1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
|
//! [![github]](https://github.com/dtolnay/itoa) [![crates-io]](https://crates.io/crates/itoa) [![docs-rs]](https://docs.rs/itoa)
//!
//! [github]: https://img.shields.io/badge/github-8da0cb?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=github
//! [crates-io]: https://img.shields.io/badge/crates.io-fc8d62?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=rust
//! [docs-rs]: https://img.shields.io/badge/docs.rs-66c2a5?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=docs.rs
//!
//! <br>
//!
//! This crate provides a fast conversion of integer primitives to decimal
//! strings. The implementation comes straight from [libcore] but avoids the
//! performance penalty of going through [`core::fmt::Formatter`].
//!
//! See also [`ryu`] for printing floating point primitives.
//!
//! [libcore]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/b8214dc6c6fc20d0a660fb5700dca9ebf51ebe89/src/libcore/fmt/num.rs#L201-L254
//! [`core::fmt::Formatter`]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/fmt/struct.Formatter.html
//! [`ryu`]: https://github.com/dtolnay/ryu
//!
//! # Example
//!
//! ```
//! fn main() {
//! let mut buffer = itoa::Buffer::new();
//! let printed = buffer.format(128u64);
//! assert_eq!(printed, "128");
//! }
//! ```
//!
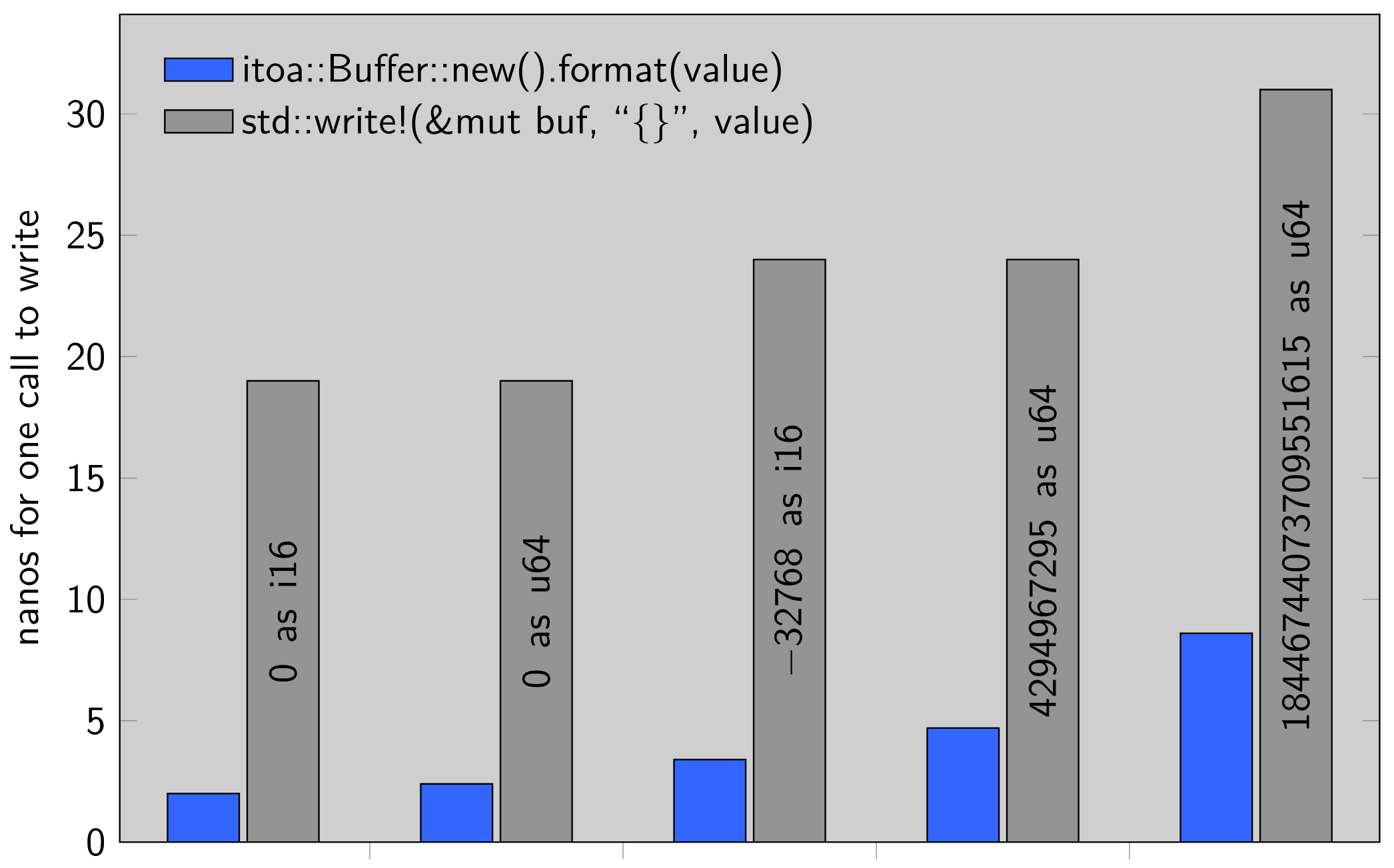
//! # Performance (lower is better)
//!
//! 
#![doc(html_root_url = "https://docs.rs/itoa/1.0.3")]
#![no_std]
#![allow(
clippy::cast_lossless,
clippy::cast_possible_truncation,
clippy::must_use_candidate,
clippy::unreadable_literal
)]
mod udiv128;
use core::mem::{self, MaybeUninit};
use core::{ptr, slice, str};
/// A correctly sized stack allocation for the formatted integer to be written
/// into.
///
/// # Example
///
/// ```
/// let mut buffer = itoa::Buffer::new();
/// let printed = buffer.format(1234);
/// assert_eq!(printed, "1234");
/// ```
pub struct Buffer {
bytes: [MaybeUninit<u8>; I128_MAX_LEN],
}
impl Default for Buffer {
#[inline]
fn default() -> Buffer {
Buffer::new()
}
}
impl Clone for Buffer {
#[inline]
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
Buffer::new()
}
}
impl Buffer {
/// This is a cheap operation; you don't need to worry about reusing buffers
/// for efficiency.
#[inline]
pub fn new() -> Buffer {
let bytes = [MaybeUninit::<u8>::uninit(); I128_MAX_LEN];
Buffer { bytes }
}
/// Print an integer into this buffer and return a reference to its string
/// representation within the buffer.
pub fn format<I: Integer>(&mut self, i: I) -> &str {
i.write(unsafe {
&mut *(&mut self.bytes as *mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; I128_MAX_LEN]
as *mut <I as private::Sealed>::Buffer)
})
}
}
/// An integer that can be written into an [`itoa::Buffer`][Buffer].
///
/// This trait is sealed and cannot be implemented for types outside of itoa.
pub trait Integer: private::Sealed {}
// Seal to prevent downstream implementations of the Integer trait.
mod private {
pub trait Sealed: Copy {
type Buffer: 'static;
fn write(self, buf: &mut Self::Buffer) -> &str;
}
}
const DEC_DIGITS_LUT: &[u8] = b"\
0001020304050607080910111213141516171819\
2021222324252627282930313233343536373839\
4041424344454647484950515253545556575859\
6061626364656667686970717273747576777879\
8081828384858687888990919293949596979899";
// Adaptation of the original implementation at
// https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/b8214dc6c6fc20d0a660fb5700dca9ebf51ebe89/src/libcore/fmt/num.rs#L188-L266
macro_rules! impl_Integer {
($($max_len:expr => $t:ident),* as $conv_fn:ident) => {$(
impl Integer for $t {}
impl private::Sealed for $t {
type Buffer = [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len];
#[allow(unused_comparisons)]
#[inline]
fn write(self, buf: &mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len]) -> &str {
let is_nonnegative = self >= 0;
let mut n = if is_nonnegative {
self as $conv_fn
} else {
// convert the negative num to positive by summing 1 to it's 2 complement
(!(self as $conv_fn)).wrapping_add(1)
};
let mut curr = buf.len() as isize;
let buf_ptr = buf.as_mut_ptr() as *mut u8;
let lut_ptr = DEC_DIGITS_LUT.as_ptr();
unsafe {
// need at least 16 bits for the 4-characters-at-a-time to work.
if mem::size_of::<$t>() >= 2 {
// eagerly decode 4 characters at a time
while n >= 10000 {
let rem = (n % 10000) as isize;
n /= 10000;
let d1 = (rem / 100) << 1;
let d2 = (rem % 100) << 1;
curr -= 4;
ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d1), buf_ptr.offset(curr), 2);
ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d2), buf_ptr.offset(curr + 2), 2);
}
}
// if we reach here numbers are <= 9999, so at most 4 chars long
let mut n = n as isize; // possibly reduce 64bit math
// decode 2 more chars, if > 2 chars
if n >= 100 {
let d1 = (n % 100) << 1;
n /= 100;
curr -= 2;
ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d1), buf_ptr.offset(curr), 2);
}
// decode last 1 or 2 chars
if n < 10 {
curr -= 1;
*buf_ptr.offset(curr) = (n as u8) + b'0';
} else {
let d1 = n << 1;
curr -= 2;
ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d1), buf_ptr.offset(curr), 2);
}
if !is_nonnegative {
curr -= 1;
*buf_ptr.offset(curr) = b'-';
}
}
let len = buf.len() - curr as usize;
let bytes = unsafe { slice::from_raw_parts(buf_ptr.offset(curr), len) };
unsafe { str::from_utf8_unchecked(bytes) }
}
}
)*};
}
const I8_MAX_LEN: usize = 4;
const U8_MAX_LEN: usize = 3;
const I16_MAX_LEN: usize = 6;
const U16_MAX_LEN: usize = 5;
const I32_MAX_LEN: usize = 11;
const U32_MAX_LEN: usize = 10;
const I64_MAX_LEN: usize = 20;
const U64_MAX_LEN: usize = 20;
impl_Integer!(
I8_MAX_LEN => i8,
U8_MAX_LEN => u8,
I16_MAX_LEN => i16,
U16_MAX_LEN => u16,
I32_MAX_LEN => i32,
U32_MAX_LEN => u32
as u32);
impl_Integer!(I64_MAX_LEN => i64, U64_MAX_LEN => u64 as u64);
#[cfg(target_pointer_width = "16")]
impl_Integer!(I16_MAX_LEN => isize, U16_MAX_LEN => usize as u16);
#[cfg(target_pointer_width = "32")]
impl_Integer!(I32_MAX_LEN => isize, U32_MAX_LEN => usize as u32);
#[cfg(target_pointer_width = "64")]
impl_Integer!(I64_MAX_LEN => isize, U64_MAX_LEN => usize as u64);
macro_rules! impl_Integer128 {
($($max_len:expr => $t:ident),*) => {$(
impl Integer for $t {}
impl private::Sealed for $t {
type Buffer = [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len];
#[allow(unused_comparisons)]
#[inline]
fn write(self, buf: &mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len]) -> &str {
let is_nonnegative = self >= 0;
let n = if is_nonnegative {
self as u128
} else {
// convert the negative num to positive by summing 1 to it's 2 complement
(!(self as u128)).wrapping_add(1)
};
let mut curr = buf.len() as isize;
let buf_ptr = buf.as_mut_ptr() as *mut u8;
unsafe {
// Divide by 10^19 which is the highest power less than 2^64.
let (n, rem) = udiv128::udivmod_1e19(n);
let buf1 = buf_ptr.offset(curr - U64_MAX_LEN as isize) as *mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; U64_MAX_LEN];
curr -= rem.write(&mut *buf1).len() as isize;
if n != 0 {
// Memset the base10 leading zeros of rem.
let target = buf.len() as isize - 19;
ptr::write_bytes(buf_ptr.offset(target), b'0', (curr - target) as usize);
curr = target;
// Divide by 10^19 again.
let (n, rem) = udiv128::udivmod_1e19(n);
let buf2 = buf_ptr.offset(curr - U64_MAX_LEN as isize) as *mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; U64_MAX_LEN];
curr -= rem.write(&mut *buf2).len() as isize;
if n != 0 {
// Memset the leading zeros.
let target = buf.len() as isize - 38;
ptr::write_bytes(buf_ptr.offset(target), b'0', (curr - target) as usize);
curr = target;
// There is at most one digit left
// because u128::max / 10^19 / 10^19 is 3.
curr -= 1;
*buf_ptr.offset(curr) = (n as u8) + b'0';
}
}
if !is_nonnegative {
curr -= 1;
*buf_ptr.offset(curr) = b'-';
}
let len = buf.len() - curr as usize;
let bytes = slice::from_raw_parts(buf_ptr.offset(curr), len);
str::from_utf8_unchecked(bytes)
}
}
}
)*};
}
const U128_MAX_LEN: usize = 39;
const I128_MAX_LEN: usize = 40;
impl_Integer128!(I128_MAX_LEN => i128, U128_MAX_LEN => u128);
|
