep() +{ + # grep for something in dmesg, ensuring that the dmesg buffer + # has not been truncated + dmesg_grepped='' + if ! dmesg | grep -qE -e '(^|\] )Linux version [0-9]' -e '^FreeBSD is a registered' ; then + # dmesg truncated + return 2 + fi + dmesg_grepped=$(dmesg | grep -E "$1" | head -1) + # not found: + [ -z "$dmesg_grepped" ] && return 1 + # found, output is in $dmesg_grepped + return 0 +} + +is_coreos() +{ + command -v coreos-install >/dev/null 2>&1 && command -v toolbox >/dev/null 2>&1 && return 0 + return 1 +} + +parse_cpu_details() +{ + [ "${parse_cpu_details_done:-}" = 1 ] && return 0 + + if command -v nproc >/dev/null; then + number_of_cores=$(nproc) + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + number_of_cores=$(sysctl -n hw.ncpu 2>/dev/null || echo 1) + elif [ -e "$procfs/cpuinfo" ]; then + number_of_cores=$(grep -c ^processor "$procfs/cpuinfo" 2>/dev/null || echo 1) + else + # if we don't know, default to 1 CPU + number_of_cores=1 + fi + max_core_id=$(( number_of_cores - 1 )) + + if [ -e "$procfs/cpuinfo" ]; then + cpu_vendor=$( grep '^vendor_id' "$procfs/cpuinfo" | awk '{print $3}' | head -1) + cpu_friendly_name=$(grep '^model name' "$procfs/cpuinfo" | cut -d: -f2- | head -1 | sed -e 's/^ *//') + # special case for ARM follows + if grep -qi 'CPU implementer[[:space:]]*:[[:space:]]*0x41' "$procfs/cpuinfo"; then + cpu_vendor='ARM' + # some devices (phones or other) have several ARMs and as such different part numbers, + # an example is "bigLITTLE", so we need to store the whole list, this is needed for is_cpu_affected + cpu_part_list=$(awk '/CPU part/ {print $4}' "$procfs/cpuinfo") + cpu_arch_list=$(awk '/CPU architecture/ {print $3}' "$procfs/cpuinfo") + # take the first one to fill the friendly name, do NOT quote the vars below + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + cpu_arch=$(echo $cpu_arch_list | awk '{ print $1 }') + # shellcheck disable=SC2086 + cpu_part=$(echo $cpu_part_list | awk '{ print $1 }') + [ "$cpu_arch" = "AArch64" ] && cpu_arch=8 + cpu_friendly_name="ARM" + [ -n "$cpu_arch" ] && cpu_friendly_name="$cpu_friendly_name v$cpu_arch" + [ -n "$cpu_part" ] && cpu_friendly_name="$cpu_friendly_name model $cpu_part" + + elif grep -qi 'CPU implementer[[:space:]]*:[[:space:]]*0x43' "$procfs/cpuinfo"; then + cpu_vendor='CAVIUM' + elif grep -qi 'CPU implementer[[:space:]]*:[[:space:]]*0x70' "$procfs/cpuinfo"; then + cpu_vendor='PHYTIUM' + fi + + cpu_family=$( grep '^cpu family' "$procfs/cpuinfo" | awk '{print $4}' | grep -E '^[0-9]+$' | head -1) + cpu_model=$( grep '^model' "$procfs/cpuinfo" | awk '{print $3}' | grep -E '^[0-9]+$' | head -1) + cpu_stepping=$(grep '^stepping' "$procfs/cpuinfo" | awk '{print $3}' | grep -E '^[0-9]+$' | head -1) + cpu_ucode=$( grep '^microcode' "$procfs/cpuinfo" | awk '{print $3}' | head -1) + else + cpu_vendor=$( dmesg | grep -i -m1 'Origin=' | cut -f2 -w | cut -f2 -d= | cut -f2 -d\" ) + cpu_family=$( dmesg | grep -i -m1 'Family=' | cut -f4 -w | cut -f2 -d= ) + cpu_family=$(( cpu_family )) + cpu_model=$( dmesg | grep -i -m1 'Model=' | cut -f5 -w | cut -f2 -d= ) + cpu_model=$(( cpu_model )) + cpu_stepping=$( dmesg | grep -i -m1 'Stepping=' | cut -f6 -w | cut -f2 -d= ) + cpu_friendly_name=$(sysctl -n hw.model 2>/dev/null) + fi + + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CPU_FRIENDLY_NAME:-}" ]; then + cpu_friendly_name="$SMC_MOCK_CPU_FRIENDLY_NAME" + _debug "parse_cpu_details: MOCKING cpu friendly name to $cpu_friendly_name" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPU_FRIENDLY_NAME='$cpu_friendly_name'") + fi + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CPU_VENDOR:-}" ]; then + cpu_vendor="$SMC_MOCK_CPU_VENDOR" + _debug "parse_cpu_details: MOCKING cpu vendor to $cpu_vendor" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPU_VENDOR='$cpu_vendor'") + fi + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CPU_FAMILY:-}" ]; then + cpu_family="$SMC_MOCK_CPU_FAMILY" + _debug "parse_cpu_details: MOCKING cpu family to $cpu_family" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPU_FAMILY='$cpu_family'") + fi + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CPU_MODEL:-}" ]; then + cpu_model="$SMC_MOCK_CPU_MODEL" + _debug "parse_cpu_details: MOCKING cpu model to $cpu_model" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPU_MODEL='$cpu_model'") + fi + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CPU_STEPPING:-}" ]; then + cpu_stepping="$SMC_MOCK_CPU_STEPPING" + _debug "parse_cpu_details: MOCKING cpu stepping to $cpu_stepping" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPU_STEPPING='$cpu_stepping'") + fi + + # get raw cpuid, it's always useful (referenced in the Intel doc for firmware updates for example) + if read_cpuid 0x1 0x0 $EAX 0 0xFFFFFFFF; then + cpu_cpuid="$read_cpuid_value" + else + cpu_cpuid=0 + fi + + # under BSD, linprocfs often doesn't export ucode information, so fetch it ourselves the good old way + if [ -z "$cpu_ucode" ] && [ "$os" != Linux ]; then + load_cpuid + if [ -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + # init MSR with NULLs + cpucontrol -m 0x8b=0 /dev/cpuctl0 + # call CPUID + cpucontrol -i 1 /dev/cpuctl0 >/dev/null + # read MSR + cpu_ucode=$(cpucontrol -m 0x8b /dev/cpuctl0 | awk '{print $3}') + # convert to decimal + cpu_ucode=$(( cpu_ucode )) + # convert back to hex + cpu_ucode=$(printf "0x%x" "$cpu_ucode") + fi + fi + + # if we got no cpu_ucode (e.g. we're in a vm), fall back to 0x0 + : "${cpu_ucode:=0x0}" + + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CPU_UCODE:-}" ]; then + cpu_ucode="$SMC_MOCK_CPU_UCODE" + _debug "parse_cpu_details: MOCKING cpu ucode to $cpu_ucode" + mocked=1 + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPU_UCODE='$cpu_ucode'") + fi + + echo "$cpu_ucode" | grep -q ^0x && cpu_ucode=$(( cpu_ucode )) + ucode_found=$(printf "family 0x%x model 0x%x stepping 0x%x ucode 0x%x cpuid 0x%x" "$cpu_family" "$cpu_model" "$cpu_stepping" "$cpu_ucode" "$cpu_cpuid") + + # also define those that we will need in other funcs + # taken from https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/include/asm/intel-family.h + # curl -s 'https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/plain/arch/x86/include/asm/intel-family.h' | awk '/#define INTEL_FAM6/ {print $2"=$(( "$3" )) # "$4,$5,$6,$7,$8,$9}' | sed -re 's/ +$//' + # shellcheck disable=SC2034 + { + INTEL_FAM6_CORE_YONAH=$(( 0x0E )) # + INTEL_FAM6_CORE2_MEROM=$(( 0x0F )) # + INTEL_FAM6_CORE2_MEROM_L=$(( 0x16 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_CORE2_PENRYN=$(( 0x17 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_CORE2_DUNNINGTON=$(( 0x1D )) # + INTEL_FAM6_NEHALEM=$(( 0x1E )) # + INTEL_FAM6_NEHALEM_G=$(( 0x1F )) # /* Auburndale / Havendale */ + INTEL_FAM6_NEHALEM_EP=$(( 0x1A )) # + INTEL_FAM6_NEHALEM_EX=$(( 0x2E )) # + INTEL_FAM6_WESTMERE=$(( 0x25 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_WESTMERE_EP=$(( 0x2C )) # + INTEL_FAM6_WESTMERE_EX=$(( 0x2F )) # + INTEL_FAM6_SANDYBRIDGE=$(( 0x2A )) # + INTEL_FAM6_SANDYBRIDGE_X=$(( 0x2D )) # + INTEL_FAM6_IVYBRIDGE=$(( 0x3A )) # + INTEL_FAM6_IVYBRIDGE_X=$(( 0x3E )) # + INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL=$(( 0x3C )) # + INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_X=$(( 0x3F )) # + INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_L=$(( 0x45 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_G=$(( 0x46 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL=$(( 0x3D )) # + INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_G=$(( 0x47 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_X=$(( 0x4F )) # + INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_D=$(( 0x56 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_L=$(( 0x4E )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE=$(( 0x5E )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X=$(( 0x55 )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_L=$(( 0x8E )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE=$(( 0x9E )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_COMETLAKE=$(( 0xA5 )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_COMETLAKE_L=$(( 0xA6 )) # /* Sky Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_CANNONLAKE_L=$(( 0x66 )) # /* Palm Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_ICELAKE_X=$(( 0x6A )) # /* Sunny Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_ICELAKE_D=$(( 0x6C )) # /* Sunny Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_ICELAKE=$(( 0x7D )) # /* Sunny Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_ICELAKE_L=$(( 0x7E )) # /* Sunny Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_ICELAKE_NNPI=$(( 0x9D )) # /* Sunny Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_LAKEFIELD=$(( 0x8A )) # /* Sunny Cove / Tremont */ + INTEL_FAM6_ROCKETLAKE=$(( 0xA7 )) # /* Cypress Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_TIGERLAKE_L=$(( 0x8C )) # /* Willow Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_TIGERLAKE=$(( 0x8D )) # /* Willow Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_SAPPHIRERAPIDS_X=$(( 0x8F )) # /* Golden Cove */ + INTEL_FAM6_ALDERLAKE=$(( 0x97 )) # /* Golden Cove / Gracemont */ + INTEL_FAM6_ALDERLAKE_L=$(( 0x9A )) # /* Golden Cove / Gracemont */ + INTEL_FAM6_RAPTORLAKE=$(( 0xB7 )) # + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL=$(( 0x1C )) # /* Diamondville, Pineview */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_BONNELL_MID=$(( 0x26 )) # /* Silverthorne, Lincroft */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL=$(( 0x36 )) # /* Cedarview */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_MID=$(( 0x27 )) # /* Penwell */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SALTWELL_TABLET=$(( 0x35 )) # /* Cloverview */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT=$(( 0x37 )) # /* Bay Trail, Valleyview */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_D=$(( 0x4D )) # /* Avaton, Rangely */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_SILVERMONT_MID=$(( 0x4A )) # /* Merriefield */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT=$(( 0x4C )) # /* Cherry Trail, Braswell */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT_MID=$(( 0x5A )) # /* Moorefield */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_AIRMONT_NP=$(( 0x75 )) # /* Lightning Mountain */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT=$(( 0x5C )) # /* Apollo Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_D=$(( 0x5F )) # /* Denverton */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_GOLDMONT_PLUS=$(( 0x7A )) # /* Gemini Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_TREMONT_D=$(( 0x86 )) # /* Jacobsville */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_TREMONT=$(( 0x96 )) # /* Elkhart Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_ATOM_TREMONT_L=$(( 0x9C )) # /* Jasper Lake */ + INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNL=$(( 0x57 )) # /* Knights Landing */ + INTEL_FAM6_XEON_PHI_KNM=$(( 0x85 )) # /* Knights Mill */ + } + parse_cpu_details_done=1 +} +is_hygon() +{ + [ "$cpu_vendor" = HygonGenuine ] && return 0 + return 1 +} + +is_amd() +{ + [ "$cpu_vendor" = AuthenticAMD ] && return 0 + return 1 +} + +is_intel() +{ + [ "$cpu_vendor" = GenuineIntel ] && return 0 + return 1 +} + +is_cpu_smt_enabled() +{ + # SMT / HyperThreading is enabled if siblings != cpucores + if [ -e "$procfs/cpuinfo" ]; then + _siblings=$(awk '/^siblings/ {print $3;exit}' "$procfs/cpuinfo") + _cpucores=$(awk '/^cpu cores/ {print $4;exit}' "$procfs/cpuinfo") + if [ -n "$_siblings" ] && [ -n "$_cpucores" ]; then + if [ "$_siblings" = "$_cpucores" ]; then + return 1 + else + return 0 + fi + fi + fi + # we can't tell + return 2 +} + +is_ucode_blacklisted() +{ + parse_cpu_details + # if it's not an Intel, don't bother: it's not blacklisted + is_intel || return 1 + # it also needs to be family=6 + [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ] || return 1 + # now, check each known bad microcode + # source: https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/kernel/cpu/intel.c#n105 + # 2018-02-08 update: https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2018/02/microcode-update-guidance.pdf + # model,stepping,microcode + for tuple in \ + $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE,0x0B,0x80 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE,0x0A,0x80 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE,0x09,0x80 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_L,0x0A,0x80 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_L,0x09,0x80 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X,0x03,0x0100013e \ + $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X,0x04,0x02000036 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X,0x04,0x0200003a \ + $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X,0x04,0x0200003c \ + $INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL,0x04,0x28 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_G,0x01,0x1b \ + $INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_D,0x02,0x14 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_D,0x03,0x07000011 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_BROADWELL_X,0x01,0x0b000025 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_L,0x01,0x21 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_G,0x01,0x18 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL,0x03,0x23 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_X,0x02,0x3b \ + $INTEL_FAM6_HASWELL_X,0x04,0x10 \ + $INTEL_FAM6_IVYBRIDGE_X,0x04,0x42a \ + $INTEL_FAM6_SANDYBRIDGE_X,0x06,0x61b \ + $INTEL_FAM6_SANDYBRIDGE_X,0x07,0x712 + do + model=$(echo "$tuple" | cut -d, -f1) + stepping=$(( $(echo "$tuple" | cut -d, -f2) )) + if [ "$cpu_model" = "$model" ] && [ "$cpu_stepping" = "$stepping" ]; then + ucode=$(( $(echo "$tuple" | cut -d, -f3) )) + if [ "$cpu_ucode" = "$ucode" ]; then + _debug "is_ucode_blacklisted: we have a match! ($cpu_model/$cpu_stepping/$cpu_ucode)" + return 0 + fi + fi + done + _debug "is_ucode_blacklisted: no ($cpu_model/$cpu_stepping/$cpu_ucode)" + return 1 +} + +is_skylake_cpu() +{ + # is this a skylake cpu? + # return 0 if yes, 1 otherwise + #if (boot_cpu_data.x86_vendor == X86_VENDOR_INTEL && + # boot_cpu_data.x86 == 6) { + # switch (boot_cpu_data.x86_model) { + # case INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_MOBILE: + # case INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_DESKTOP: + # case INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X: + # case INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_MOBILE: + # case INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_DESKTOP: + # return true; + parse_cpu_details + is_intel || return 1 + [ "$cpu_family" = 6 ] || return 1 + if [ "$cpu_model" = $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_L ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = $INTEL_FAM6_SKYLAKE_X ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE_L ] || \ + [ "$cpu_model" = $INTEL_FAM6_KABYLAKE ]; then + return 0 + fi + return 1 +} + +is_vulnerable_to_empty_rsb() +{ + if is_intel && [ -z "$capabilities_rsba" ]; then + _warn "is_vulnerable_to_empty_rsb() called before ARCH CAPABILITIES MSR was read" + fi + if is_skylake_cpu || [ "$capabilities_rsba" = 1 ]; then + return 0 + fi + return 1 +} + +is_zen_cpu() +{ + # is this CPU from the AMD ZEN family ? (ryzen, epyc, ...) + parse_cpu_details + is_amd || return 1 + [ "$cpu_family" = 23 ] && return 0 + return 1 +} +is_moksha_cpu() +{ + parse_cpu_details + is_hygon || return 1 + [ "$cpu_family" = 24 ] && return 0 + return 1 +} + +# Test if the current host is a Xen PV Dom0 / DomU +is_xen() { + if [ ! -d "$procfs/xen" ]; then + return 1 + fi + + # XXX do we have a better way that relying on dmesg? + dmesg_grep 'Booting paravirtualized kernel on Xen$'; ret=$? + if [ $ret -eq 2 ]; then + _warn "dmesg truncated, Xen detection will be unreliable. Please reboot and relaunch this script" + return 1 + elif [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then + return 0 + else + return 1 + fi +} + +is_xen_dom0() +{ + if ! is_xen; then + return 1 + fi + + if [ -e "$procfs/xen/capabilities" ] && grep -q "control_d" "$procfs/xen/capabilities"; then + return 0 + else + return 1 + fi +} + +is_xen_domU() +{ + if ! is_xen; then + return 1 + fi + + # PVHVM guests also print 'Booting paravirtualized kernel', so we need this check. + dmesg_grep 'Xen HVM callback vector for event delivery is enabled$'; ret=$? + if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then + return 1 + fi + + if ! is_xen_dom0; then + return 0 + else + return 1 + fi +} + +builtin_dbversion=$(awk '/^# %%% MCEDB / { print $4 }' "$0") +if [ -r "$mcedb_cache" ]; then + # we have a local cache file, but it might be older than the builtin version we have + local_dbversion=$( awk '/^# %%% MCEDB / { print $4 }' "$mcedb_cache") + # sort -V sorts by version number + older_dbversion=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$local_dbversion" "$builtin_dbversion" | sort -V | head -n1) + if [ "$older_dbversion" = "$builtin_dbversion" ]; then + mcedb_source="$mcedb_cache" + mcedb_info="local firmwares DB $local_dbversion" + fi +fi +# if mcedb_source is not set, either we don't have a local cached db, or it is older than the builtin db +if [ -z "${mcedb_source:-}" ]; then + mcedb_source="$0" + mcedb_info="builtin firmwares DB $builtin_dbversion" +fi +read_mcedb() +{ + awk '{ if (DELIM==1) { print $2 } } /^# %%% MCEDB / { DELIM=1 }' "$mcedb_source" +} + +is_latest_known_ucode() +{ + # 0: yes, 1: no, 2: unknown + parse_cpu_details + if [ "$cpu_cpuid" = 0 ]; then + ucode_latest="couldn't get your cpuid" + return 2 + fi + ucode_latest="latest microcode version for your CPU model is unknown" + if is_intel; then + cpu_brand_prefix=I + elif is_amd; then + cpu_brand_prefix=A + else + return 2 + fi + for tuple in $(read_mcedb | grep "$(printf "^$cpu_brand_prefix,0x%08X," "$cpu_cpuid")") + do + ucode=$(( $(echo "$tuple" | cut -d, -f3) )) + ucode_date=$(echo "$tuple" | cut -d, -f4 | sed -r 's=(....)(..)(..)=\1/\2/\3=') + _debug "is_latest_known_ucode: with cpuid $cpu_cpuid has ucode $cpu_ucode, last known is $ucode from $ucode_date" + ucode_latest=$(printf "latest version is 0x%x dated $ucode_date according to $mcedb_info" "$ucode") + if [ "$cpu_ucode" -ge "$ucode" ]; then + return 0 + else + return 1 + fi + done + _debug "is_latest_known_ucode: this cpuid is not referenced ($cpu_cpuid)" + return 2 +} + +get_cmdline() +{ + if [ -n "${kernel_cmdline:-}" ]; then + return + fi + + if [ -n "${SMC_MOCK_CMDLINE:-}" ]; then + mocked=1 + _debug "get_cmdline: using mocked cmdline '$SMC_MOCK_CMDLINE'" + kernel_cmdline="$SMC_MOCK_CMDLINE" + return + else + kernel_cmdline=$(cat "$procfs/cmdline") + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CMDLINE='$kernel_cmdline'") + fi +} + +# ENTRYPOINT + +# we can't do anything useful under WSL +if uname -a | grep -qE -- '-Microsoft #[0-9]+-Microsoft '; then + _warn "This script doesn't work under Windows Subsystem for Linux" + _warn "You should use the official Microsoft tool instead." + _warn "It can be found under https://aka.ms/SpeculationControlPS" + exit 1 +fi + +# or other UNIX-ish OSes non-Linux non-supported-BSDs +if [ "$os" = Darwin ] || [ "$os" = VMkernel ]; then + _warn "You're running under the $os OS, but this script" + _warn "only works under Linux and some BSD systems, sorry." + _warn "Please read the README and FAQ for more information." + exit 1 +fi + +# check for mode selection inconsistency +if [ "$opt_hw_only" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$opt_cve_all" = 0 ]; then + show_usage + echo "$0: error: incompatible modes specified, --hw-only vs --variant" >&2 + exit 255 + else + opt_cve_all=0 + opt_cve_list='' + fi +fi + +# coreos mode +if [ "$opt_coreos" = 1 ]; then + if ! is_coreos; then + _warn "CoreOS mode asked, but we're not under CoreOS!" + exit 255 + fi + _warn "CoreOS mode, starting an ephemeral toolbox to launch the script" + load_msr + load_cpuid + mount_debugfs + toolbox --ephemeral --bind-ro /dev/cpu:/dev/cpu -- sh -c "dnf install -y binutils which && /media/root$PWD/$0 $* --coreos-within-toolbox" + exitcode=$? + exit $exitcode +else + if is_coreos; then + _warn "You seem to be running CoreOS, you might want to use the --coreos option for better results" + _warn + fi +fi + +# if we're under a BSD, try to mount linprocfs for "$procfs/cpuinfo" +procfs=/proc +if echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + _debug "We're under BSD, check if we have procfs" + procfs=$(mount | awk '/^linprocfs/ { print $3; exit; }') + if [ -z "$procfs" ]; then + _debug "we don't, try to mount it" + procfs=/proc + [ -d /compat/linux/proc ] && procfs=/compat/linux/proc + test -d $procfs || mkdir $procfs + if mount -t linprocfs linprocfs $procfs 2>/dev/null; then + mounted_procfs=1 + _debug "procfs just mounted at $procfs" + else + procfs='' + fi + else + _debug "We do: $procfs" + fi +fi + +# define a few vars we might reference later without these being inited +mockme='' +mocked=0 +specex_knob_dir=/dev/no_valid_path + +# if /tmp doesn't exist and TMPDIR is not set, try to set it to a sane default for Android +if [ -z "${TMPDIR:-}" ] && ! [ -d "/tmp" ] && [ -d "/data/local/tmp" ]; then + TMPDIR=/data/local/tmp + export TMPDIR +fi + +parse_cpu_details +get_cmdline + +if [ "$opt_cpu" != all ] && [ "$opt_cpu" -gt "$max_core_id" ]; then + echo "$0: error: --cpu can't be higher than $max_core_id, got $opt_cpu" >&2 + exit 255 +fi + +if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # root check (only for live mode, for offline mode, we already checked if we could read the files) + if [ "$(id -u)" -ne 0 ]; then + _warn "Note that you should launch this script with root privileges to get accurate information." + _warn "We'll proceed but you might see permission denied errors." + _warn "To run it as root, you can try the following command: sudo $0" + _warn + fi + _info "Checking for vulnerabilities on current system" + _info "Kernel is \033[35m$os $(uname -r) $(uname -v) $(uname -m)\033[0m" + _info "CPU is \033[35m$cpu_friendly_name\033[0m" + + # try to find the image of the current running kernel + if [ -n "$opt_kernel" ]; then + # specified by user on cmdline, with --live, don't override + : + # first, look for the BOOT_IMAGE hint in the kernel cmdline + elif echo "$kernel_cmdline" | grep -q 'BOOT_IMAGE='; then + opt_kernel=$(echo "$kernel_cmdline" | grep -Eo 'BOOT_IMAGE=[^ ]+' | cut -d= -f2) + _debug "found opt_kernel=$opt_kernel in $procfs/cmdline" + # if the boot partition is within a btrfs subvolume, strip the subvolume name + # if /boot is a separate subvolume, the remainder of the code in this section should handle it + if echo "$opt_kernel" | grep -q "^/@"; then opt_kernel=$(echo "$opt_kernel" | sed "s:/@[^/]*::"); fi + # if we have a dedicated /boot partition, our bootloader might have just called it / + # so try to prepend /boot and see if we find anything + [ -e "/boot/$opt_kernel" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/$opt_kernel" + # special case for CoreOS if we're inside the toolbox + [ -e "/media/root/boot/$opt_kernel" ] && opt_kernel="/media/root/boot/$opt_kernel" + _debug "opt_kernel is now $opt_kernel" + # else, the full path is already there (most probably /boot/something) + fi + # if we didn't find a kernel, default to guessing + if [ ! -e "$opt_kernel" ]; then + # Fedora: + [ -e "/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/vmlinuz" ] && opt_kernel="/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/vmlinuz" + # Slackware: + [ -e "/boot/vmlinuz" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/vmlinuz" + # Arch aarch64: + [ -e "/boot/Image" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/Image" + # Arch armv5/armv7: + [ -e "/boot/zImage" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/zImage" + # Arch arm7: + [ -e "/boot/kernel7.img" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/kernel7.img" + # Linux-Libre: + [ -e "/boot/vmlinuz-linux-libre" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/vmlinuz-linux-libre" + # pine64 + [ -e "/boot/pine64/Image" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/pine64/Image" + # generic: + [ -e "/boot/vmlinuz-$(uname -r)" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/vmlinuz-$(uname -r)" + [ -e "/boot/kernel-$( uname -r)" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/kernel-$( uname -r)" + [ -e "/boot/bzImage-$(uname -r)" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/bzImage-$(uname -r)" + # Gentoo: + [ -e "/boot/kernel-genkernel-$(uname -m)-$(uname -r)" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/kernel-genkernel-$(uname -m)-$(uname -r)" + # NixOS: + [ -e "/run/booted-system/kernel" ] && opt_kernel="/run/booted-system/kernel" + # systemd kernel-install: + [ -e "/etc/machine-id" ] && [ -e "/boot/$(cat /etc/machine-id)/$(uname -r)/linux" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/$(cat /etc/machine-id)/$(uname -r)/linux" + # Clear Linux: + str_uname=$(uname -r) + clear_linux_kernel="/lib/kernel/org.clearlinux.${str_uname##*.}.${str_uname%.*}" + [ -e "$clear_linux_kernel" ] && opt_kernel=$clear_linux_kernel + # Custom Arch seems to have the kernel path in its cmdline in the form "\directory\kernelimage", + # with actual \'s instead of /'s: + custom_arch_kernel=$(echo "$kernel_cmdline" | grep -Eo "(^|\s)\\\\[\\\\a-zA-Z0-9_.-]+" | tr "\\\\" "/" | tr -d '[:space:]') + if [ -n "$custom_arch_kernel" ] && [ -e "$custom_arch_kernel" ]; then + opt_kernel="$custom_arch_kernel" + fi + # FreeBSD: + [ -e "/boot/kernel/kernel" ] && opt_kernel="/boot/kernel/kernel" + fi + + # system.map + if [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + # specified by user on cmdline, with --live, don't override + : + elif [ -e "$procfs/kallsyms" ] ; then + opt_map="$procfs/kallsyms" + elif [ -e "/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/System.map" ] ; then + opt_map="/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/System.map" + elif [ -e "/boot/System.map-$(uname -r)" ] ; then + opt_map="/boot/System.map-$(uname -r)" + elif [ -e "/lib/kernel/System.map-$(uname -r)" ]; then + opt_map="/lib/kernel/System.map-$(uname -r)" + fi + + # config + if [ -n "$opt_config" ]; then + # specified by user on cmdline, with --live, don't override + : + elif [ -e "$procfs/config.gz" ] ; then + dumped_config="$(mktemp -t smc-config-XXXXXX)" + gunzip -c "$procfs/config.gz" > "$dumped_config" + # dumped_config will be deleted at the end of the script + opt_config="$dumped_config" + elif [ -e "/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/config" ]; then + opt_config="/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/config" + elif [ -e "/boot/config-$(uname -r)" ]; then + opt_config="/boot/config-$(uname -r)" + elif [ -e "/etc/kernels/kernel-config-$(uname -m)-$(uname -r)" ]; then + opt_config="/etc/kernels/kernel-config-$(uname -m)-$(uname -r)" + elif [ -e "/lib/kernel/config-$(uname -r)" ]; then + opt_config="/lib/kernel/config-$(uname -r)" + fi +else + _info "Checking for vulnerabilities against specified kernel" + _info "CPU is \033[35m$cpu_friendly_name\033[0m" +fi + +if [ -n "$opt_kernel" ]; then + _verbose "Will use kernel image \033[35m$opt_kernel\033[0m" +else + _verbose "Will use no kernel image (accuracy might be reduced)" + bad_accuracy=1 +fi + +if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + if [ -n "$opt_config" ] && ! grep -q '^CONFIG_' "$opt_config"; then + # given file is invalid! + _warn "The kernel config file seems invalid, was expecting a plain-text file, ignoring it!" + opt_config='' + fi + + if [ -n "${dumped_config:-}" ] && [ -n "$opt_config" ]; then + _verbose "Will use kconfig \033[35m$procfs/config.gz (decompressed)\033[0m" + elif [ -n "$opt_config" ]; then + _verbose "Will use kconfig \033[35m$opt_config\033[0m" + else + _verbose "Will use no kconfig (accuracy might be reduced)" + bad_accuracy=1 + fi + + if [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + _verbose "Will use System.map file \033[35m$opt_map\033[0m" + else + _verbose "Will use no System.map file (accuracy might be reduced)" + bad_accuracy=1 + fi + + if [ "${bad_accuracy:=0}" = 1 ]; then + _warn "We're missing some kernel info (see -v), accuracy might be reduced" + fi +fi + +if [ -e "$opt_kernel" ]; then + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}readelf" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + _debug "readelf not found" + kernel_err="missing '${opt_arch_prefix}readelf' tool, please install it, usually it's in the 'binutils' package" + elif [ "$opt_sysfs_only" = 1 ] || [ "$opt_hw_only" = 1 ]; then + kernel_err='kernel image decompression skipped' + else + extract_kernel "$opt_kernel" + fi +else + _debug "no opt_kernel defined" + kernel_err="couldn't find your kernel image in /boot, if you used netboot, this is normal" +fi +if [ -z "$kernel" ] || [ ! -r "$kernel" ]; then + [ -z "$kernel_err" ] && kernel_err="couldn't extract your kernel from $opt_kernel" +else + # vanilla kernels have with ^Linux version + # also try harder with some kernels (such as Red Hat) that don't have ^Linux version before their version string + # and check for FreeBSD + kernel_version=$("${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" 2>/dev/null | grep -E \ + -e '^Linux version ' \ + -e '^[[:alnum:]][^[:space:]]+ \([^[:space:]]+\) #[0-9]+ .+ (19|20)[0-9][0-9]$' \ + -e '^FreeBSD [0-9]' | head -1) + if [ -z "$kernel_version" ]; then + # try even harder with some kernels (such as ARM) that split the release (uname -r) and version (uname -v) in 2 adjacent strings + kernel_version=$("${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" 2>/dev/null | grep -E -B1 '^#[0-9]+ .+ (19|20)[0-9][0-9]$' | tr "\n" " ") + fi + if [ -n "$kernel_version" ]; then + # in live mode, check if the img we found is the correct one + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + _verbose "Kernel image is \033[35m$kernel_version" + if ! echo "$kernel_version" | grep -qF "$(uname -r)"; then + _warn "Possible discrepancy between your running kernel '$(uname -r)' and the image '$kernel_version' we found ($opt_kernel), results might be incorrect" + fi + else + _info "Kernel image is \033[35m$kernel_version" + fi + else + _verbose "Kernel image version is unknown" + fi +fi + +_info + +# end of header stuff + +# now we define some util functions and the check_*() funcs, as +# the user can choose to execute only some of those + +sys_interface_check() +{ + file="$1" + regex="${2:-}" + mode="${3:-}" + msg='' + fullmsg='' + + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_no_sysfs" = 0 ] && [ -r "$file" ]; then + : + else + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_SYSFS_$(basename "$file")_RET=1") + return 1 + fi + + _mockvarname="SMC_MOCK_SYSFS_$(basename "$file")_RET" + # shellcheck disable=SC2086,SC1083 + if [ -n "$(eval echo \${$_mockvarname:-})" ]; then + _debug "sysfs: MOCKING enabled for $file func returns $(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + mocked=1 + return "$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + fi + + [ -n "$regex" ] || regex='.*' + _mockvarname="SMC_MOCK_SYSFS_$(basename "$file")" + # shellcheck disable=SC2086,SC1083 + if [ -n "$(eval echo \${$_mockvarname:-})" ]; then + fullmsg="$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + msg=$(echo "$fullmsg" | grep -Eo "$regex") + _debug "sysfs: MOCKING enabled for $file, will return $fullmsg" + mocked=1 + else + fullmsg=$(cat "$file") + msg=$(grep -Eo "$regex" "$file") + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_SYSFS_$(basename "$file")='$fullmsg'") + fi + if [ "$mode" = silent ]; then + return 0 + elif [ "$mode" = quiet ]; then + _info "* Information from the /sys interface: $fullmsg" + return 0 + fi + _info_nol "* Mitigated according to the /sys interface: " + if echo "$msg" | grep -qi '^not affected'; then + # Not affected + status=OK + pstatus green YES "$fullmsg" + elif echo "$msg" | grep -qEi '^(kvm: )?mitigation'; then + # Mitigation: PTI + status=OK + pstatus green YES "$fullmsg" + elif echo "$msg" | grep -qi '^vulnerable'; then + # Vulnerable + status=VULN + pstatus yellow NO "$fullmsg" + else + status=UNK + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$fullmsg" + fi + _debug "sys_interface_check: $file=$msg (re=$regex)" + return 0 +} + +# write_msr +# param1 (mandatory): MSR, can be in hex or decimal. +# param2 (optional): CPU index, starting from 0. Default 0. +WRITE_MSR_RET_OK=0 +WRITE_MSR_RET_KO=1 +WRITE_MSR_RET_ERR=2 +WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN=3 +write_msr() +{ + if [ "$opt_cpu" != all ]; then + # we only have one core to write to, do it and return the result + write_msr_one_core $opt_cpu "$@" + return $? + fi + + # otherwise we must write on all cores + for _core in $(seq 0 $max_core_id); do + write_msr_one_core "$_core" "$@"; ret=$? + if [ "$_core" = 0 ]; then + # save the result of the first core, for comparison with the others + _first_core_ret=$ret + else + # compare first core with the other ones + if [ $_first_core_ret != $ret ]; then + write_msr_msg="result is not homogeneous between all cores, at least core 0 and $_core differ!" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_ERR + fi + fi + done + # if we're here, all cores agree, return the result + return $ret +} + +write_msr_one_core() +{ + _core="$1" + _msr_dec=$(( $2 )) + _msr=$(printf "0x%x" "$_msr_dec") + + write_msr_msg='unknown error' + : "${msr_locked_down:=0}" + + _mockvarname="SMC_MOCK_WRMSR_${_msr}_RET" + # shellcheck disable=SC2086,SC1083 + if [ -n "$(eval echo \${$_mockvarname:-})" ]; then + _debug "write_msr: MOCKING enabled for msr $_msr func returns $(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + mocked=1 + [ "$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" = $WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN ] && msr_locked_down=1 + return "$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + fi + + if [ ! -e /dev/cpu/0/msr ] && [ ! -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + # try to load the module ourselves (and remember it so we can rmmod it afterwards) + load_msr + fi + if [ ! -e /dev/cpu/0/msr ] && [ ! -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + read_msr_msg="is msr kernel module available?" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_ERR + fi + + _write_denied=0 + if [ "$os" != Linux ]; then + cpucontrol -m "$_msr=0" "/dev/cpuctl$_core" >/dev/null 2>&1; ret=$? + else + # for Linux + # convert to decimal + if [ ! -w /dev/cpu/"$_core"/msr ]; then + write_msr_msg="No write permission on /dev/cpu/$_core/msr" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_ERR + # if wrmsr is available, use it + elif command -v wrmsr >/dev/null 2>&1 && [ "${SMC_NO_WRMSR:-}" != 1 ]; then + _debug "write_msr: using wrmsr" + wrmsr $_msr_dec 0 2>/dev/null; ret=$? + # ret=4: msr doesn't exist, ret=127: msr.allow_writes=off + [ "$ret" = 127 ] && _write_denied=1 + # or fallback to dd if it supports seek_bytes, we prefer it over perl because we can tell the difference between EPERM and EIO + elif dd if=/dev/null of=/dev/null bs=8 count=1 seek="$_msr_dec" oflag=seek_bytes 2>/dev/null && [ "${SMC_NO_DD:-}" != 1 ]; then + _debug "write_msr: using dd" + dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/cpu/"$_core"/msr bs=8 count=1 seek="$_msr_dec" oflag=seek_bytes 2>/dev/null; ret=$? + # if it failed, inspect stderrto look for EPERM + if [ "$ret" != 0 ]; then + if dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/cpu/"$_core"/msr bs=8 count=1 seek="$_msr_dec" oflag=seek_bytes 2>&1 | grep -qF 'Operation not permitted'; then + _write_denied=1 + fi + fi + # or if we have perl, use it, any 5.x version will work + elif command -v perl >/dev/null 2>&1 && [ "${SMC_NO_PERL:-}" != 1 ]; then + _debug "write_msr: using perl" + ret=1 + perl -e "open(M,'>','/dev/cpu/$_core/msr') and seek(M,$_msr_dec,0) and exit(syswrite(M,pack('H16',0)))"; [ $? -eq 8 ] && ret=0 + else + _debug "write_msr: got no wrmsr, perl or recent enough dd!" + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_WRMSR_${_msr}_RET=$WRITE_MSR_RET_ERR") + write_msr_msg="missing tool, install either msr-tools or perl" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_ERR + fi + if [ "$ret" != 0 ]; then + # * Fedora (and probably Red Hat) have a "kernel lock down" feature that prevents us to write to MSRs + # when this mode is enabled and EFI secure boot is enabled (see issue #303) + # https://src.fedoraproject.org/rpms/kernel/blob/master/f/efi-lockdown.patch + # when this happens, any write will fail and dmesg will have a msg printed "msr: Direct access to MSR" + # * A version of this patch also made it to vanilla in 5.4+, in that case the message is: 'raw MSR access is restricted' + # * we don't use dmesg_grep() because we don't care if dmesg is truncated here, as the message has just been printed + # yet more recent versions of the msr module can be set to msr.allow_writes=off, in which case no dmesg message is printed, + # but the write fails + if [ "$_write_denied" = 1 ]; then + _debug "write_msr: writing to msr has been denied" + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_WRMSR_${_msr}_RET=$WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN") + msr_locked_down=1 + write_msr_msg="your kernel is configured to deny writes to MSRs from user space" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN + elif dmesg | grep -qF "msr: Direct access to MSR"; then + _debug "write_msr: locked down kernel detected (Red Hat / Fedora)" + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_WRMSR_${_msr}_RET=$WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN") + msr_locked_down=1 + write_msr_msg="your kernel is locked down (Fedora/Red Hat), please reboot without secure boot and retry" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN + elif dmesg | grep -qF "raw MSR access is restricted"; then + _debug "write_msr: locked down kernel detected (vanilla)" + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_WRMSR_${_msr}_RET=$WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN") + msr_locked_down=1 + write_msr_msg="your kernel is locked down, please reboot with lockdown=none in the kernel cmdline and retry" + return $WRITE_MSR_RET_LOCKDOWN + fi + unset _write_denied + fi + fi + + # normalize ret + if [ "$ret" = 0 ]; then + ret=$WRITE_MSR_RET_OK + else + ret=$WRITE_MSR_RET_KO + fi + _debug "write_msr: for cpu $_core on msr $_msr, ret=$ret" + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_WRMSR_${_msr}_RET=$ret") + return $ret +} + +# read_msr +# param1 (mandatory): MSR, can be in hex or decimal. +# param2 (optional): CPU index, starting from 0. Default 0. +# returned data is available in $read_msr_value +READ_MSR_RET_OK=0 +READ_MSR_RET_KO=1 +READ_MSR_RET_ERR=2 +read_msr() +{ + if [ "$opt_cpu" != all ]; then + # we only have one core to read, do it and return the result + read_msr_one_core $opt_cpu "$@" + return $? + fi + + # otherwise we must read all cores + for _core in $(seq 0 $max_core_id); do + read_msr_one_core "$_core" "$@"; ret=$? + if [ "$_core" = 0 ]; then + # save the result of the first core, for comparison with the others + _first_core_ret=$ret + _first_core_value=$read_msr_value + else + # compare first core with the other ones + if [ $_first_core_ret != $ret ] || [ "$_first_core_value" != "$read_msr_value" ]; then + read_msr_msg="result is not homogeneous between all cores, at least core 0 and $_core differ!" + return $READ_MSR_RET_ERR + fi + fi + done + # if we're here, all cores agree, return the result + return $ret +} + +read_msr_one_core() +{ + _core="$1" + _msr_dec=$(( $2 )) + _msr=$(printf "0x%x" "$_msr_dec") + + read_msr_value='' + read_msr_msg='unknown error' + + _mockvarname="SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}" + # shellcheck disable=SC2086,SC1083 + if [ -n "$(eval echo \${$_mockvarname:-})" ]; then + read_msr_value="$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + _debug "read_msr: MOCKING enabled for msr $_msr, returning $read_msr_value" + mocked=1 + return $READ_MSR_RET_OK + fi + + _mockvarname="SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}_RET" + # shellcheck disable=SC2086,SC1083 + if [ -n "$(eval echo \${$_mockvarname:-})" ] && [ "$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" -ne 0 ]; then + _debug "read_msr: MOCKING enabled for msr $_msr func returns $(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + mocked=1 + return "$(eval echo \$$_mockvarname)" + fi + + if [ ! -e /dev/cpu/0/msr ] && [ ! -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + # try to load the module ourselves (and remember it so we can rmmod it afterwards) + load_msr + fi + if [ ! -e /dev/cpu/0/msr ] && [ ! -e /dev/cpuctl0 ]; then + read_msr_msg="is msr kernel module available?" + return $READ_MSR_RET_ERR + fi + + if [ "$os" != Linux ]; then + # for BSD + _msr=$(cpucontrol -m "$_msr" "/dev/cpuctl$_core" 2>/dev/null); ret=$? + if [ $ret -ne 0 ]; then + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}_RET=$READ_MSR_RET_KO") + return $READ_MSR_RET_KO + fi + # MSR 0x10: 0x000003e1 0xb106dded + _msr_h=$(echo "$_msr" | awk '{print $3}'); + _msr_l=$(echo "$_msr" | awk '{print $4}'); + read_msr_value=$(( _msr_h << 32 | _msr_l )) + else + # for Linux + if [ ! -r /dev/cpu/"$_core"/msr ]; then + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}_RET=$READ_MSR_RET_ERR") + read_msr_msg="No read permission for /dev/cpu/$_core/msr" + return $READ_MSR_RET_ERR + # if rdmsr is available, use it + elif command -v rdmsr >/dev/null 2>&1 && [ "${SMC_NO_RDMSR:-}" != 1 ]; then + _debug "read_msr: using rdmsr on $_msr" + read_msr_value=$(rdmsr -r $_msr_dec 2>/dev/null | od -t u8 -A n) + # or if we have perl, use it, any 5.x version will work + elif command -v perl >/dev/null 2>&1 && [ "${SMC_NO_PERL:-}" != 1 ]; then + _debug "read_msr: using perl on $_msr" + read_msr_value=$(perl -e "open(M,'<','/dev/cpu/$_core/msr') and seek(M,$_msr_dec,0) and read(M,\$_,8) and print" | od -t u8 -A n) + # fallback to dd if it supports skip_bytes + elif dd if=/dev/null of=/dev/null bs=8 count=1 skip="$_msr_dec" iflag=skip_bytes 2>/dev/null; then + _debug "read_msr: using dd on $_msr" + read_msr_value=$(dd if=/dev/cpu/"$_core"/msr bs=8 count=1 skip="$_msr_dec" iflag=skip_bytes 2>/dev/null | od -t u8 -A n) + else + _debug "read_msr: got no rdmsr, perl or recent enough dd!" + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}_RET=$READ_MSR_RET_ERR") + read_msr_msg='missing tool, install either msr-tools or perl' + return $READ_MSR_RET_ERR + fi + if [ -z "$read_msr_value" ]; then + # MSR doesn't exist, don't check for $? because some versions of dd still return 0! + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}_RET=$READ_MSR_RET_KO") + return $READ_MSR_RET_KO + fi + # remove sparse spaces od might give us + read_msr_value=$(( read_msr_value )) + fi + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_RDMSR_${_msr}='$read_msr_value'") + _debug "read_msr: MSR=$_msr value is $read_msr_value" + return $READ_MSR_RET_OK +} + +check_cpu() +{ + _info "\033[1;34mHardware check\033[0m" + + if ! uname -m | grep -qwE 'x86_64|i[3-6]86|amd64'; then + return + fi + + _info "* Hardware support (CPU microcode) for mitigation techniques" + _info " * Indirect Branch Restricted Speculation (IBRS)" + _info_nol " * SPEC_CTRL MSR is available: " + # the new MSR 'SPEC_CTRL' is at offset 0x48 + read_msr 0x48; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_MSR_RET_OK ]; then + spec_ctrl_msr=1 + pstatus green YES + elif [ $ret = $READ_MSR_RET_KO ]; then + spec_ctrl_msr=0 + pstatus yellow NO + else + spec_ctrl_msr=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_msr_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU indicates IBRS capability: " + # from kernel src: { X86_FEATURE_SPEC_CTRL, CPUID_EDX,26, 0x00000007, 0 }, + # amd: https://developer.amd.com/wp-content/resources/Architecture_Guidelines_Update_Indirect_Branch_Control.pdf + # amd: 8000_0008 EBX[14]=1 + cpuid_ibrs='' + if is_intel; then + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 26 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES "SPEC_CTRL feature bit" + cpuid_spec_ctrl=1 + cpuid_ibrs='SPEC_CTRL' + fi + elif is_amd || is_hygon; then + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 14 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES "IBRS_SUPPORT feature bit" + cpuid_ibrs='IBRS_SUPPORT' + fi + else + ret=invalid + pstatus yellow NO "unknown CPU" + fi + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + cpuid_spec_ctrl=-1 + fi + + if is_amd || is_hygon; then + _info_nol " * CPU indicates preferring IBRS always-on: " + # amd or hygon + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 16 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU indicates preferring IBRS over retpoline: " + # amd or hygon + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 18 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + fi + + # IBPB + _info " * Indirect Branch Prediction Barrier (IBPB)" + + if [ "$opt_allow_msr_write" = 1 ]; then + _info_nol " * PRED_CMD MSR is available: " + # the new MSR 'PRED_CTRL' is at offset 0x49, write-only + write_msr 0x49; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $WRITE_MSR_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ $ret = $WRITE_MSR_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$write_msr_msg" + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU indicates IBPB capability: " + # CPUID EAX=0x80000008, ECX=0x00 return EBX[12] indicates support for just IBPB. + if [ "$cpuid_spec_ctrl" = 1 ]; then + # spec_ctrl implies ibpb + cpuid_ibpb='SPEC_CTRL' + pstatus green YES "SPEC_CTRL feature bit" + elif is_intel; then + if [ "$cpuid_spec_ctrl" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "is cpuid kernel module available?" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + elif is_amd || is_hygon; then + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 12 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ibpb='IBPB_SUPPORT' + pstatus green YES "IBPB_SUPPORT feature bit" + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + fi + + # STIBP + _info " * Single Thread Indirect Branch Predictors (STIBP)" + _info_nol " * SPEC_CTRL MSR is available: " + if [ "$spec_ctrl_msr" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ "$spec_ctrl_msr" = 0 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "is msr kernel module available?" + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU indicates STIBP capability: " + # intel: A processor supports STIBP if it enumerates CPUID (EAX=7H,ECX=0):EDX[27] as 1 + # amd: 8000_0008 EBX[15]=1 + if is_intel; then + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 27 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES "Intel STIBP feature bit" + #cpuid_stibp='Intel STIBP' + fi + elif is_amd; then + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 15 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES "AMD STIBP feature bit" + #cpuid_stibp='AMD STIBP' + fi + elif is_hygon; then + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 15 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES "HYGON STIBP feature bit" + #cpuid_stibp='HYGON STIBP' + fi + else + ret=invalid + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "unknown CPU" + fi + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + + if is_amd || is_hygon; then + _info_nol " * CPU indicates preferring STIBP always-on: " + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 17 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + fi + + # variant 4 + if is_intel; then + _info " * Speculative Store Bypass Disable (SSBD)" + _info_nol " * CPU indicates SSBD capability: " + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 31 1 1; ret24=$?; ret25=$ret24 + if [ $ret24 = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='Intel SSBD' + fi + elif is_amd; then + _info " * Speculative Store Bypass Disable (SSBD)" + _info_nol " * CPU indicates SSBD capability: " + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 24 1 1; ret24=$? + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 25 1 1; ret25=$? + if [ $ret24 = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='AMD SSBD in SPEC_CTRL' + #cpuid_ssbd_spec_ctrl=1 + elif [ $ret25 = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='AMD SSBD in VIRT_SPEC_CTRL' + #cpuid_ssbd_virt_spec_ctrl=1 + elif [ "$cpu_family" -ge 21 ] && [ "$cpu_family" -le 23 ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='AMD non-architectural MSR' + fi + elif is_hygon; then + _info " * Speculative Store Bypass Disable (SSBD)" + _info_nol " * CPU indicates SSBD capability: " + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 24 1 1; ret24=$? + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 25 1 1; ret25=$? + + if [ $ret24 = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='HYGON SSBD in SPEC_CTRL' + #hygon cpuid_ssbd_spec_ctrl=1 + elif [ $ret25 = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='HYGON SSBD in VIRT_SPEC_CTRL' + #hygon cpuid_ssbd_virt_spec_ctrl=1 + elif [ "$cpu_family" -ge 24 ]; then + cpuid_ssbd='HYGON non-architectural MSR' + fi + fi + + if [ -n "${cpuid_ssbd:=}" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$cpuid_ssbd" + elif [ "$ret24" = $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR ] && [ "$ret25" = $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + amd_ssb_no=0 + hygon_ssb_no=0 + if is_amd; then + # similar to SSB_NO for intel + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 26 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + amd_ssb_no=1 + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR ]; then + amd_ssb_no=-1 + fi + elif is_hygon; then + # indicate when speculative store bypass disable is no longer needed to prevent speculative loads bypassing older stores + read_cpuid 0x80000008 0x0 $EBX 26 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + hygon_ssb_no=1 + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_ERR ]; then + hygon_ssb_no=-1 + fi + fi + + _info " * L1 data cache invalidation" + + if [ "$opt_allow_msr_write" = 1 ]; then + _info_nol " * FLUSH_CMD MSR is available: " + # the new MSR 'FLUSH_CMD' is at offset 0x10b, write-only + write_msr 0x10b; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $WRITE_MSR_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES + cpu_flush_cmd=1 + elif [ $ret = $WRITE_MSR_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + cpu_flush_cmd=0 + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$write_msr_msg" + cpu_flush_cmd=-1 + fi + fi + + # CPUID of L1D + _info_nol " * CPU indicates L1D flush capability: " + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 28 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES "L1D flush feature bit" + cpuid_l1df=1 + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + cpuid_l1df=0 + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + cpuid_l1df=-1 + fi + + # if we weren't allowed to probe the write-only MSR but the CPUID + # bit says that it shoul be there, make the assumption that it is + if [ "$opt_allow_msr_write" != 1 ]; then + cpu_flush_cmd=$cpuid_l1df + fi + + if is_intel; then + _info " * Microarchitectural Data Sampling" + _info_nol " * VERW instruction is available: " + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 10 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_md_clear=1 + pstatus green YES "MD_CLEAR feature bit" + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + cpuid_md_clear=0 + pstatus yellow NO + else + cpuid_md_clear=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + fi + + if is_intel; then + _info " * Indirect Branch Predictor Controls" + _info_nol " * Indirect Predictor Disable feature is available: " + read_cpuid 0x7 0x2 $EDX 1 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_ipred=1 + pstatus green YES "IPRED_CTRL feature bit" + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + cpuid_ipred=0 + pstatus yellow NO + else + cpuid_ipred=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * Bottomless RSB Disable feature is available: " + read_cpuid 0x7 0x2 $EDX 2 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_rrsba=1 + pstatus green YES "RRSBA_CTRL feature bit" + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + cpuid_rrsba=0 + pstatus yellow NO + else + cpuid_rrsba=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * BHB-Focused Indirect Predictor Disable feature is available: " + read_cpuid 0x7 0x2 $EDX 2 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_bhi=1 + pstatus green YES "BHI_CTRL feature bit" + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + cpuid_bhi=0 + pstatus yellow NO + else + cpuid_bhi=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + # make shellcheck happy while we're not yet using these new cpuid values in our checks + export cpuid_ipred cpuid_rrsba cpuid_bhi + fi + + if is_intel; then + _info " * Enhanced IBRS (IBRS_ALL)" + _info_nol " * CPU indicates ARCH_CAPABILITIES MSR availability: " + cpuid_arch_capabilities=-1 + # A processor supports the ARCH_CAPABILITIES MSR if it enumerates CPUID (EAX=7H,ECX=0):EDX[29] as 1 + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 29 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus green YES + cpuid_arch_capabilities=1 + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + cpuid_arch_capabilities=0 + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * ARCH_CAPABILITIES MSR advertises IBRS_ALL capability: " + capabilities_taa_no=-1 + capabilities_mds_no=-1 + capabilities_rdcl_no=-1 + capabilities_ibrs_all=-1 + capabilities_rsba=-1 + capabilities_l1dflush_no=-1 + capabilities_ssb_no=-1 + capabilities_pschange_msc_no=-1 + capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr=-1 + if [ "$cpuid_arch_capabilities" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$cpuid_arch_capabilities" != 1 ]; then + capabilities_rdcl_no=0 + capabilities_taa_no=0 + capabilities_mds_no=0 + capabilities_ibrs_all=0 + capabilities_rsba=0 + capabilities_l1dflush_no=0 + capabilities_ssb_no=0 + capabilities_pschange_msc_no=0 + capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr=0 + pstatus yellow NO + else + # the new MSR 'ARCH_CAPABILITIES' is at offset 0x10a + read_msr 0x10a; ret=$? + capabilities_rdcl_no=0 + capabilities_taa_no=0 + capabilities_mds_no=0 + capabilities_ibrs_all=0 + capabilities_rsba=0 + capabilities_l1dflush_no=0 + capabilities_ssb_no=0 + capabilities_pschange_msc_no=0 + capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr=0 + if [ $ret = $READ_MSR_RET_OK ]; then + capabilities=$read_msr_value + # https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/arch/x86/include/asm/msr-index.h#n82 + _debug "capabilities MSR is $capabilities (decimal)" + [ $(( capabilities >> 0 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_rdcl_no=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 1 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_ibrs_all=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 2 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_rsba=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 3 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_l1dflush_no=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 4 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_ssb_no=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 5 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_mds_no=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 6 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_pschange_msc_no=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 7 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr=1 + [ $(( capabilities >> 8 & 1 )) -eq 1 ] && capabilities_taa_no=1 + _debug "capabilities says rdcl_no=$capabilities_rdcl_no ibrs_all=$capabilities_ibrs_all rsba=$capabilities_rsba l1dflush_no=$capabilities_l1dflush_no ssb_no=$capabilities_ssb_no mds_no=$capabilities_mds_no taa_no=$capabilities_taa_no pschange_msc_no=$capabilities_pschange_msc_no" + if [ "$capabilities_ibrs_all" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + elif [ $ret = $READ_MSR_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_msr_msg" + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU explicitly indicates not being affected by Meltdown/L1TF (RDCL_NO): " + if [ "$capabilities_rdcl_no" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_rdcl_no" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU explicitly indicates not being affected by Variant 4 (SSB_NO): " + if [ "$capabilities_ssb_no" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_ssb_no" = 1 ] || [ "$amd_ssb_no" = 1 ] || [ "$hygon_ssb_no" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU/Hypervisor indicates L1D flushing is not necessary on this system: " + if [ "$capabilities_l1dflush_no" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_l1dflush_no" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * Hypervisor indicates host CPU might be affected by RSB underflow (RSBA): " + if [ "$capabilities_rsba" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_rsba" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow YES + else + pstatus blue NO + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU explicitly indicates not being affected by Microarchitectural Data Sampling (MDS_NO): " + if [ "$capabilities_mds_no" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_mds_no" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU explicitly indicates not being affected by TSX Asynchronous Abort (TAA_NO): " + if [ "$capabilities_taa_no" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_taa_no" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU explicitly indicates not being affected by iTLB Multihit (PSCHANGE_MSC_NO): " + if [ "$capabilities_pschange_msc_no" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_pschange_msc_no" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU explicitly indicates having MSR for TSX control (TSX_CTRL_MSR): " + if [ "$capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + elif [ "$capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + if [ "$capabilities_tsx_ctrl_msr" = 1 ]; then + read_msr 0x122; ret=$? + if [ "$ret" = $READ_MSR_RET_OK ]; then + tsx_ctrl_msr=$read_msr_value + tsx_ctrl_msr_rtm_disable=$(( tsx_ctrl_msr >> 0 & 1 )) + tsx_ctrl_msr_cpuid_clear=$(( tsx_ctrl_msr >> 1 & 1 )) + fi + + _info_nol " * TSX_CTRL MSR indicates TSX RTM is disabled: " + if [ "$tsx_ctrl_msr_rtm_disable" = 1 ]; then + pstatus blue YES + elif [ "$tsx_ctrl_msr_rtm_disable" = 0 ]; then + pstatus blue NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't read MSR" + fi + + _info_nol " * TSX_CTRL MSR indicates TSX CPUID bit is cleared: " + if [ "$tsx_ctrl_msr_cpuid_clear" = 1 ]; then + pstatus blue YES + elif [ "$tsx_ctrl_msr_cpuid_clear" = 0 ]; then + pstatus blue NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't read MSR" + fi + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU supports Transactional Synchronization Extensions (TSX): " + ret=$READ_CPUID_RET_KO + cpuid_rtm=0 + if is_intel; then + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EBX 11 1 1; ret=$? + fi + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpuid_rtm=1 + pstatus green YES "RTM feature bit" + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + cpuid_rtm=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU supports Software Guard Extensions (SGX): " + ret=$READ_CPUID_RET_KO + cpuid_sgx=0 + if is_intel; then + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EBX 2 1 1; ret=$? + fi + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus blue YES + cpuid_sgx=1 + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus green NO + else + cpuid_sgx=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU supports Special Register Buffer Data Sampling (SRBDS): " + # A processor supports SRBDS if it enumerates CPUID (EAX=7H,ECX=0):EDX[9] as 1 + # That means the mitigation disabling SRBDS exists + ret=$READ_CPUID_RET_KO + cpuid_srbds=0 + srbds_on=0 + if is_intel; then + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EDX 9 1 1; ret=$? + fi + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + pstatus blue YES + cpuid_srbds=1 + read_msr 0x123; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_MSR_RET_OK ]; then + if [ $read_msr_value = 0 ]; then + #SRBDS mitigation control exists and is enabled via microcode + srbds_on=1 + else + #SRBDS mitigation control exists but is disabled via microcode + srbds_on=0 + fi + else + srbds_on=-1 + fi + elif [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_KO ]; then + pstatus green NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$read_cpuid_msg" + cpuid_srbds=0 + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU microcode is known to cause stability problems: " + if is_ucode_blacklisted; then + pstatus red YES "$ucode_found" + _warn + _warn "The microcode your CPU is running on is known to cause instability problems," + _warn "such as intempestive reboots or random crashes." + _warn "You are advised to either revert to a previous microcode version (that might not have" + _warn "the mitigations for Spectre), or upgrade to a newer one if available." + _warn + else + pstatus blue NO "$ucode_found" + fi + + _info_nol " * CPU microcode is the latest known available version: " + is_latest_known_ucode; ret=$? + if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then + pstatus green YES "$ucode_latest" + elif [ $ret -eq 1 ]; then + pstatus red NO "$ucode_latest" + else + pstatus blue UNKNOWN "$ucode_latest" + fi +} + +check_cpu_vulnerabilities() +{ + _info "* CPU vulnerability to the speculative execution attack variants" + for cve in $supported_cve_list; do + _info_nol " * Affected by $cve ($(cve2name "$cve")): " + if is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + pstatus yellow YES + else + pstatus green NO + fi + done +} + +check_redhat_canonical_spectre() +{ + # if we were already called, don't do it again + [ -n "${redhat_canonical_spectre:-}" ] && return + + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + redhat_canonical_spectre=-1 + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + redhat_canonical_spectre=-2 + else + # Red Hat / Ubuntu specific variant1 patch is difficult to detect, + # let's use the two same tricks than the official Red Hat detection script uses: + if "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -qw noibrs && "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -qw noibpb; then + # 1) detect their specific variant2 patch. If it's present, it means + # that the variant1 patch is also present (both were merged at the same time) + _debug "found redhat/canonical version of the variant2 patch (implies variant1)" + redhat_canonical_spectre=1 + elif "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -q 'x86/pti:'; then + # 2) detect their specific variant3 patch. If it's present, but the variant2 + # is not, it means that only variant1 is present in addition to variant3 + _debug "found redhat/canonical version of the variant3 patch (implies variant1 but not variant2)" + redhat_canonical_spectre=2 + else + redhat_canonical_spectre=0 + fi + fi +} + +check_has_vmm() +{ + _info_nol "* This system is a host running a hypervisor: " + has_vmm=$opt_vmm + if [ "$has_vmm" = -1 ] && [ "$opt_paranoid" = 1 ]; then + # In paranoid mode, if --vmm was not specified on the command-line, + # we want to be secure before everything else, so assume we're running + # a hypervisor, as this requires more mitigations + has_vmm=2 + elif [ "$has_vmm" = -1 ]; then + # Here, we want to know if we are hosting a hypervisor, and running some VMs on it. + # If we find no evidence that this is the case, assume we're not (to avoid scaring users), + # this can always be overridden with --vmm in any case. + has_vmm=0 + if command -v pgrep >/dev/null 2>&1; then + # remove xenbus and xenwatch, also present inside domU + # remove libvirtd as it can also be used to manage containers and not VMs + # for each binary we want to grep, get the pids + for _binary in qemu kvm xenstored xenconsoled + do + for _pid in $(pgrep -x $_binary) + do + # resolve the exe symlink, if it doesn't resolve with -m, + # which doesn't even need the dest to exist, it means the symlink + # is null, which is the case for kernel threads: ignore those to + # avoid false positives (such as [kvm-irqfd-clean] under at least RHEL 7.6/7.7) + if ! [ "$(readlink -m "/proc/$_pid/exe")" = "/proc/$_pid/exe" ]; then + _debug "has_vmm: found PID $_pid" + has_vmm=1 + fi + done + done + unset _binary _pid + else + # ignore SC2009 as `ps ax` is actually used as a fallback if `pgrep` isn't installed + # shellcheck disable=SC2009 + if command -v ps >/devnull && ps ax | grep -vw grep | grep -q -e '\<qemu' -e '/qemu' -e '<\kvm' -e '/kvm' -e '/xenstored' -e '/xenconsoled'; then + has_vmm=1 + fi + fi + fi + if [ "$has_vmm" = 0 ]; then + if [ "$opt_vmm" != -1 ]; then + pstatus green NO "forced from command line" + else + pstatus green NO + fi + else + if [ "$opt_vmm" != -1 ]; then + pstatus blue YES "forced from command line" + elif [ "$has_vmm" = 2 ]; then + pstatus blue YES "paranoid mode" + else + pstatus blue YES + fi + fi +} + +################### +# SPECTRE 1 SECTION + +# bounds check bypass aka 'Spectre Variant 1' +check_CVE_2017_5753() +{ + cve='CVE-2017-5753' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2017_5753_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2017_5753_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2017_5753_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v1"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + # v0.33+: don't. some kernels have backported the array_index_mask_nospec() workaround without + # modifying the vulnerabilities/spectre_v1 file. that's bad. we can't trust it when it says Vulnerable :( + # see "silent backport" detection at the bottom of this func + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + # no /sys interface (or offline mode), fallback to our own ways + _info_nol "* Kernel has array_index_mask_nospec: " + # vanilla: look for the Linus' mask aka array_index_mask_nospec() + # that is inlined at least in raw_copy_from_user (__get_user_X symbols) + #mov PER_CPU_VAR(current_task), %_ASM_DX + #cmp TASK_addr_limit(%_ASM_DX),%_ASM_AX + #jae bad_get_user + # /* array_index_mask_nospec() are the 2 opcodes that follow */ + #+sbb %_ASM_DX, %_ASM_DX + #+and %_ASM_DX, %_ASM_AX + #ASM_STAC + # x86 64bits: jae(0x0f 0x83 0x?? 0x?? 0x?? 0x??) sbb(0x48 0x19 0xd2) and(0x48 0x21 0xd0) + # x86 32bits: cmp(0x3b 0x82 0x?? 0x?? 0x00 0x00) jae(0x73 0x??) sbb(0x19 0xd2) and(0x21 0xd0) + # + # arm32 + ##ifdef CONFIG_THUMB2_KERNEL + ##define CSDB ".inst.w 0xf3af8014" + ##else + ##define CSDB ".inst 0xe320f014" e320f014 + ##endif + #asm volatile( + # "cmp %1, %2\n" e1500003 + #" sbc %0, %1, %1\n" e0c03000 + #CSDB + #: "=r" (mask) + #: "r" (idx), "Ir" (sz) + #: "cc"); + # + # http://git.arm.linux.org.uk/cgit/linux-arm.git/commit/?h=spectre&id=a78d156587931a2c3b354534aa772febf6c9e855 + v1_mask_nospec='' + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + elif ! command -v perl >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing 'perl' binary, please install it" + else + perl -ne '/\x0f\x83....\x48\x19\xd2\x48\x21\xd0/ and $found++; END { exit($found) }' "$kernel"; ret=$? + if [ $ret -gt 0 ]; then + pstatus green YES "$ret occurrence(s) found of x86 64 bits array_index_mask_nospec()" + v1_mask_nospec="x86 64 bits array_index_mask_nospec" + else + perl -ne '/\x3b\x82..\x00\x00\x73.\x19\xd2\x21\xd0/ and $found++; END { exit($found) }' "$kernel"; ret=$? + if [ $ret -gt 0 ]; then + pstatus green YES "$ret occurrence(s) found of x86 32 bits array_index_mask_nospec()" + v1_mask_nospec="x86 32 bits array_index_mask_nospec" + else + ret=$("${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" $objdump_options "$kernel" | grep -w -e f3af8014 -e e320f014 -B2 | grep -B1 -w sbc | grep -w -c cmp) + if [ "$ret" -gt 0 ]; then + pstatus green YES "$ret occurrence(s) found of arm 32 bits array_index_mask_nospec()" + v1_mask_nospec="arm 32 bits array_index_mask_nospec" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + fi + fi + + _info_nol "* Kernel has the Red Hat/Ubuntu patch: " + check_redhat_canonical_spectre + if [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing '${opt_arch_prefix}strings' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + elif [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = -2 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + elif [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = 2 ]; then + pstatus green YES "but without IBRS" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol "* Kernel has mask_nospec64 (arm64): " + #.macro mask_nospec64, idx, limit, tmp + #sub \tmp, \idx, \limit + #bic \tmp, \tmp, \idx + #and \idx, \idx, \tmp, asr #63 + #csdb + #.endm + #$ aarch64-linux-gnu-objdump -d vmlinux | grep -w bic -A1 -B1 | grep -w sub -A2 | grep -w and -B2 + #ffffff8008082e44: cb190353 sub x19, x26, x25 + #ffffff8008082e48: 8a3a0273 bic x19, x19, x26 + #ffffff8008082e4c: 8a93ff5a and x26, x26, x19, asr #63 + #ffffff8008082e50: d503229f hint #0x14 + # /!\ can also just be "csdb" instead of "hint #0x14" for native objdump + # + # if we have v1_mask_nospec or redhat_canonical_spectre>0, don't bother disassembling the kernel, the answer is no. + if [ -n "$v1_mask_nospec" ] || [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" -gt 0 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + elif ! command -v perl >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing 'perl' binary, please install it" + elif ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing '${opt_arch_prefix}objdump' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + else + "${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" $objdump_options "$kernel" | perl -ne 'push @r, $_; /\s(hint|csdb)\s/ && $r[0]=~/\ssub\s+(x\d+)/ && $r[1]=~/\sbic\s+$1,\s+$1,/ && $r[2]=~/\sand\s/ && exit(9); shift @r if @r>3'; ret=$? + if [ "$ret" -eq 9 ]; then + pstatus green YES "mask_nospec64 macro is present and used" + v1_mask_nospec="arm64 mask_nospec64" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + + _info_nol "* Kernel has array_index_nospec (arm64): " + # in 4.19+ kernels, the mask_nospec64 asm64 macro is replaced by array_index_nospec, defined in nospec.h, and used in invoke_syscall() + # ffffff8008090a4c: 2a0203e2 mov w2, w2 + # ffffff8008090a50: eb0200bf cmp x5, x2 + # ffffff8008090a54: da1f03e2 ngc x2, xzr + # ffffff8008090a58: d503229f hint #0x14 + # /!\ can also just be "csdb" instead of "hint #0x14" for native objdump + # + # if we have v1_mask_nospec or redhat_canonical_spectre>0, don't bother disassembling the kernel, the answer is no. + if [ -n "$v1_mask_nospec" ] || [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" -gt 0 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + elif ! command -v perl >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing 'perl' binary, please install it" + elif ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing '${opt_arch_prefix}objdump' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + else + "${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" -d "$kernel" | perl -ne 'push @r, $_; /\s(hint|csdb)\s/ && $r[0]=~/\smov\s+(w\d+),\s+(w\d+)/ && $r[1]=~/\scmp\s+(x\d+),\s+(x\d+)/ && $r[2]=~/\sngc\s+$2,/ && exit(9); shift @r if @r>3'; ret=$? + if [ "$ret" -eq 9 ]; then + pstatus green YES "array_index_nospec macro is present and used" + v1_mask_nospec="arm64 array_index_nospec" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ] || { [ -z "$v1_mask_nospec" ] && [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" != 1 ] && [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" != 2 ]; }; then + # this is a slow heuristic and we don't need it if we already know the kernel is patched + # but still show it in verbose mode + _info_nol "* Checking count of LFENCE instructions following a jump in kernel... " + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + else + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing '${opt_arch_prefix}objdump' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + else + # here we disassemble the kernel and count the number of occurrences of the LFENCE opcode + # in non-patched kernels, this has been empirically determined as being around 40-50 + # in patched kernels, this is more around 70-80, sometimes way higher (100+) + # v0.13: 68 found in a 3.10.23-xxxx-std-ipv6-64 (with lots of modules compiled-in directly), which doesn't have the LFENCE patches, + # so let's push the threshold to 70. + # v0.33+: now only count lfence opcodes after a jump, way less error-prone + # non patched kernel have between 0 and 20 matches, patched ones have at least 40-45 + nb_lfence=$("${opt_arch_prefix}objdump" $objdump_options "$kernel" 2>/dev/null | grep -w -B1 lfence | grep -Ewc 'jmp|jne|je') + if [ "$nb_lfence" -lt 30 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO "only $nb_lfence jump-then-lfence instructions found, should be >= 30 (heuristic)" + else + v1_lfence=1 + pstatus green YES "$nb_lfence jump-then-lfence instructions found, which is >= 30 (heuristic)" + fi + fi + fi + fi + + else + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + # report status + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -z "$msg" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ -n "$v1_mask_nospec" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Kernel source has been patched to mitigate the vulnerability ($v1_mask_nospec)" + elif [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = 1 ] || [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = 2 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Kernel source has been patched to mitigate the vulnerability (Red Hat/Ubuntu patch)" + elif [ "$v1_lfence" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Kernel source has PROBABLY been patched to mitigate the vulnerability (jump-then-lfence instructions heuristic)" + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve UNK "Couldn't find kernel image or tools missing to execute the checks" + explain "Re-run this script with root privileges, after installing the missing tools indicated above" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Kernel source needs to be patched to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "Your kernel is too old to have the mitigation for Variant 1, you should upgrade to a newer kernel. If you're using a Linux distro and didn't compile the kernel yourself, you should upgrade your distro to get a newer kernel." + fi + else + if [ "$msg" = "Vulnerable" ] && [ -n "$v1_mask_nospec" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Kernel source has been patched to mitigate the vulnerability (silent backport of array_index_mask_nospec)" + else + if [ "$msg" = "Vulnerable" ]; then + msg="Kernel source needs to be patched to mitigate the vulnerability" + _explain="Your kernel is too old to have the mitigation for Variant 1, you should upgrade to a newer kernel. If you're using a Linux distro and didn't compile the kernel yourself, you should upgrade your distro to get a newer kernel." + fi + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + [ -n "${_explain:-}" ] && explain "$_explain" + unset _explain + fi + fi +} + +check_CVE_2017_5753_bsd() +{ + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "no mitigation for BSD yet" + fi +} + +################### +# SPECTRE 2 SECTION + +# branch target injection aka 'Spectre Variant 2' +check_CVE_2017_5715() +{ + cve='CVE-2017-5715' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2017_5715_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2017_5715_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2017_5715_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spectre_v2"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info "* Mitigation 1" + + ibrs_can_tell=0 + ibrs_supported='' + ibrs_enabled='' + ibpb_can_tell=0 + ibpb_supported='' + ibpb_enabled='' + + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # in live mode, we can check for the ibrs_enabled file in debugfs + # all versions of the patches have it (NOT the case of IBPB or KPTI) + ibrs_can_tell=1 + mount_debugfs + for dir in \ + /sys/kernel/debug \ + /sys/kernel/debug/x86 \ + "$procfs/sys/kernel"; do + if [ -e "$dir/ibrs_enabled" ]; then + # if the file is there, we have IBRS compiled-in + # /sys/kernel/debug/ibrs_enabled: vanilla + # /sys/kernel/debug/x86/ibrs_enabled: Red Hat (see https://access.redhat.com/articles/3311301) + # /proc/sys/kernel/ibrs_enabled: OpenSUSE tumbleweed + specex_knob_dir=$dir + ibrs_supported="$dir/ibrs_enabled exists" + ibrs_enabled=$(cat "$dir/ibrs_enabled" 2>/dev/null) + _debug "ibrs: found $dir/ibrs_enabled=$ibrs_enabled" + # if ibrs_enabled is there, ibpb_enabled will be in the same dir + if [ -e "$dir/ibpb_enabled" ]; then + # if the file is there, we have IBPB compiled-in (see note above for IBRS) + ibpb_supported="$dir/ibpb_enabled exists" + ibpb_enabled=$(cat "$dir/ibpb_enabled" 2>/dev/null) + _debug "ibpb: found $dir/ibpb_enabled=$ibpb_enabled" + else + _debug "ibpb: $dir/ibpb_enabled file doesn't exist" + fi + break + else + _debug "ibrs: $dir/ibrs_enabled file doesn't exist" + fi + done + # on some newer kernels, the spec_ctrl_ibrs flag in "$procfs/cpuinfo" + # is set when ibrs has been administratively enabled (usually from cmdline) + # which in that case means ibrs is supported *and* enabled for kernel & user + # as per the ibrs patch series v3 + if [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ]; then + if grep ^flags "$procfs/cpuinfo" | grep -qw spec_ctrl_ibrs; then + _debug "ibrs: found spec_ctrl_ibrs flag in $procfs/cpuinfo" + ibrs_supported="spec_ctrl_ibrs flag in $procfs/cpuinfo" + # enabled=2 -> kernel & user + ibrs_enabled=2 + # XXX and what about ibpb ? + fi + fi + if [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + # when IBPB is enabled on 4.15+, we can see it in sysfs + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -q 'IBPB'; then + _debug "ibpb: found enabled in sysfs" + [ -z "$ibpb_supported" ] && ibpb_supported='IBPB found enabled in sysfs' + [ -z "$ibpb_enabled" ] && ibpb_enabled=1 + fi + # when IBRS_FW is enabled on 4.15+, we can see it in sysfs + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -q ', IBRS_FW'; then + _debug "ibrs: found IBRS_FW in sysfs" + [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ] && ibrs_supported='found IBRS_FW in sysfs' + ibrs_fw_enabled=1 + fi + # when IBRS is enabled on 4.15+, we can see it in sysfs + # on a more recent kernel, classic "IBRS" is not even longer an option, because of the performance impact. + # only "Enhanced IBRS" is available (on CPUs with the IBRS_ALL flag) + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -q -e '\<IBRS\>' -e 'Indirect Branch Restricted Speculation'; then + _debug "ibrs: found IBRS in sysfs" + [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ] && ibrs_supported='found IBRS in sysfs' + [ -z "$ibrs_enabled" ] && ibrs_enabled=3 + fi + # checking for 'Enhanced IBRS' in sysfs, enabled on CPUs with IBRS_ALL + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -q -e 'Enhanced IBRS'; then + [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ] && ibrs_supported='found Enhanced IBRS in sysfs' + # 4 isn't actually a valid value of the now extinct "ibrs_enabled" flag file, + # that only went from 0 to 3, so we use 4 as "enhanced ibrs is enabled" + ibrs_enabled=4 + fi + fi + # in live mode, if ibrs or ibpb is supported and we didn't find these are enabled, then they are not + [ -n "$ibrs_supported" ] && [ -z "$ibrs_enabled" ] && ibrs_enabled=0 + [ -n "$ibpb_supported" ] && [ -z "$ibpb_enabled" ] && ibpb_enabled=0 + fi + if [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ]; then + check_redhat_canonical_spectre + if [ "$redhat_canonical_spectre" = 1 ]; then + ibrs_supported="Red Hat/Ubuntu variant" + ibpb_supported="Red Hat/Ubuntu variant" + fi + fi + if [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ] && [ -n "$kernel" ]; then + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + : + else + ibrs_can_tell=1 + ibrs_supported=$("${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -Fw -e ', IBRS_FW' | head -1) + if [ -n "$ibrs_supported" ]; then + _debug "ibrs: found ibrs evidence in kernel image ($ibrs_supported)" + ibrs_supported="found '$ibrs_supported' in kernel image" + fi + fi + fi + if [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ] && [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + ibrs_can_tell=1 + if grep -q spec_ctrl "$opt_map"; then + ibrs_supported="found spec_ctrl in symbols file" + _debug "ibrs: found '*spec_ctrl*' symbol in $opt_map" + fi + fi + # recent (4.15) vanilla kernels have IBPB but not IBRS, and without the debugfs tunables of Red Hat + # we can detect it directly in the image + if [ -z "$ibpb_supported" ] && [ -n "$kernel" ]; then + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + : + else + ibpb_can_tell=1 + ibpb_supported=$("${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -Fw -e 'ibpb' -e ', IBPB' | head -1) + if [ -n "$ibpb_supported" ]; then + _debug "ibpb: found ibpb evidence in kernel image ($ibpb_supported)" + ibpb_supported="found '$ibpb_supported' in kernel image" + fi + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * Kernel is compiled with IBRS support: " + if [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ]; then + if [ "$ibrs_can_tell" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + # problem obtaining/inspecting kernel or strings not installed, but if the later is true, + # then readelf is not installed either (both in binutils) which makes the former true, so + # either way kernel_err should be set + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + fi + else + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ]; then + pstatus green YES "$ibrs_supported" + else + pstatus green YES + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * IBRS enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$ibpb_enabled" = 2 ]; then + # if ibpb=2, ibrs is forcefully=0 + pstatus blue NO "IBPB used instead of IBRS in all kernel entrypoints" + else + # 0 means disabled + # 1 is enabled only for kernel space + # 2 is enabled for kernel and user space + # 3 is enabled + # 4 is enhanced ibrs enabled + case "$ibrs_enabled" in + 0) + if [ "$ibrs_fw_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pstatus blue YES "for firmware code only" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + ;; + 1) if [ "$ibrs_fw_enabled" = 1 ]; then pstatus green YES "for kernel space and firmware code"; else pstatus green YES "for kernel space"; fi;; + 2) if [ "$ibrs_fw_enabled" = 1 ]; then pstatus green YES "for kernel, user space, and firmware code" ; else pstatus green YES "for both kernel and user space"; fi;; + 3) if [ "$ibrs_fw_enabled" = 1 ]; then pstatus green YES "for kernel and firmware code"; else pstatus green YES; fi;; + 4) pstatus green YES "Enhanced flavor, performance impact will be greatly reduced";; + *) if [ "$cpuid_ibrs" != 'SPEC_CTRL' ] && [ "$cpuid_ibrs" != 'IBRS_SUPPORT' ] && [ "$cpuid_spec_ctrl" != -1 ]; + then pstatus yellow NO; _debug "ibrs: known cpu not supporting SPEC-CTRL or IBRS"; + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN; fi;; + esac + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + + _info_nol " * Kernel is compiled with IBPB support: " + if [ -z "$ibpb_supported" ]; then + if [ "$ibpb_can_tell" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + # if we're in offline mode without System.map, we can't really know + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "in offline mode, we need the kernel image to be able to tell" + fi + else + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ]; then + pstatus green YES "$ibpb_supported" + else + pstatus green YES + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * IBPB enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + case "$ibpb_enabled" in + "") + if [ "$ibrs_supported" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + ;; + 0) + pstatus yellow NO + ;; + 1) pstatus green YES;; + 2) pstatus green YES "IBPB used instead of IBRS in all kernel entrypoints";; + *) pstatus yellow UNKNOWN;; + esac + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + + _info "* Mitigation 2" + _info_nol " * Kernel has branch predictor hardening (arm): " + bp_harden_can_tell=0 + bp_harden='' + if [ -r "$opt_config" ]; then + bp_harden_can_tell=1 + bp_harden=$(grep -w 'CONFIG_HARDEN_BRANCH_PREDICTOR=y' "$opt_config") + if [ -n "$bp_harden" ]; then + pstatus green YES + _debug "bp_harden: found '$bp_harden' in $opt_config" + fi + fi + if [ -z "$bp_harden" ] && [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + bp_harden_can_tell=1 + bp_harden=$(grep -w bp_hardening_data "$opt_map") + if [ -n "$bp_harden" ]; then + pstatus green YES + _debug "bp_harden: found '$bp_harden' in $opt_map" + fi + fi + if [ -z "$bp_harden" ]; then + if [ "$bp_harden_can_tell" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + fi + fi + + _info_nol " * Kernel compiled with retpoline option: " + # We check the RETPOLINE kernel options + retpoline=0 + if [ -r "$opt_config" ]; then + if grep -q '^CONFIG_RETPOLINE=y' "$opt_config"; then + pstatus green YES + retpoline=1 + # shellcheck disable=SC2046 + _debug 'retpoline: found '$(grep '^CONFIG_RETPOLINE' "$opt_config")" in $opt_config" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't read your kernel configuration" + fi + + if [ "$retpoline" = 1 ]; then + # Now check if the compiler used to compile the kernel knows how to insert retpolines in generated asm + # For gcc, this is -mindirect-branch=thunk-extern (detected by the kernel makefiles) + # See gcc commit https://github.com/hjl-tools/gcc/commit/23b517d4a67c02d3ef80b6109218f2aadad7bd79 + # In latest retpoline LKML patches, the noretpoline_setup symbol exists only if CONFIG_RETPOLINE is set + # *AND* if the compiler is retpoline-compliant, so look for that symbol + # + # if there is "retpoline" in the file and NOT "minimal", then it's full retpoline + # (works for vanilla and Red Hat variants) + # + # since 5.15.28, this is now "Retpolines" as the implementation was switched to a generic one, + # so we look for both "retpoline" and "retpolines" + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qwi -e retpoline -e retpolines; then + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qwi minimal; then + retpoline_compiler=0 + retpoline_compiler_reason="kernel reports minimal retpoline compilation" + else + retpoline_compiler=1 + retpoline_compiler_reason="kernel reports full retpoline compilation" + fi + fi + elif [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + # look for the symbol + if grep -qw noretpoline_setup "$opt_map"; then + retpoline_compiler=1 + retpoline_compiler_reason="noretpoline_setup symbol found in System.map" + fi + elif [ -n "$kernel" ]; then + # look for the symbol + if command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}nm" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + # the proper way: use nm and look for the symbol + if "${opt_arch_prefix}nm" "$kernel" 2>/dev/null | grep -qw 'noretpoline_setup'; then + retpoline_compiler=1 + retpoline_compiler_reason="noretpoline_setup found in kernel symbols" + fi + elif grep -q noretpoline_setup "$kernel"; then + # if we don't have nm, nevermind, the symbol name is long enough to not have + # any false positive using good old grep directly on the binary + retpoline_compiler=1 + retpoline_compiler_reason="noretpoline_setup found in kernel" + fi + fi + if [ -n "$retpoline_compiler" ]; then + _info_nol " * Kernel compiled with a retpoline-aware compiler: " + if [ "$retpoline_compiler" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$retpoline_compiler_reason" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$retpoline_compiler_reason" + else + pstatus green YES + fi + else + if [ -n "$retpoline_compiler_reason" ]; then + pstatus red NO "$retpoline_compiler_reason" + else + pstatus red NO + fi + fi + fi + fi + + # only Red Hat has a tunable to disable it on runtime + retp_enabled=-1 + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ -e "$specex_knob_dir/retp_enabled" ]; then + retp_enabled=$(cat "$specex_knob_dir/retp_enabled" 2>/dev/null) + _debug "retpoline: found $specex_knob_dir/retp_enabled=$retp_enabled" + _info_nol " * Retpoline is enabled: " + if [ "$retp_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + fi + + # only for information, in verbose mode + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ]; then + _info_nol " * Local gcc is retpoline-aware: " + if command -v gcc >/dev/null 2>&1; then + if [ -n "$(gcc -mindirect-branch=thunk-extern --version 2>&1 >/dev/null)" ]; then + pstatus blue NO + else + pstatus green YES + fi + else + pstatus blue NO "gcc is not installed" + fi + fi + + if is_vulnerable_to_empty_rsb || [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ]; then + _info_nol " * Kernel supports RSB filling: " + rsb_filling=0 + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_no_sysfs" != 1 ]; then + # if we're live and we aren't denied looking into /sys, let's do it + if echo "$msg" | grep -qw RSB; then + rsb_filling=1 + pstatus green YES + fi + fi + if [ "$rsb_filling" = 0 ]; then + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + else + if grep -qw -e 'Filling RSB on context switch' "$kernel"; then + rsb_filling=1 + pstatus green YES + else + rsb_filling=0 + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + fi + fi + + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$retpoline" = 1 ] && [ "$retpoline_compiler" = 1 ] && [ "$retp_enabled" != 0 ] && [ -n "$ibpb_enabled" ] && [ "$ibpb_enabled" -ge 1 ] && ( ! is_vulnerable_to_empty_rsb || [ "$rsb_filling" = 1 ] ); then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Full retpoline + IBPB are mitigating the vulnerability" + elif [ "$retpoline" = 1 ] && [ "$retpoline_compiler" = 1 ] && [ "$retp_enabled" != 0 ] && [ "$opt_paranoid" = 0 ] && ( ! is_vulnerable_to_empty_rsb || [ "$rsb_filling" = 1 ] ); then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Full retpoline is mitigating the vulnerability" + if [ -n "$cpuid_ibpb" ]; then + _warn "You should enable IBPB to complete retpoline as a Variant 2 mitigation" + else + _warn "IBPB is considered as a good addition to retpoline for Variant 2 mitigation, but your CPU microcode doesn't support it" + fi + elif [ -n "$ibrs_enabled" ] && [ -n "$ibpb_enabled" ] && [ "$ibrs_enabled" -ge 1 ] && [ "$ibpb_enabled" -ge 1 ]; then + if [ "$ibrs_enabled" = 4 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Enhanced IBRS + IBPB are mitigating the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve OK "IBRS + IBPB are mitigating the vulnerability" + fi + elif [ "$ibpb_enabled" = 2 ] && ! is_cpu_smt_enabled; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Full IBPB is mitigating the vulnerability" + elif [ -n "$bp_harden" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Branch predictor hardening mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ -z "$bp_harden" ] && [ "$cpu_vendor" = ARM ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Branch predictor hardening is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "Your kernel has not been compiled with the CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 option, recompile it with this option enabled." + elif [ "$opt_live" != 1 ]; then + if [ "$retpoline" = 1 ] && [ -n "$ibpb_supported" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "offline mode: kernel supports retpoline + IBPB to mitigate the vulnerability" + elif [ -n "$ibrs_supported" ] && [ -n "$ibpb_supported" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "offline mode: kernel supports IBRS + IBPB to mitigate the vulnerability" + elif [ "$ibrs_can_tell" != 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve UNK "offline mode: not enough information" + explain "Re-run this script with root privileges, and give it the kernel image (--kernel), the kernel configuration (--config) and the System.map file (--map) corresponding to the kernel you would like to inspect." + fi + fi + + # if we arrive here and didn't already call pvulnstatus, then it's VULN, let's explain why + if [ "$pvulnstatus_last_cve" != "$cve" ]; then + # explain what's needed for this CPU + if is_vulnerable_to_empty_rsb; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "IBRS+IBPB or retpoline+IBPB+RSB filling, is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "To mitigate this vulnerability, you need either IBRS + IBPB, both requiring hardware support from your CPU microcode in addition to kernel support, or a kernel compiled with retpoline and IBPB, with retpoline requiring a retpoline-aware compiler (re-run this script with -v to know if your version of gcc is retpoline-aware) and IBPB requiring hardware support from your CPU microcode. You also need a recent-enough kernel that supports RSB filling if you plan to use retpoline. For Skylake+ CPUs, the IBRS + IBPB approach is generally preferred as it guarantees complete protection, and the performance impact is not as high as with older CPUs in comparison with retpoline. More information about how to enable the missing bits for those two possible mitigations on your system follow. You only need to take one of the two approaches." + elif is_zen_cpu || is_moksha_cpu; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "retpoline+IBPB is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "To mitigate this vulnerability, You need a kernel compiled with retpoline + IBPB support, with retpoline requiring a retpoline-aware compiler (re-run this script with -v to know if your version of gcc is retpoline-aware) and IBPB requiring hardware support from your CPU microcode." + elif is_intel || is_amd || is_hygon; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "IBRS+IBPB or retpoline+IBPB is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "To mitigate this vulnerability, you need either IBRS + IBPB, both requiring hardware support from your CPU microcode in addition to kernel support, or a kernel compiled with retpoline and IBPB, with retpoline requiring a retpoline-aware compiler (re-run this script with -v to know if your version of gcc is retpoline-aware) and IBPB requiring hardware support from your CPU microcode. The retpoline + IBPB approach is generally preferred as the performance impact is lower. More information about how to enable the missing bits for those two possible mitigations on your system follow. You only need to take one of the two approaches." + else + # in that case, we might want to trust sysfs if it's there + if [ -n "$msg" ]; then + [ "$msg" = Vulnerable ] && msg="no known mitigation exists for your CPU vendor ($cpu_vendor)" + pvulnstatus $cve $status "$msg" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "no known mitigation exists for your CPU vendor ($cpu_vendor)" + fi + fi + fi + + # if we are in live mode, we can check for a lot more stuff and explain further + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && [ "$vulnstatus" != "OK" ]; then + _explain_hypervisor="An updated CPU microcode will have IBRS/IBPB capabilities indicated in the Hardware Check section above. If you're running under a hypervisor (KVM, Xen, VirtualBox, VMware, ...), the hypervisor needs to be up to date to be able to export the new host CPU flags to the guest. You can run this script on the host to check if the host CPU is IBRS/IBPB. If it is, and it doesn't show up in the guest, upgrade the hypervisor. You may need to reconfigure your VM to use a CPU model that has IBRS capability; in Libvirt, such CPUs are listed with an IBRS suffix." + # IBPB (amd & intel) + if { [ -z "$ibpb_enabled" ] || [ "$ibpb_enabled" = 0 ]; } && { is_intel || is_amd || is_hygon; }; then + if [ -z "$cpuid_ibpb" ]; then + explain "The microcode of your CPU needs to be upgraded to be able to use IBPB. This is usually done at boot time by your kernel (the upgrade is not persistent across reboots which is why it's done at each boot). If you're using a distro, make sure you are up to date, as microcode updates are usually shipped alongside with the distro kernel. Availability of a microcode update for you CPU model depends on your CPU vendor. You can usually find out online if a microcode update is available for your CPU by searching for your CPUID (indicated in the Hardware Check section). $_explain_hypervisor" + fi + if [ -z "$ibpb_supported" ]; then + explain "Your kernel doesn't have IBPB support, so you need to either upgrade your kernel (if you're using a distro) or recompiling a more recent kernel." + fi + if [ -n "$cpuid_ibpb" ] && [ -n "$ibpb_supported" ]; then + if [ -e "$specex_knob_dir/ibpb_enabled" ]; then + # newer (April 2018) Red Hat kernels have ibpb_enabled as ro, and automatically enables it with retpoline + if [ ! -w "$specex_knob_dir/ibpb_enabled" ] && [ -e "$specex_knob_dir/retp_enabled" ]; then + explain "Both your CPU and your kernel have IBPB support, but it is currently disabled. You kernel should enable IBPB automatically if you enable retpoline. You may enable it with \`echo 1 > $specex_knob_dir/retp_enabled\`." + else + explain "Both your CPU and your kernel have IBPB support, but it is currently disabled. You may enable it with \`echo 1 > $specex_knob_dir/ibpb_enabled\`." + fi + else + explain "Both your CPU and your kernel have IBPB support, but it is currently disabled. You may enable it. Check in your distro's documentation on how to do this." + fi + fi + elif [ "$ibpb_enabled" = 2 ] && is_cpu_smt_enabled; then + explain "You have ibpb_enabled set to 2, but it only offers sufficient protection when simultaneous multi-threading (aka SMT or HyperThreading) is disabled. You should reboot your system with the kernel parameter \`nosmt\`." + fi + # /IBPB + + # IBRS (amd & intel) + if { [ -z "$ibrs_enabled" ] || [ "$ibrs_enabled" = 0 ]; } && { is_intel || is_amd || is_hygon; }; then + if [ -z "$cpuid_ibrs" ]; then + explain "The microcode of your CPU needs to be upgraded to be able to use IBRS. This is usually done at boot time by your kernel (the upgrade is not persistent across reboots which is why it's done at each boot). If you're using a distro, make sure you are up to date, as microcode updates are usually shipped alongside with the distro kernel. Availability of a microcode update for you CPU model depends on your CPU vendor. You can usually find out online if a microcode update is available for your CPU by searching for your CPUID (indicated in the Hardware Check section). $_explain_hypervisor" + fi + if [ -z "$ibrs_supported" ]; then + explain "Your kernel doesn't have IBRS support, so you need to either upgrade your kernel (if you're using a distro) or recompiling a more recent kernel." + fi + if [ -n "$cpuid_ibrs" ] && [ -n "$ibrs_supported" ]; then + if [ -e "$specex_knob_dir/ibrs_enabled" ]; then + explain "Both your CPU and your kernel have IBRS support, but it is currently disabled. You may enable it with \`echo 1 > $specex_knob_dir/ibrs_enabled\`." + else + explain "Both your CPU and your kernel have IBRS support, but it is currently disabled. You may enable it. Check in your distro's documentation on how to do this." + fi + fi + fi + # /IBRS + unset _explain_hypervisor + + # RETPOLINE (amd & intel &hygon ) + if is_amd || is_intel || is_hygon; then + if [ "$retpoline" = 0 ]; then + explain "Your kernel is not compiled with retpoline support, so you need to either upgrade your kernel (if you're using a distro) or recompile your kernel with the CONFIG_RETPOLINE option enabled. You also need to compile your kernel with a retpoline-aware compiler (re-run this script with -v to know if your version of gcc is retpoline-aware)." + elif [ "$retpoline" = 1 ] && [ "$retpoline_compiler" = 0 ]; then + explain "Your kernel is compiled with retpoline, but without a retpoline-aware compiler (re-run this script with -v to know if your version of gcc is retpoline-aware)." + elif [ "$retpoline" = 1 ] && [ "$retpoline_compiler" = 1 ] && [ "$retp_enabled" = 0 ]; then + explain "Your kernel has retpoline support and has been compiled with a retpoline-aware compiler, but retpoline is disabled. You should enable it with \`echo 1 > $specex_knob_dir/retp_enabled\`." + fi + fi + # /RETPOLINE + fi + fi + # sysfs msgs: + #1 "Vulnerable" + #2 "Vulnerable: Minimal generic ASM retpoline" + #2 "Vulnerable: Minimal AMD ASM retpoline" + # "Mitigation: Full generic retpoline" + # "Mitigation: Full AMD retpoline" + # $MITIGATION + ", IBPB" + # $MITIGATION + ", IBRS_FW" + #5 $MITIGATION + " - vulnerable module loaded" + # Red Hat only: + #2 "Vulnerable: Minimal ASM retpoline", + #3 "Vulnerable: Retpoline without IBPB", + #4 "Vulnerable: Retpoline on Skylake+", + #5 "Vulnerable: Retpoline with unsafe module(s)", + # "Mitigation: Full retpoline", + # "Mitigation: Full retpoline and IBRS (user space)", + # "Mitigation: IBRS (kernel)", + # "Mitigation: IBRS (kernel and user space)", + # "Mitigation: IBP disabled", +} + +check_CVE_2017_5715_bsd() +{ + _info "* Mitigation 1" + _info_nol " * Kernel supports IBRS: " + ibrs_disabled=$(sysctl -n hw.ibrs_disable 2>/dev/null) + if [ -z "$ibrs_disabled" ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus green YES + fi + + _info_nol " * IBRS enabled and active: " + ibrs_active=$(sysctl -n hw.ibrs_active 2>/dev/null) + if [ "$ibrs_active" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info "* Mitigation 2" + _info_nol " * Kernel compiled with RETPOLINE: " + retpoline=0 + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't check ($kernel_err)" + else + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}readelf" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing '${opt_arch_prefix}readelf' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + else + nb_thunks=$("${opt_arch_prefix}readelf" -s "$kernel" | grep -c -e __llvm_retpoline_ -e __llvm_external_retpoline_ -e __x86_indirect_thunk_) + if [ "$nb_thunks" -gt 0 ]; then + retpoline=1 + pstatus green YES "found $nb_thunks thunk(s)" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ "$retpoline" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Retpoline mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ "$ibrs_active" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "IBRS mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ "$ibrs_disabled" = 0 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "IBRS is supported by your kernel but your CPU microcode lacks support" + explain "The microcode of your CPU needs to be upgraded to be able to use IBRS. Availability of a microcode update for you CPU model depends on your CPU vendor. You can usually find out online if a microcode update is available for your CPU by searching for your CPUID (indicated in the Hardware Check section). To do a microcode update, you can search the ports for the \`cpupdate\` tool. Microcode updates done this way are not reboot-proof, so be sure to do it every time the system boots up." + elif [ "$ibrs_disabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "IBRS is supported but administratively disabled on your system" + explain "To enable IBRS, use \`sysctl hw.ibrs_disable=0\`" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "IBRS is needed to mitigate the vulnerability but your kernel is missing support" + explain "You need to either upgrade your kernel or recompile yourself a more recent version having IBRS support" + fi +} + +################## +# MELTDOWN SECTION + +# no security impact but give a hint to the user in verbose mode +# about PCID/INVPCID cpuid features that must be present to avoid +# too big a performance impact with PTI +# refs: +# https://marc.info/?t=151532047900001&r=1&w=2 +# https://groups.google.com/forum/m/#!topic/mechanical-sympathy/L9mHTbeQLNU +pti_performance_check() +{ + _info_nol " * Reduced performance impact of PTI: " + if [ -e "$procfs/cpuinfo" ] && grep ^flags "$procfs/cpuinfo" | grep -qw pcid; then + cpu_pcid=1 + else + read_cpuid 0x1 0x0 $ECX 17 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpu_pcid=1 + fi + fi + + if [ -e "$procfs/cpuinfo" ] && grep ^flags "$procfs/cpuinfo" | grep -qw invpcid; then + cpu_invpcid=1 + else + read_cpuid 0x7 0x0 $EBX 10 1 1; ret=$? + if [ $ret = $READ_CPUID_RET_OK ]; then + cpu_invpcid=1 + fi + fi + + if [ "$cpu_invpcid" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES 'CPU supports INVPCID, performance impact of PTI will be greatly reduced' + elif [ "$cpu_pcid" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES 'CPU supports PCID, performance impact of PTI will be reduced' + else + pstatus blue NO 'PCID/INVPCID not supported, performance impact of PTI will be significant' + fi +} + +# rogue data cache load aka 'Meltdown' aka 'Variant 3' +check_CVE_2017_5754() +{ + cve='CVE-2017-5754' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2017_5754_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2017_5754_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2017_5754_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/meltdown"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* Kernel supports Page Table Isolation (PTI): " + kpti_support='' + kpti_can_tell=0 + if [ -n "$opt_config" ]; then + kpti_can_tell=1 + kpti_support=$(grep -w -e CONFIG_PAGE_TABLE_ISOLATION=y -e CONFIG_KAISER=y -e CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0=y "$opt_config") + if [ -n "$kpti_support" ]; then + _debug "kpti_support: found option '$kpti_support' in $opt_config" + fi + fi + if [ -z "$kpti_support" ] && [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + # it's not an elif: some backports don't have the PTI config but still include the patch + # so we try to find an exported symbol that is part of the PTI patch in System.map + # parse_kpti: arm + kpti_can_tell=1 + kpti_support=$(grep -w -e kpti_force_enabled -e parse_kpti "$opt_map") + if [ -n "$kpti_support" ]; then + _debug "kpti_support: found '$kpti_support' in $opt_map" + fi + fi + if [ -z "$kpti_support" ] && [ -n "$kernel" ]; then + # same as above but in case we don't have System.map and only kernel, look for the + # nopti option that is part of the patch (kernel command line option) + # 'kpti=': arm + kpti_can_tell=1 + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing '${opt_arch_prefix}strings' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + else + kpti_support=$("${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -w -e nopti -e kpti=) + if [ -n "$kpti_support" ]; then + _debug "kpti_support: found '$kpti_support' in $kernel" + fi + fi + fi + + if [ -n "$kpti_support" ]; then + if [ "$opt_verbose" -ge 2 ]; then + pstatus green YES "found '$kpti_support'" + else + pstatus green YES + fi + elif [ "$kpti_can_tell" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "couldn't read your kernel configuration nor System.map file" + fi + + mount_debugfs + _info_nol " * PTI enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + dmesg_grep="Kernel/User page tables isolation: enabled" + dmesg_grep="$dmesg_grep|Kernel page table isolation enabled" + dmesg_grep="$dmesg_grep|x86/pti: Unmapping kernel while in userspace" + # aarch64 + dmesg_grep="$dmesg_grep|CPU features: detected( feature)?: Kernel page table isolation \(KPTI\)" + if grep ^flags "$procfs/cpuinfo" | grep -qw pti; then + # vanilla PTI patch sets the 'pti' flag in cpuinfo + _debug "kpti_enabled: found 'pti' flag in $procfs/cpuinfo" + kpti_enabled=1 + elif grep ^flags "$procfs/cpuinfo" | grep -qw kaiser; then + # kernel line 4.9 sets the 'kaiser' flag in cpuinfo + _debug "kpti_enabled: found 'kaiser' flag in $procfs/cpuinfo" + kpti_enabled=1 + elif [ -e /sys/kernel/debug/x86/pti_enabled ]; then + # Red Hat Backport creates a dedicated file, see https://access.redhat.com/articles/3311301 + kpti_enabled=$(cat /sys/kernel/debug/x86/pti_enabled 2>/dev/null) + _debug "kpti_enabled: file /sys/kernel/debug/x86/pti_enabled exists and says: $kpti_enabled" + elif is_xen_dom0; then + pti_xen_pv_domU=$(xl dmesg | grep 'XPTI' | grep 'DomU enabled' | head -1) + + [ -n "$pti_xen_pv_domU" ] && kpti_enabled=1 + fi + if [ -z "$kpti_enabled" ]; then + dmesg_grep "$dmesg_grep"; ret=$? + if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then + _debug "kpti_enabled: found hint in dmesg: $dmesg_grepped" + kpti_enabled=1 + elif [ $ret -eq 2 ]; then + _debug "kpti_enabled: dmesg truncated" + kpti_enabled=-1 + fi + fi + if [ -z "$kpti_enabled" ]; then + _debug "kpti_enabled: couldn't find any hint that PTI is enabled" + kpti_enabled=0 + fi + if [ "$kpti_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + elif [ "$kpti_enabled" = -1 ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "dmesg truncated, please reboot and relaunch this script" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + + pti_performance_check + + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + + # Test if the current host is a Xen PV Dom0 / DomU + xen_pv_domo=0 + xen_pv_domu=0 + is_xen_dom0 && xen_pv_domo=1 + is_xen_domU && xen_pv_domu=1 + + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # checking whether we're running under Xen PV 64 bits. If yes, we are affected by variant3 + # (unless we are a Dom0) + _info_nol "* Running as a Xen PV DomU: " + if [ "$xen_pv_domu" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow YES + else + pstatus blue NO + fi + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -z "$msg" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$kpti_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "PTI mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ "$xen_pv_domo" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Xen Dom0s are safe and do not require PTI" + elif [ "$xen_pv_domu" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Xen PV DomUs are vulnerable and need to be run in HVM, PVHVM, PVH mode, or the Xen hypervisor must have the Xen's own PTI patch" + explain "Go to https://blog.xenproject.org/2018/01/22/xen-project-spectre-meltdown-faq-jan-22-update/ for more information" + elif [ "$kpti_enabled" = -1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve UNK "couldn't find any clue of PTI activation due to a truncated dmesg, please reboot and relaunch this script" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "PTI is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + if [ -n "$kpti_support" ]; then + if [ -e "/sys/kernel/debug/x86/pti_enabled" ]; then + explain "Your kernel supports PTI but it's disabled, you can enable it with \`echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/x86/pti_enabled\`" + elif echo "$kernel_cmdline" | grep -q -w -e nopti -e pti=off; then + explain "Your kernel supports PTI but it has been disabled on command-line, remove the nopti or pti=off option from your bootloader configuration" + else + explain "Your kernel supports PTI but it has been disabled, check \`dmesg\` right after boot to find clues why the system disabled it" + fi + else + explain "If you're using a distro kernel, upgrade your distro to get the latest kernel available. Otherwise, recompile the kernel with the CONFIG_PAGE_TABLE_ISOLATION option (named CONFIG_KAISER for some kernels), or the CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 option (for ARM64)" + fi + fi + else + if [ -n "$kpti_support" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "offline mode: PTI will mitigate the vulnerability if enabled at runtime" + elif [ "$kpti_can_tell" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "PTI is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "If you're using a distro kernel, upgrade your distro to get the latest kernel available. Otherwise, recompile the kernel with the CONFIG_PAGE_TABLE_ISOLATION option (named CONFIG_KAISER for some kernels), or the CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 option (for ARM64)" + else + pvulnstatus $cve UNK "offline mode: not enough information" + explain "Re-run this script with root privileges, and give it the kernel image (--kernel), the kernel configuration (--config) and the System.map file (--map) corresponding to the kernel you would like to inspect." + fi + fi + else + if [ "$xen_pv_domo" = 1 ]; then + msg="Xen Dom0s are safe and do not require PTI" + status="OK" + elif [ "$xen_pv_domu" = 1 ]; then + msg="Xen PV DomUs are vulnerable and need to be run in HVM, PVHVM, PVH mode, or the Xen hypervisor must have the Xen's own PTI patch" + status="VULN" + _explain="Go to https://blog.xenproject.org/2018/01/22/xen-project-spectre-meltdown-faq-jan-22-update/ for more information" + elif [ "$msg" = "Vulnerable" ]; then + msg="PTI is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + _explain="If you're using a distro kernel, upgrade your distro to get the latest kernel available. Otherwise, recompile the kernel with the CONFIG_PAGE_TABLE_ISOLATION option (named CONFIG_KAISER for some kernels), or the CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 option (for ARM64)" + fi + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + [ -z "${_explain:-}" ] && [ "$msg" = "Vulnerable" ] && _explain="If you're using a distro kernel, upgrade your distro to get the latest kernel available. Otherwise, recompile the kernel with the CONFIG_PAGE_TABLE_ISOLATION option (named CONFIG_KAISER for some kernels), or the CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0 option (for ARM64)" + [ -n "${_explain:-}" ] && explain "$_explain" + unset _explain + fi + + # Warn the user about XSA-254 recommended mitigations + if [ "$xen_pv_domo" = 1 ]; then + _warn + _warn "This host is a Xen Dom0. Please make sure that you are running your DomUs" + _warn "in HVM, PVHVM or PVH mode to prevent any guest-to-host / host-to-guest attacks." + _warn + _warn "See https://blog.xenproject.org/2018/01/22/xen-project-spectre-meltdown-faq-jan-22-update/ and XSA-254 for details." + fi +} + +check_CVE_2017_5754_bsd() +{ + _info_nol "* Kernel supports Page Table Isolation (PTI): " + kpti_enabled=$(sysctl -n vm.pmap.pti 2>/dev/null) + if [ -z "$kpti_enabled" ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus green YES + fi + + _info_nol " * PTI enabled and active: " + if [ "$kpti_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + pti_performance_check + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ "$kpti_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "PTI mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ -n "$kpti_enabled" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "PTI is supported but disabled on your system" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "PTI is needed to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi +} + +#################### +# VARIANT 3A SECTION + +# rogue system register read aka 'Variant 3a' +check_CVE_2018_3640() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-3640' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + + _info_nol "* CPU microcode mitigates the vulnerability: " + if [ -n "$cpuid_ssbd" ]; then + # microcodes that ship with SSBD are known to also fix variant3a + # there is no specific cpuid bit as far as we know + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -n "$cpuid_ssbd" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU microcode mitigates the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "an up-to-date CPU microcode is needed to mitigate this vulnerability" + explain "The microcode of your CPU needs to be upgraded to mitigate this vulnerability. This is usually done at boot time by your kernel (the upgrade is not persistent across reboots which is why it's done at each boot). If you're using a distro, make sure you are up to date, as microcode updates are usually shipped alongside with the distro kernel. Availability of a microcode update for you CPU model depends on your CPU vendor. You can usually find out online if a microcode update is available for your CPU by searching for your CPUID (indicated in the Hardware Check section). The microcode update is enough, there is no additional OS, kernel or software change needed." + fi +} + +################### +# VARIANT 4 SECTION + +# speculative store bypass aka 'Variant 4' +check_CVE_2018_3639() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-3639' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2018_3639_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2018_3639_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_3639_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/spec_store_bypass"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* Kernel supports disabling speculative store bypass (SSB): " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if grep -Eq 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null; then + kernel_ssb="found in $procfs/self/status" + _debug "found Speculation.Store.Bypass: in $procfs/self/status" + fi + fi + # arm64 kernels can have cpu_show_spec_store_bypass with ARM64_SSBD, so exclude them + if [ -z "$kernel_ssb" ] && [ -n "$kernel" ] && ! grep -q 'arm64_sys_' "$kernel"; then + kernel_ssb=$("${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep spec_store_bypass | head -n1); + [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ] && kernel_ssb="found $kernel_ssb in kernel" + fi + # arm64 kernels can have cpu_show_spec_store_bypass with ARM64_SSBD, so exclude them + if [ -z "$kernel_ssb" ] && [ -n "$opt_map" ] && ! grep -q 'arm64_sys_' "$opt_map"; then + kernel_ssb=$(grep spec_store_bypass "$opt_map" | awk '{print $3}' | head -n1) + [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ] && kernel_ssb="found $kernel_ssb in System.map" + fi + # arm64 only: + if [ -z "$kernel_ssb" ] && [ -n "$opt_map" ]; then + kernel_ssb=$(grep -w cpu_enable_ssbs "$opt_map" | awk '{print $3}' | head -n1) + [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ] && kernel_ssb="found $kernel_ssb in System.map" + fi + if [ -z "$kernel_ssb" ] && [ -n "$opt_config" ]; then + kernel_ssb=$(grep -w 'CONFIG_ARM64_SSBD=y' "$opt_config") + [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ] && kernel_ssb="CONFIG_ARM64_SSBD enabled in kconfig" + fi + if [ -z "$kernel_ssb" ] && [ -n "$kernel" ]; then + # this string only appears in kernel if CONFIG_ARM64_SSBD is set + kernel_ssb=$(grep -w "Speculative Store Bypassing Safe (SSBS)" "$kernel") + [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ] && kernel_ssb="found 'Speculative Store Bypassing Safe (SSBS)' in kernel" + fi + # /arm64 only + + if [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$kernel_ssb" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + kernel_ssbd_enabled=-1 + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.0/source/fs/proc/array.c#L340 + _info_nol "* SSB mitigation is enabled and active: " + if grep -Eq 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:[[:space:]]+thread' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null; then + kernel_ssbd_enabled=1 + pstatus green YES "per-thread through prctl" + elif grep -Eq 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:[[:space:]]+globally mitigated' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null; then + kernel_ssbd_enabled=2 + pstatus green YES "global" + elif grep -Eq 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:[[:space:]]+vulnerable' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null; then + kernel_ssbd_enabled=0 + pstatus yellow NO + elif grep -Eq 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:[[:space:]]+not vulnerable' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null; then + kernel_ssbd_enabled=-2 + pstatus blue NO "not vulnerable" + elif grep -Eq 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:[[:space:]]+unknown' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null; then + kernel_ssbd_enabled=0 + pstatus blue NO + else + pstatus blue UNKNOWN "unknown value: $(grep -E 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:' "$procfs/self/status" 2>/dev/null | cut -d: -f2-)" + fi + + if [ "$kernel_ssbd_enabled" = 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* SSB mitigation currently active for selected processes: " + # silence grep's stderr here to avoid ENOENT errors from processes that have exited since the shell's expansion of the * + mitigated_processes=$(find /proc -mindepth 2 -maxdepth 2 -type f -name status -print0 2>/dev/null \ + | xargs -r0 grep -El 'Speculation.?Store.?Bypass:[[:space:]]+thread (force )?mitigated' 2>/dev/null \ + | sed s/status/exe/ | xargs -r -n1 readlink -f 2>/dev/null | xargs -r -n1 basename | sort -u | tr "\n" " " | sed 's/ $//') + if [ -n "$mitigated_processes" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$mitigated_processes" + else + pstatus yellow NO "no process found using SSB mitigation through prctl" + fi + fi + fi + + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -z "$msg" ] || [ "$msg" = "Vulnerable" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ -n "$cpuid_ssbd" ]; then + if [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ]; then + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$kernel_ssbd_enabled" -gt 0 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU and kernel both support SSBD and mitigation is enabled" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "your CPU and kernel both support SSBD but the mitigation is not active" + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your system provides the necessary tools for software mitigation" + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "your kernel needs to be updated" + explain "You have a recent-enough CPU microcode but your kernel is too old to use the new features exported by your CPU's microcode. If you're using a distro kernel, upgrade your distro to get the latest kernel available. Otherwise, recompile the kernel from recent-enough sources." + fi + else + if [ -n "$kernel_ssb" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your CPU doesn't support SSBD" + explain "Your kernel is recent enough to use the CPU microcode features for mitigation, but your CPU microcode doesn't actually provide the necessary features for the kernel to use. The microcode of your CPU hence needs to be upgraded. This is usually done at boot time by your kernel (the upgrade is not persistent across reboots which is why it's done at each boot). If you're using a distro, make sure you are up to date, as microcode updates are usually shipped alongside with the distro kernel. Availability of a microcode update for you CPU model depends on your CPU vendor. You can usually find out online if a microcode update is available for your CPU by searching for your CPUID (indicated in the Hardware Check section)." + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Neither your CPU nor your kernel support SSBD" + explain "Both your CPU microcode and your kernel are lacking support for mitigation. If you're using a distro kernel, upgrade your distro to get the latest kernel available. Otherwise, recompile the kernel from recent-enough sources. The microcode of your CPU also needs to be upgraded. This is usually done at boot time by your kernel (the upgrade is not persistent across reboots which is why it's done at each boot). If you're using a distro, make sure you are up to date, as microcode updates are usually shipped alongside with the distro kernel. Availability of a microcode update for you CPU model depends on your CPU vendor. You can usually find out online if a microcode update is available for your CPU by searching for your CPUID (indicated in the Hardware Check section)." + fi + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_3639_bsd() +{ + _info_nol "* Kernel supports speculation store bypass: " + if sysctl hw.spec_store_bypass_disable >/dev/null 2>&1; then + kernel_ssb=1 + pstatus green YES + else + kernel_ssb=0 + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol "* Speculation store bypass is administratively enabled: " + ssb_enabled=$(sysctl -n hw.spec_store_bypass_disable 2>/dev/null) + _debug "hw.spec_store_bypass_disable=$ssb_enabled" + case "$ssb_enabled" in + 0) pstatus yellow NO "disabled";; + 1) pstatus green YES "enabled";; + 2) pstatus green YES "auto mode";; + *) pstatus yellow NO "unavailable";; + esac + + _info_nol "* Speculation store bypass is currently active: " + ssb_active=$(sysctl -n hw.spec_store_bypass_disable_active 2>/dev/null) + _debug "hw.spec_store_bypass_disable_active=$ssb_active" + case "$ssb_active" in + 1) pstatus green YES;; + *) pstatus yellow NO;; + esac + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$ssb_active" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "SSBD mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ -n "$cpuid_ssbd" ]; then + if [ "$kernel_ssb" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "you need to enable SSBD through sysctl to mitigate the vulnerability" + explain "To enable SSBD right now, you can run \`sysctl hw.spec_store_bypass_disable=2'. To make this change persistent across reboots, you can add 'sysctl hw.spec_store_bypass_disable=2' to /etc/sysctl.conf." + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "your kernel needs to be updated" + fi + else + if [ "$kernel_ssb" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your CPU doesn't support SSBD" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Neither your CPU nor your kernel support SSBD" + fi + fi + fi +} + +########################### +# L1TF / FORESHADOW SECTION + +# L1 terminal fault (SGX) aka 'Foreshadow' +check_CVE_2018_3615() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-3615' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + + _info_nol "* CPU microcode mitigates the vulnerability: " + if { [ "$cpu_flush_cmd" = 1 ] || { [ "$msr_locked_down" = 1 ] && [ "$cpuid_l1df" = 1 ]; }; } && [ "$cpuid_sgx" = 1 ]; then + # no easy way to detect a fixed SGX but we know that + # microcodes that have the FLUSH_CMD MSR also have the + # fixed SGX (for CPUs that support it), because Intel + # delivered fixed microcodes for both issues at the same time + # + # if the system we're running on is locked down (no way to write MSRs), + # make the assumption that if the L1D flush CPUID bit is set, probably + # that FLUSH_CMD MSR is here too + pstatus green YES + elif [ "$cpuid_sgx" = 1 ]; then + pstatus red NO + else + pstatus blue N/A + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ "$cpu_flush_cmd" = 1 ] || { [ "$msr_locked_down" = 1 ] && [ "$cpuid_l1df" = 1 ]; } ; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU microcode mitigates the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "your CPU supports SGX and the microcode is not up to date" + fi +} + +# L1 terminal fault (OS) aka 'Foreshadow-NG (OS)' +check_CVE_2018_3620() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-3620' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2018_3620_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2018_3620_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_3620_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/l1tf"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* Kernel supports PTE inversion: " + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "missing 'strings' tool, please install it" + pteinv_supported=-1 + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$kernel_err" + pteinv_supported=-1 + else + if "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -Fq 'PTE Inversion'; then + pstatus green YES "found in kernel image" + _debug "pteinv: found pte inversion evidence in kernel image" + pteinv_supported=1 + else + pstatus yellow NO + pteinv_supported=0 + fi + fi + + _info_nol "* PTE inversion enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -q 'Mitigation: PTE Inversion'; then + pstatus green YES + pteinv_active=1 + else + pstatus yellow NO + pteinv_active=0 + fi + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "sysfs interface not available" + pteinv_active=-1 + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -z "$msg" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ "$pteinv_supported" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$pteinv_active" = 1 ] || [ "$opt_live" != 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "PTE inversion mitigates the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel supports PTE inversion but it doesn't seem to be enabled" + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel doesn't support PTE inversion, update it" + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_3620_bsd() +{ + _info_nol "* Kernel reserved the memory page at physical address 0x0: " + if ! kldstat -q -m vmm; then + kldload vmm 2>/dev/null && kldload_vmm=1 + _debug "attempted to load module vmm, kldload_vmm=$kldload_vmm" + else + _debug "vmm module already loaded" + fi + if sysctl hw.vmm.vmx.l1d_flush >/dev/null 2>&1; then + # https://security.FreeBSD.org/patches/SA-18:09/l1tf-11.2.patch + # this is very difficult to detect that the kernel reserved the 0 page, but this fix + # is part of the exact same patch than the other L1TF CVE, so we detect it + # and deem it as OK if the other patch is there + pstatus green YES + bsd_zero_reserved=1 + else + pstatus yellow NO + bsd_zero_reserved=0 + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$bsd_zero_reserved" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "kernel mitigates the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "your kernel needs to be updated" + fi + fi +} + +# L1TF VMM +check_CVE_2018_3646() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-3646' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2018_3646_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2018_3646_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_3646_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/l1tf" '.*' quiet; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + l1d_mode=-1 + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + check_has_vmm + + _info "* Mitigation 1 (KVM)" + _info_nol " * EPT is disabled: " + ept_disabled=-1 + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if ! [ -r /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/ept ]; then + pstatus blue N/A "the kvm_intel module is not loaded" + elif [ "$(cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/ept)" = N ]; then + pstatus green YES + ept_disabled=1 + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + + _info "* Mitigation 2" + _info_nol " * L1D flush is supported by kernel: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && grep -qw flush_l1d "$procfs/cpuinfo"; then + l1d_kernel="found flush_l1d in $procfs/cpuinfo" + fi + if [ -z "$l1d_kernel" ]; then + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + l1d_kernel_err="missing '${opt_arch_prefix}strings' tool, please install it, usually it's in the binutils package" + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + l1d_kernel_err="$kernel_err" + elif "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -qw flush_l1d; then + l1d_kernel='found flush_l1d in kernel image' + fi + fi + + if [ -n "$l1d_kernel" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$l1d_kernel" + elif [ -n "$l1d_kernel_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$l1d_kernel_err" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol " * L1D flush enabled: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + # vanilla: VMX: $l1dstatus, SMT $smtstatus + # Red Hat: VMX: SMT $smtstatus, L1D $l1dstatus + # $l1dstatus is one of (auto|vulnerable|conditional cache flushes|cache flushes|EPT disabled|flush not necessary) + # $smtstatus is one of (vulnerable|disabled) + # can also just be "Not affected" + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -Eq -e 'Not affected' -e '(VMX:|L1D) (EPT disabled|vulnerable|flush not necessary)'; then + l1d_mode=0 + pstatus yellow NO + elif echo "$fullmsg" | grep -Eq '(VMX:|L1D) conditional cache flushes'; then + l1d_mode=1 + pstatus green YES "conditional flushes" + elif echo "$fullmsg" | grep -Eq '(VMX:|L1D) cache flushes'; then + l1d_mode=2 + pstatus green YES "unconditional flushes" + else + if is_xen_dom0; then + l1d_xen_hardware=$(xl dmesg | grep 'Hardware features:' | grep 'L1D_FLUSH' | head -1) + l1d_xen_hypervisor=$(xl dmesg | grep 'Xen settings:' | grep 'L1D_FLUSH' | head -1) + l1d_xen_pv_domU=$(xl dmesg | grep 'PV L1TF shadowing:' | grep 'DomU enabled' | head -1) + + if [ -n "$l1d_xen_hardware" ] && [ -n "$l1d_xen_hypervisor" ] && [ -n "$l1d_xen_pv_domU" ]; then + l1d_mode=5 + pstatus green YES "for XEN guests" + elif [ -n "$l1d_xen_hardware" ] && [ -n "$l1d_xen_hypervisor" ]; then + l1d_mode=4 + pstatus yellow YES "for XEN guests (HVM only)" + elif [ -n "$l1d_xen_pv_domU" ]; then + l1d_mode=3 + pstatus yellow YES "for XEN guests (PV only)" + else + l1d_mode=0 + pstatus yellow NO "for XEN guests" + fi + else + l1d_mode=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "unrecognized mode" + fi + fi + else + l1d_mode=-1 + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "can't find or read /sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/l1tf" + fi + else + l1d_mode=-1 + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + + _info_nol " * Hardware-backed L1D flush supported: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if grep -qw flush_l1d "$procfs/cpuinfo" || [ -n "$l1d_xen_hardware" ]; then + pstatus green YES "performance impact of the mitigation will be greatly reduced" + else + pstatus blue NO "flush will be done in software, this is slower" + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + + _info_nol " * Hyper-Threading (SMT) is enabled: " + is_cpu_smt_enabled; smt_enabled=$? + if [ "$smt_enabled" = 0 ]; then + pstatus yellow YES + elif [ "$smt_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pstatus green NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + fi + + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + l1d_mode=-1 + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ "$fullmsg" = "Not affected" ]; then + # just in case a very recent kernel knows better than we do + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your kernel reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ "$has_vmm" = 0 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "this system is not running a hypervisor" + else + if [ "$ept_disabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "EPT is disabled which mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ "$opt_paranoid" = 0 ]; then + if [ "$l1d_mode" -ge 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "L1D flushing is enabled and mitigates the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "disable EPT or enable L1D flushing to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + else + if [ "$l1d_mode" -ge 2 ]; then + if [ "$smt_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "L1D unconditional flushing and Hyper-Threading disabled are mitigating the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Hyper-Threading must be disabled to fully mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + else + if [ "$smt_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "L1D unconditional flushing should be enabled to fully mitigate the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "enable L1D unconditional flushing and disable Hyper-Threading to fully mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + fi + fi + + if [ $l1d_mode -gt 3 ]; then + _warn + _warn "This host is a Xen Dom0. Please make sure that you are running your DomUs" + _warn "with a kernel which contains CVE-2018-3646 mitigations." + _warn + _warn "See https://www.suse.com/support/kb/doc/?id=7023078 and XSA-273 for details." + fi + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_3646_bsd() +{ + _info_nol "* Kernel supports L1D flushing: " + if sysctl hw.vmm.vmx.l1d_flush >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus green YES + kernel_l1d_supported=1 + else + pstatus yellow NO + kernel_l1d_supported=0 + fi + + _info_nol "* L1D flushing is enabled: " + kernel_l1d_enabled=$(sysctl -n hw.vmm.vmx.l1d_flush 2>/dev/null) + case "$kernel_l1d_enabled" in + 0) pstatus yellow NO;; + 1) pstatus green YES;; + "") pstatus yellow NO;; + *) pstatus yellow UNKNOWN;; + esac + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$kernel_l1d_enabled" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "L1D flushing mitigates the vulnerability" + elif [ "$kernel_l1d_supported" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "L1D flushing is supported by your kernel but is disabled" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "your kernel needs to be updated" + fi + fi +} + +################### +# MSBDS SECTION + +# Microarchitectural Store Buffer Data Sampling +check_CVE_2018_12126() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-12126' + check_mds $cve +} + +################### +# MFBDS SECTION + +# Microarchitectural Fill Buffer Data Sampling +check_CVE_2018_12130() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-12130' + check_mds $cve +} + +################### +# MLPDS SECTION + +# Microarchitectural Load Port Data Sampling +check_CVE_2018_12127() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-12127' + check_mds $cve +} + +################### +# MDSUM SECTION + +# Microarchitectural Data Sampling Uncacheable Memory +check_CVE_2019_11091() +{ + cve='CVE-2019-11091' + check_mds $cve +} + +# Microarchitectural Data Sampling +check_mds() +{ + cve=$1 + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_mds_linux "$cve" + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_mds_bsd "$cve" + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_mds_bsd() +{ + _info_nol "* Kernel supports using MD_CLEAR mitigation: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if sysctl hw.mds_disable >/dev/null 2>&1; then + pstatus green YES + kernel_md_clear=1 + else + pstatus yellow NO + kernel_md_clear=0 + fi + else + if grep -Fq hw.mds_disable $opt_kernel; then + pstatus green YES + kernel_md_clear=1 + else + kernel_md_clear=0 + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + + _info_nol "* CPU Hyper-Threading (SMT) is disabled: " + if sysctl machdep.hyperthreading_allowed >/dev/null 2>&1; then + kernel_smt_allowed=$(sysctl -n machdep.hyperthreading_allowed 2>/dev/null) + if [ "$kernel_smt_allowed" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus green YES + fi + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "sysctl machdep.hyperthreading_allowed doesn't exist" + fi + + _info_nol "* Kernel mitigation is enabled: " + if [ "$kernel_md_clear" = 1 ]; then + kernel_mds_enabled=$(sysctl -n hw.mds_disable 2>/dev/null) + else + kernel_mds_enabled=0 + fi + case "$kernel_mds_enabled" in + 0) pstatus yellow NO;; + 1) pstatus green YES "with microcode support";; + 2) pstatus green YES "software-only support (SLOW)";; + 3) pstatus green YES;; + *) pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "unknown value $kernel_mds_enabled" + esac + + _info_nol "* Kernel mitigation is active: " + if [ "$kernel_md_clear" = 1 ]; then + kernel_mds_state=$(sysctl -n hw.mds_disable_state 2>/dev/null) + else + kernel_mds_state=inactive + fi + # https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd/blob/master/sys/x86/x86/cpu_machdep.c#L953 + case "$kernel_mds_state" in + inactive) pstatus yellow NO;; + VERW) pstatus green YES "with microcode support";; + software*) pstatus green YES "software-only support (SLOW)";; + *) pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + esac + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$cpuid_md_clear" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$kernel_md_clear" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # mitigation must also be enabled + if [ "$kernel_mds_enabled" -ge 1 ]; then + if [ "$opt_paranoid" != 1 ] || [ "$kernel_smt_allowed" = 0 ]; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation, and mitigation is enabled" + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation, but you must disable SMT (Hyper-Threading) for a complete mitigation" + fi + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation, but the mitigation is not active" + explain "To enable mitigation, run \`sysctl hw.mds_disable=1'. To make this change persistent across reboots, you can add 'hw.mds_disable=1' to /etc/sysctl.conf." + fi + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation" + fi + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your microcode supports mitigation, but your kernel doesn't, upgrade it to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + else + if [ "$kernel_md_clear" = 1 ]; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your kernel supports mitigation, but your CPU microcode also needs to be updated to mitigate the vulnerability" + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Neither your kernel or your microcode support mitigation, upgrade both to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + fi + fi +} + +check_mds_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/mds" '^[^;]+'; then + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* Kernel supports using MD_CLEAR mitigation: " + kernel_md_clear='' + kernel_md_clear_can_tell=1 + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && grep ^flags "$procfs/cpuinfo" | grep -qw md_clear; then + kernel_md_clear="md_clear found in $procfs/cpuinfo" + pstatus green YES "$kernel_md_clear" + fi + if [ -z "$kernel_md_clear" ]; then + if ! command -v "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + kernel_md_clear_can_tell=0 + elif [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + kernel_md_clear_can_tell=0 + elif "${opt_arch_prefix}strings" "$kernel" | grep -q 'Clear CPU buffers'; then + _debug "md_clear: found 'Clear CPU buffers' string in kernel image" + kernel_md_clear='found md_clear implementation evidence in kernel image' + pstatus green YES "$kernel_md_clear" + fi + fi + if [ -z "$kernel_md_clear" ]; then + if [ "$kernel_md_clear_can_tell" = 1 ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN + fi + fi + + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ] && [ "$sys_interface_available" = 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* Kernel mitigation is enabled and active: " + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qi ^mitigation; then + mds_mitigated=1 + pstatus green YES + else + mds_mitigated=0 + pstatus yellow NO + fi + _info_nol "* SMT is either mitigated or disabled: " + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -Eq 'SMT (disabled|mitigated)'; then + mds_smt_mitigated=1 + pstatus green YES + else + mds_smt_mitigated=0 + pstatus yellow NO + fi + fi + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + # compute mystatus and mymsg from our own logic + if [ "$cpuid_md_clear" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$kernel_md_clear" ]; then + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # mitigation must also be enabled + if [ "$mds_mitigated" = 1 ]; then + if [ "$opt_paranoid" != 1 ] || [ "$mds_smt_mitigated" = 1 ]; then + mystatus=OK + mymsg="Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation, and mitigation is enabled" + else + mystatus=VULN + mymsg="Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation, but you must disable SMT (Hyper-Threading) for a complete mitigation" + fi + else + mystatus=VULN + mymsg="Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation, but the mitigation is not active" + fi + else + mystatus=OK + mymsg="Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for this mitigation" + fi + else + mystatus=VULN + mymsg="Your microcode supports mitigation, but your kernel doesn't, upgrade it to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + else + if [ -n "$kernel_md_clear" ]; then + mystatus=VULN + mymsg="Your kernel supports mitigation, but your CPU microcode also needs to be updated to mitigate the vulnerability" + else + mystatus=VULN + mymsg="Neither your kernel or your microcode support mitigation, upgrade both to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + fi + else + # sysfs only: return the status/msg we got + pvulnstatus "$cve" "$status" "$fullmsg" + return + fi + + # if we didn't get a msg+status from sysfs, use ours + if [ -z "$msg" ]; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" "$mystatus" "$mymsg" + elif [ "$opt_paranoid" = 1 ]; then + # if paranoid mode is enabled, we now that we won't agree on status, so take ours + pvulnstatus "$cve" "$mystatus" "$mymsg" + elif [ "$status" = "$mystatus" ]; then + # if we agree on status, we'll print the common status and our message (more detailed than the sysfs one) + pvulnstatus "$cve" "$status" "$mymsg" + else + # if we don't agree on status, maybe our logic is flawed due to a new kernel/mitigation? use the one from sysfs + pvulnstatus "$cve" "$status" "$msg" + fi + fi +} + + +################### +# TAA SECTION + +# Transactional Synchronization Extension (TSX) Asynchronous Abort +check_CVE_2019_11135() +{ + cve='CVE-2019-11135' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2019_11135_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2019_11135_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2019_11135_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/tsx_async_abort"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* TAA mitigation is supported by kernel: " + kernel_taa='' + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + kernel_taa_err="$kernel_err" + elif grep -q 'tsx_async_abort' "$kernel"; then + kernel_taa="found tsx_async_abort in kernel image" + fi + if [ -n "$kernel_taa" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$kernel_taa" + elif [ -n "$kernel_taa_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$kernel_taa_err" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol "* TAA mitigation enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qE '^Mitigation'; then + pstatus green YES "$fullmsg" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + else + pstatus yellow NO "tsx_async_abort not found in sysfs hierarchy" + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve" ; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -z "$msg" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # if we're in live mode and $msg is empty, sysfs file is not there so kernel is too old + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel doesn't support TAA mitigation, update it" + else + if [ -n "$kernel_taa" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Your kernel supports TAA mitigation" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel doesn't support TAA mitigation, update it" + fi + fi + else + if [ "$opt_paranoid" = 1 ]; then + # in paranoid mode, TSX or SMT enabled are not OK, even if TAA is mitigated + if ! echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qF 'TSX disabled'; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "TSX must be disabled for full mitigation" + elif echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qF 'SMT vulnerable'; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "SMT (HyperThreading) must be disabled for full mitigation" + else + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + fi + fi +} + +check_CVE_2019_11135_bsd() +{ + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve" ; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" UNK "your CPU is affected, but mitigation detection has not yet been implemented for BSD in this script" + fi +} + +####################### +# iTLB Multihit section + +check_CVE_2018_12207() +{ + cve='CVE-2018-12207' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2018_12207_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2018_12207_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_12207_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/itlb_multihit"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + check_has_vmm + + _info_nol "* iTLB Multihit mitigation is supported by kernel: " + kernel_itlbmh='' + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + kernel_itlbmh_err="$kernel_err" + # commit 5219505fcbb640e273a0d51c19c38de0100ec5a9 + elif grep -q 'itlb_multihit' "$kernel"; then + kernel_itlbmh="found itlb_multihit in kernel image" + fi + if [ -n "$kernel_itlbmh" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$kernel_itlbmh" + elif [ -n "$kernel_itlbmh_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$kernel_itlbmh_err" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + _info_nol "* iTLB Multihit mitigation enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qF 'Mitigation'; then + pstatus green YES "$fullmsg" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + else + pstatus yellow NO "itlb_multihit not found in sysfs hierarchy" + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve" ; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ "$has_vmm" = 0 ]; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "this system is not running a hypervisor" + elif [ -z "$msg" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # if we're in live mode and $msg is empty, sysfs file is not there so kernel is too old + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel doesn't support iTLB Multihit mitigation, update it" + else + if [ -n "$kernel_itlbmh" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Your kernel supports iTLB Multihit mitigation" + else + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel doesn't support iTLB Multihit mitigation, update it" + fi + fi + else + pvulnstatus $cve "$status" "$msg" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2018_12207_bsd() +{ + _info_nol "* Kernel supports disabling superpages for executable mappings under EPT: " + kernel_2m_x_ept=$(sysctl -n vm.pmap.allow_2m_x_ept 2>/dev/null) + if [ -z "$kernel_2m_x_ept" ]; then + pstatus yellow NO + else + pstatus green YES + fi + + _info_nol "* Superpages are disabled for executable mappings under EPT: " + if [ "$kernel_2m_x_ept" = 0 ]; then + pstatus green YES + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + elif [ -z "$kernel_2m_x_ept" ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel doesn't support mitigating this CVE, you should update it" + elif [ "$kernel_2m_x_ept" != 0 ]; then + pvulnstatus $cve VULN "Your kernel supports mitigating this CVE, but the mitigation is disabled" + explain "To enable the mitigation, use \`sysctl vm.pmap.allow_2m_x_ept=0\`" + else + pvulnstatus $cve OK "Your kernel has support for mitigation and the mitigation is enabled" + fi +} + +################### +# SRBDS SECTION + +# Special Register Buffer Data Sampling (SRBDS) +check_CVE_2020_0543() +{ + cve='CVE-2020-0543' + _info "\033[1;34m$cve aka '$(cve2name "$cve")'\033[0m" + if [ "$os" = Linux ]; then + check_CVE_2020_0543_linux + elif echo "$os" | grep -q BSD; then + check_CVE_2020_0543_bsd + else + _warn "Unsupported OS ($os)" + fi +} + +check_CVE_2020_0543_linux() +{ + status=UNK + sys_interface_available=0 + msg='' + if sys_interface_check "/sys/devices/system/cpu/vulnerabilities/srbds"; then + # this kernel has the /sys interface, trust it over everything + sys_interface_available=1 + fi + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + _info_nol "* SRBDS mitigation control is supported by the kernel: " + kernel_srbds='' + if [ -n "$kernel_err" ]; then + kernel_srbds_err="$kernel_err" + elif grep -q 'Dependent on hypervisor' "$kernel"; then + kernel_srbds="found SRBDS implementation evidence in kernel image. Your kernel is up to date for SRBDS mitigation" + fi + if [ -n "$kernel_srbds" ]; then + pstatus green YES "$kernel_srbds" + elif [ -n "$kernel_srbds_err" ]; then + pstatus yellow UNKNOWN "$kernel_srbds_err" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + _info_nol "* SRBDS mitigation control is enabled and active: " + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + if [ -n "$fullmsg" ]; then + if echo "$fullmsg" | grep -qE '^Mitigation'; then + pstatus green YES "$fullmsg" + else + pstatus yellow NO + fi + else + pstatus yellow NO "SRBDS not found in sysfs hierarchy" + fi + else + pstatus blue N/A "not testable in offline mode" + fi + elif [ "$sys_interface_available" = 0 ]; then + # we have no sysfs but were asked to use it only! + msg="/sys vulnerability interface use forced, but it's not available!" + status=UNK + fi + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve" ; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + if [ "$opt_sysfs_only" != 1 ]; then + if [ "$cpuid_srbds" = 1 ]; then + # SRBDS mitigation control exists + if [ "$srbds_on" = 1 ]; then + # SRBDS mitigation control is enabled + if [ -z "$msg" ]; then + # if msg is empty, sysfs check didn't fill it, rely on our own test + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # if we're in live mode and $msg is empty, sysfs file is not there so kernel is too old + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "Your microcode is up to date for SRBDS mitigation control. The kernel needs to be updated" + fi + else + if [ -n "$kernel_srbds" ]; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for SRBDS mitigation control. Mitigation is enabled" + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" OK "Your microcode is up to date for SRBDS mitigation control. The kernel needs to be updated" + fi + fi + elif [ "$srbds_on" = 0 ]; then + # SRBDS mitigation control is disabled + if [ -z "$msg" ]; then + if [ "$opt_live" = 1 ]; then + # if we're in live mode and $msg is empty, sysfs file is not there so kernel is too old + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your microcode is up to date for SRBDS mitigation control. The kernel needs to be updated. Mitigation is disabled" + fi + else + if [ -n "$kernel_srbds" ]; then + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your microcode and kernel are both up to date for SRBDS mitigation control. Mitigation is disabled" + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your microcode is up to date for SRBDS mitigation control. The kernel needs to be updated. Mitigation is disabled" + fi + fi + else + # rdmsr: CPU 0 cannot read MSR 0x00000123 + pvulnstatus "$cve" UNK "Not able to enumerate MSR for SRBDS mitigation control" + fi + else + # [ $cpuid_srbds != 1 ] + pvulnstatus "$cve" VULN "Your CPU microcode may need to be updated to mitigate the vulnerability" + fi + else + # sysfs only: return the status/msg we got + pvulnstatus "$cve" "$status" "$fullmsg" + return + fi + fi +} + +check_CVE_2020_0543_bsd() +{ + if ! is_cpu_affected "$cve"; then + # override status & msg in case CPU is not vulnerable after all + pvulnstatus $cve OK "your CPU vendor reported your CPU model as not affected" + else + pvulnstatus "$cve" UNK "your CPU is affected, but mitigation detection has not yet been implemented for BSD in this script" + fi +} + +####################### +# END OF VULNS SECTIONS + +if [ "$opt_no_hw" = 0 ] && [ -z "$opt_arch_prefix" ]; then + check_cpu + check_cpu_vulnerabilities + _info +fi + +# now run the checks the user asked for +for cve in $supported_cve_list +do + if [ "$opt_cve_all" = 1 ] || echo "$opt_cve_list" | grep -qw "$cve"; then + check_"$(echo "$cve" | tr - _)" + _info + fi +done + +if [ -n "$final_summary" ]; then + _info "> \033[46m\033[30mSUMMARY:\033[0m$final_summary" + _info "" +fi + +if [ "$bad_accuracy" = 1 ]; then + _warn "We're missing some kernel info (see -v), accuracy might be reduced" +fi + +_vars=$(set | grep -Ev '^[A-Z_[:space:]]' | grep -v -F 'mockme=' | sort | tr "\n" '|') +_debug "variables at end of script: $_vars" + +if [ -n "$mockme" ] && [ "$opt_mock" = 1 ]; then + if command -v "gzip" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + # not a useless use of cat: gzipping cpuinfo directly doesn't work well + # shellcheck disable=SC2002 + if command -v "base64" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + mock_cpuinfo="$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | gzip -c | base64 -w0)" + elif command -v "uuencode" >/dev/null 2>&1; then + mock_cpuinfo="$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | gzip -c | uuencode -m - | grep -Fv 'begin-base64' | grep -Fxv -- '====' | tr -d "\n")" + fi + fi + if [ -n "$mock_cpuinfo" ]; then + mockme=$(printf "%b\n%b" "$mockme" "SMC_MOCK_CPUINFO='$mock_cpuinfo'") + unset mock_cpuinfo + fi + _info "" + # shellcheck disable=SC2046 + _warn "To mock this CPU, set those vars: "$(echo "$mockme" | sort -u) +fi + +if [ "$opt_explain" = 0 ]; then + _info "Need more detailed information about mitigation options? Use --explain" +fi + +_info "A false sense of security is worse than no security at all, see --disclaimer" + +if [ "$mocked" = 1 ]; then + _info "" + _warn "One or several values have been mocked. This should only be done when debugging/testing this script." + _warn "The results do NOT reflect the actual status of the system we're running on." +fi + +if [ "$opt_batch" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_batch_format" = "nrpe" ]; then + if [ -n "$nrpe_vuln" ]; then + echo "Vulnerable:$nrpe_vuln" + else + echo "OK" + fi +fi + +if [ "$opt_batch" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_batch_format" = "short" ]; then + _echo 0 "${short_output% }" +fi + +if [ "$opt_batch" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_batch_format" = "json" ]; then + _echo 0 "${json_output%?}]" +fi + +if [ "$opt_batch" = 1 ] && [ "$opt_batch_format" = "prometheus" ]; then + echo "# TYPE specex_vuln_status untyped" + echo "# HELP specex_vuln_status Exposure of system to speculative execution vulnerabilities" + printf "%b\n" "$prometheus_output" +fi + +# exit with the proper exit code +[ "$global_critical" = 1 ] && exit 2 # critical +[ "$global_unknown" = 1 ] && exit 3 # unknown +exit 0 # ok + +# We're using MCE.db from the excellent platomav's MCExtractor project +# The builtin version follows, but the user can download an up-to-date copy (to be stored in his $HOME) by using --update-fwdb +# To update the builtin version itself (by *modifying* this very file), use --update-builtin-fwdb + +# %%% MCEDB v222+i20220208 +# I,0x00000611,0x00000B27,19961218 +# I,0x00000612,0x000000C6,19961210 +# I,0x00000616,0x000000C6,19961210 +# I,0x00000617,0x000000C6,19961210 +# I,0x00000619,0x000000D2,19980218 +# I,0x00000630,0x00000013,19960827 +# I,0x00000632,0x00000020,19960903 +# I,0x00000633,0x00000036,19980923 +# I,0x00000634,0x00000037,19980923 +# I,0x00000650,0x00000045,19990525 +# I,0x00000651,0x00000042,19990525 +# I,0x00000652,0x0000002D,19990518 +# I,0x00000653,0x00000010,19990628 +# I,0x00000660,0x0000000A,19990505 +# I,0x00000665,0x00000003,19990505 +# I,0x0000066A,0x0000000D,19990505 +# I,0x0000066D,0x00000007,19990505 +# I,0x00000670,0x00000007,19980602 +# I,0x00000671,0x00000014,19980811 +# I,0x00000672,0x00000038,19990922 +# I,0x00000673,0x0000002E,19990910 +# I,0x00000680,0x00000017,19990610 +# I,0x00000681,0x00000014,19991209 +# I,0x00000683,0x00000014,20010206 +# I,0x00000686,0x00000008,20000505 +# I,0x0000068A,0x00000005,20001207 +# I,0x00000690,0x00000004,20000206 +# I,0x00000691,0x00000001,20020527 +# I,0x00000692,0x00000001,20020620 +# I,0x00000694,0x00000002,20020926 +# I,0x00000695,0x00000047,20041109 +# I,0x00000696,0x00000001,20000707 +# I,0x000006A0,0x00000003,20000110 +# I,0x000006A1,0x00000001,20000306 +# I,0x000006A4,0x00000001,20000616 +# I,0x000006B0,0x0000001A,20010129 +# I,0x000006B1,0x0000001D,20010220 +# I,0x000006B4,0x00000002,20020111 +# I,0x000006D0,0x00000006,20030522 +# I,0x000006D1,0x00000009,20030709 +# I,0x000006D2,0x00000010,20030814 +# I,0x000006D6,0x00000018,20041017 +# I,0x000006D8,0x00000021,20060831 +# I,0x000006E0,0x00000008,20050215 +# I,0x000006E1,0x0000000C,20050413 +# I,0x000006E4,0x00000026,20050816 +# I,0x000006E8,0x0000003C,20060208 +# I,0x000006EC,0x0000005B,20070208 +# I,0x000006F0,0x00000005,20050818 +# I,0x000006F1,0x00000012,20051129 +# I,0x000006F2,0x0000005D,20101002 +# I,0x000006F4,0x00000028,20060417 +# I,0x000006F5,0x00000039,20060727 +# I,0x000006F6,0x000000D2,20101001 +# I,0x000006F7,0x0000006B,20101002 +# I,0x000006F9,0x00000084,20061012 +# I,0x000006FA,0x00000095,20101002 +# I,0x000006FB,0x000000C1,20111004 +# I,0x000006FD,0x000000A4,20101002 +# I,0x00000F00,0xFFFF0001,20000130 +# I,0x00000F01,0xFFFF0007,20000404 +# I,0x00000F02,0xFFFF000B,20000518 +# I,0x00000F03,0xFFFF0001,20000518 +# I,0x00000F04,0xFFFF0010,20000803 +# I,0x00000F05,0x0000000C,20000824 +# I,0x00000F06,0x00000004,20000911 +# I,0x00000F07,0x00000012,20020716 +# I,0x00000F08,0x00000008,20001101 +# I,0x00000F09,0x00000008,20010104 +# I,0x00000F0A,0x00000015,20020821 +# I,0x00000F11,0x0000000A,20030729 +# I,0x00000F12,0x0000002F,20030502 +# I,0x00000F13,0x00000005,20030508 +# I,0x00000F20,0x00000001,20010423 +# I,0x00000F21,0x00000003,20010529 +# I,0x00000F22,0x00000005,20030729 +# I,0x00000F23,0x0000000D,20010817 +# I,0x00000F24,0x00000021,20030610 +# I,0x00000F25,0x0000002C,20040826 +# I,0x00000F26,0x00000010,20040805 +# I,0x00000F27,0x00000039,20030604 +# I,0x00000F29,0x0000002F,20040811 +# I,0x00000F30,0x00000013,20030815 +# I,0x00000F31,0x0000000B,20031021 +# I,0x00000F32,0x0000000A,20040511 +# I,0x00000F33,0x0000000C,20050421 +# I,0x00000F34,0x00000017,20050421 +# I,0x00000F36,0x00000007,20040309 +# I,0x00000F37,0x00000003,20031218 +# I,0x00000F40,0x00000006,20040318 +# I,0x00000F41,0x00000017,20050422 +# I,0x00000F42,0x00000003,20050421 +# I,0x00000F43,0x00000005,20050421 +# I,0x00000F44,0x00000006,20050421 +# I,0x00000F46,0x00000004,20050411 +# I,0x00000F47,0x00000003,20050421 +# I,0x00000F48,0x0000000E,20080115 +# I,0x00000F49,0x00000003,20050421 +# I,0x00000F4A,0x00000004,20051214 +# I,0x00000F60,0x00000005,20050124 +# I,0x00000F61,0x00000008,20050610 +# I,0x00000F62,0x0000000F,20051215 +# I,0x00000F63,0x00000005,20051010 +# I,0x00000F64,0x00000004,20051223 +# I,0x00000F65,0x0000000B,20070510 +# I,0x00000F66,0x0000001B,20060310 +# I,0x00000F68,0x00000009,20060714 +# I,0x00001632,0x00000002,19980610 +# I,0x00010650,0x00000002,20060513 +# I,0x00010660,0x00000004,20060612 +# I,0x00010661,0x00000045,20101004 +# I,0x00010670,0x00000005,20070209 +# I,0x00010671,0x00000106,20070329 +# I,0x00010674,0x84050100,20070726 +# I,0x00010676,0x00000612,20150802 +# I,0x00010677,0x0000070D,20150802 +# I,0x0001067A,0x00000A0E,20150729 +# I,0x000106A0,0xFFFF001A,20071128 +# I,0x000106A1,0xFFFF000B,20080220 +# I,0x000106A2,0xFFFF0019,20080714 +# I,0x000106A4,0x00000013,20150630 +# I,0x000106A5,0x0000001D,20180511 +# I,0x000106C0,0x00000007,20070824 +# I,0x000106C1,0x00000109,20071203 +# I,0x000106C2,0x00000219,20090410 +# I,0x000106C9,0x00000007,20090213 +# I,0x000106CA,0x00000107,20090825 +# I,0x000106D0,0x00000005,20071204 +# I,0x000106D1,0x0000002A,20150803 +# I,0x000106E0,0xFFFF0022,20090116 +# I,0x000106E1,0xFFFF000D,20090206 +# I,0x000106E2,0xFFFF0011,20090924 +# I,0x000106E3,0xFFFF0011,20090512 +# I,0x000106E4,0x00000003,20130701 +# I,0x000106E5,0x0000000A,20180508 +# I,0x000106F0,0xFFFF0009,20090210 +# I,0x000106F1,0xFFFF0007,20090210 +# I,0x00020650,0xFFFF0008,20090218 +# I,0x00020651,0xFFFF0018,20090818 +# I,0x00020652,0x00000011,20180508 +# I,0x00020654,0xFFFF0007,20091124 +# I,0x00020655,0x00000007,20180423 +# I,0x00020661,0x00000105,20110718 +# I,0x000206A0,0x00000029,20091102 +# I,0x000206A1,0x00000007,20091223 +# I,0x000206A2,0x00000027,20100502 +# I,0x000206A3,0x00000009,20100609 +# I,0x000206A4,0x00000022,20100414 +# I,0x000206A5,0x00000007,20100722 +# I,0x000206A6,0x90030028,20100924 +# I,0x000206A7,0x0000002F,20190217 +# I,0x000206C0,0xFFFF001C,20091214 +# I,0x000206C1,0x00000006,20091222 +# I,0x000206C2,0x0000001F,20180508 +# I,0x000206D0,0x80000006,20100816 +# I,0x000206D1,0x80000106,20101201 +# I,0x000206D2,0xAF506958,20110714 +# I,0x000206D3,0xAF50696A,20110816 +# I,0x000206D5,0xAF5069E5,20120118 +# I,0x000206D6,0x00000621,20200304 +# I,0x000206D7,0x0000071A,20200324 +# I,0x000206E0,0xE3493401,20090108 +# I,0x000206E1,0xE3493402,20090224 +# I,0x000206E2,0xFFFF0004,20081001 +# I,0x000206E3,0xE4486547,20090701 +# I,0x000206E4,0xFFFF0008,20090619 +# I,0x000206E5,0xFFFF0018,20091215 +# I,0x000206E6,0x0000000D,20180515 +# I,0x000206F0,0x00000005,20100729 +# I,0x000206F1,0x00000008,20101013 +# I,0x000206F2,0x0000003B,20180516 +# I,0x00030650,0x00000009,20120118 +# I,0x00030651,0x00000110,20131014 +# I,0x00030660,0x00000003,20101103 +# I,0x00030661,0x0000010F,20150721 +# I,0x00030669,0x0000010D,20130515 +# I,0x00030671,0x00000117,20130410 +# I,0x00030672,0x0000022E,20140401 +# I,0x00030673,0x83290100,20190916 +# I,0x00030678,0x00000838,20190422 +# I,0x00030679,0x0000090D,20190710 +# I,0x000306A0,0x00000007,20110407 +# I,0x000306A2,0x0000000C,20110725 +# I,0x000306A4,0x00000007,20110908 +# I,0x000306A5,0x00000009,20111110 +# I,0x000306A6,0x00000004,20111114 +# I,0x000306A8,0x00000010,20120220 +# I,0x000306A9,0x00000021,20190213 +# I,0x000306C0,0xFFFF0013,20111110 +# I,0x000306C1,0xFFFF0014,20120725 +# I,0x000306C2,0xFFFF0006,20121017 +# I,0x000306C3,0x00000028,20191112 +# I,0x000306D1,0xFFFF0009,20131015 +# I,0x000306D2,0xFFFF0009,20131219 +# I,0x000306D3,0xE3121338,20140825 +# I,0x000306D4,0x0000002F,20191112 +# I,0x000306E0,0xE920080F,20121113 +# I,0x000306E2,0xE9220827,20130523 +# I,0x000306E3,0x00000308,20130321 +# I,0x000306E4,0x0000042E,20190314 +# I,0x000306E6,0x00000600,20130619 +# I,0x000306E7,0x00000715,20190314 +# I,0x000306F0,0xFFFF0017,20130730 +# I,0x000306F1,0xD141D629,20140416 +# I,0x000306F2,0x00000049,20210811 +# I,0x000306F3,0x0000000D,20160211 +# I,0x000306F4,0x0000001A,20210524 +# I,0x00040650,0xFFFF000B,20121206 +# I,0x00040651,0x00000026,20191112 +# I,0x00040660,0xFFFF0011,20121012 +# I,0x00040661,0x0000001C,20191112 +# I,0x00040670,0xFFFF0006,20140304 +# I,0x00040671,0x00000022,20191112 +# I,0x000406A0,0x80124001,20130521 +# I,0x000406A8,0x0000081F,20140812 +# I,0x000406A9,0x0000081F,20140812 +# I,0x000406C1,0x0000010B,20140814 +# I,0x000406C2,0x00000221,20150218 +# I,0x000406C3,0x00000368,20190423 +# I,0x000406C4,0x00000411,20190423 +# I,0x000406D0,0x0000000E,20130612 +# I,0x000406D8,0x0000012D,20190916 +# I,0x000406E1,0x00000020,20141111 +# I,0x000406E2,0x0000002C,20150521 +# I,0x000406E3,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000406E8,0x00000026,20160414 +# I,0x000406F0,0x00000014,20150702 +# I,0x000406F1,0x0B000040,20210519 +# I,0x00050650,0x8000002B,20160208 +# I,0x00050651,0x8000002B,20160208 +# I,0x00050652,0x80000037,20170502 +# I,0x00050653,0x0100015C,20210526 +# I,0x00050654,0x02006C0A,20210616 +# I,0x00050655,0x03000012,20190412 +# I,0x00050656,0x0400320A,20210813 +# I,0x00050657,0x0500320A,20210813 +# I,0x0005065A,0x86002302,20210416 +# I,0x0005065B,0x07002402,20210604 +# I,0x00050661,0xF1000008,20150130 +# I,0x00050662,0x0000001C,20190617 +# I,0x00050663,0x0700001C,20210612 +# I,0x00050664,0x0F00001A,20210612 +# I,0x00050665,0x0E000014,20210918 +# I,0x00050670,0xFFFF0030,20151113 +# I,0x00050671,0x000001B6,20180108 +# I,0x000506A0,0x00000038,20150112 +# I,0x000506C2,0x00000014,20180511 +# I,0x000506C8,0x90011010,20160323 +# I,0x000506C9,0x00000046,20210510 +# I,0x000506CA,0x00000022,20210622 +# I,0x000506D1,0x00000102,20150605 +# I,0x000506E0,0x00000018,20141119 +# I,0x000506E1,0x0000002A,20150602 +# I,0x000506E2,0x0000002E,20150815 +# I,0x000506E3,0x000000F0,20211112 +# I,0x000506E8,0x00000034,20160710 +# I,0x000506F0,0x00000010,20160607 +# I,0x000506F1,0x00000036,20210510 +# I,0x00060660,0x0000000C,20160821 +# I,0x00060661,0x0000000E,20170128 +# I,0x00060662,0x00000022,20171129 +# I,0x00060663,0x0000002A,20180417 +# I,0x000606A0,0x80000031,20200308 +# I,0x000606A4,0x0B000280,20200817 +# I,0x000606A5,0x0C0002F0,20210308 +# I,0x000606A6,0x0D000332,20211217 +# I,0x000606E0,0x0000000B,20161104 +# I,0x000606E1,0x00000108,20190423 +# I,0x000706A0,0x00000026,20170712 +# I,0x000706A1,0x00000038,20210510 +# I,0x000706A8,0x0000001C,20210510 +# I,0x000706E0,0x0000002C,20180614 +# I,0x000706E1,0x00000042,20190420 +# I,0x000706E2,0x00000042,20190420 +# I,0x000706E3,0x81000008,20181002 +# I,0x000706E4,0x00000046,20190905 +# I,0x000706E5,0x000000A8,20210526 +# I,0x00080650,0x00000018,20180108 +# I,0x00080664,0x0B00000F,20210217 +# I,0x00080665,0x0B00000F,20210217 +# I,0x000806A0,0x00000010,20190507 +# I,0x000806A1,0x0000002D,20210902 +# I,0x000806C0,0x00000068,20200402 +# I,0x000806C1,0x0000009C,20211026 +# I,0x000806C2,0x00000022,20210716 +# I,0x000806D0,0x00000050,20201217 +# I,0x000806D1,0x0000003C,20210716 +# I,0x000806E9,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000806EA,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000806EB,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000806EC,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x00090660,0x00000009,20200617 +# I,0x00090661,0x00000015,20210921 +# I,0x00090670,0x00000019,20201111 +# I,0x00090671,0x0000001C,20210614 +# I,0x00090672,0x0000001F,20220303 +# I,0x00090674,0x00000219,20210425 +# I,0x00090675,0x0000001F,20220303 +# I,0x000906A0,0x0000001C,20210614 +# I,0x000906A1,0x0000011F,20211104 +# I,0x000906A2,0x00000315,20220102 +# I,0x000906A3,0x0000041B,20220308 +# I,0x000906A4,0x0000041B,20220308 +# I,0x000906C0,0x2400001F,20210809 +# I,0x000906E9,0x000000F0,20211112 +# I,0x000906EA,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000906EB,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000906EC,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000906ED,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000A0650,0x000000BE,20191010 +# I,0x000A0651,0x000000C2,20191113 +# I,0x000A0652,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000A0653,0x000000EC,20210428 +# I,0x000A0654,0x000000C6,20200123 +# I,0x000A0655,0x000000EE,20210428 +# I,0x000A0660,0x000000EA,20210428 +# I,0x000A0661,0x000000EC,20210429 +# I,0x000A0670,0x0000002C,20201124 +# I,0x000A0671,0x00000050,20210829 +# I,0x000A0680,0x80000002,20200121 +# I,0x000B0670,0x00000009,20211115 +# I,0x000B06F2,0x0000001F,20220303 +# I,0x000B06F5,0x0000001F,20220303 +# A,0x00000F00,0x02000008,20070614 +# A,0x00000F01,0x0000001C,20021031 +# A,0x00000F10,0x00000003,20020325 +# A,0x00000F11,0x0000001F,20030220 +# A,0x00000F48,0x00000046,20040719 +# A,0x00000F4A,0x00000047,20040719 +# A,0x00000F50,0x00000024,20021212 +# A,0x00000F51,0x00000025,20030115 +# A,0x00010F50,0x00000041,20040225 +# A,0x00020F10,0x0000004D,20050428 +# A,0x00040F01,0xC0012102,20050916 +# A,0x00040F0A,0x00000068,20060920 +# A,0x00040F13,0x0000007A,20080508 +# A,0x00040F14,0x00000062,20060127 +# A,0x00040F1B,0x0000006D,20060920 +# A,0x00040F33,0x0000007B,20080514 +# A,0x00060F80,0x00000083,20060929 +# A,0x000C0F1B,0x0000006E,20060921 +# A,0x000F0F00,0x00000005,20020627 +# A,0x000F0F01,0x00000015,20020627 +# A,0x00100F00,0x01000020,20070326 +# A,0x00100F20,0x010000CA,20100331 +# A,0x00100F22,0x010000C9,20100331 +# A,0x00100F40,0x01000085,20080501 +# A,0x00100F41,0x010000DB,20111024 +# A,0x00100F42,0x01000092,20081021 +# A,0x00100F43,0x010000C8,20100311 +# A,0x00100F62,0x010000C7,20100311 +# A,0x00100F80,0x010000DA,20111024 +# A,0x00100F81,0x010000D9,20111012 +# A,0x00100FA0,0x010000DC,20111024 +# A,0x00120F00,0x03000002,20100324 +# A,0x00200F30,0x02000018,20070921 +# A,0x00200F31,0x02000057,20080502 +# A,0x00200F32,0x02000034,20080307 +# A,0x00300F01,0x0300000E,20101004 +# A,0x00300F10,0x03000027,20111309 +# A,0x00500F00,0x0500000B,20100601 +# A,0x00500F01,0x0500001A,20100908 +# A,0x00500F10,0x05000029,20130121 +# A,0x00500F20,0x05000119,20130118 +# A,0x00580F00,0x0500000B,20100601 +# A,0x00580F01,0x0500001A,20100908 +# A,0x00580F10,0x05000028,20101124 +# A,0x00580F20,0x05000103,20110526 +# A,0x00600F00,0x06000017,20101029 +# A,0x00600F01,0x0600011F,20110227 +# A,0x00600F10,0x06000425,20110408 +# A,0x00600F11,0x0600050D,20110627 +# A,0x00600F12,0x0600063E,20180207 +# A,0x00600F20,0x06000852,20180206 +# A,0x00610F00,0x0600100E,20111102 +# A,0x00610F01,0x0600111F,20180305 +# A,0x00630F00,0x0600301C,20130817 +# A,0x00630F01,0x06003109,20180227 +# A,0x00660F00,0x06006012,20141014 +# A,0x00660F01,0x0600611A,20180126 +# A,0x00670F00,0x06006705,20180220 +# A,0x00680F00,0x06000017,20101029 +# A,0x00680F01,0x0600011F,20110227 +# A,0x00680F10,0x06000410,20110314 +# A,0x00690F00,0x06001009,20110613 +# A,0x00700F00,0x0700002A,20121218 +# A,0x00700F01,0x07000110,20180209 +# A,0x00730F00,0x07030009,20131206 +# A,0x00730F01,0x07030106,20180209 +# A,0x00800F00,0x0800002A,20161006 +# A,0x00800F10,0x0800100C,20170131 +# A,0x00800F11,0x08001138,20190204 +# A,0x00800F12,0x0800126E,20211111 +# A,0x00800F82,0x0800820D,20190416 +# A,0x00810F00,0x08100004,20161120 +# A,0x00810F10,0x08101016,20190430 +# A,0x00810F11,0x08101103,20190417 +# A,0x00810F80,0x08108002,20180605 +# A,0x00810F81,0x08108109,20190417 +# A,0x00820F00,0x08200002,20180214 +# A,0x00820F01,0x08200103,20190417 +# A,0x00830F00,0x08300027,20190401 +# A,0x00830F10,0x08301052,20211111 +# A,0x00850F00,0x08500004,20180212 +# A,0x00860F00,0x0860000E,20200127 +# A,0x00860F01,0x08600106,20200619 +# A,0x00860F81,0x08608103,20200702 +# A,0x00870F00,0x08700004,20181206 +# A,0x00870F10,0x08701021,20200125 +# A,0x00A00F00,0x0A000033,20200413 +# A,0x00A00F10,0x0A001053,20211217 +# A,0x00A00F11,0x0A00115D,20211119 +# A,0x00A00F12,0x0A001227,20211215 +# A,0x00A00F80,0x0A008003,20211015 +# A,0x00A00F82,0x0A008204,20211015 +# A,0x00A20F00,0x0A200025,20200121 +# A,0x00A20F10,0x0A201016,20210408 +# A,0x00A20F12,0x0A201205,20210719 +# A,0x00A50F00,0x0A50000C,20201208 |
