diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'docs')
143 files changed, 2042 insertions, 4881 deletions
diff --git a/docs/Demo-Sites.md b/docs/Demo-Sites.md index 177a37d16..291e3a5e3 100644 --- a/docs/Demo-Sites.md +++ b/docs/Demo-Sites.md @@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ sidebar_position: "90" # Live demos -See the live Netdata Cloud demo with rooms (listed below) for specific use cases at **https://app.netdata.cloud/spaces/netdata-demo** +See the live Netdata Cloud demo with Rooms (listed below) for specific use cases at **https://app.netdata.cloud/spaces/netdata-demo** | Location | Netdata Demo URL | 60 mins reqs | VM donated by | | :------------------ | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| :------------------------------------------------- | diff --git a/docs/alerts-and-notifications/creating-alerts-with-netdata-alerts-configuration-manager.md b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/creating-alerts-with-netdata-alerts-configuration-manager.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..f9a443c9d --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/creating-alerts-with-netdata-alerts-configuration-manager.md @@ -0,0 +1,44 @@ +# Creating Alerts with Netdata Alerts Configuration Manager + +The Netdata Alerts Configuration Manager enables subscribers to easily set up Alerts directly from the Netdata Dashboard. More details on subscriptions can be found [here](https://www.netdata.cloud/pricing/). + +## Using the Alerts Configuration Manager + +1. Navigate to the **Metrics** tab and select the chart you want to configure for Alerts. +2. Click the **Alert icon** in the top right corner of the chart. +3. The Alert Configuration Manager will open, showing the default thresholds. Modify these thresholds as needed; the Alert definition on the right will update automatically. +4. For additional settings, toggle **Show advanced**. +5. After configuring the Alert, copy the generated Alert definition from the code box. Paste this into an existing or new custom health configuration file located at `<path to netdata install>/etc/netdata/health.d/` on a Parent Agent or a Standalone Child Agent. The guide to edit health configuration files is available [here](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#edit-health-configuration-files). +6. To activate the new Alert, run the command `<path to netdata install>/usr/sbin/netdatacli reload-health`. + +## Alerts Configuration Manager Sections + +### Alert Detection Method + +An Alert is triggered whenever a metric crosses a threshold: + +- **Standard Threshold**: Triggered when a metric crosses a predefined value. +- **Metric Variance**: Triggered based on the variance of the metric. +- **Anomaly Rate**: Triggered based on the anomaly rate of the metric. + +### Metrics Lookup, Filtering, and Formula Section + +You can read more about the different options in the [Alerts reference documentation](/src/health/REFERENCE.md). + +- **Metrics Lookup**: Adjust the database lookup parameters directly in the UI, including method (`avg`, `sum`, `min`, `max`, etc.), computation style, dimensions, duration, and options like `absolute` or `percentage`. +- **Alert Filtering**: The **show advanced** checkbox allows filtering of Alert health checks for specific infrastructure components. Options include selecting hosts, nodes, instances, chart labels, and operating systems. +- **Formula / Calculation**: The **show advanced** checkbox allows defining a formula for the metric value, which is then used to set Alert thresholds. + +### Alerting Conditions + +- **Thresholds**: Set thresholds for warning and critical Alert states, specifying whether the Alert should trigger above or below these thresholds. Advanced settings allow for custom formulas. + - **Recovery Thresholds**: Set thresholds for downgrading the Alert from critical to warning or from warning to clear. +- **Check Interval**: Define how frequently the health check should run. +- **Delay Notifications**: Manage notification delays for Alert escalations or de-escalations. +- **Agent Specific Options**: Options exclusive to the Netdata Agent, like repeat notification frequencies and notification recipients. + - **Custom Exec Script**: Define custom scripts to execute when an Alert triggers. + +### Alert Name, Description, and Summary Section + +- **Alert Template Name**: Provide a unique name for the Alert. +- **Alert Template Description**: Offer a brief explanation of what the Alert diff --git a/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/README.md b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/README.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..3368b4e14 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,7 @@ +# Notifications + +This section includes the documentation of the integrations for both of Netdata's notification methods. + +- Netdata Cloud provides centralized alert notifications, utilizing the health status data already sent to Netdata Cloud from connected nodes to send alerts to configured integrations. [Supported integrations](/docs/alerts-&-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications) include Amazon SNS, Discord, Slack, Splunk, and others. + +- The Netdata Agent offers a [wider range of notification options](/docs/alerts-&-notifications/notifications/agent-dispatched-notifications) directly from the agent itself. You can choose from over a dozen services, including email, Slack, PagerDuty, Twilio, and others, for more granular control over notifications on each node. diff --git a/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..c9570c470 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md @@ -0,0 +1,69 @@ +# Centralized Cloud Notifications Reference + +Netdata Cloud sends Alert notifications for nodes in warning, critical, or unreachable states, ensuring Alerts are managed centrally and efficiently. + +## Benefits of Centralized Notifications + +- Consolidate health status views across all infrastructure in one place. +- Set up and [manage your Alert notifications easily](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md). +- Expedite troubleshooting with tools like [Metric Correlations](/docs/metric-correlations.md) and the [Anomaly Advisor](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/anomaly-advisor-tab.md). + +> **Note** +> +> To avoid notification overload, **flood protection** is triggered when a node frequently disconnects or sends excessive Alerts, highlighting potential issues. + +Administrators must [enable Alert notifications](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#manage-space-notification-settings) for their Space(s). All users can then customize their notification preferences through their [account menu](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#manage-user-notification-settings). + +> **Note** +> +> Centralized Alerts in Netdata Cloud are separate from the [Netdata Agent](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/README.md) notifications. Agent Alerts must be [configured individually](/src/health/REFERENCE.md) on each node. + +## Alert Notifications + +Notifications can be sent via email or through third-party services like PagerDuty or Slack. Administrators can manage notification settings for the entire Space, while individual users can personalize settings in their profile. + +### Service Level + +#### Personal + +Notifications are sent to user-specific destinations, such as email, which are managed by users under their profile settings. + +#### System + +These notifications go to general targets like a Slack channel, with administrators setting rules for notification targets based on workspace or Alert level. + +### Service Classification + +#### Community + +Available to all plans, includes basic methods like Email and Discord. + +#### Business + +Exclusive to [paid plans](/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md), includes advanced services like PagerDuty and Slack. + +## Alert Notification Silencing Rules + +Netdata Cloud offers a silencing rule engine to mute Alert notifications based on specific conditions related to nodes or Alert types. Learn how to manage these settings [here](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md). + +## Flood Protection + +If a node repeatedly changes state or raises Alerts, flood protection limits notifications to prevent overload. You can still access node details through Netdata Cloud or directly via the local Agent dashboard. + +## Anatomy of an Email Alert Notification + +Email notifications provide comprehensive details: + +- The Space's name +- The node's name +- Alert status: critical, warning, cleared +- Previous Alert status +- Time at which the Alert triggered +- Chart context that triggered the Alert +- Name and information about the triggered Alert +- Alert value +- Total number of warning and critical Alerts on that node +- Threshold for triggering the given Alert state +- Calculation or database lookups that Netdata uses to compute the value +- Source of the Alert, including which file you can edit to configure this Alert on an individual node +- Direct link to the node’s chart in Cloud dashboards. diff --git a/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..d537ef7ea --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md @@ -0,0 +1,60 @@ +# Manage Alert Notification Silencing Rules + +From the Cloud interface, you can manage your space's Alert notification silencing rules settings as well as allow users to define their personal ones. + +## Prerequisites + +To manage **space's Alert notification silencing rule settings**, you will need the following: + +- A Netdata Cloud account +- Access to the space as an **administrator** or **manager** (**troubleshooters** can only view space rules) + +To manage your **personal Alert notification silencing rule settings**, you will need the following: + +- A Netdata Cloud account +- Access to the space with any role except **billing** + +### Steps + +1. Click on the **Space settings** cog (located above your profile icon). +2. Click on the **Alert & Notification** tab on the left-hand side. +3. Click on the **Notification Silencing Rules** tab. +4. You will be presented with a table of the configured Alert notification silencing rules for: + + - The space (if you aren't an **observer**) + - Yourself + + You will be able to: + + 1. **Add a new** Alert notification silencing rule configuration. + - Choose if it applies to **All users** or **Myself** (All users is only available for **administrators** and **managers**). + - You need to provide a name for the configuration so you can easily refer to it. + - Define criteria for Nodes, to which Rooms will the rule apply, on what Nodes and whether or not it applies to host labels key-value pairs. + - Define criteria for Alerts, such as Alert name is being targeted and on what Alert context. You can also specify if it will apply to a specific Alert role. + - Define when it will be applied: + - Immediately, from now until it is turned off or until a specific duration (start and end date automatically set). + - Scheduled, you can specify the start and end time for when the rule becomes active and then inactive (time is set according to your browser's local timezone). + Note: You are only able to add a rule if your space is on a [paid plan](/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md). + 2. **Edit an existing** Alert notification silencing rule configuration. You will be able to change: + - The name provided for it + - Who it applies to + - Selection criteria for Nodes and Alerts + - When it will be applied + 3. **Enable/Disable** a given Alert notification silencing rule configuration. + - Use the toggle to enable or disable + 4. **Delete an existing** Alert notification silencing rule. + - Use the trash icon to delete your configuration + +## Silencing Rules Examples + +| Rule name | Rooms | Nodes | Host Label | Alert name | Alert context | Alert instance | Alert role | Description | +|:---------------------------------|:-------------------|:---------|:-------------------------|:-------------------------------------------------|:--------------|:-------------------------|:------------|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Space silencing | All Rooms | * | * | * | * | * | * | This rule silences the entire space, targets all nodes, and for all users. E.g. infrastructure-wide maintenance window. | +| DB Servers Rooms | PostgreSQL Servers | * | * | * | * | * | * | This rule silences the nodes in the Room named PostgreSQL Servers, for example, it doesn't silence the `All Nodes` Room. E.g. My team with membership to this Room doesn't want to receive notifications for these nodes. | +| Node child1 | All Rooms | `child1` | * | * | * | * | * | This rule silences all Alert state transitions for node `child1` in all Rooms and for all users. E.g. node could be going under maintenance. | +| Production nodes | All Rooms | * | `environment:production` | * | * | * | * | This rule silences all Alert state transitions for nodes with the host label key-value pair `environment:production`. E.g. Maintenance window on nodes with specific host labels. | +| Third party maintenance | All Rooms | * | * | `httpcheck_posthog_netdata_cloud.request_status` | * | * | * | This rule silences this specific Alert since the third-party partner will be undergoing maintenance. | +| Intended stress usage on CPU | All Rooms | * | * | * | `system.cpu` | * | * | This rule silences specific Alerts across all nodes and their CPU cores. | +| Silence role webmaster | All Rooms | * | * | * | * | * | `webmaster` | This rule silences all Alerts configured with the role `webmaster`. | +| Silence Alert on node | All Rooms | `child1` | * | `httpcheck_posthog_netdata_cloud.request_status` | * | * | * | This rule silences the specific Alert on the `child1` node. | +| Disk Space Alerts on mount point | All Rooms | * | * | `disk_space_usage` | `disk.space` | `disk_space_opt_baddisk` | * | This rule silences the specific Alert instance on all nodes `/opt/baddisk`. | diff --git a/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..463b10101 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md @@ -0,0 +1,71 @@ +# Manage Notification Methods + +From the Cloud interface, you can manage your Space's notification settings as well as allow users to personalize their notification settings. + +## Manage Space Notification Settings + +### Prerequisites + +To manage Space notification settings, you will need the following: + +- A Netdata Cloud account +- Access to the Space as an **administrator** + +### Available Actions per Notification Method Based on Service Level + +| **Action** | **Personal Service Level** | **System Service Level** | +|:------------------------------------------------|:--------------------------:|:------------------------:| +| Enable / Disable | X | X | +| Edit | | X | +| Delete | X | X | +| Add multiple configurations for the same method | | X | + +> **Notes** +> +> - For Netdata provided ones, you can't delete the existing notification method configuration. +> - Enable, Edit, and Add actions over specific notification methods will only be allowed if your plan has access to those ([service classification](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md#service-classification)). + +### Steps + +1. Click on the **Space settings** cog (located above your profile icon). +2. Click on the **Alerts & Notifications** tab on the left-hand side. +3. Click on the **Notification Methods** tab. +4. You will be presented with a table of the configured notification methods for the Space. You will be able to: + 1. **Add a new** notification method configuration. + - Choose the service from the list of available ones. The available options will depend on your subscription plan. + - You can optionally provide a name for the configuration so you can easily refer to it. + - You can define the filtering criteria, regarding which Rooms the method will apply, and what notifications you want to receive (All Alerts and unreachable, All Alerts, Critical only). + - Depending on the service, different inputs will be present. Please note that there are mandatory and optional inputs. + - If you have doubts on how to configure the service, you can find a link at the top of the modal that takes you to the specific documentation page to help you. + 2. **Edit an existing** notification method configuration. Personal level ones can't be edited here, see [Manage User Notification Settings](#manage-user-notification-settings). You will be able to change: + - The name provided for it + - Filtering criteria + - Service-specific inputs + 3. **Enable/Disable** a given notification method configuration. + - Use the toggle to enable or disable the notification method configuration. + 4. **Delete an existing** notification method configuration. Netdata provided ones can't be deleted, e.g., Email. + - Use the trash icon to delete your configuration. + +## Manage User Notification Settings + +### Prerequisites + +To manage user-specific notification settings, you will need the following: + +- A Cloud account +- Access to, at least, a Space + +Note: If an administrator has disabled a Personal [service level](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md#service-level) notification method, this will override any user-specific setting. + +### Steps + +1. Click on the **User notification settings** shortcut on top of the help button. +2. You are presented with: + - The Personal [service level](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md#service-level) notification methods you can manage. + - The list of Spaces and Rooms inside those where you have access to. +3. On this modal you will be able to: + 1. **Enable/Disable** the notification method for you; this applies across all Spaces and Rooms. + - Use the toggle to enable or disable the notification method. + 2. **Define what notifications you want** per Space/Room: All Alerts and unreachable, All Alerts, Critical only, or No notifications. + 3. **Activate notifications** for a Room you aren't a member of. + - From the **All Rooms** tab, click on the Join button for the Room(s) you want. diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md deleted file mode 100644 index af7b0df82..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,38 +0,0 @@ -# Accessing Netdata Dashboards - -This section contains documentation on how you can access the Netdata dashboard, which are the same both for the Agent and Cloud. - -A user accessing the Netdata dashboard **from the Cloud** will always be presented with the latest Netdata dashboard version. - -A user accessing the Netdata dashboard **from the Agent** will, by default, be presented with the latest Netdata dashboard version (the same as Netdata Cloud) except in the following scenarios: -* Agent doesn't have Internet access, and is unable to get the latest Netdata dashboards, as a result it falls back to the Netdata dashboard version that -was shipped with the agent. -* Users have defined, e.g. through URL bookmark, that they want to see the previous version of the dashboard (accessible `http://NODE:19999/v1`, replacing `NODE` with the IP address or hostname of your Agent). - -## Main sections - -The Netdata dashboard consists of the following main sections: -* [Netdata charts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) -* [Infrastructure Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md) -* [Nodes view](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md) -* [Custom dashboards](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/visualizations/custom-dashboards) -* [Alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md) -* [Anomaly Advisor](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md) -* [Functions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md) -* [Events feed](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md) - -> ⚠️ Some sections of the dashboard, when accessed through the agent, may require the user to be signed in to Netdata Cloud or having the Agent claimed to Netdata Cloud for their full functionality. Examples include saving visualization settings on charts or custom dashboards, claiming the node to Netdata Cloud, or executing functions on an Agent. - -## How to access the dashboards? - -### Netdata Cloud - -You can access the dashboard at https://app.netdata.cloud/ and [sign-in](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md) with an account or [sign-up](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md#dont-have-a-netdata-cloud-account-yet) if you don't have an account yet. - -### Netdata Agent - -Netdata starts a web server for its dashboard at port `19999`. Open up your web browser of choice and -navigate to `http://NODE:19999`, replacing `NODE` with the IP address or hostname of your Agent. If installed on localhost, you can access it through `http://localhost:19999`. - - -Documentation for previous Agent dashboard can still be found [here](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/gui/README.md).
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/install-netdata-on-embedded-systems.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/install-netdata-on-embedded-systems.md deleted file mode 100644 index dfaa4482c..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/install-netdata-on-embedded-systems.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Install Netdata on Embedded Systems Overview - -This section contains documentation for installation methods when it comes to Embedded Systems.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/install-with-a-cicd-provisioning-system.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/install-with-a-cicd-provisioning-system.md deleted file mode 100644 index 30a5a706c..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/install-with-a-cicd-provisioning-system.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Install with a CI/CD Provisioning System Overview - -This section contains documentation on all the installation methods through a CI/CD system.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/installation-overview.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/installation-overview.md deleted file mode 100644 index 703ca26b9..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/installation-overview.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,10 +0,0 @@ -# Installation - -In this category you can find instructions on all the possible ways you can install Netdata on the -[supported platforms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/versions-and-platforms.md). - -If this is your first time using Netdata, we recommend that you first start with the -[quick installation guide](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/packaging/installer/README.md) and then -go into the more advanced options available to you. - - diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/integrations-overview.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/integrations-overview.md deleted file mode 100644 index afd4cf306..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/integrations-overview.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,31 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Integrations" -sidebar_label: "Integrations" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/category-overview-pages/integrations-overview.md" -description: "Available integrations in Netdata" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_rel_path: "Integrations" -sidebar_position: 60 ---> - -# Integrations - -Netdata's ability to monitor out of the box every potentially useful aspect of a node's operation is unparalleled. -But Netdata also provides out of the box, meaningful charts and alerts for hundreds of applications, with the ability -to be easily extended to monitor anything. See the full list of Netdata's capabilities and how you can extend them in the -[supported collectors list](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md). - -Our out of the box alerts were created by expert professionals and have been validated on the field, countless times. -Use them to trigger [alert notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md) -either centrally, via the -[Cloud alert notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md) -, or by configuring individual -[agent notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/README.md). - -We designed Netdata with interoperability in mind. The Agent collects thousands of metrics every second, and then what -you do with them is up to you. You can -[store metrics in the database engine](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md), -or send them to another time series database for long-term storage or further analysis using -Netdata's [exporting engine](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/src/exporting/README.md). - - diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/logs.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/logs.md deleted file mode 100644 index fbaf85631..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/logs.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Logs - -This section talks about ways Netdata collects and visualizes logs, while also providing useful guides on log centralization setups that can be used with Netdata. diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/machine-learning-and-assisted-troubleshooting.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/machine-learning-and-assisted-troubleshooting.md index 9a0e4b381..f41089bba 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/machine-learning-and-assisted-troubleshooting.md +++ b/docs/category-overview-pages/machine-learning-and-assisted-troubleshooting.md @@ -1,97 +1,7 @@ # Machine Learning and Anomaly Detection -Machine learning (ML) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. +Netdata provides advanced Machine Learning features to help you identify and troubleshoot anomalies and unexpected behavior in your infrastructure before they become critical issues: -In observability, machine learning can be used to detect patterns and anomalies in large datasets, enabling users to identify potential issues before they become critical. - -Machine Learning for observability is usually misunderstood, and frequently leads to unrealistic expectations. Check for example the [presentation Google gave at SreCON19](https://www.usenix.org/conference/srecon19emea/presentation/underwood) explaining that all ideas that Google SREs and DevOps came up with, about the use of Machine Learning in observability were bad, and as Todd notes they should feel bad about it. - -At Netdata we are approaching machine learning in a completely different way. Instead of trying to make machine learning do something it cannot achieve, we tried to understand if and what useful insights it can provide and eventually we turned it to an assistant that can improve troubleshooting, reduce mean time to resolution and in many case prevent issues from escalating. - -## Design Principles - -The following are the high level design principles of Machine Learning in Netdata: - -1. **Unsupervised** - - In other words: whatever machine learning can do, it should do it by itself, without any help or assistance from users. - -2. **Real-time** - - We understand that Machine Learning will have some impact on resource utilization, especially in CPU utilization, but it shouldn't prevent Netdata from being real-time and high-fidelity. - -3. **Integrated** - - Everything achieved with machine learning should be tightly integrated to the infrastructure exploration and troubleshooting practices we are used to. - -4. **Assist, Advice, Consult** - - If we can't be sure that a decision made by Machine Learning is 100% accurate, we should use this to assist and consult users in their journey. - - In other words, we don't want to wake up someone at 3 AM, just because a machine learning model detected something. - -## Machine Learning per Time-Series - -Given the samples recently collected for a time-series, Machine Learning is used to detect if a sample just collected is an outlier or not. - -Since the query combinations are infinite, Netdata detects anomalies at the time-series level, and then combines the anomaly rates of all time-series involved in each query, to provide the anomaly rate for the query. - -When a collected sample is an outlier, we set the Anomaly Bit of the collected sample and we store it together with the sample value in the time-series database. - -## Multiple Machine Learning Models per Time-Series to Eliminate Noise - -Unsupervised machine learning has some noise, random false positives. - -To remove this noise, Netdata trains multiple machine learning models for each time-series, covering more than the last 2 days, in total. - -Netdata uses all of the available ML models to detect anomalies. So, all machine learning models of a time-series need to agree that a collected sample is an outlier, for it to be marked as an anomaly. - -This process removes 99% of the false positives, offering reliable unsupervised anomaly detection. - -## Node Level Anomaly - -When a metric becomes anomalous, in many cases a lot other metrics get anomalous too. - -For example, an anomaly on a web server may also introduce unusual network bandwidth, cpu usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, context switches, interrupts, etc. If the web server is serving an API that has an application server and a database server we may see anomalies being propagated to them too. - -To represent the spread of an anomaly in a node, Netdata computes a **Node Level Anomaly**. This is the percentage of the metrics of a node being concurrently anomalous, vs the total number of metrics of that node. - -## Node Anomaly Events - -Netdata produces a "node anomaly event" when a the percentage of concurrently anomalous time-series is high enough and persists over time. - -This anomaly event signals that there was sufficient evidence among all the time-series that some strange behavior might have been detected in a more global sense across the node. - -## What is the Anomaly Bit? - -Each sample collected, carries an Anomaly Bit. This bit (true/false) is set when the collected sample found to be an outlier, based on the machine learning models available for it so far. - -This bit is embedded into the custom floating point number the Netdata database uses, so it does not introduce any overheads in memory or disk footprint. - -The query engine of Netdata uses this bit to compute anomaly rates while it executes normal time-series queries. This eliminates to need for additional queries for anomaly rates, as all `/api/v2` time-series query include anomaly rate information. - -## What is the Anomaly Rate (AR)? - -The Anomaly Rate of a query, is a percentage, representing the number of samples in the query found anomalous, vs the total number of samples participating in the query. - -## How it works - a more technical presentation - -For each time-series Netdata trains every 3 hours, a `k-means clustering` model, using the last 6 hours of samples collected for it. - -Rather than using raw samples of each time-series, the model works on a preprocessed "feature vector" of recent smoothed and differenced values. - -This enables the model to detect a wider range of potentially anomalous patterns as opposed to just point anomalies like big spikes or drops. - -Some of the types of anomalies Netdata detects are: - -1. **Point Anomalies** or **Strange Points**: Single points that represent very big or very small values, not seen before (in some statistical sense). -2. **Contextual Anomalies** or **Strange Patterns**: Not strange points in their own, but unexpected sequences of points, given the history of the time-series. -3. **Collective Anomalies** or **Strange Multivariate Patterns**: Neither strange points nor strange patterns, but in global sense something looks off. -4. **Concept Drifts** or **Strange Trends**: A slow and steady drift to a new state. -5. **Change Point Detection** or **Strange Step**: A shift occurred and gradually a new normal is established. - -For a visual representation, check this infographic: - - - -A more detailed explanation can be found on [this (informal) presentation](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/18zkCvU3nKP-Bw_nQZuXTEa4PIVM6wppH3VUnAauq-RU/edit#slide=id.p). +- K-means clustering [Machine Learning models](/src/ml/README.md) are trained to power the [Anomaly Advisor](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/anomaly-advisor-tab.md) on the dashboard, which allows you to identify Anomalies in your infrastructure. +- [Metric Correlations](/docs/metric-correlations.md) are possible through the dashboard using the [Two-sample Kolmogorov Smirnov](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolmogorov%E2%80%93Smirnov_test#Two-sample_Kolmogorov%E2%80%93Smirnov_test) statistical test and Volume heuristic measures. +- The [Netdata Assistant](/docs/netdata-assistant.md) is able to answer your prompts when it comes to troubleshooting Alerts and Anomalies. diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/maintenance-operations-on-netdata-agents.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/maintenance-operations-on-netdata-agents.md index 207a0bd32..1867d863f 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/maintenance-operations-on-netdata-agents.md +++ b/docs/category-overview-pages/maintenance-operations-on-netdata-agents.md @@ -1,3 +1,8 @@ # Maintenance operations on Netdata Agents Overview -This section provides information on various actions you can take when maintaining a Netdata Agent.
\ No newline at end of file +This section provides information on various actions you can take while maintaining a Netdata Agent. + +- [Starting and Stopping Netdata Agents](/docs/netdata-agent/start-stop-restart.md) +- [Update Netdata Agents](/packaging/installer/UPDATE.md) +- [Reinstall Netdata Agents](/packaging/installer/REINSTALL.md) +- [Uninstall Netdata Agents](/packaging/installer/UNINSTALL.md) diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/metrics-streaming-and-replication.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/metrics-streaming-and-replication.md deleted file mode 100644 index f473105fd..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/metrics-streaming-and-replication.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,175 +0,0 @@ -# Netdata Parents (Streaming and Replication) - -## What are they and why do we need them? - -A “Parent” is a Netdata Agent, like the ones we install on all our systems, but is configured as a central node that receives, stores and processes metrics data from other Netdata “Child” nodes in our infrastructure. - -Netdata Parents are flexible. You can have one big active-active cluster of Netdata Parents, or you can spread a lot of independent Parents across the infrastructure. - -This “distributed still centralized” setup provides a lot of benefits. Let’s see them: - -## Infrastructure-Level Dashboards: All Nodes in One Dashboard - -A Parent node receives and aggregates metrics data from all child nodes that push metrics to it, presenting all of them on a single, centralized dashboard. - -Metrics streaming between Netdata nodes is real-time and low-latency, so that the Parent can provide the same resolution and detail its children provide. - -Each chart on the Parent’s dashboard is automatically turned into a multi-node chart, allowing instant aggregation of the data across the entire dashboard. This is transparent and automatic for all kinds of charts, even application-specific ones. For example, when you have 2 PostgreSQL servers in your infrastructure, the parent will present one set of charts for PostgreSQL and these charts will include data from both servers. - -## Increased Data Retention: Store More, Learn More - -Netdata’s database (`dbengine`), supports multiple tiers of variable resolution for storing metrics’ samples. Tier 0 is the high-resolution one and usually stores per second data. Tier 1 is the middle resolution one, downsampling data to per minute. Tier 2 is the low-resolution one, downsampling data to per hour. With this setup, a default Netdata setup is usually able to maintain 2-3 days of high resolution and up to a year of low-resolution data, all in less than 1 GB of disk space. - -In many cases, however, organizations require a lot more retention than this. A Netdata Parent can be configured to have weeks or even months of high-resolution data and several years of low-resolution data for all its Child nodes, by allowing the Netdata database to grow to hundreds of GiBs or even several TiBs. - -## Monitoring Ephemeral Nodes: No Node Left Behind - -Production systems are often ephemeral by nature. In containerized and orchestrated environments, like Kubernetes, nodes may come and go due to scaling policies, maintenance tasks, or as part of regular operations. - -Netdata Parents come to the rescue in such scenarios. They can continuously receive metrics from ephemeral nodes during their lifecycle. As these nodes are removed or replaced, the Parent retains their performance history, essentially archiving the life of each node. - -The Netdata dashboards on the Parents automatically bring into the charts data from archived nodes when users pan the dashboard to the time-window these nodes were alive. This means that no data is lost and visibility is maintained across the entire lifespan of every node, regardless of its ephemeral nature. - -## Unified Alerts Management: Silence the Noise - -Each Netdata Agent is able to run health checks, trigger alerts and send notifications on its own. However, in a large-scale infrastructure with numerous nodes, each capable of generating alerts, managing these notifications can quickly become a challenge. Duplicate alerts and non-centralized management can lead to unnecessary noise, causing alert fatigue and possibly overlooking critical warnings. - -Netdata Parents provide a solution to this problem. By configuring a Parent node to handle all alerts and health checks, and disabling health monitoring on the Child nodes, you centralize your alerts management, meaning that all alerts are now generated from a single place, reducing noise and ensuring that each unique issue only triggers a single notification. - -In addition to making alert management more straightforward, this setup also allows for more refined control over your alert configurations. Instead of managing alert settings across multiple nodes, you can handle all configurations in one place, ensuring consistency and ease of management. - -## Offloading Production Systems: Prioritize Performance - -In a production environment, every bit of system resources is crucial. Minimizing the overhead due to monitoring and observability is vital to ensure optimal system performance. Although the Netdata Agent is designed to be lightweight and efficient, using a Netdata Parent can allow the Netdata Agents on your production systems to focus on the absolutely necessary for collecting metrics and pushing them to their Parent. - -On your production systems, by configuring the Netdata Agents to use the `alloc` database mode with 5-10 minutes of retention time and disabling health monitoring and Machine Learning (ML) processing, you significantly reduce the system resources consumed by the monitoring system. - -Netdata, with the `alloc` database mode, doesn't touch the disk at all (apart from logging - which can also be disabled). This approach eliminates any potential disk I/O impact from Netdata on your production applications, which could be particularly beneficial in I/O-sensitive environments. - -## Fault Tolerance and Redundancy: Ensure Continuous Monitoring - -Netdata Agents stream metrics to one Netdata Parent at a time. But more than one Parent can be configured on each child. The first available at any given time is used. - -Similarly, Netdata Parents can be configured to stream/proxy the data they receive to another Netdata Parent. And they can support multiple Parents too, one of which will be used at any given time. - -Configuration allows setting up a circular streaming setup. Parent A streams to Parent B and Parent B streams to Parent A. Child nodes are configured to stream to any of Parents A and B and they will automatically fall back and switch parents as necessary. - -With the replication feature (enabled by default), all nodes replicate missing data on their Parent, before streaming live metrics, filling up any gap the Parent may have. - -The same setup can work for 2 or even more parents, to form an active-active multi-node cluster. Child nodes can connect to any of the parent nodes available and the parent nodes will automatically replicate and stream metrics to each other. - -The setup is optimized even for wide-area connections between child nodes and parents, or for cases where the bandwidth between child nodes and parents has a cost associated with it. At any given time each child node sends its data only once. The parents then replicate and stream this data to each other. - -## Security and Isolation: Protect Your Production Systems - -Parent nodes can be set up in your organization's Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), acting as a protective barrier or application firewall, shielding your production Netdata agents from the outside world. - -With Netdata Parents configured, the Netdata Agents running on your production systems need only one connection to these parents. They don’t need to run data queries, they will never send alert notifications, or even connect to Netdata Cloud. - -Especially for Netdata Cloud, when the Parent node is connected to Netdata Cloud, it registers its Child nodes to it and can serve all functions required by the Cloud on behalf of the Child nodes. So, although only the parent is connected to Netdata Cloud, there is no difference in the user features you enjoy on Netdata Cloud in regard to your production systems. They will all be there. - -## FAQ about Netdata Parents - -### How much can a Parent node scale? - -For about 1 million real-time metrics, with a default configuration: - -- collected and streamed to it per second, -- stored in 3 database tiers (high, mid, low resolution), -- with ML training and anomaly detection running, -- health for alerts and notifications - -And about 2 TiB of storage for metrics, you will need about 5-8 CPU cores and 32GiB of RAM. On such a setup you can have: - -- 15 days of high resolution metrics -- 3 months of mid resolution metrics -- 1 year of low resolution metrics - -For such a setup, we recommend a 16 CPU cores system so that there is spare capacity for queries. More RAM and faster disks will give faster queries. - -So, depending on the number of metrics per node you have and the size of your Parents, you may be able to aggregate 200 to 500 nodes per Parent. - -### If I set up 2 active-active parents, will I be able to have more Child nodes stream to them? - -No. When you set up an active-active cluster, even if child nodes connect randomly to one or the other, all the parent nodes receive all the metrics of all the child nodes. So, all of them do all the work. - -There is a feature we currently work on, to allow Parent nodes to detect that they receive ML information with the streamed metric data (they receive it already but they ignore it), to prevent them from training their own ML models and running anomaly detection again for the child node. But this is not ready yet. - -### How much retention do the child nodes need? - -Child nodes need to have only the retention required in order to connect to another Parent if one fails or stops for maintenance. - -- If you have an active-active cluster of parents, 5 to 10 minutes in `alloc` mode is enough. -- If you have only 1 parent, it would be better to run the child nodes with `dbengine` so that they will have enough retention to backfill the parent nodes if it stops for a few hours for maintenance. - -### Does streaming between child nodes and parents support encryption? - -Yes. You can configure your parent nodes to enable TLS and configure the child nodes to connect with TLS to it. The streaming connection is also compressed with LZ4 and this works even on top of TLS. - -### Can I have an HTTP proxy between parent and child nodes? - -No. The streaming protocol works on the same port as the internal web server of Netdata Agents, but the protocol is not HTTP-friendly and cannot be understood by HTTP proxy servers. - -### Should I load balance the parents with a TCP load balancer? - -Although this can be done and for streaming between child and parent nodes it could work, we recommend not doing it. It can lead to several kinds of problems. - -It is better to configure all the parent nodes directly in the child nodes `stream.conf`. The child nodes will do everything in their power to find a parent node to connect and they will never give up. - -### When I have an active-active cluster of parents, will I receive alert notifications from both of them? - -If both are configured to run health checks and trigger alerts, yes. - -We recommend using Netdata Cloud to avoid receiving duplicate alert notifications. Netdata Cloud deduplicates alert notifications so that you will receive them only once. On top of that, you can control silencing and routing directly from the Netdata Cloud UI. - -### When I have only Parents connected to Netdata Cloud, will I be able to use the Functions feature on my child nodes? - -Yes. - -Functions is a feature of data collection plugins to expose functions that can be run from the dashboard to view more detailed information about a data collection. For example, apps.plugin exposes the processes function that returns a list of all the processes running, together with information about their CPU utilization, memory consumption, disk I/O operations, bandwidth, and a lot more. - -When a parent receives a Function request, it forwards it to the plugin that exposes it. If the plugin is available over a streaming connection, the parent will forward the request to the socket it receives metrics from. This process will be repeated even if many parents are chained in order to reach the child. - -### If I have a set of 2 active-active parents and get one out for maintenance for a few hours, will it have missing data when it returns back online? - -There are 2 reasons you may have gaps in your data after you bring it back online: - -1. Replication does not replicate metrics that are not actively collected. So, when the parent comes back, if there are samples that this parent does not have, for metrics that are not currently being collected, these samples will not be propagated to that parent. [We are working to fix this issue](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/issues/15198). -2. If the parent has been offline for a long time and the child nodes run in db mode `alloc`, you need to plan how you will bring this parent back online. Child nodes in this mode do not have enough retention to backfill the parent and if they connect to it before the other parent, you will end up with missing information on that parent. - -The simplest way to solve this is to block at the firewall all connections to port 19999 from child nodes, but allow connections from the other parent nodes. Once replication finishes for all nodes, you can unblock the connections from child nodes to it. - -### I got a parent out of maintenance but it replicates (backfills) missing data slowly. Can I speed it up? - -Yes, there is a setting on `netdata.conf` under section `[db]` called `replication threads`. The default value is 1. - -Usually, each thread is able to replicate about 2-5 million samples per second. We suggest setting this to 5 threads for all parents. Generally do not use too many threads because you are risking congesting the disks and/or the CPU cores available. Keep in mind that the sending parent needs this setting. - -There is no need to increase this number on child nodes. Each node has one replication sender, so when hundreds of nodes are replicating to a parent, there are already a lot of senders pushing metrics to it. - -### I have multiple active-active parents. Which one is used by Netdata Cloud for queries? - -When you have multiple parents available, the one that is further away from the child node is used by Netdata Cloud, unless it does not have the data required. - -This works like this: The child has `hops = 0`. Each parent receiving metrics for this child increases the `hops` by 1. So the first parent will have `hops = 1`, the second parent will have `hops = 2` and so on. - -Netdata Cloud knows the retention of each parent. So, when it needs data from this child, it first checks the available retention each parent has for it and then it uses the parent with the higher `hops`. If no parent is available and the child node is directly connected to Netdata Cloud, it uses the child. - -### Is there a way to balance child nodes to the parent nodes of an active-active cluster? - -If you have 2 parent nodes A and B, you can configure them on half the child nodes as A, B, and the other half as B, A. The child nodes will connect to the first available (left to right). If both A and B are online, half of the child nodes will connect to A and the other half to B. - -Keep in mind, however, that if you restart a parent, all the child nodes that were connected to it will automatically reconnect to the other parent. Once this happens, the child nodes will stay connected to it. - -### Is there a way to get notified when a child gets disconnected? - -There are 2 kinds of production nodes: -1. **Permanent nodes** - These are nodes that should be available permanently and if they disconnect an alert should be triggered to notify you. - By default, all nodes are considered permanent (not ephemeral). -2. **Ephemeral nodes** - These are nodes that are ephemeral by nature and they may shutdown at any point in time without any impact on the services you run. - -To set the ephemeral flag on a node, edit its `netdata.conf` and in the `[health]` section set is `ephemeral = yes`. This setting is propagated to parent nodes and Netdata Cloud. - -When using Netdata Cloud (via a parent or directly) and a permanent node gets disconnected, Netdata Cloud sends node disconnection notifications. diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/misc-overview.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/misc-overview.md deleted file mode 100644 index dbb11e9bc..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/misc-overview.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Miscellaneous material - -This section contains material that will be moved to new locations as we see fit. We keep it here to make it accessible while we make these changes.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/monitor-your-infrastructure.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/monitor-your-infrastructure.md deleted file mode 100644 index 3582e88a6..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/monitor-your-infrastructure.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Monitor your Infrastructure Overview - -This section contains documentation on how you can use Netdata Cloud and it's features to monitor your entire infrastructure.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-apis.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-apis.md deleted file mode 100644 index 82d1c1752..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-apis.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,5 +0,0 @@ -# Netdata APIs Overview - -This section contains information about Netdata's APIs. - -You can access the Netdata Agent's API through swagger UI [here](/api).
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-architecture.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-architecture.md deleted file mode 100644 index 70f126597..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-architecture.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Netdata Architecture Overview - -This section's purpose is to explain the architecture of Netdata, the role of the Agent and the Cloud, and more.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-dashboards-and-visualizations.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-dashboards-and-visualizations.md deleted file mode 100644 index cc9304365..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/netdata-dashboards-and-visualizations.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,3 +0,0 @@ -# Netdata Dashboards and Visualizations Overview - -This section provides documentation about all the visualization operations, features and insights that Netdata provides.
\ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/troubleshooting-overview.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/troubleshooting-overview.md deleted file mode 100644 index 60406edd6..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/troubleshooting-overview.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,5 +0,0 @@ -# Troubleshooting and machine learning - -In this section you can learn about Netdata's advanced tools that can assist you in troubleshooting issues with -your infrastructure, to facilitate the identification of a root cause. - diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/visualizations-overview.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/visualizations-overview.md deleted file mode 100644 index d07af062c..000000000 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/visualizations-overview.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,4 +0,0 @@ -# Visualizations, charts and dashboards - -In this section you can learn about the various ways Netdata visualizes the collected metrics at an infrastructure level with Netdata Cloud -and at a single node level, with the Netdata Agent Dashboard. diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/working-with-logs.md b/docs/category-overview-pages/working-with-logs.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..e1f027529 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/category-overview-pages/working-with-logs.md @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +# Working with Logs + +This section talks about ways Netdata collects and visualizes logs. + +The [systemd journal plugin](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/) is the core Netdata component for reading systemd journal logs. + +For structured logs, Netdata provides tools like [log2journal](/src/collectors/log2journal/README.md) and [systemd-cat-native](/src/libnetdata/log/systemd-cat-native.md) to convert them into compatible systemd journal entries. + +You can also find useful guides on how to set up log centralization points in the [Observability Cetralization Points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md) section of our docs. diff --git a/docs/cloud/alerts-configuration-manager.md b/docs/cloud/alerts-configuration-manager.md deleted file mode 100644 index cedae0eb4..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/alerts-configuration-manager.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,71 +0,0 @@ -# Creating Alerts with Netdata Alerts Configuration Manager - -The Netdata Alerts Configuration Manager enables users with [Business subscriptions](https://www.netdata.cloud/pricing/) to create alerts from the Netdata Dashboard with an intuitive user interface. - -## Using Alerts Configuration Manager - -1. Go to the **Metrics** tab and navigate to the chart you want to configure an alert for. - -2. Click the **Alert icon** on the top right corner of the chart. - <!--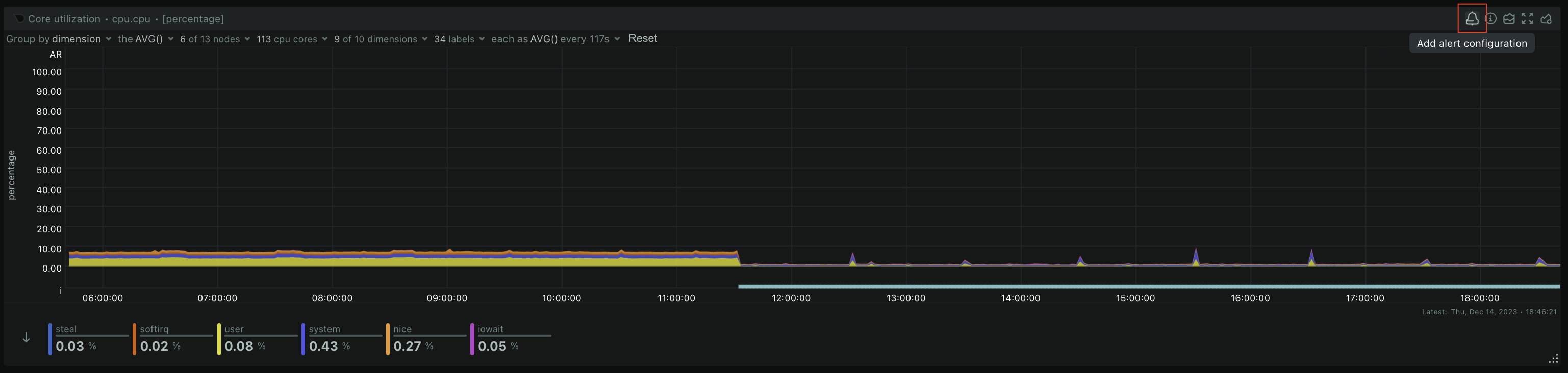--> - -3. The Alert Configuration Manager will open up with the default thresholds. You can modify the configuration as required and the alert definition on the right will be updated dynamically. - <!--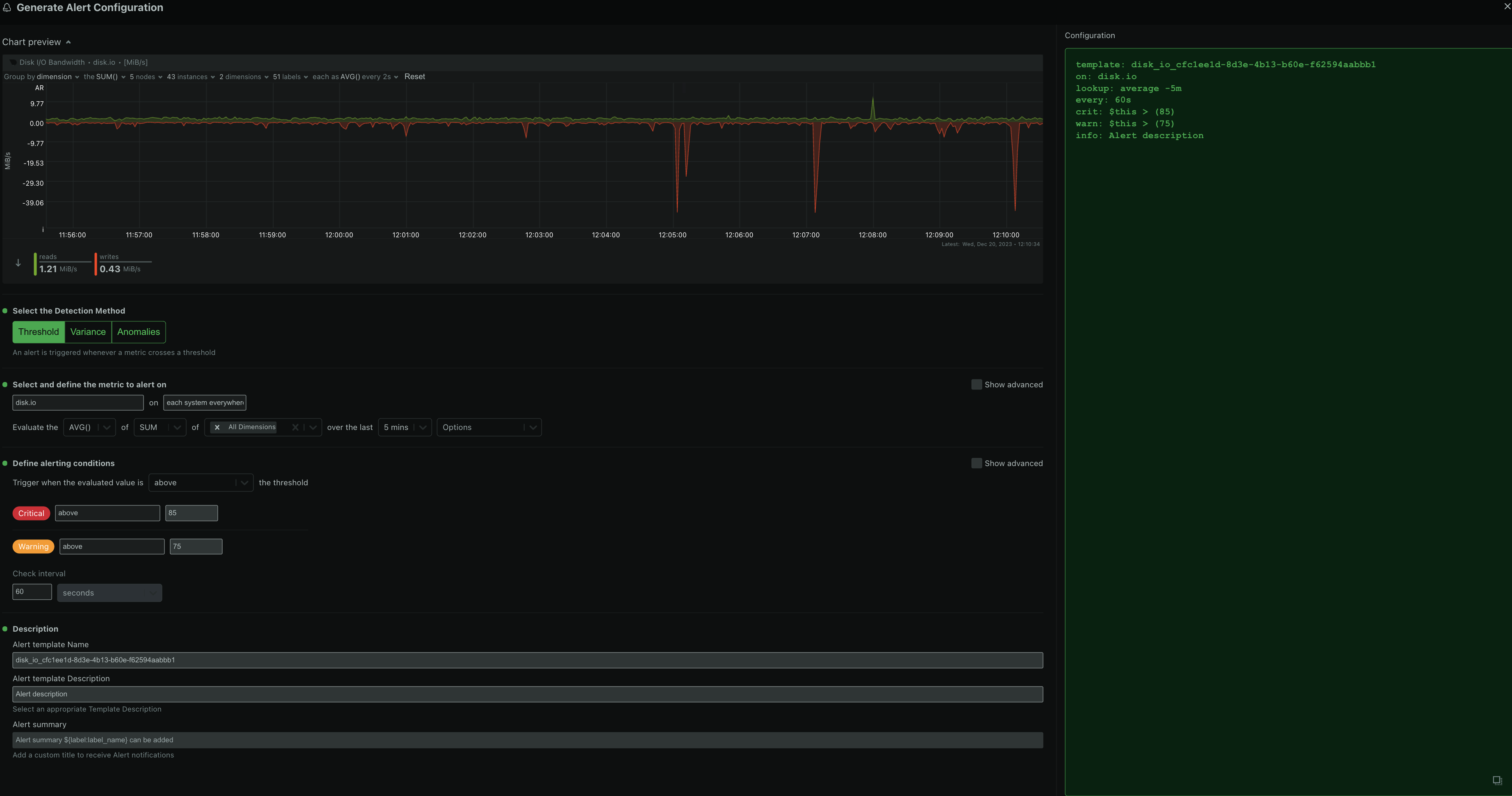--> - -4. If you want more fine-grained control or access to more advanced settings, enable **Show advanced** - <!--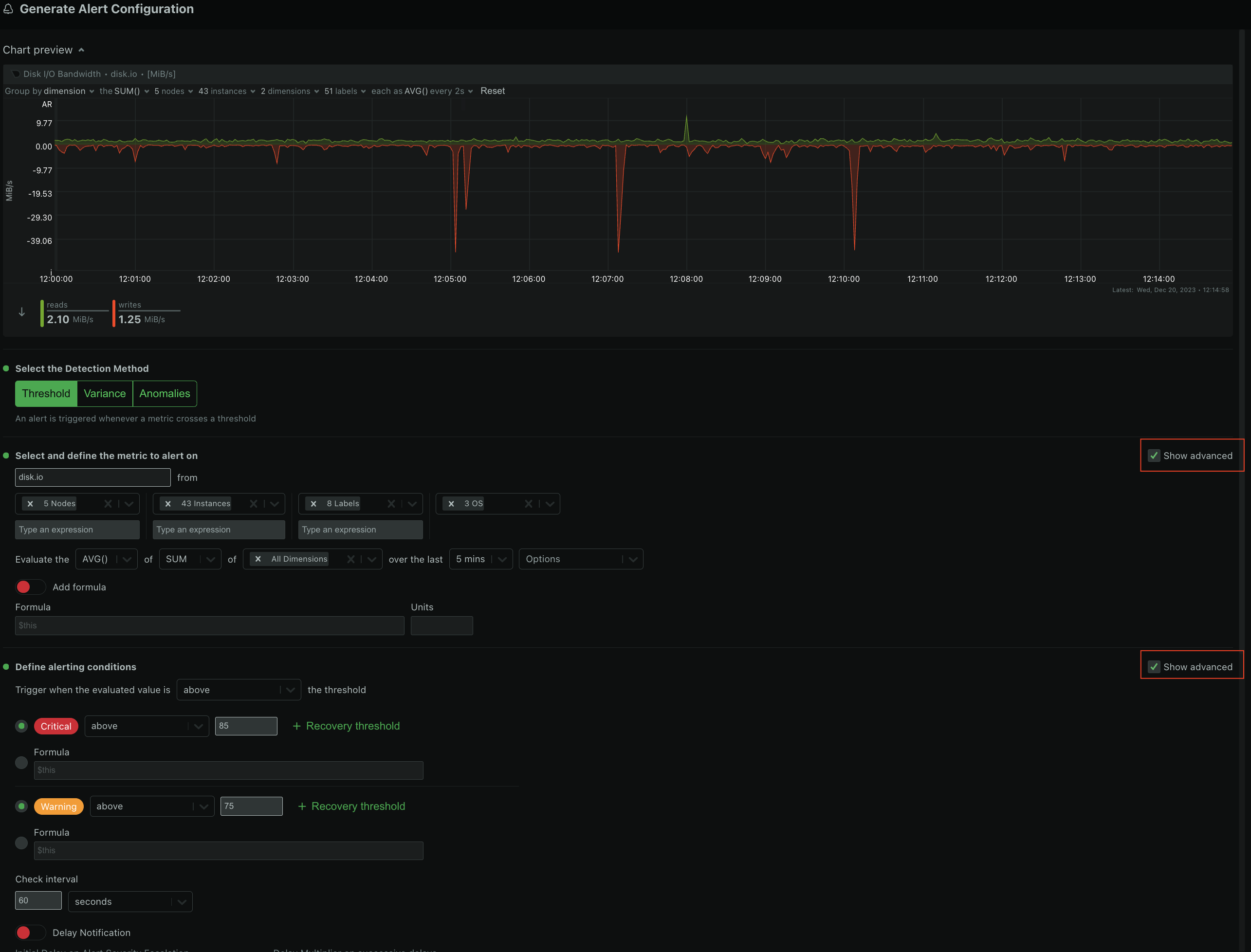--> - -5. Copy the alert definition that is generated in the code box and add it to an existing [health configuration file](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#edit-health-configuration-files) or a new custom file under `<path to netdata install>/etc/netdata/health.d/` on a Parent Agent or a Standalone Child Agent. - <!----> - -6. Reload Netdata Alert Health checks `<path to netdata install>/usr/sbin/netdatacli reload-health` and the new alert is now configured. - - -## Alerts Configuration Manager Sections - -- **Alert Detection Method** - <!----> - An alert is triggered whenever a metric crosses a threshold: - - Based on a standard `threshold` - - Based on metric `variance` - - Based on the `anomaly rate` of the metric - - -- **Metrics Lookup, Filtering and Formula Section** - <!----> - - - **Metrics Lookup**: This is the **Evaluate** line of fields in the modal and it defines the parameters for the database lookup that is needed to get the value that will be compared against the alert definition. It corresponds to the [`lookup`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-lookup) line of the Alert configuration file. The Alerts Configuration Manager provides a default selection for the lookup and can be modified to suit your requirements. The parameters that can be modified are: - - METHOD (`avg`, `sum`, `min`, `max`, `cv`, `stddev`) - - COMPUTATION (sum of all dimensions or individually for each dimension) - - DIMENSIONS (All dimensions, or a selection of dimensions) - - DURATION (the period in time to run the lookup) - - OPTIONS (`absolute`, `unaligned`, `percentage`, `min2max`) - - - **Alert Filtering**: This functionality can be accessed through the **Show advanced** checkbox and it allows for filtering the alert health checks to be run only for specific components of the infrastructure. It helps in achieving a fine-grained configuration for any given alert. - - `HOSTS` / `NODES` - By default all hosts are selected. You can pick nodes from the dropdown list, or enter a wildcard matching a list of hosts that you want the alert health check to run on. This field corresponds to the [`hosts`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-hosts) line of the Alert configuration file. - - `INSTANCES` - All instances are selected by default. You can pick instances from the dropdown list, or enter a wildcard matching a list of instances that you want the alert health check to run on. This field corresponds to the [`charts`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-charts) line of the Alert configuration file. - - `CHART LABELS` - All chart labels are selected by default. You can pick a chart label from the dropdown list or enter a wildcard matching a list of chart labels that you want the alert health check to run on. This field corresponds to the [`chart labels`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-chart-labels) line of the Alert configuration file. - - `OS` - All Operating Systems are selected by default. You can choose which OS(s) an alert health check should run on. This field corresponds to the [`os`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-os) line of the Alert configuration file. - - - **Formula / Calculation**: This field is available through the **Show advanced** checkbox and it is used to define a formula to be run on top of the `lookup` value. The result of the lookup is available in the `$this` variable, and after the formula is run, the result is also stored in `$this` and can be accessed while setting the alert thresholds. This field corresponds to the [`calc`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-calc) line of the Alert configuration file. - -- **Alerting conditions** - <!----> - - **Warning and Critical Thresholds**: These fields are used to set the thresholds for the `Warning` and `Critical` alert states, while also having the option to set the condition for the alert to be raised if it is `above` or `below` the given threshold. If the advanced settings are selected, a **formula** option can also be used, to define a custom formula instead of a threshold. These fields correspond to the [`warn` and `crit`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-lines-warn-and-crit) lines of the Alert configuration file. - - **Recovery Thresholds**: This field is available through the **Show advanced** checkbox, and it is used to set the threshold that the metric value needs to meet to de-escalate from a given severity status, like `Critical to Warning` and from `Warning to Clear`. The logic is appended to the `warn` and `crit` lines of the Alert configuration file and resembles a one-line `IF-THEN-ELSE` clause. - - **Check Interval**: This field is used to define the frequency of the health check for the alert and corresponds to the [`every`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-every) line of the Alert configuration file. - - **Delay Notifications**: This field is available through the **Show advanced** checkbox and it is used to set delay parameters on notifications for an alert severity `escalation` or `de-escalation`. It corresponds to the [`delay`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-delay) line of the Alert configuration file. - - - **Agent Specific Options**: These options are only available on the `Netdata Agent` and not honored on `Netdata Cloud`. They can be accessed through the **Show advanced** checkbox. - <!----> - - **Repeat Notifications**: This field defines the repeat frequency for the alert notification when the alert is in either `warning` or `critical` status and corresponds to the [`repeat`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-repeat) line of the Alert configuration file. - - **Send to**: This field is used to define a user role to which the alert notifications will be sent. If set to `silent`, then the alert won't be sent to any role. It corresponds to the [`to`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-to) line of the Alert configuration file. - - **Custom Exec Script**: This field is used to define a custom script that will be executed when the alert is triggered (but needs to be carefully designed as it needs to call the `health_alarm_notify.sh` module) and corresponds to the [`exec`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-exec) line of the Alert configuration file. - -- **Alert Name, Description and Summary Section** - <!----> - - - **Alert Template Name**: This field uniquely identifies an alert and corresponds to the [`template`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-alarm-or-template) field of the Alert configuration file. - The Alerts Configuration Manager provides a default name for an Alert template but we recommend you modify this to have a meaningful name for your configured alert. - - **Alert Template Description**: This field provides a brief explanation of the alert and corresponds to the [`info`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-info) line of the Alert configuration file. - - **Alert Summary**: This field enables the users to create a custom title for the alert notification (via [Notification integrations](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/alerting/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications)) and corresponds to the [`summary`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-summary) line of the Alert configuration file. diff --git a/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md b/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md deleted file mode 100644 index b9806c6fa..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,58 +0,0 @@ -# Manage alert notification silencing rules - -From the Cloud interface, you can manage your space's alert notification silencing rules settings as well as allow users to define their personal ones. - -## Prerequisites - -To manage **space's alert notification silencing rule settings**, you will need the following: - -- A Netdata Cloud account -- Access to the space as an **administrator** or **manager** (**troubleshooters** can only view space rules) - - -To manage your **personal alert notification silencing rule settings**, you will need the following: - -- A Netdata Cloud account -- Access to the space with any roles except **billing** - -### Steps - -1. Click on the **Space settings** cog (located above your profile icon) -1. Click on the **Alert & Notification** tab on the left hand-side -1. Click on the **Notification Silencing Rules** tab -1. You will be presented with a table of the configured alert notification silencing rules for: - * the space (if aren't an **observer**) - * yourself - - You will be able to: - 1. **Add a new** alert notification silencing rule configuration. - - Choose if it applies to **All users** or **Myself** (All users is only available for **administrators** and **managers**) - - You need to provide a name for the configuration so you can easily refer to it - - Define criteria for Nodes: To which Rooms will this apply? What Nodes? Does it apply to host labels key-value pairs? - - Define criteria for Alerts: Which alert name is being targeted? What alert context? Will it apply to a specific alert role? - - Define when it will be applied: - - Immediately, from now till until it is turned off or until a specific duration (start and end date automatically set) - - Scheduled, you specify the start and end time for when the rule becomes active and then inactive (time is set according to your browser local timezone) - Note: You are only able to add a rule if your space is on a [paid plan](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md). - 1. **Edit an existing** alert notification silencing rule configurations. You will be able to change: - - The name provided for it - - Who it applies to - - Selection criteria for Nodes and Alert - - When it will be applied - 1. **Enable/Disable** a given alert notification silencing rule configuration. - - Use the toggle to enable or disable - 1. **Delete an existing** alert notification silencing rule. - - Use the trash icon to delete your configuration - -## Silencing rules examples - -| Rule name | War Rooms | Nodes | Host Label | Alert name | Alert context | Alert role | Description | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | :--| -| Space silencing | All Rooms | * | * | * | * | * | This rule silences the entire space, targets all nodes and for all users. E.g. infrastructure wide maintenance window. | -| DB Servers Rooms | PostgreSQL Servers | * | * | * | * | * | This rules silences the nodes in the room named PostgreSQL Servers, for example it doesn't silence the `All Nodes` room. E.g. My team with membership to this room doesn't want to receive notifications for these nodes. | -| Node child1 | All Rooms | `child1` | * | * | * | * | This rule silences all alert state transitions for node `child1` on all rooms and for all users. E.g. node could be going under maintenance. | -| Production nodes | All Rooms | * | `environment:production` | * | * | * | This rule silences all alert state transitions for nodes with the host label key-value pair `environment:production`. E.g. Maintenance window on nodes with specific host labels. | -| Third party maintenance | All Rooms | * | * | `httpcheck_posthog_netdata_cloud.request_status` | * | * | This rule silences this specific alert since third party partner will be undergoing maintenance. | -| Intended stress usage on CPU | All Rooms | * | * | * | `system.cpu` | * | This rule silences specific alerts across all nodes and their CPU cores. | -| Silence role webmaster | All Rooms | * | * | * | * | `webmaster` | This rule silences all alerts configured with the role `webmaster`. | -| Silence alert on node | All Rooms | `child1` | * | `httpcheck_posthog_netdata_cloud.request_status` | * | * | This rule silences the specific alert on the `child1` node. | diff --git a/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md b/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md deleted file mode 100644 index 87271bd6a..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,73 +0,0 @@ -# Manage notification methods - -From the Cloud interface, you can manage your space's notification settings as well as allow users to personalize their notifications setting - -## Manage space notification settings - -### Prerequisites - -To manage space notification settings, you will need the following: - -- A Netdata Cloud account -- Access to the space as an **administrator** - -### Available actions per notification methods based on service level - -| **Action** | **Personal service level** | **System service level** | -| :- | :-: | :-: | -| Enable / Disable | X | X | -| Edit | | X | | -| Delete | X | X | -| Add multiple configurations for same method | | X | - -Notes: -* For Netadata provided ones you can't delete the existing notification method configuration. -* Enable, Edit and Add actions over specific notification methods will only be allowed if your plan has access to those ([service classification](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#service-classification)) - -### Steps - -1. Click on the **Space settings** cog (located above your profile icon) -1. Click on the **Alerts & Notification** tab on the left hand-side -1. Click on the **Notification Methods** tab -1. You will be presented with a table of the configured notification methods for the space. You will be able to: - 1. **Add a new** notification method configuration. - - Choose the service from the list of the available ones, you'll may see a list of unavailable options if your plan doesn't allow some of them (you will see on the - card the plan level that allows a specific service) - - You can optionally provide a name for the configuration so you can easily refer to what it - - Define filtering criteria. To which Rooms will this apply? What notifications I want to receive? (All Alerts and unreachable, All Alerts, Critical only) - - Depending on the service different inputs will be present, please note that there are mandatory and optional inputs - - If you doubts on how to configure the service you can find a link at the top of the modal that takes you to the specific documentation page to help you - 1. **Edit an existing** notification method configuration. Personal level ones can't be edited here, see [Manage user notification settings](#manage-user-notification-settings). You will be able to change: - - The name provided for it - - Filtering criteria - - Service specific inputs - 1. **Enable/Disable** a given notification method configuration. - - Use the toggle to enable or disable the notification method configuration - 1. **Delete an existing** notification method configuration. Netdata provided ones can't be deleted, e.g. Email - - Use the trash icon to delete your configuration - -## Manage user notification settings - -### Prerequisites - -To manage user specific notification settings, you will need the following: - -- A Cloud account -- Have access to, at least, a space - -Note: If an administrator has disabled a Personal [service level](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#service-level) notification method this will override any user specific setting. - -### Steps - -1. Click on the **User notification settings** shortcut on top of the help button -1. You are presented with: - - The Personal [service level](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#service-level) notification methods you can manage - - The list spaces and rooms inside those where you have access to - - If you're an administrator, Manager or Troubleshooter you'll also see the Rooms from a space you don't have access to on **All Rooms** tab and you can activate notifications for them by joining the room -1. On this modal you will be able to: - 1. **Enable/Disable** the notification method for you, this applies accross all spaces and rooms - - Use the toggle enable or disable the notification method - 1. **Define what notifications you want** to per space/room: All Alerts and unreachable, All Alerts, Critical only or No notifications - 1. **Activate notifications** for a room you aren't a member of - - From the **All Rooms** tab click on the Join button for the room(s) you want - diff --git a/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md b/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md deleted file mode 100644 index 822fef01a..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,147 +0,0 @@ -# Cloud alert notifications - -import Callout from '@site/src/components/Callout' - -Netdata Cloud can send centralized alert notifications to your team whenever a node enters a warning, critical, or -unreachable state. By enabling notifications, you ensure no alert, on any node in your infrastructure, goes unnoticed by -you or your team. - -Having this information centralized helps you: -* Have a clear view of the health across your infrastructure, seeing all alerts in one place. -* Easily [set up your alert notification process](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md): -methods to use and where to use them, filtering rules, etc. -* Quickly troubleshoot using [Metric Correlations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md) -or [Anomaly Advisor](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md) - -If a node is getting disconnected often or has many alerts, we protect you and your team from alert fatigue by sending -you a flood protection notification. Getting one of these notifications is a good signal of health or performance issues -on that node. - -Admins must enable alert notifications for their [Space(s)](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#manage-space-notification-settings). All users in a -Space can then personalize their notifications settings from within their [account -menu](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/#manage-user-notification-settings). - -<Callout type="notice"> - -Centralized alert notifications from Netdata Cloud is a independent process from [notifications from -Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md). You can enable one or the other, or both, based on your needs. However, -the alerts you see in Netdata Cloud are based on those streamed from your Netdata-monitoring nodes. If you want to tweak -or add new alert that you see in Netdata Cloud, and receive via centralized alert notifications, you must -[configure](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md) each node's alert watchdog. - -</Callout> - -## Alert notifications - -Netdata Cloud can send centralized alert notifications to your team whenever a node enters a warning, critical, or unreachable state. By enabling notifications, -you ensure no alert, on any node in your infrastructure, goes unnoticed by you or your team. - -If a node is getting disconnected often or has many alerts, we protect you and your team from alert fatigue by sending you a flood protection notification. -Getting one of these notifications is a good signal of health or performance issues on that node. - -Alert notifications can be delivered through different methods, these can go from an Email sent from Netdata to the use of a 3rd party tool like PagerDuty. - -Notification methods are classified on two main attributes: -* Service level: Personal or System -* Service classification: Community or Business - -Only administrators are able to manage the space's alert notification settings. -All users in a Space can personalize their notifications settings, for Personal service level notification methods, from within their profile menu. - -> ⚠️ Netdata Cloud supports different notification methods and their availability will depend on the plan you are at. -> For more details check [Service classification](#service-classification) or [netdata.cloud/pricing](https://www.netdata.cloud/pricing). - -### Service level - -#### Personal - -The notifications methods classified as **Personal** are what we consider generic, meaning that these can't have specific rules for them set by the administrators. - -These notifications are sent to the destination of the channel which is a user-specific attribute, e.g. user's e-mail, and the users are the ones that will then be able to -manage what specific configurations they want for the Space / Room(s) and the desired Notification level, they can achieve this from their User Profile page under -**Notifications**. - -One example of such a notification method is the E-mail. - -#### System - -For **System** notification methods, the destination of the channel will be a target that usually isn't specific to a single user, e.g. slack channel. - -These notification methods allow for fine-grain rule settings to be done by administrators and more than one configuration can exist for them since. You can specify -different targets depending on Rooms or Notification level settings. - -Some examples of such notification methods are: Webhook, PagerDuty, Slack. - -### Service classification - -#### Community - -Notification methods classified as Community can be used by everyone independent on the plan your space is at. -These are: Email and discord - -#### Pro - -Notification methods classified as Pro are only available for **Pro** and **Business** plans -These are: webhook - -#### Business - -Notification methods classified as Business are only available for **Business** plans -These are: PagerDuty, Slack, Opsgenie - -## Silencing Alert notifications - -Netdata Cloud provides you a Silencing Rule engine which allows you to mute alert notifications. This muting action is specific to alert state transition notifications, it doesn't include node unreachable state transitions. - -The Silencing Rule engine is flexible and allows you to enter silence rules for the two main entities involved on alert notifications and can be set using different attributes. The main entities you can enter are **Nodes** and **Alerts** which can be used in combination or isolation to target specific needs - see some examples [here](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md#silencing-rules-examples). - -### Scope definition for Nodes -* **Space:** silencing the space, selecting `All Rooms`, silences all alert state transitions from any node claimed to the space. -* **War Room:** silencing a specific room will silence all alert state transitions from any node in that room. Please note if the node belongs to -another room which isn't silenced it can trigger alert notifications to the users with membership to that other room. -* **Node:** silencing a specific node can be done for the entire space, selecting `All Rooms`, or for specific war room(s). The main difference is -if the node should be silenced for the entire space or just for specific rooms (when specific rooms are selected only users with membership to that room won't receive notifications). - -### Scope definition for Alerts -* **Alert name:** silencing a specific alert name silences all alert state transitions for that specific alert. -* **Alert context:** silencing a specific alert context will silence all alert state transitions for alerts targeting that chart context, for more details check [alert configuration docs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-on). -* **Alert role:** silencing a specific alert role will silence all the alert state transitions for alerts that are configured to be specific role recipients, for more details check [alert configuration docs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-to). - -Beside the above two main entities there are another two important settings that you can define on a silencing rule: -* Who does the rule affect? **All user** in the space or **Myself** -* When does is to apply? **Immediately** or on a **Schedule** (when setting immediately you can set duration) - -For further help on setting alert notification silencing rules go to [Manage Alert Notification Silencing Rules](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md). - -> ⚠️ This feature is only available for [Netdata paid plans](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md). - -## Flood protection - -If a node has too many state changes like firing too many alerts or going from reachable to unreachable, Netdata Cloud -enables flood protection. As long as a node is in flood protection mode, Netdata Cloud does not send notifications about -this node. Even with flood protection active, it is possible to access the node directly, either via Netdata Cloud or -the local Agent dashboard at `http://NODE:19999`. - -## Anatomy of an alert notification - -Email alert notifications show the following information: - -- The Space's name -- The node's name -- Alert status: critical, warning, cleared -- Previous alert status -- Time at which the alert triggered -- Chart context that triggered the alert -- Name and information about the triggered alert -- Alert value -- Total number of warning and critical alerts on that node -- Threshold for triggering the given alert state -- Calculation or database lookups that Netdata uses to compute the value -- Source of the alert, including which file you can edit to configure this alert on an individual node - -Email notifications also feature a **Go to Node** button, which takes you directly to the offending chart for that node -within Cloud's embedded dashboards. - -Here's an example email notification for the `ram_available` chart, which is in a critical state: - -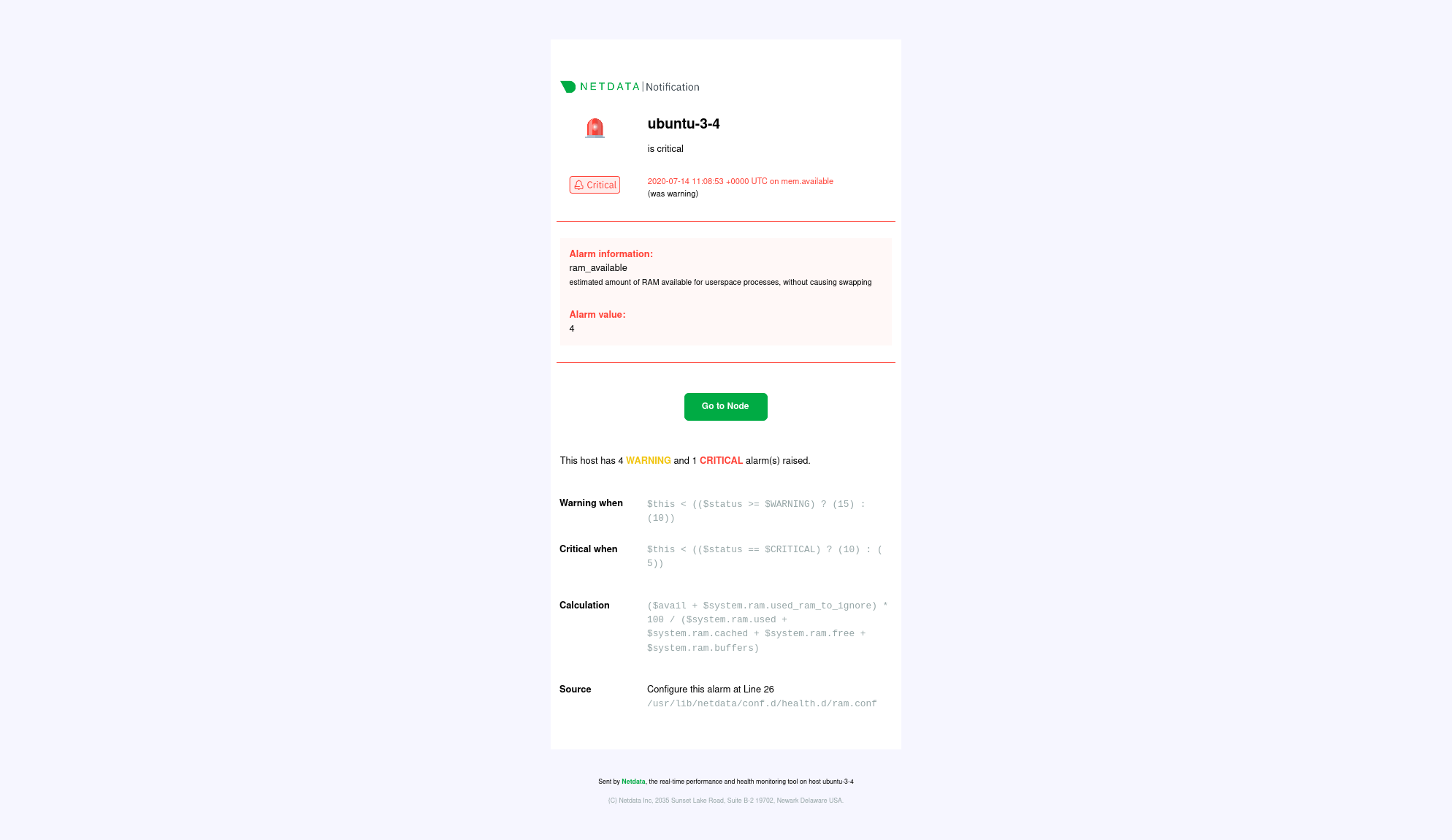 diff --git a/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md b/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md deleted file mode 100644 index 611ddc5e9..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,87 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Anomaly Advisor" -description: "Quickly find anomalous metrics anywhere in your infrastructure." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md" -sidebar_label: "Anomaly Advisor" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Tasks" -learn_rel_path: "Operations" ---> - -# Anomaly Advisor - -import ReactPlayer from 'react-player' - -The Anomaly Advisor feature lets you quickly surface potentially anomalous metrics and charts related to a particular highlight window of -interest. - -<ReactPlayer playing true controls true url='https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/24860547/165943403-1acb9759-7446-4704-8955-c566d04ad7ab.mp4' /> - -## Getting Started - -If you are running a Netdata version higher than `v1.35.0-29-nightly` you will be able to use the Anomaly Advisor out of the box with zero configuration. If you are on an earlier Netdata version you will need to first enable ML on your nodes by following the steps below. - -To enable the Anomaly Advisor you must first enable ML on your nodes via a small config change in `netdata.conf`. Once the anomaly detection models have trained on the Agent (with default settings this takes a couple of hours until enough data has been seen to train the models) you will then be able to enable the Anomaly Advisor feature in Netdata Cloud. - -### Enable ML on Netdata Agent - -To enable ML on your Netdata Agent, you need to edit the `[ml]` section in your `netdata.conf` to look something like the following example. - -```bash -[ml] - enabled = yes -``` - -At a minimum you just need to set `enabled = yes` to enable ML with default params. More details about configuration can be found in the [Netdata Agent ML docs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md#configuration). - -When you have finished your configuration, restart Netdata with a command like `sudo systemctl restart netdata` for the config changes to take effect. You can find more info on restarting Netdata [here](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation). - -After a brief delay, you should see the number of `trained` dimensions start to increase on the "dimensions" chart of the "Anomaly Detection" menu on the Overview page. By default the `minimum num samples to train = 3600` parameter means at least 1 hour of data is required to train initial models, but you could set this to `900` if you want to train initial models quicker but on less data. Over time, they will retrain on up to `maximum num samples to train = 14400` (4 hours by default), but you could increase this is you wanted to train on more data. - -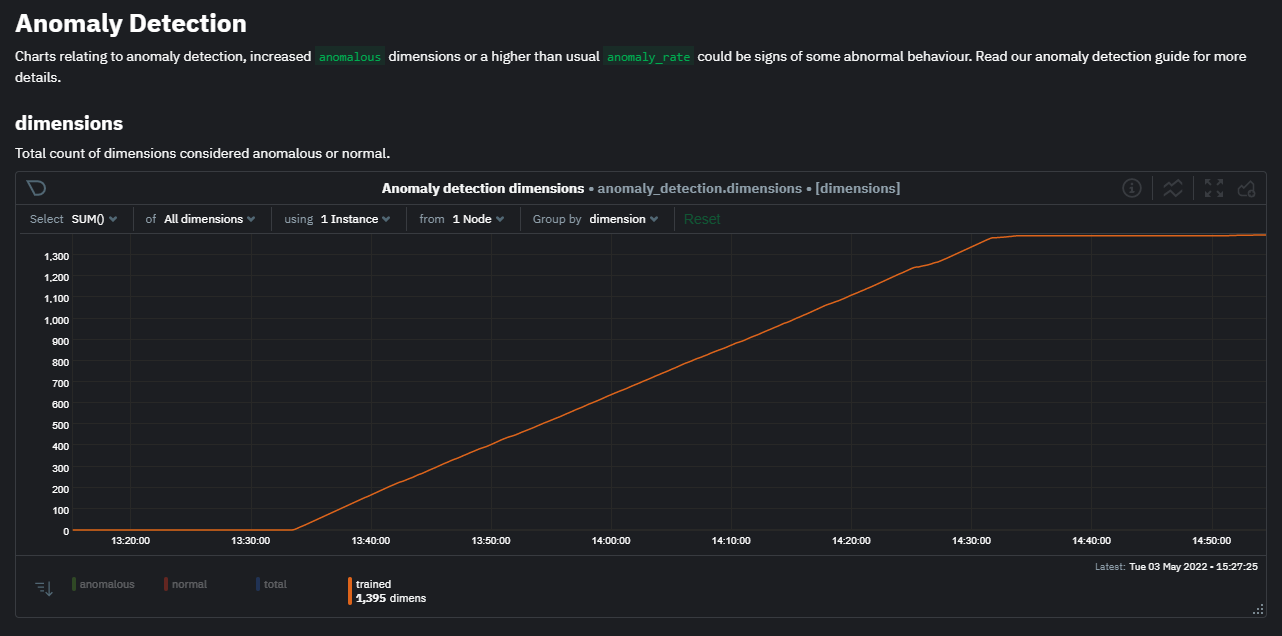 - -Once this line flattens out all configured metrics should have models trained and predicting anomaly scores each second, ready to be used by the new "anomalies" tab of the Anomaly Advisor. - -## Using Anomaly Advisor - -To use the Anomaly Advisor, go to the "anomalies" tab. Once you highlight a particular timeframe of interest, a selection of the most anomalous dimensions will appear below. - -The aim here is to surface the most anomalous metrics in the space or room for the highlighted window to try and cut down on the amount of manual searching required to get to the root cause of your issues. - -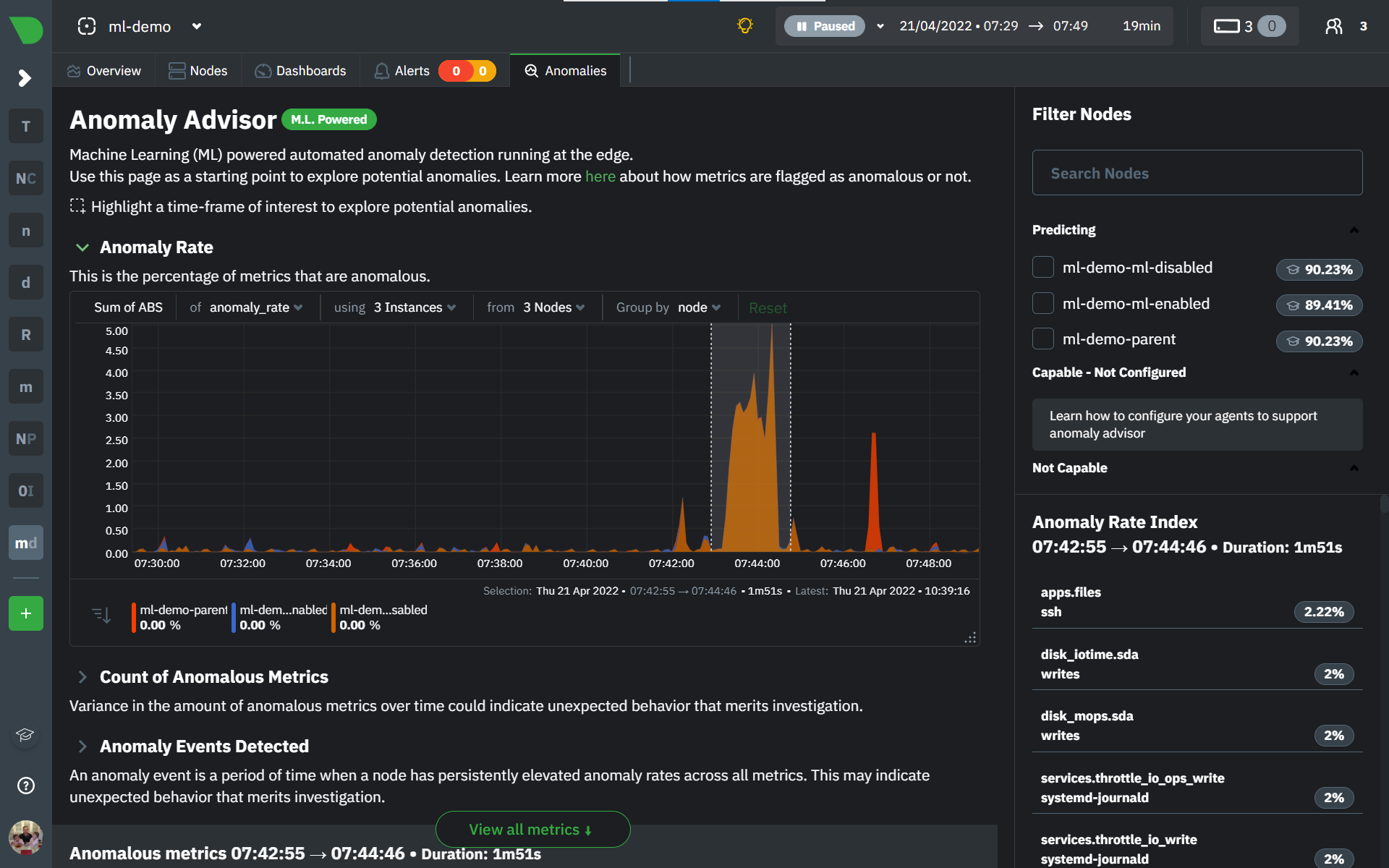 - -The "Anomaly Rate" chart shows the percentage of anomalous metrics over time per node. For example, in the following image, 3.21% of the metrics on the "ml-demo-ml-disabled" node were considered anomalous. This elevated anomaly rate could be a sign of something worth investigating. - -**Note**: in this example the anomaly rates for this node are actually being calculated on the parent it streams to, you can run ml on the Agent itselt or on a parent the Agent stream to. Read more about the various configuration options in the [Agent docs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md). - -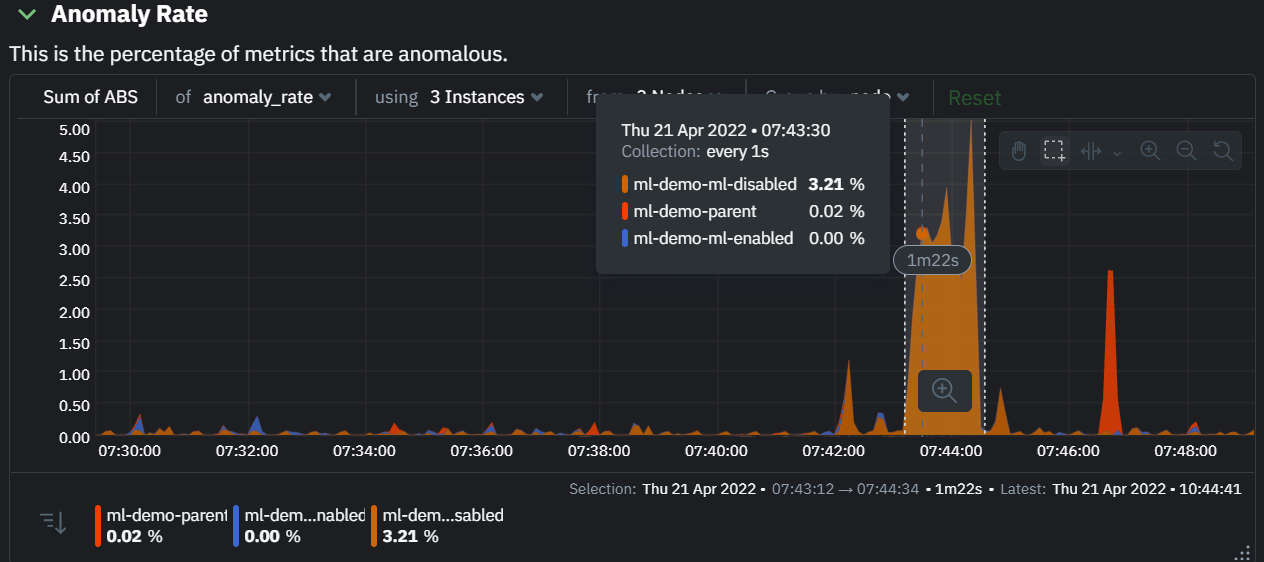 - -The "Count of Anomalous Metrics" chart (collapsed by default) shows raw counts of anomalous metrics per node so may often be similar to the anomaly rate chart, apart from where nodes may have different numbers of metrics. - -The "Anomaly Events Detected" chart (collapsed by default) shows if the anomaly rate per node was sufficiently elevated to trigger a node level anomaly. Anomaly events will appear slightly after the anomaly rate starts to increase in the timeline, this is because a significant number of metrics in the node need to be anomalous before an anomaly event is triggered. - -Once you have highlighted a window of interest, you should see an ordered list of anomaly rate sparklines in the "Anomalous metrics" section like below. - -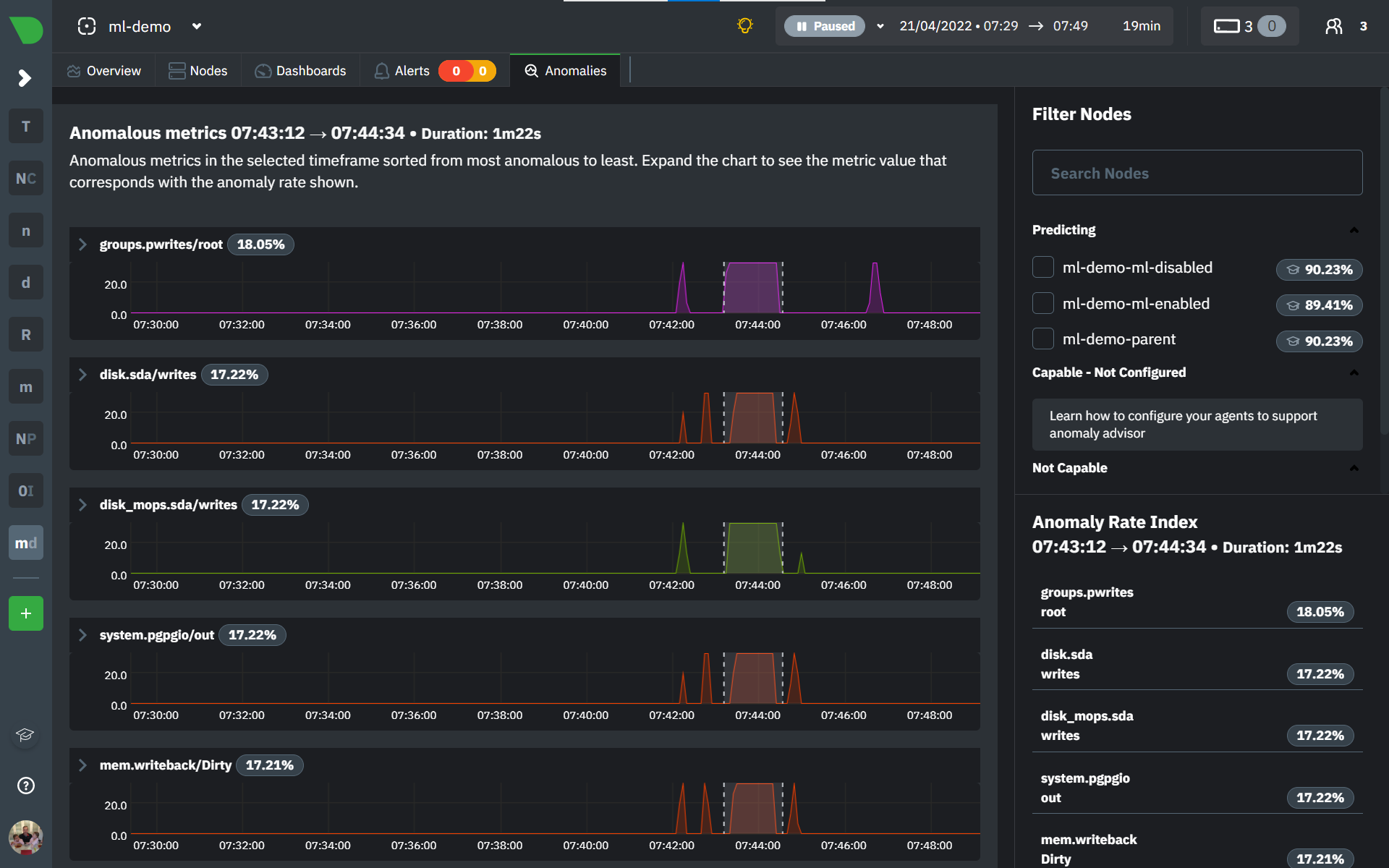 - -You can expand any sparkline chart to see the underlying raw data to see how it relates to the corresponding anomaly rate. - -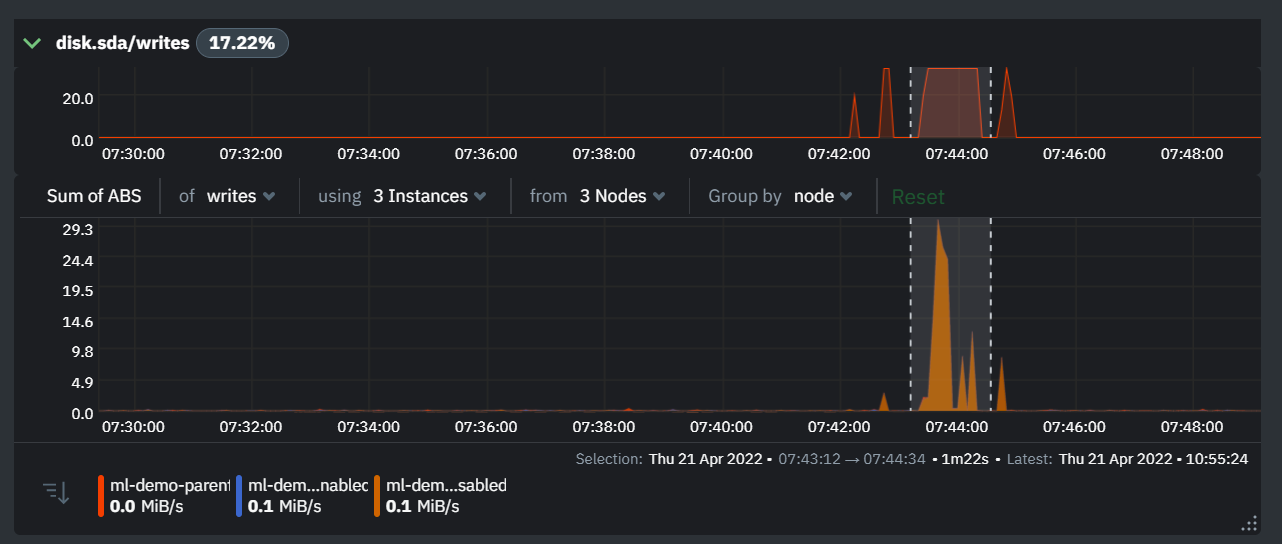 - -On the upper right hand side of the page you can select which nodes to filter on if you wish to do so. The ML training status of each node is also displayed. - -On the lower right hand side of the page an index of anomaly rates is displayed for the highlighted timeline of interest. The index is sorted from most anomalous metric (highest anomaly rate) to least (lowest anomaly rate). Clicking on an entry in the index will scroll the rest of the page to the corresponding anomaly rate sparkline for that metric. - -### Usage Tips - -- If you are interested in a subset of specific nodes then filtering to just those nodes before highlighting tends to give better results. This is because when you highlight a region, Netdata Cloud will ask the Agents for a ranking over all metrics so if you can filter this early to just the subset of nodes you are interested in, less 'averaging' will occur and so you might be a less noisy ranking. -- Ideally try and highlight close to a spike or window of interest so that the resulting ranking can narrow in more easily on the timeline you are interested in. - -You can read more detail on how anomaly detection in the Netdata Agent works in our [Agent docs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md). - -🚧 **Note**: This functionality is still **under active development** and considered experimental. We dogfood it internally and among early adopters within the Netdata community to build the feature. If you would like to get involved and help us with feedback, you can reach us through any of the following channels: - -- Email us at analytics-ml-team@netdata.cloud -- Comment on the [beta launch post](https://community.netdata.cloud/t/anomaly-advisor-beta-launch/2717) in the Netdata community -- Join us in the [🤖-ml-powered-monitoring](https://discord.gg/4eRSEUpJnc) channel of the Netdata discord. -- Or open a discussion in GitHub if that's more your thing diff --git a/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md b/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md deleted file mode 100644 index a56877ab1..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,99 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Events feed" -sidebar_label: "Events feed" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md" -sidebar_position: "2800" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Concepts" -learn_docs_purpose: "Present the Netdata Events feed." ---> - -# Events feed - -Netdata Cloud provides the Events feed which is a powerful feature that tracks events that happen on your infrastructure, or in your Space. The feed lets you investigate events that occurred in the past, which is invaluable for troubleshooting. Common use cases are ones like when a node goes offline, and you want to understand what events happened before that. A detailed event history can also assist in attributing sudden pattern changes in a time series to specific changes in your environment. - -## What are the available events? - -At a high-level view, these are the domains from which the Events feed will provide visibility into. - -> ⚠️ Based on your space's plan, different allowances are defined to query past data. - -| **Domains of events** | **Community** | **Pro** | **Business** | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | -| **[Auditing events](#auditing-events)** - <br/>Events related to actions done on your Space, e.g. invite user, change user role or change plan.| 4 hours | 7 days | 90 days | -| **[Topology events](#topology-events)**<br/>Node state transition events, e.g. live or offline.| 4 hours | 7 days | 14 days | -| **[Alert events](#alert-events)**<br/>Alert state transition events, can be seen as an alert history log.| 4 hours | 7 days | 90 days | - -### Auditing events - -| **Event name** | **Description** | **Example** | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | -| Space Created | The space was created.| Space `Acme Space` was **created** | -| Room Created | A room was created on the Space.| Room `DB Servers` was **created** by `John Doe` | -| Room Deleted | A room was deleted from the Space. | Room `DB servers` was **deleted** by `John Doe` | -| User Invited to Space | A user was invited to join the Space.| User `John Smith` was **invited** to this space by `Alan Doe` | -| User Uninvited from Space | An invitation for a user to join the space was revoked.| User `John Smith` was **uninvited** from this space | -| User Added to Space | A user was added to the Space from an invitation (user accepted the invitation).| User `John Smith` was **added** to this space by invite of `Alan Doe` | -| User Removed from Space | A user was added to the Space from an invitation. | User `John Smith` was **removed** from this space by `Alan Doe` | -| User Added to Room | A user was added to a room on the Space. | User `John Smith` was **added** to room `DB servers` | -| User Removed from Room | A user was removed from a room on the Space. | User `John Smith` was **removed** from room `DB Servers` by `Alan Doe` | -| User Space Properties Changed | The properties of a user on the Space have changed, e.g. change user role | User role for `John Smith` was **changed** to `troubleshooter` by `Alan Doe` | -| Node Added To Room | The node was added to a room on the Space. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **added** to room `DB Servers` by `John Doe` | -| Node Removed To Room | The node was removed from a room on the Space. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **removed** from room `DB Servers` by `John Doe` | -| Silencing Rule Created | A new alert notification silencing rule was created on the Space. | Silencing rule `DB Servers schedule silencing` on rooms `All nodes` and `DB Servers` was **created** by `John Smith` | -| Silencing Rule Changed | An existing alert notification silencing rule was modified on the Space. | Silencing rule `DB Servers schedule silencing` on rooms `All nodes` and `DB Servers` was **changed** by `John Doe` | -| Silencing Rule Deleted | An existing alert notifications silencing rule was removed from the Space. | Silencing rule `DB Servers schedule silencing` on rooms `All nodes` and `DB Servers` was **changed** by `Alan Smith` | - -### Topology events - -| **Event name** | **Description** | **Example** | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | -| Node Became Live | The node is collecting and streaming metrics to Cloud.| Node `netdata-k8s-state-xyz` was **live** | -| Node Became Stale | The node is offline and not streaming metrics to Cloud. It can show historical data from a parent node. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **stale** | -| Node Became Offline | The node is offline, not streaming metrics to Cloud and not available in any parent node.| Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **offline** | -| Node Created | The node is created but it is still `Unseen` on Cloud, didn't establish a successful connection yet.| Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **created** | -| Node Removed |The node was removed from the Space, for example by using the `Delete` action on the node. This is a soft delete in that the node gets marked as deleted, but retains the association with this space. If it becomes live again, it will be restored (see `Node Restored` below) and reappear in this space as before. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **deleted (soft)** | -| Node Restored | The node was restored. See `Node Removed` above. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **restored** | -| Node Deleted | The node was deleted from the Space. This is a hard delete and no information on the node is retained. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **deleted (hard)** | -| Agent Connected | The agent connected to the Cloud MQTT server (Agent-Cloud Link established).<br/>These events can only be seen on _All nodes_ War Room. | Agent with claim ID `7d87bqs9-cv42-4823-8sd4-3614548850c7` has connected to Cloud. | -| Agent Disconnected | The agent disconnected from the Cloud MQTT server (Agent-Cloud Link severed).<br/>These events can only be seen on _All nodes_ War Room. | Agent with claim ID `7d87bqs9-cv42-4823-8sd4-3614548850c7` has disconnected from Cloud: **Connection Timeout**. | -| Space Statistics | Daily snapshot of space node statistics.<br/>These events can only be seen on _All nodes_ War Room. | Space statistics. Nodes: **22 live**, **21 stale**, **18 removed**, **61 total**. | - - -### Alert events - -| **Event name** | **Description** | **Example** | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | -| Node Alert State Changed | These are node alert state transition events and can be seen as an alert history log. You will be able to see transitions to or from any of these states: Cleared, Warning, Critical, Removed, Error or Unknown | Transition to Cleared:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` recovered with value **8.33%**<br/><br/>Transition from Cleared to Warning or Critical:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` was raised to **WARNING** with value **10%**<br/><br/>Transition from Warning to Critical:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` escalated to **CRITICAL** with value **25%**<br/><br/>Transition from Critical to Warning:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` was demoted to **WARNING** with value **10%**<br/><br/>Transition to Removed:<br/>Alert `httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` is no longer available, state can't be assessed.<br/><br/>Transition to Error:<br/>For this alert `httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` related to `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` we couldn't calculate the current value ⓘ| - -## Who can access the events? - -All users will be able to see events from the Topology and Alerts domain but Auditing events, once these are added, only be accessible to administrators. For more details checkout [Netdata Role-Based Access model](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md). - -## How to use the events feed - -1. Click on the **Events** tab (located near the top of your screen) -1. You will be presented with a table listing the events that occurred from the timeframe defined on the date time picker -1. You can use the filtering capabilities available on right-hand bar to slice through the results provided. See more details on event types and filters - -Note: When you try to query a longer period than what your space allows you will see an error message highlighting that you are querying data outside of your plan. - -### Event types and filters - -| Event type | Tags | Nodes | Alert Status | Alert Names | Chart Names | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | -| Node Became Live | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Became Stale | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Became Offline | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Created | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Removed | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Restored | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Deleted | node, lifecycle | Node name | - | - | - | -| Agent Claimed | agent | - | - | - | - | -| Agent Connected | agent | - | - | - | - | -| Agent Disconnected | agent | - | - | - | - | -| Agent Authenticated | agent | - | - | - | - | -| Agent Authentication Failed | agent | - | - | - | - | -| Space Statistics | space, node, statistics | Node name | - | - | - | -| Node Alert State Changed | alert, node | Node name | Cleared, Warning, Critical, Removed, Error or Unknown | Alert name | Chart name | diff --git a/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md b/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md deleted file mode 100644 index 1f3828556..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,169 +0,0 @@ -# Organize Your Infrastructure and Invite your Team - -Netdata Cloud provides you with features such as [Spaces](#netdata-cloud-spaces) and [War Rooms](#netdata-cloud-war-rooms) that allow you to better organize your infrastructure and ensure your team can also have access to it through invites. - -## Netdata Cloud Spaces - -Organize your multi-organization infrastructure monitoring on Netdata Cloud by creating Spaces to completely isolate access to your Agent-monitored nodes. - -A Space is a high-level container. It's a collaboration space where you can organize team members, access levels and the -nodes you want to monitor. - -Let's talk through some strategies for creating the most intuitive Cloud experience for your team. - -### How to organize your Netdata Cloud - -You can use any number of Spaces you want, but as you organize your Cloud experience, keep in mind that _you can only -add any given node to a single Space_. This 1:1 relationship between node and Space may dictate whether you use one -encompassing Space for your entire team and separate them by War Rooms, or use different Spaces for teams monitoring -discrete parts of your infrastructure. - -If you have been invited to Netdata Cloud by another user by default you will able to see that space. If you are a new -user the first space is already created. - -The other consideration for the number of Spaces you use to organize your Netdata Cloud experience is the size and -complexity of your organization. - -For smaller teams and infrastructures, we recommend sticking to a single Space so that you can keep all your nodes and their -respective metrics in one place. You can then use -multiple [War Rooms](#netdata-cloud-war-rooms) -to further organize your infrastructure monitoring. - -Enterprises may want to create multiple Spaces for each of their larger teams, particularly if those teams have -different responsibilities or parts of the overall infrastructure to monitor. For example, you might have one SRE team -for your user-facing SaaS application and a second team for infrastructure tooling. If they don't need to monitor the -same nodes, you can create separate Spaces for each team. - -### Navigate between spaces - -Click on any of the boxes to switch between available Spaces. - -Netdata Cloud abbreviates each Space to the first letter of the name, or the first two letters if the name is two words -or more. Hover over each icon to see the full name in a tooltip. - -To add a new Space click on the green **+** button. Enter the name of the Space and click **Save**. - - - -### Manage Spaces - -Manage your spaces by selecting a particular space and clicking on the small gear icon in the lower left corner. This -will open a side tab in which you can: - -1. _Configure this Space*_, in the first tab (**Space**) you can change the name, description or/and some privilege - options of this space - -2. _Edit the War Rooms*_, click on the **War rooms** tab to add or remove War Rooms. - -3. _Connect nodes*_, click on **Nodes** tab. Copy the claiming script to your node and run it. See the - [connect to Cloud doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md) for details. - -4. _Manage the users*_, click on **Users**. - The [invitation doc](#invite-your-team) - details the invitation process. - -5. _Manage notification setting*_, click on **Notifications** tab to turn off/on notification methods. - -6. _Manage your bookmarks*_, click on the **Bookmarks** tab to add or remove bookmarks that you need. - -> #### Note -> -> \* This action requires admin rights for this space - -### Obsoleting offline nodes from a Space - -Netdata admin users now have the ability to remove obsolete nodes from a space. - -- Only admin users have the ability to obsolete nodes -- Only offline nodes can be marked obsolete (Live nodes and stale nodes cannot be obsoleted) -- Node obsoletion works across the entire space, so the obsoleted node will be removed from all rooms belonging to the - space -- If the obsoleted nodes eventually become live or online once more they will be automatically re-added to the space - - - -## Netdata Cloud War rooms - -Netdata Cloud uses War Rooms to organize your connected nodes and provide infrastructure-wide dashboards using real-time metrics and visualizations. - -Once you add nodes to a Space, all of your nodes will be visible in the **All nodes** War Room. This is a special War Room -which gives you an overview of all of your nodes in this particular Space. Then you can create functional separations of -your nodes into more War Rooms. Every War Room has its own dashboards, navigation, indicators, and management tools. - - - -### War Room organization - -We recommend a few strategies for organizing your War Rooms. - -- **Service, purpose, location, etc.** - You can group War Rooms by a service (Nginx, MySQL, Pulsar, and so on), their purpose (webserver, database, application), their physical location, whether they're "bare metal" or a Docker container, the PaaS/cloud provider it runs on, and much more. - This allows you to see entire slices of your infrastructure by moving from one War Room to another. - -- **End-to-end apps/services** - If you have a user-facing SaaS product, or an internal service that this said product relies on, you may want to monitor that entire stack in a single War Room. This might include Kubernetes clusters, Docker containers, proxies, databases, web servers, brokers, and more. - End-to-end War Rooms are valuable tools for ensuring the health and performance of your organization's essential services. - -- **Incident response** - You can also create new War Rooms as one of the first steps in your incident response process. - For example, you have a user-facing web app that relies on Apache Pulsar for a message queue, and one of your nodes using the [Pulsar collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/pulsar/README.md) begins reporting a suspiciously low messages rate. - You can create a War Room called `$year-$month-$day-pulsar-rate`, add all your Pulsar nodes in addition to nodes they connect to, and begin diagnosing the root cause in a War Room optimized for getting to resolution as fast as possible. - -### Add War Rooms - -To add new War Rooms to any Space, click on the green plus icon **+** next to the **War Rooms** heading on the left (Space's) sidebar. - -In the panel, give the War Room a name and description, and choose whether it's public or private. -Anyone in your Space can join public War Rooms, but can only join private War Rooms with an invitation. - -### Manage War Rooms - -All the users and nodes involved in a particular Space can be part of a War Room. - -Any user can change simple settings of a War room, like the name or the users participating in it. -Click on the gear icon of the War Room's name in the top of the page to do that. A sidebar will open with options for this War Room: - -1. To **change a War Room's name, description, or public/private status**, click on **War Room** tab. - -2. To **include an existing node** to a War Room or **connect a new node\*** click on **Nodes** tab. Choose any connected node you want to add to this War Room by clicking on the checkbox next to its hostname, then click **+ Add** at the top of the panel. - -3. To **add existing users to a War Room**, click on **Add Users**. - See our [invite section](#invite-your-team) for details on inviting new users to your Space in Netdata Cloud. - -> #### Note -> ->\* This action requires **admin** rights for this Space - -#### More actions - -To **view or remove nodes** in a War Room, click on the **Nodes tab**. To remove a node from the current War Room, click on -the **🗑** icon. - -> #### Info -> -> Removing a node from a War Room does not remove it from your Space. - -## Invite your team - -Invite your entire SRE, DevOPs, or ITOps team to Netdata Cloud, to give everyone insights into your infrastructure from a single pane of glass. - -Invite new users to your Space by clicking on **Invite Users** in -the [Space](#netdata-cloud-spaces) management area. - - - - -You will be prompted to enter the email addresses of the users you want to invite to your Space. You can enter any number of email addresses, separated by a comma, to send multiple invitations at once. - -Next, choose the War Rooms you want to invite these users to. Once logged in, these users are not restricted only to -these War Rooms. They can be invited to others, or join any that are public. - -Next, pick a role for the invited user. You can read more about [which roles are available](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md#what-roles-are-available) based on your [subscription plan](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md). - -Click the **Send** button to send an email invitation, which will prompt them -to [sign up](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md) and join your Space. - -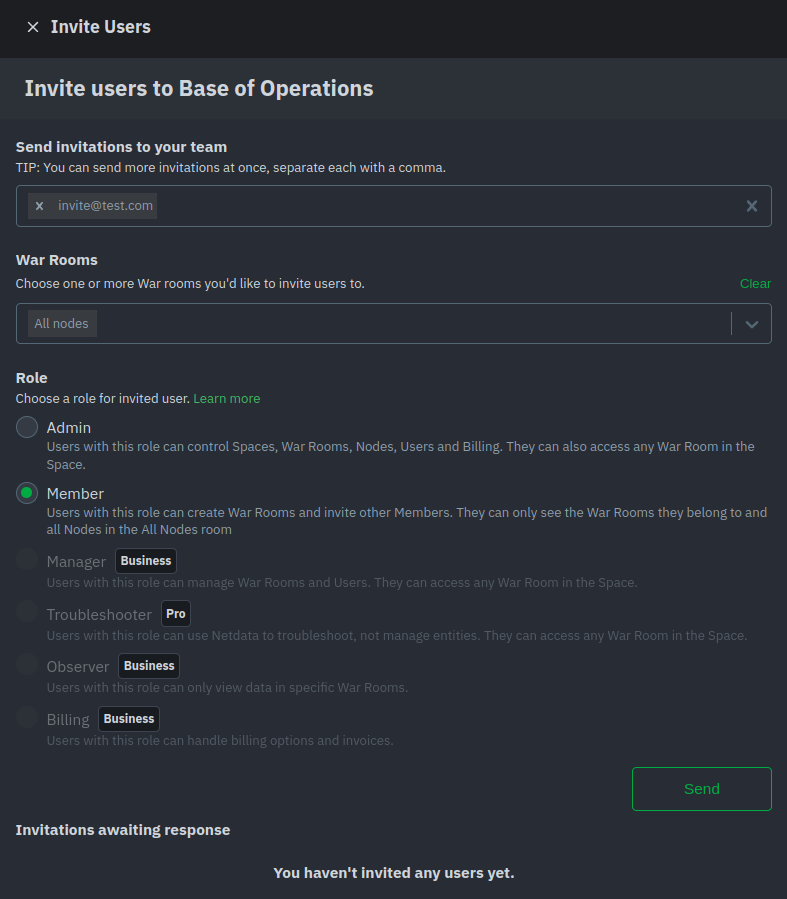 - -Any unaccepted invitations remain under **Invitations awaiting response**. These invitations can be rescinded at any -time by clicking the trash can icon. diff --git a/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md b/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md deleted file mode 100644 index 9b21575fc..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,123 +0,0 @@ -# Netdata Plans - -This page will guide you through the differences between the Community, Pro, Business and Enterprise plans. - -At Netdata, we believe in providing free and unrestricted access to high-quality monitoring solutions, and our commitment to this principle will not change. We offer our free SaaS offering - what we call **Community plan** - and Open Source Agent, which features unlimited nodes and users, unlimited metrics, and retention, providing real-time, high-fidelity, out-of-the-box infrastructure monitoring for packaged applications, containers, and operating systems. - -We also provide paid subscriptions that designed to provide additional features and capabilities for businesses that need tighter and customizable integration of the free monitoring solution to their processes. These are divided into three different plans: **Pro**, **Business**, and **Enterprise**. Each plan will offers a different set of features and capabilities to meet the needs of businesses of different sizes and with different monitoring requirements. - -> ### Note -> To not disrupt the existing space user's access rights we will keep them in the **Early Bird** plan. The reason for this is to allow users to -> keep using the legacy **Member** role with the exact same permissions as it has currently. -> -> If you move from the **Early Bird** plan to a paid plan, you will not be able to return to the **Early Bird** plan again. The **Community** free plan will always be available to you, but it does not allow -> you to invite or change users using the Member role. See more details on our [roles and plans](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md#what-roles-are-available) documentation. - -### Plans - -The plan is an attribute that is directly attached to your space(s) and that dictates what capabilities and customizations you have on your space. If you have different spaces you can have different Netdata plans on them. This gives you flexibility to chose what is more adequate for your needs on each of your spaces. - -Netdata Cloud plans, with the exception of Community, work as subscriptions and overall consist of two pricing components: - -* A flat fee component, that is applied on yearly subscriptions for the [comitted-nodes](#committed-nodes) charte (space subscription fee has been waived off) -* An on-demand metered component, that is related to your usage of Netdata which directly links to the [number of nodes you have running](#running-nodes-and-billing) - -Netdata provides two billing frequency options: - -* Monthly - Pay as you go, where we charge both the flat fee and the on-demand component every month -* Yearly - Annual prepayment, where we charge upfront the flat fee and committed amount related to your estimated usage of Netdata (more details [here](#committed-nodes)) - -For more details on the plans and subscription conditions please check <https://netdata.cloud/pricing>. - -#### Running nodes and billing - -The only dynamic variable we consider for billing is the number of concurrently running nodes or agents. We only charge you for your active running nodes, so we don't count: - -* offline nodes -* stale nodes, nodes that are available to query through a Netdata parent agent but are not actively connecting metrics at the moment - -To ensure we don't overcharge you due to sporadic spikes throughout a month or even at a certain point in a day we are: - -* Calculate a daily P90 figure for your running nodes. To achieve that, we take a daily snapshot of your running nodes, and using the node state change events (live, offline) we guarantee that a daily P90 figure is calculated to remove any daily spikes -* On top of the above, we do a running P90 calculation from the start to the end of your billing cycle. Even if you have an yearly billing frequency we keep a monthly subscription linked to that to identify any potential overage over your [committed nodes](#committed-nodes). - -#### Committed nodes - -When you subscribe to an Yearly plan you will need to specify the number of nodes that you will commit to. On these nodes, a discounted price of less 25% than the original cost per node of the plan is applied. This amount will be part of your annual prepayment. - -``` -Node plan discounted price x committed nodes x 12 months -``` - -If, for a given month, your usage is over these committed nodes we will charge the original cost per node for the nodes above the committed number. - -#### Plan changes and credit balance - -It is ok to change your mind. We allow to change your plan, billing frequency or adjust the committed nodes, on yearly plans, at any time. - -To achieve this you can check the [Update plan](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/view-plan-billing.md#update-plan) section. - -> ⚠️ On a downgrade (going to a new plan with less benefits) or cancellation of an active subscription, please note that you will have all your notification methods configurations active **for a period of 24 hours**. -> After that, any notification methods unavailable in your new plan at that time will be automatically disabled. You can always re-enable them once you move to a paid plan that includes them. - -> ⚠️ Downgrade or cancellation may affect users in your Space. Please check what roles are available on the [each plans](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#areas-impacted-by-plans). Users with unavailable roles on the new plan will immediately have restricted access to the Space. - -> ⚠️ Any credit given to you will be available to use on future paid subscriptions with us. It will be available until the **end of the following year**. - -### Areas impacted by plans - -##### Role-Based Access model - -Depending on the plan associated to your space you will have different roles available: - -| **Role** | **Community** | **Pro** | **Business** | **Early Bird** | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | -| **Administrators**<p>Users with this role can control Spaces, War Rooms, Nodes, Users and Billing.</p><p>They can also access any War Room in the Space.</p> | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | -| **Managers**<p>Users with this role can manage War Rooms and Users.</p><p>They can access any War Room in the Space.</p> | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Troubleshooters**<p>Users with this role can use Netdata to troubleshoot, not manage entities.</p><p>They can access any War Room in the Space.</p> | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Observers**<p>Users with this role can only view data in specific War Rooms.</p>💡 Ideal for restricting your customer's access to their own dedicated rooms.<p></p> | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Billing**<p>Users with this role can handle billing options and invoices.</p> | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Member** ⚠️ Legacy role<p>Users with this role can create War Rooms and invite other Members.</p><p>They can only see the War Rooms they belong to and all Nodes in the All Nodes room.</p>| - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - -For more details check the documentation under [Role-Based Access model](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md). - -##### Events feed - -The plan you have subscribed on your space will determine the amount of historical data you will be able to query: - -| **Type of events** | **Community** | **Pro** | **Business** | -| :-- | :-- | :-- | :-- | -| **Auditing events** - COMING SOON<p>Events related to actions done on your Space, e.g. invite user, change user role or create room.</p>| 4 hours | 7 days | 90 days | -| **Topology events**<p>Node state transition events, e.g. live or offline.</p>| 4 hours | 7 days | 14 days | -| **Alert events**<p>Alert state transition events, can be seen as an alert history log.</p>| 4 hours | 7 days | 90 days | - -For more details check the documentation under [Events feed](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md). - -##### Notification integrations - -The plan on your space will determine what type of notifications methods will be available to you: - -* **Community** - Email and Discord -* **Pro** - Email, Discord and webhook -* **Business** - Unlimited, this includes Slack, PagerDuty, Opsgenie etc. - -For more details check the documentation under [Alert Notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#alert-notifications). - -##### Alert notification silencing rules - -The plan on your space will determine if you are able to add alert notification silencing rules since this feature will only be available for paid plans: **Pro** or **Business**. - -For more details check the documentation under [Alert Notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#silencing-alert-notifications). - -### Related Topics - -#### **Related Concepts** - -* [Spaces](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces) -* [Alert Notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md) -* [Events feed](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md) -* [Role-Based Access model](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md) - -#### Related Tasks - -* [View Plan & Billing](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/view-plan-billing.md) diff --git a/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md b/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md deleted file mode 100644 index 4bfb65f2e..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,145 +0,0 @@ -# Role-Based Access model - -Netdata Cloud's role-based-access mechanism allows you to control what functionalities in the app users can access. Each user can be assigned only one role, which fully specifies all the capabilities they are afforded. - -## What roles are available? - -With the advent of the paid plans we revamped the roles to cover needs expressed by Netdata users, like providing more limited access to their customers, or -being able to join any room. We also aligned the offered roles to the target audience of each plan. The end result is the following: - -| **Role** | **Community** | **Pro** | **Business** | **Early Bird** | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | -| **Administrators**<p>Users with this role can control Spaces, War Rooms, Nodes, Users and Billing.</p><p>They can also access any War Room in the Space.</p> | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | -| **Managers**<p>Users with this role can manage War Rooms and Users.</p><p>They can access any War Room in the Space.</p> | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Troubleshooters**<p>Users with this role can use Netdata to troubleshoot, not manage entities.</p><p>They can access any War Room in the Space.</p> | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Observers**<p>Users with this role can only view data in specific War Rooms.</p>💡 Ideal for restricting your customer's access to their own dedicated rooms.<p></p> | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Billing**<p>Users with this role can handle billing options and invoices.</p> | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | -| **Member** ⚠️ Legacy role<p>Users with this role can create War Rooms and invite other Members.</p><p>They can only see the War Rooms they belong to and all Nodes in the All Nodes room.</p>| - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - -## What happens to the previous Member role? - -We will maintain a Early Bird plan for existing users, which will continue to provide access to the Member role. - -## Which functionalities are available for each role? - -In more detail, you can find on the following tables which functionalities are available for each role on each domain. - -### Space Management - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | -| See Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Leave Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Delete Space | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | -| Change name | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | -| Change description | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | -| Change slug | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | -| Change preferred nodes | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | - -### Node Management - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See all Nodes in Space (_All Nodes_ room) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | Members are always on the _All Nodes_ room | -| Connect Node to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | - | -| Delete Node from Space | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | - | - -### User Management - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See all Users in Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Invite new User to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | You can't invite a user with a role you don't have permissions to appoint to (see below) | -| Delete Pending Invitation to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Delete User from Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | You can't delete a user if he has a role you don't have permissions to appoint to (see below) | -| Appoint Administrators | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | -| Appoint Billing user | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | -| Appoint Managers | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Appoint Troubleshooters | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Appoint Observer | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Appoint Member | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | Only available on Early Bird plans | -| See all Users in a Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Invite existing user to Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | User already invited to the Space | -| Remove user from Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | - -### Room Management - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See all Rooms in a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | | -| Join any Room in a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | By joining a room you will be enabled to get notifications from nodes on that room | -| Leave Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Create a new Room in a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Delete Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Change Room name | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | If not the _All Nodes_ room | -| Change Room description | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Add existing Nodes to Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | Node already connected to the Space | -| Remove Nodes from Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | - -### Notifications Management - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See all configured notifications on a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Add new configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | -| Enable/Disable configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | -| Edit configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | Some exceptions apply depending on [service level](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#available-actions-per-notification-methods-based-on-service-level) | -| Delete configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | -| Edit personal level notification settings | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | [Manage user notification settings](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#manage-user-notification-settings) | -| See space alert notification silencing rules | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | | -| Add new space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Enable/Disable space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Edit space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| Delete space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | -| See, add, edit or delete personal level alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | | - - -Notes: -* Enable, Edit and Add actions over specific notification methods will only be allowed if your plan has access to those ([service classification](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#service-classification)) - -### Dashboards - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | -| See all dashboards in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Add new dashboard to Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Edit any dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Edit own dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Delete any dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Delete own dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - -### Functions - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See all functions in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Run any function in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | -| Run read-only function in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| Run sensitive function in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | There isn't any function on this category yet, so subject to change. | - -### Events feed - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See Alert or Topology events | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | -| See Auditing events | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | These are coming soon, not currently available | - -### Billing - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :-- | -| See Plan & Billing details | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | Current plan and usage figures | -| Update plans | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | This includes cancelling current plan (going to Community plan) | -| See invoices | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | | -| Manage payment methods | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | | -| Update billing email | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | | - -### Other permissions - -| **Functionality** | **Administrator** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | -| :-- | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | :--: | -| See Bookmarks in Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Add Bookmark to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Delete Bookmark from Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| See Visited Nodes | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | -| Update Visited Nodes | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | diff --git a/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md b/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md deleted file mode 100644 index 53ea3a22a..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,81 +0,0 @@ -# Sign in to Netdata - -This page explains how to sign in to Netdata with your email, Google account, or GitHub account, and provides some tips if you're having trouble signing in. - -You can [sign in to Netdata](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=spaces?utm_source=docs&utm_content=sign_in_button_first_section) through one of three methods: email, Google, or GitHub. Email uses a -time-sensitive link that authenticates your browser, and Google/GitHub both use OAuth to associate your email address -with a Netdata Cloud account. - -No matter the method, your Netdata Cloud account is based around your email address. Netdata Cloud does not store -passwords. - -## Email - -To sign in with email, visit [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=spaces?utm_source=docs&utm_content=sign_in_button_email_section), enter your email address, and click -the **Sign in by email** button. - - - -Click the **Verify** button in the email to begin using Netdata Cloud. - -To use this same Netdata Cloud account on additional devices, request another sign in email, open the email on that -device, and sign in. - -### Don't have a Netdata Cloud account yet? - -If you don't already have a Netdata Cloud account, you don't need to worry about this. During the sign-in process we will create one for you and make the process seamless to you. - -After your account is created and you sign in to Netdata, you first are asked to agree to Netdata Cloud's [Privacy -Policy](https://www.netdata.cloud/privacy/) and [Terms of Use](https://www.netdata.cloud/terms/). Once you agree with these you are directed -through the Netdata Cloud onboarding process, which is explained in the [Netdata Cloud -quickstart](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md). - -### Troubleshooting - -You should receive your sign in email in less than a minute. The subject is **Verify your email!** for new sign-ups, **Sign in to Netdata** for sign ins. -The sender is `no-reply@netdata.cloud` via `sendgrid.net`. - -If you don't see the email, try the following: - -- Check your spam folder. -- In Gmail, check the **Updates** category. -- Check [Netdata Cloud status](https://status.netdata.cloud) for ongoing issues with our infrastructure. -- Request another sign in email via the [sign-in page](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=spaces?utm_source=docs&utm_content=sign_in_button_troubleshooting_section). - -You may also want to add `no-reply@netdata.cloud` to your address book or contacts list, especially if you're using -a public email service, such as Gmail. You may also want to whitelist/allowlist either the specific email or the entire -`netdata.cloud` domain. - -In some cases, temporary issues with your mail server or email account may result in your email address being added to a Bounce list by Sendgrid. -If you are added to that list, no Netdata cloud email can reach you, including alert notifications. Let us know in Discord that you have trouble receiving -any email from us and someone will ask you to provide your email address privately, so we can check if you are on the Bounce list. - -## Google and GitHub OAuth - -When you use Google/GitHub OAuth, your Netdata Cloud account is associated with the email address that Netdata Cloud -receives via OAuth. - -To sign in with Google or GitHub OAuth, visit [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=spaces?utm_source=docs&utm_content=sign_in_button_google_github_section) and click the -**Continue with Google/GitHub** or button. Enter your Google/GitHub username and your password. Complete two-factor -authentication if you or your organization has it enabled. - -You are then signed in to Netdata Cloud or directed to the new-user onboarding if you have not signed up previously. - -## Reset a password - -Netdata Cloud does not store passwords and does not support password resets. All of our sign in methods do not -require passwords, and use either links in emails or Google/GitHub OAuth for authentication. - -## Switch between sign in methods - -You can switch between sign in methods if the email account associated with each method is the same. - -For example, you first sign in via your email account, `user@example.com`, and later sign out. You later attempt to sign -in via a GitHub account associated with `user@example.com`. Netdata Cloud recognizes that the two are the same and signs -you in to your original account. - -However, if you first sign in via your `user@example.com` email account and then sign in via a Google account associated -with `user2@example.com`, Netdata Cloud creates a new account and begins the onboarding process. - -It is not currently possible to link an account created with `user@example.com` to a Google account associated with -`user2@example.com`. diff --git a/docs/cloud/manage/view-plan-billing.md b/docs/cloud/manage/view-plan-billing.md deleted file mode 100644 index 5d381f952..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/manage/view-plan-billing.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,141 +0,0 @@ -# View Plan & Billing - -From the Cloud interface, you can view and manage your space's plan and billing settings, and see the space's usage in terms of running nodes. - -To view and manage some specific settings, related to billing options and invoices, you'll be redirected to our billing provider Customer Portal. - -## Prerequisites - -To see your plan and billing setting you need: - -- A Cloud account -- Access to the space as an Administrator or Billing user - -## Steps - -### View current plan and Billing options and Invoices - -1. Click on the **Space settings** cog (located above your profile icon) -1. Click on the **Plan & Billing** tab -1. On this page you will be presented with information on your current plan, billing settings, and usage information: - 1. At the top of the page you will see: - - **Credit** amount which refers to any amount you have available to use on future invoices or subscription changes ([Plan changes and credit balance](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#plan-changes-and-credit-balance)) - this is displayed once you have had an active paid subscription with us - - **Billing email** the email that was specified to be linked to tha plan subscription. This is where invoices, payment, and subscription-related notifications will be sent. - - **Billing options and Invoices** is the link to our billing provider Customer Portal where you will be able to: - - See the current subscription. There will always be 2 subscriptions active for the two pricing components mentioned on [Netdata Plans documentation page](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#plans) - - Change directly the payment method associated to current subscriptions - - View, add, delete or change your default payment methods - - View or change or Billing information: - - Billing email - - Address - - Phone number - - Tax ID - - View your invoice history - 1. At the middle, you'll see details on your current plan as well as means to: - - Upgrade or cancel your plan - - View **All Plans** details page - 1. At the bottom, you will find your Usage chart that displays: - - Daily count - The weighted 90th percentile of the live node count during the day, taking time as the weight. If you have 30 live nodes throughout the day - except for a two hour peak of 44 live nodes, the daily value is 31. - - Period count: The 90th percentile of the daily counts for this period up to the date. The last value for the period is used as the number of nodes for the bill for that period. See more details in [running nodes and billing](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#running-nodes-and-billing) (only applicable if you are on a paid plan subscription) - - Committed nodes: The number of nodes committed to in the yearly plan. In case the period count is higher than the number of committed nodes, the difference is billed as overage. - - -### Update plan - -1. Click on the **Space settings** cog (located above your profile icon) -1. Click on the **Plan & Billing** tab -1. On this page you will be presented with information on your current plan, billing settings, and usage information - 1. Depending on your plan there could be shortcuts to immediately take you to change, for example, the billing frequency to **Yearly** - 1. Most actions will be available under the **Change plan** link that take you to the **All plans** details page where you can - 1. Downgrade or upgrade your plan - 1. Change the billing frequency - 1. Change committed nodes, in case you are on a Yearly plan - 1. Once you chose an action to update your plan a modal will pop-up on the right with - 1. Billing frequency displayed on the top right-corner - 1. Committed Nodes, when applicable - 1. Current billing information: - - Billing email - - Default payment method - - Business name and VAT number, when these are applicable - - Billing Address - Note: Any changes to these need to done through our billing provider Customer Portal prior to confirm the checkout. You can click on the link **Change billing info and payment method** to access it. - 1. Promotion code, so you can review any applied promotion or enter one you may have - 1. Detailed view on Node and Space charges - 1. Breakdown of: - - Subscription Total - - Discount from promotion codes, if applicable - - credit value for Unused time from current plan, if applicable - - Credit amount used from balance, if applicable - - Total Before Tax - - VAT rate and amount, if applicable - 1. Summary of: - - Total payable amount - - credit adjustment value for any Remaining Unused time from current plan, if applicable - - Final credit balance - -Notes: -* Since there is an active plan you won't be redirected to our billing provider, the checkout if performed as soon as you click on **Checkout** -* The change to your plan will be applied as soon as the checkout process is completed successfully -* Downgrade or cancellations may have impacts on some of notification method settings or user accesses to your space, for more details please check [Plan changes and credit balance](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#plan-changes-and-credit-balance) - -## FAQ - -### 1. What Payment Methods are accepted? - -You can easily pay online via most major Credit/Debit Cards. More payment options are expected to become available in the near future. - -### 2. What happens if a renewal payment fails? - -After an initial failed payment, we will attempt to process your payment every week for the next 15 days. After three failed attempts your Space will be moved to the **Community** plan (free forever). - -For the next 24 hours, you will be able to use all your current notification method configurations. After 24 hours, any of the notification method configurations that aren't available on your space's plan will be automatically disabled. - -Cancellation might affect users in your Space. Please check what roles are available on the [Community plan](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#areas-impacted-by-plans). Users with unavailable roles on the Community plan will immediately have restricted access to the Space. - -### 3. Which currencies do you support? - -We currently accept payments only in US Dollars (USD). We currently have plans to also accept payments in Euros (EUR), but do not currently have an estimate for when such support will be available. - -### 4. Can I get a refund? How? - -Payments for Netdata subscriptions are refundable **only** if you cancel your subscription within 14 days of purchase. The refund will be credited to the Credit/Debit Card used for making the purchase. To request a refund, please email us at [billing@netdata.cloud](mailto:billing@netdata.cloud). - -### 5. How do I cancel my paid Plan? - -Your annual or monthly Netdata Subscription plan will automatically renew until you cancel it. You can cancel your paid plan at any time by clicking ‘Cancel Plan’ from the **Plan & Billing** section under settings. You can also cancel your paid Plan by clicking the _Select_ button under **Community** plan in the **Plan & Billing** Section under Settings. - -### 6. How can I access my Invoices/Receipts after I paid for a Plan? - -You can visit the _Billing Options & Invoices_ in the **Plan & Billing** section under settings in your Netdata Space where you can find all your Invoicing history. - -### 7. Why do I see two separate Invoices? - -Every time you purchase or renew a Plan, two separate Invoices are generated: - -- One Invoice includes the recurring fees of the Plan you have chosen - - We have waived off the space subscription free ($0.00), so the only recurring fee will be on annual plans for the committed nodes. - -- The other Invoice includes your monthly “On Demand - Usage”. - - Right after the activation of your subscription, you will receive a zero value Invoice since you had no usage when you subscribed. - - On the following month you will receive an Invoice based on your monthly usage. - -You can find some further details on the [Netdata Plans page](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md#plans). - -> ⚠️ We expect this to change to a single invoice in the future, but currently do not have a concrete timeline for when this change will happen. - -### 8. How is the **Total Before Tax** value calculated on plan changes? - -When you change your plan we will be calculating the residual before tax value you have from the _Unused time on your current plan_ in order to credit you with this value. - -After that, we will be performing the following calculations: - -1. Get the **Subscription total** (total amount to be paid for Nodes and Space) -2. Deduct any Discount applicable from promotion codes -3. If an amount remains, then we deduct the sum of the _Unused time on current plan_ then and the Credit amount from any existing credit balance. -4. The result, if positive, is the Total Before Tax, if applicable, any sales tax (VAT or other) will apply. - -If the calculation of step 3 returns a negative amount then this amount will be your new customer credit balance. diff --git a/docs/cloud/runtime-troubleshooting-with-functions.md b/docs/cloud/runtime-troubleshooting-with-functions.md deleted file mode 100644 index 193ba33ca..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/runtime-troubleshooting-with-functions.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,34 +0,0 @@ -# Run-time troubleshooting with Functions - -Netdata Functions feature allows you to execute on-demand a pre-defined routine on a node where a Netdata Agent is running. These routines are exposed by a given collector. -These routines can be used to retrieve additional information to help you troubleshoot or to trigger some action to happen on the node itself. - - -### Prerequisites - -The following is required to be able to run Functions from Netdata Cloud. -* At least one of the nodes claimed to your Space should be on a Netdata agent version higher than `v1.37.1` -* Ensure that the node has the collector that exposes the function you want enabled ([see current available functions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md#what-functions-are-currently-available)) - -### Execute a function (from the Functions tab) - -1. From the right-hand bar select the **Function** you want to run -2. Still on the right-hand bar select the **Node** where you want to run it -3. Results will be displayed in the central area for you to interact with -4. Additional filtering capabilities, depending on the function, should be available on right-hand bar - -### Execute a function (from the Nodes tab) - -1. Click on the functions icon for a node that has this active -2. You are directed to the **Functions** tab -3. Follow the above instructions from step 3. - -> ⚠️ If you get an error saying that your node can't execute Functions please check the [prerequisites](#prerequisites). - -## Related Topics - -### **Related Concepts** -- [Netdata Functions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md) - -#### Related References documentation -- [External plugins overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md#function) diff --git a/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md b/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md deleted file mode 100644 index 4b4baf426..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,101 +0,0 @@ -# Build new dashboards - -With Netdata Cloud, you can build new dashboards that target your infrastructure's unique needs. Put key metrics from -any number of distributed systems in one place for a bird's eye view of your infrastructure. - -Click on the **Dashboards** tab in any War Room to get started. - -## Create your first dashboard - -From the Dashboards tab, click on the **+** button. - -<img width="98" alt=" Green plus button " src="https://github.com/netdata/netdata/assets/73346910/511e2b38-e751-4a88-bc7d-bcd49764b7f6"/> - - -In the modal, give your new dashboard a name, and click **+ Add**. - -- The **Add Chart** button on the top right of the interface adds your first chart card. From the dropdown, select either **All Nodes** or a specific -node. Next, select the context. You'll see a preview of the chart before you finish adding it. In this modal you can also [interact with the chart](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md), meaning you can configure all the aspects of the [NIDL framework](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#nidl-framework) of the chart and more in detail, you can: - - define which `group by` method to use - - select the aggregation function over the data source - - select nodes - - select instances - - select dimensions - - select labels - - select the aggregation function over time - - After you are done configuring the chart, you can also change the type of the chart from the right hand side of the [Title bar](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#title-bar), and select which of the final dimensions you want to be visible and in what order, from the [Dimensions bar](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#dimensions-bar). - -- The **Add Text** button on the top right of the interface creates a new card with user-defined text, which you can use to describe or document a -particular dashboard's meaning and purpose. - -> ### Important -> -> Be sure to click the **Save** button any time you make changes to your dashboard. - - -## Using your dashboard - -Dashboards are designed to be interactive and flexible so you can design them to your exact needs. Dashboards are made -of any number of **cards**, which can contain charts or text. - -### Chart cards - -The charts you add to any dashboard are [fully interactive](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md), just like any other Netdata chart. You can zoom in and out, highlight timeframes, and more. - -Charts also synchronize as you interact with them, even across contexts _or_ nodes. - -### Text cards - -You can use text cards as notes to explain to other members of the [War Room](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms) the purpose of the dashboard's arrangement. - -### Move cards - -To move any card, click and hold on **Drag & rearrange** at the top right of the card and drag it to a new location. A red placeholder indicates the -new location. Once you release your mouse, other charts re-sort to the grid system automatically. - -### Resize cards - -To resize any card on a dashboard, click on the bottom-right corner and drag to the card's new size. Other cards re-sort -to the grid system automatically. - -## Go to chart - -Quickly jump to the location of the chart in either the Overview tab or if the card refers to a single node, its single node dashboard by clicking the 3-dot icon in the corner of any card to open a menu. Hit the **Go to Chart** item. - -You'll land directly on that chart of interest, but you can now scroll up and down to correlate your findings with other -charts. Of course, you can continue to zoom, highlight, and pan through time just as you're used to with Netdata Charts. - -## Managing your dashboard - -To see dashboards associated with the current War Room, click the **Dashboards** tab in any War Room. You can select -dashboards and delete them using the 🗑️ icon. - -### Update/save a dashboard - -If you've made changes to a dashboard, such as adding or moving cards, the **Save** button is enabled. Click it to save -your most recent changes. Any other members of the War Room will be able to see these changes the next time they load -this dashboard. - -If multiple users attempt to make concurrent changes to the same dashboard, the second user who hits Save will be -prompted to either overwrite the dashboard or reload to see the most recent changes. - -### Remove an individual card - -Click on the 3-dot icon in the corner of any card to open a menu. Click the **Remove** item to remove the card. - -### Delete a dashboard - -Delete any dashboard by navigating to it and clicking the **Delete** button. This will remove this entry from the -dropdown for every member of this War Room. - -### Minimum browser viewport - -Because of the visual complexity of individual charts, dashboards require a minimum browser viewport of 800px. - -## What's next? - -Once you've designed a dashboard or two, make sure -to [invite your team](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team) if -you haven't already. You can add these new users to the same War Room to let them see the same dashboards without any -effort. diff --git a/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md b/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md deleted file mode 100644 index 82c33fd3e..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,142 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Kubernetes visualizations" -description: "Netdata Cloud features rich, zero-configuration Kubernetes monitoring for the resource utilization and application metrics of Kubernetes (k8s) clusters." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md" -sidebar_label: "Kubernetes visualizations" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Operations/Visualizations" ---> - -# Kubernetes visualizations - -Netdata Cloud features enhanced visualizations for the resource utilization of Kubernetes (k8s) clusters, embedded in -the default [Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md) dashboard. - -These visualizations include a health map for viewing the status of k8s pods/containers, in addition to composite charts -for viewing per-second CPU, memory, disk, and networking metrics from k8s nodes. - -See our [Kubernetes deployment instructions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md) for details on -installation and connecting to Netdata Cloud. - -## Available Kubernetes metrics - -Netdata Cloud organizes and visualizes the following metrics from your Kubernetes cluster from every container: - -- `cpu_limit`: CPU utilization as a percentage of the limit defined by the [pod specification - `spec.containers[].resources.limits.cpu`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#resource-requests-and-limits-of-pod-and-container) - or a [`LimitRange` - object](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/manage-resources/cpu-default-namespace/#create-a-limitrange-and-a-pod). -- `cpu`: CPU utilization of the pod/container. 100% usage equals 1 fully-utilized core, 200% equals 2 fully-utilized - cores, and so on. -- `cpu_per_core`: CPU utilization averaged across available cores. -- `mem_usage_limit`: Memory utilization, without cache, as a percentage of the limit defined by the [pod specification - `spec.containers[].resources.limits.memory`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#resource-requests-and-limits-of-pod-and-container) - or a [`LimitRange` - object](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/manage-resources/cpu-default-namespace/#create-a-limitrange-and-a-pod). -- `mem_usage`: Used memory, without cache. -- `mem`: The sum of `cache` and `rss` (resident set size) memory usage. -- `writeback`: The size of `dirty` and `writeback` cache. -- `mem_activity`: Sum of `in` and `out` bandwidth. -- `pgfaults`: Sum of page fault bandwidth, which are raised when the Kubernetes cluster tries accessing a memory page - that is mapped into the virtual address space, but not actually loaded into main memory. -- `throttle_io`: Sum of `read` and `write` per second across all PVs/PVCs attached to the container. -- `throttle_serviced_ops`: Sum of the `read` and `write` operations per second across all PVs/PVCs attached to the - container. -- `net.net`: Sum of `received` and `sent` bandwidth per second. -- `net.packets`: Sum of `multicast`, `received`, and `sent` packets. - -When viewing the [health map](#health-map), Netdata Cloud shows the above metrics per container, or aggregated based on -their associated pods. - -When viewing the [composite charts](#composite-charts), Netdata Cloud aggregates metrics from multiple nodes, pods, or -containers, depending on the grouping chosen. For example, if you group the `cpu_limit` composite chart by -`k8s_namespace`, the metrics shown will be the average of `cpu_limit` metrics from all nodes/pods/containers that are -part of that namespace. - -## Health map - -The health map places each container or pod as a single box, then varies the intensity of its color to visualize the -resource utilization of specific k8s pods/containers. - -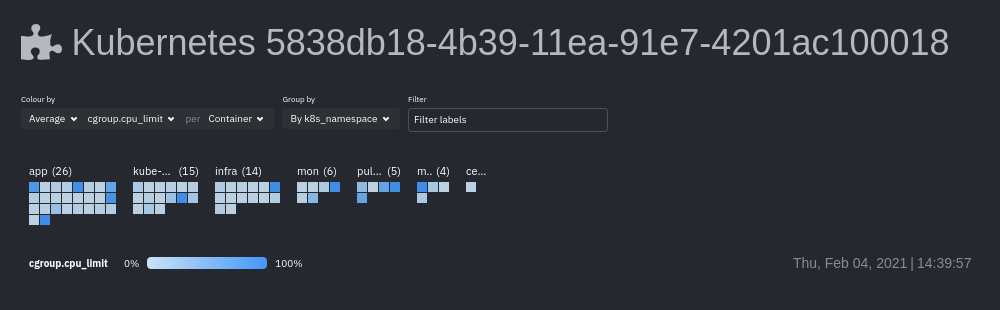 - -Change the health map's coloring, grouping, and displayed nodes to customize your experience and learn more about the -status of your k8s cluster. - -### Color by - -Color the health map by choosing an aggregate function to apply to an [available Kubernetes -metric](#available-kubernetes-metrics), then whether you to display boxes for individual pods or containers. - -The default is the _average, of CPU within the configured limit, organized by container_. - -### Group by - -Group the health map by the `k8s_cluster_id`, `k8s_controller_kind`, `k8s_controller_name`, `k8s_kind`, `k8s_namespace`, -and `k8s_node_name`. The default is `k8s_controller_name`. - -### Filtering - -Filtering behaves identically to the [node filter in War Rooms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/node-filter.md), with the ability to -filter pods/containers by `container_id` and `namespace`. - -### Detailed information - -Hover over any of the pods/containers in the map to display a modal window, which contains contextual information -and real-time metrics from that resource. - -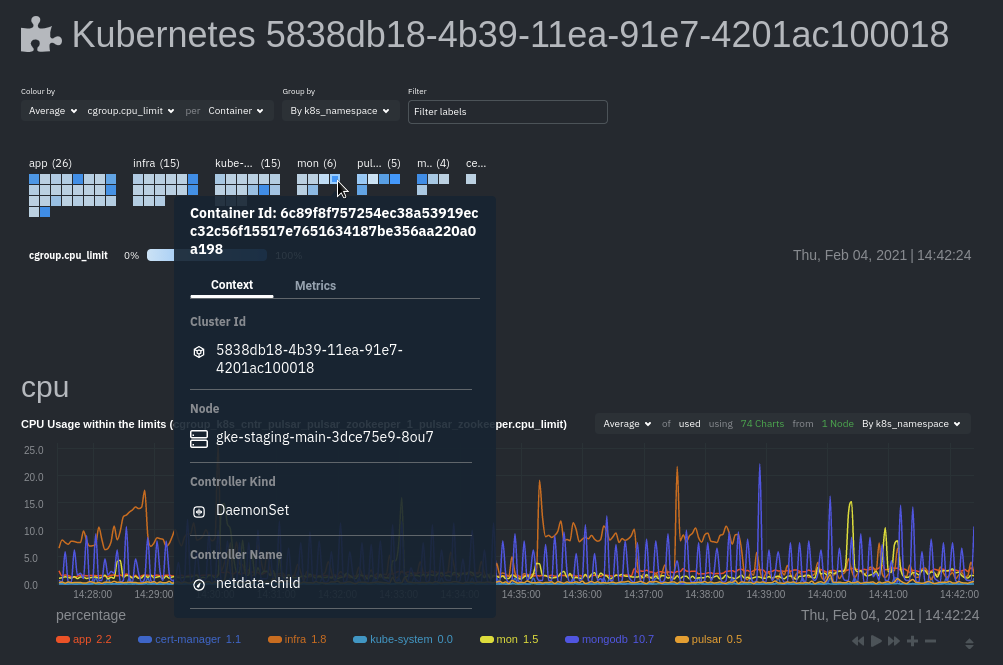 - -The **context** tab provides the following details about a container or pod: - -- Cluster ID -- Node -- Controller Kind -- Controller Name -- Pod Name -- Container -- Kind -- Pod UID - -This information helps orient you as to where the container/pod operates inside your cluster. - -The **Metrics** tab contains charts visualizing the last 15 minutes of the same metrics available in the [color by -option](#color-by). Use these metrics along with the context, to identify which containers or pods are experiencing -problematic behavior to investigate further, troubleshoot, and remediate with `kubectl` or another tool. - -## Composite charts - -The Kubernetes composite charts show real-time and historical resource utilization metrics from nodes, pods, or -containers within your Kubernetes deployment. - -See the [Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#definition-bar) doc for details on how composite charts work. These -work similarly, but in addition to visualizing _by dimension_ and _by node_, Kubernetes composite charts can also be -grouped by the following labels: - -- `k8s_cluster_id` -- `k8s_container_id` -- `k8s_container_name` -- `k8s_controller_kind` -- `k8s_kind` -- `k8s_namespace` -- `k8s_node_name` -- `k8s_pod_name` -- `k8s_pod_uid` - -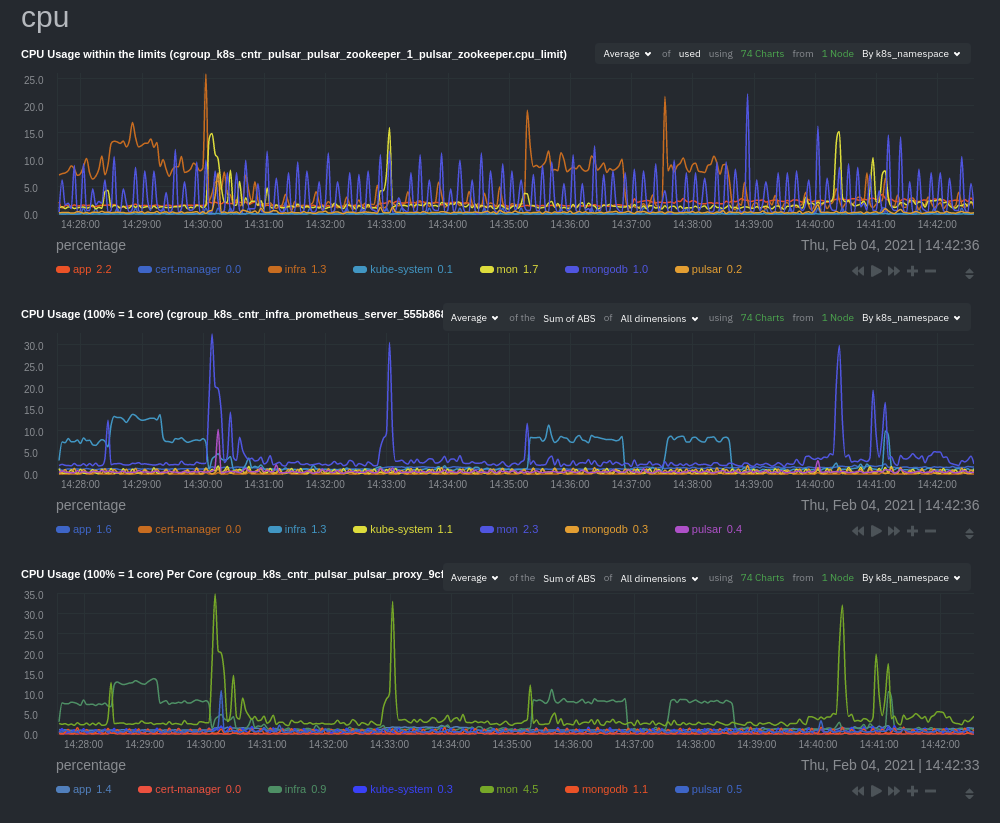 - -In addition, when you hover over a composite chart, the colors in the heat map changes as well, so you can see how -certain pod/container-level metrics change over time. - -## Caveats - -There are some caveats and known issues with Kubernetes monitoring with Netdata Cloud. - -- **No way to remove any nodes** you might have - [drained](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/safely-drain-node/) from your Kubernetes cluster. These - drained nodes will be marked "unreachable" and will show up in War Room management screens/dropdowns. The same applies - for any ephemeral nodes created and destroyed during horizontal scaling. diff --git a/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md b/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md deleted file mode 100644 index ee29d247a..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,39 +0,0 @@ -# Nodes tab - -The Nodes tab lets you see and customize key metrics from any number of Agent-monitored nodes and seamlessly navigate -to any node's dashboard for troubleshooting performance issues or anomalies using Netdata's highly-granular metrics. - -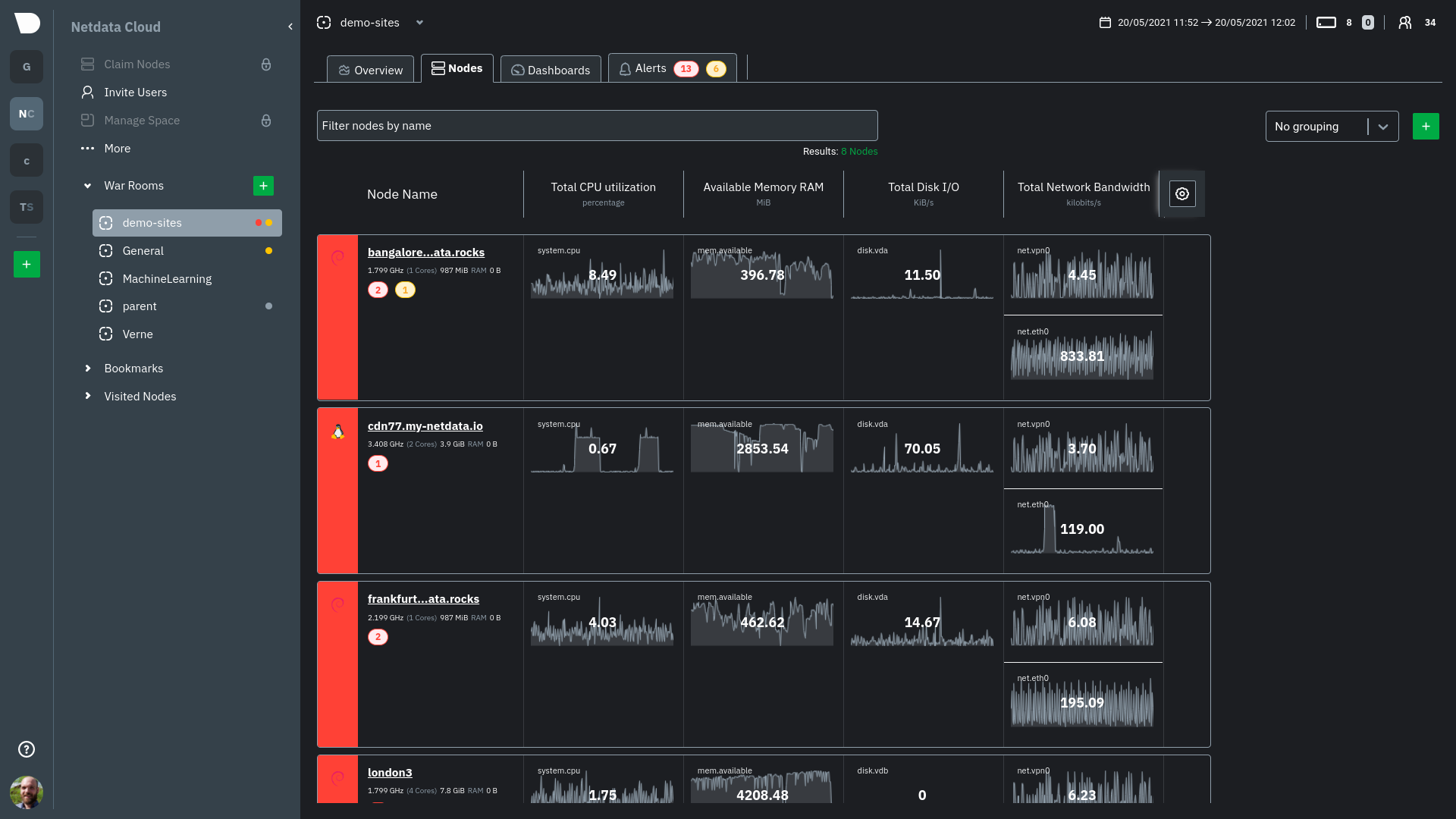 - -Each War Room's Nodes tab is populated based on the nodes you added to that specific War Room. Each node occupies a -single row, first featuring that node's alert status (yellow for warnings, red for critical alerts) and operating -system, some essential information about the node, followed by columns of user-defined key metrics represented in -real-time charts. - -Use the [Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md) for monitoring an infrastructure in real time using -composite charts and Netdata's familiar dashboard UI. - -Check the [node -filter](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/node-filter.md) and the [Visualization date time controls -selector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md) for tools available on the utility bar. - -## Add and customize metrics columns - -Add more metrics columns by clicking the gear icon. Choose the context you'd like to add, give it a relevant name, and -select whether you want to see all dimensions (the default), or only the specific dimensions your team is interested in. - -Click the gear icon and hover over any existing charts, then click the pencil icon. This opens a panel to -edit that chart. Edit the context, its title, add or remove dimensions, or delete the chart altogether. - -These customizations appear for anyone else with access to that War Room. - -## See more metrics in Netdata Cloud - -If you want to add more metrics to your War Rooms and they don't show up when you add new metrics to Nodes, you likely -need to configure those nodes to collect from additional data sources. See our [collectors configuration reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) -to learn how to use dozens of pre-installed collectors that can instantly collect from your favorite services and applications. - -If you want to see up to 30 days of historical metrics in Cloud (and more on individual node dashboards), read about [changing how long Netdata stores metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md). Also, see our -[calculator](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics) -for finding the disk and RAM you need to store metrics for a certain period of time. diff --git a/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md b/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md deleted file mode 100644 index a2935d624..000000000 --- a/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,48 +0,0 @@ -# Home, overview and single node tabs - -Learn how to use the Home, Overview, and Single Node tabs in Netdata Cloud, to explore your infrastructure and troubleshoot issues. - -## Home - -The Home tab provides a predefined dashboard of relevant information about entities in the War Room. - -This tab will automatically present summarized information in an easily digestible display. You can see information about your -nodes, data collection and retention stats, alerts, users and dashboards. - -## Overview and single node tab - -The Overview tab is another great way to monitor infrastructure using Netdata Cloud. While the interface might look -similar to local dashboards served by an Agent Overview uses **composite charts**. -These charts display real-time aggregated metrics from all the nodes (or a filtered selection) in a given War Room. - -When you [interact with composite charts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) -you can see your infrastructure from a single pane of glass, discover trends or anomalies, and perform root cause analysis. - -The Single Node tab dashboard is exactly the same as the Overview, but with a hard-coded filter to only show a single node. - -### Chart navigation Menu - -Netdata Cloud uses a similar menu to local Agent dashboards, with sections -and sub-menus aggregated from every contributing node. For example, even if only two nodes actively collect from and -monitor an Apache web server, the **Apache** section still appears and displays composite charts from those two nodes. - - - -One difference between the Netdata Cloud menu and those found in local Agent dashboards is that -the Overview condenses multiple services, families, or instances into single sections, sub-menus, and associated charts. - -For services, let's say you have two concurrent jobs with the [web_log collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/weblog/README.md), one for Apache and another for Nginx. -A single-node or local dashboard shows two section, **web_log apache** and **web_log nginx**, whereas the Overview condenses these into a -single **web_log** section containing composite charts from both jobs. - -The Cloud also condenses multiple families or multiple instances into a single **all** sub-menu and associated charts. -For example, if Node A has 5 disks, and Node B has 3, each disk contributes to a single `disk.io` composite chart. -The utility bar should show that there are 8 charts from 2 nodes contributing to that chart. -The aggregation applies to disks, network devices, and other metric types that involve multiple instances of a piece of hardware or software. - -## Persistence of composite chart settings - -Of course you can [change the filtering or grouping](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) of metrics in the composite charts that aggregate all these instances, to see only the information you are interested in, and save that tab in a custom dashboard. - -When you change a composite chart via its definition bar, Netdata Cloud persists these settings in a query string attached to the URL in your browser. -You can "save" these settings by bookmarking this particular URL, or share it with colleagues by having them copy-paste it into their browser. diff --git a/docs/collect/application-metrics.md b/docs/collect/application-metrics.md deleted file mode 100644 index f3c97ee1a..000000000 --- a/docs/collect/application-metrics.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,83 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Collect application metrics with Netdata" -sidebar_label: "Application metrics" -description: "Monitor and troubleshoot every application on your infrastructure with per-second metrics, zero configuration, and meaningful charts." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/collect/application-metrics.md" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Concepts" ---> - -# Collect application metrics with Netdata - -Netdata instantly collects per-second metrics from many different types of applications running on your systems, such as -web servers, databases, message brokers, email servers, search platforms, and much more. Metrics collectors are -pre-installed with every Netdata Agent and usually require zero configuration. Netdata also collects and visualizes -resource utilization per application on Linux systems using `apps.plugin`. - -[**apps.plugin**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md) looks at the Linux process tree every second, much like `top` or -`ps fax`, and collects resource utilization information on every running process. By reading the process tree, Netdata -shows CPU, disk, networking, processes, and eBPF for every application or Linux user. Unlike `top` or `ps fax`, Netdata -adds a layer of meaningful visualization on top of the process tree metrics, such as grouping applications into useful -dimensions, and then creates per-application charts under the **Applications** section of a Netdata dashboard, per-user -charts under **Users**, and per-user group charts under **User Groups**. - -Our most popular application collectors: - -- [Prometheus endpoints](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus/README.md): Gathers - metrics from one or more Prometheus endpoints that use the OpenMetrics exposition format. Auto-detects more than 600 - endpoints. -- [Web server logs (Apache, NGINX)](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/weblog/README.md): - Tail access logs and provide very detailed web server performance statistics. This module is able to parse 200k+ - rows in less than half a second. -- [MySQL](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/mysql/README.md): Collect database global, - replication, and per-user statistics. -- [Redis](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/redis/README.md): Monitor database status by - reading the server's response to the `INFO` command. -- [Apache](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/apache/README.md): Collect Apache web server - performance metrics via the `server-status?auto` endpoint. -- [Nginx](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/nginx/README.md): Monitor web server status - information by gathering metrics via `ngx_http_stub_status_module`. -- [Postgres](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/postgres/README.md): Collect database health - and performance metrics. -- [ElasticSearch](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/elasticsearch/README.md): Collect search - engine performance and health statistics. Optionally collects per-index metrics. -- [PHP-FPM](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/phpfpm/README.md): Collect application summary - and processes health metrics by scraping the status page (`/status?full`). - -Our [supported collectors list](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md#service-and-application-collectors) shows all Netdata's -application metrics collectors, including those for containers/k8s clusters. - -## Collect metrics from applications running on Windows - -Netdata is fully capable of collecting and visualizing metrics from applications running on Windows systems. The only -caveat is that you must [install Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md) on a separate system or a compatible VM because there -is no native Windows version of the Netdata Agent. - -Once you have Netdata running on that separate system, you can follow the [collectors configuration reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) documentation to tell the collector to look for exposed metrics on the Windows system's IP -address or hostname, plus the applicable port. - -For example, you have a MySQL database with a root password of `my-secret-pw` running on a Windows system with the IP -address 203.0.113.0. you can configure the [MySQL -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/mysql/README.md) to look at `203.0.113.0:3306`: - -```yml -jobs: - - name: local - dsn: root:my-secret-pw@tcp(203.0.113.0:3306)/ -``` - -This same logic applies to any application in our [supported collectors -list](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md#service-and-application-collectors) that can run on Windows. - -## What's next? - -If you haven't yet seen the [supported collectors list](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md) give it a once-over for any -additional applications you may want to monitor using Netdata's native collectors, or the [generic Prometheus -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus/README.md). - -Collecting all the available metrics on your nodes, and across your entire infrastructure, is just one piece of the -puzzle. Next, learn more about Netdata's famous real-time visualizations by [seeing an overview of your -infrastructure](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md) using Netdata Cloud. - - diff --git a/docs/collect/container-metrics.md b/docs/collect/container-metrics.md deleted file mode 100644 index aecf7eee2..000000000 --- a/docs/collect/container-metrics.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,101 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Collect container metrics with Netdata" -sidebar_label: "Container metrics" -description: "Use Netdata to collect per-second utilization and application-level metrics from Linux/Docker containers and Kubernetes clusters." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/collect/container-metrics.md" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Concepts" ---> - -# Collect container metrics with Netdata - -Thanks to close integration with Linux cgroups and the virtual files it maintains under `/sys/fs/cgroup`, Netdata can -monitor the health, status, and resource utilization of many different types of Linux containers. - -Netdata uses [cgroups.plugin](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md) to poll `/sys/fs/cgroup` and convert the raw data -into human-readable metrics and meaningful visualizations. Through cgroups, Netdata is compatible with **all Linux -containers**, such as Docker, LXC, LXD, Libvirt, systemd-nspawn, and more. Read more about [Docker-specific -monitoring](#collect-docker-metrics) below. - -Netdata also has robust **Kubernetes monitoring** support thanks to a -[Helmchart](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md) to automate deployment, collectors for k8s agent services, and -robust [service discovery](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery/#service-discovery) to monitor the -services running inside of pods in your k8s cluster. Read more about [Kubernetes -monitoring](#collect-kubernetes-metrics) below. - -A handful of additional collectors gather metrics from container-related services, such as -[dockerd](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/docker/README.md) or [Docker -Engine](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/docker_engine/README.md). You can find all -container collectors in our supported collectors list under the -[containers/VMs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md#containers-and-vms) and -[Kubernetes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md#containers-and-vms) headings. - -## Collect Docker metrics - -Netdata has robust Docker monitoring thanks to the aforementioned -[cgroups.plugin](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md). By polling cgroups every second, Netdata can produce meaningful -visualizations about the CPU, memory, disk, and network utilization of all running containers on the host system with -zero configuration. - -Netdata also collects metrics from applications running inside of Docker containers. For example, if you create a MySQL -database container using `docker run --name some-mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql:tag`, it exposes -metrics on port 3306. You can configure the [MySQL -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/mysql/README.md) to look at `127.0.0.0:3306` for -MySQL metrics: - -```yml -jobs: - - name: local - dsn: root:my-secret-pw@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/ -``` - -Netdata then collects metrics from the container itself, but also dozens [MySQL-specific -metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/mysql/README.md#charts) as well. - -### Collect metrics from applications running in Docker containers - -You could use this technique to monitor an entire infrastructure of Docker containers. The same [enable and configure](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) procedures apply whether an application runs on the host system or inside -a container. You may need to configure the target endpoint if it's not the application's default. - -Netdata can even [run in a Docker container](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/docker/README.md) itself, and then collect metrics about the -host system, its own container with cgroups, and any applications you want to monitor. - -See our [application metrics doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/application-metrics.md) for details about Netdata's application metrics -collection capabilities. - -## Collect Kubernetes metrics - -We already have a few complementary tools and collectors for monitoring the many layers of a Kubernetes cluster, -_entirely for free_. These methods work together to help you troubleshoot performance or availability issues across -your k8s infrastructure. - -- A [Helm chart](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart), which bootstraps a Netdata Agent pod on every node in your - cluster, plus an additional parent pod for storing metrics and managing alert notifications. -- A [service discovery plugin](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery), which discovers and creates - configuration files for [compatible - applications](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#service-discovery-and-supported-services) and any endpoints - covered by our [generic Prometheus - collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus/README.md). With these - configuration files, Netdata collects metrics from any compatible applications as they run _inside_ a pod. - Service discovery happens without manual intervention as pods are created, destroyed, or moved between nodes. -- A [Kubelet collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubelet/README.md), which runs - on each node in a k8s cluster to monitor the number of pods/containers, the volume of operations on each container, - and more. -- A [kube-proxy collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubeproxy/README.md), which - also runs on each node and monitors latency and the volume of HTTP requests to the proxy. -- A [cgroups collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md), which collects CPU, memory, and bandwidth metrics for - each container running on your k8s cluster. - -For a holistic view of Netdata's Kubernetes monitoring capabilities, see our guide: [_Monitor a Kubernetes (k8s) cluster -with Netdata_](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/monitor/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md). - -## What's next? - -Netdata is capable of collecting metrics from hundreds of applications, such as web servers, databases, messaging -brokers, and more. See more in the [application metrics doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/application-metrics.md). - -If you already have all the information you need about collecting metrics, move into Netdata's meaningful visualizations -with [seeing an overview of your infrastructure](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md) using Netdata Cloud. - - diff --git a/docs/collect/system-metrics.md b/docs/collect/system-metrics.md deleted file mode 100644 index e4051b0fa..000000000 --- a/docs/collect/system-metrics.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,62 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Collect system metrics with Netdata" -sidebar_label: "System metrics" -description: "Netdata collects thousands of metrics from physical and virtual systems, IoT/edge devices, and containers with zero configuration." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/collect/system-metrics.md" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Concepts" ---> - -# Collect system metrics with Netdata - -Netdata collects thousands of metrics directly from the operating systems of physical and virtual systems, IoT/edge -devices, and [containers](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/container-metrics.md) with zero configuration. - -To gather system metrics, Netdata uses roughly a dozen plugins, each of which has one or more collectors for very -specific metrics exposed by the host. The system metrics Netdata users interact with most for health monitoring and -performance troubleshooting are collected and visualized by `proc.plugin`, `cgroups.plugin`, and `ebpf.plugin`. - -[**proc.plugin**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/proc.plugin/README.md) gathers metrics from the `/proc` and `/sys` folders in Linux -systems, along with a few other endpoints, and is responsible for the bulk of the system metrics collected and -visualized by Netdata. It collects CPU, memory, disks, load, networking, mount points, and more with zero configuration. -It even allows Netdata to monitor its own resource utilization! - -[**cgroups.plugin**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md) collects rich metrics about containers and virtual machines -using the virtual files under `/sys/fs/cgroup`. By reading cgroups, Netdata can instantly collect resource utilization -metrics for systemd services, all containers (Docker, LXC, LXD, Libvirt, systemd-nspawn), and more. Learn more in the -[collecting container metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/container-metrics.md) doc. - -[**ebpf.plugin**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md): Netdata's extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) collector -monitors Linux kernel-level metrics for file descriptors, virtual filesystem IO, and process management. You can use our -eBPF collector to analyze how and when a process accesses files, when it makes system calls, whether it leaks memory or -creating zombie processes, and more. - -While the above plugins and associated collectors are the most important for system metrics, there are many others. You -can find all system collectors in our [supported collectors list](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md#system-collectors). - -## Collect Windows system metrics - -Netdata is also capable of monitoring Windows systems. The [Windows -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/windows/README.md) integrates with -[windows_exporter](https://github.com/prometheus-community/windows_exporter), a small Go-based binary that you can run -on Windows systems. The Windows collector then gathers metrics from an endpoint created by windows_exporter, for more -details see [the requirements](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/windows/README.md#requirements). - -Next, [configure](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/windows/README.md#configuration) the Windows -collector to point to the URL and port of your exposed endpoint. Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. You'll start seeing Windows system metrics, such as CPU -utilization, memory, bandwidth per NIC, number of processes, and much more. - -For information about collecting metrics from applications _running on Windows systems_, see the [application metrics -doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/application-metrics.md#collect-metrics-from-applications-running-on-windows). - -## What's next? - -Because there's some overlap between system metrics and [container metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/container-metrics.md), you -should investigate Netdata's container compatibility if you use them heavily in your infrastructure. - -If you don't use containers, skip ahead to collecting [application metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/application-metrics.md) with -Netdata. - - diff --git a/docs/configure/nodes.md b/docs/configure/nodes.md deleted file mode 100644 index 99e00223c..000000000 --- a/docs/configure/nodes.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,139 +0,0 @@ -# Configure the Netdata Agent - -Netdata's zero-configuration collection, storage, and visualization features work for many users, infrastructures, and -use cases, but there are some situations where you might want to configure the Netdata Agent running on your node(s), -which can be a physical or virtual machine (VM), container, cloud deployment, or edge/IoT device. - -For example, you might want to increase metrics retention, configure a collector based on your infrastructure's unique -setup, or secure the local dashboard by restricting it to only connections from `localhost`. - -Whatever the reason, Netdata users should know how to configure individual nodes to act decisively if an incident, -anomaly, or change in infrastructure affects how their Agents should perform. - -## The Netdata config directory - -On most Linux systems, using our [recommended one-line -installation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#install-on-linux-with-one-line-installer), the **Netdata config -directory** is `/etc/netdata/`. The config directory contains several configuration files with the `.conf` extension, a -few directories, and a shell script named `edit-config`. - -> Some operating systems will use `/opt/netdata/etc/netdata/` as the config directory. If you're not sure where yours -> is, navigate to `http://NODE:19999/netdata.conf` in your browser, replacing `NODE` with the IP address or hostname of -> your node, and find the `# config directory = ` setting. The value listed is the config directory for your system. - -All of Netdata's documentation assumes that your config directory is at `/etc/netdata`, and that you're running any -scripts from inside that directory. - -## Netdata's configuration files - -Upon installation, the Netdata config directory contains a few files and directories. It's okay if you don't see all -these files in your own Netdata config directory, as the next section describes how to edit any that might not already -exist. - -- `netdata.conf` is the main configuration file. This is where you'll find most configuration options. Read descriptions - for each in the [daemon config](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/config/README.md) doc. -- `edit-config` is a shell script used for [editing configuration files](#use-edit-config-to-edit-configuration-files). -- Various configuration files ending in `.conf` for [configuring plugins or - collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) behave. Examples: `go.d.conf`, - `python.d.conf`, and `ebpf.d.conf`. -- Various directories ending in `.d`, which contain other configuration files, each ending in `.conf`, for [configuring - specific collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md). -- `apps_groups.conf` is a configuration file for changing how applications/processes are grouped when viewing the - **Application** charts from [`apps.plugin`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md) or - [`ebpf.plugin`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md). -- `health.d/` is a directory that contains [health configuration files](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md). -- `health_alarm_notify.conf` enables and configures [alert notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md). -- `statsd.d/` is a directory for configuring Netdata's [statsd collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/statsd.plugin/README.md). -- `stream.conf` configures [parent-child streaming](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/streaming/README.md) between separate nodes running the Agent. -- `.environment` is a hidden file that describes the environment in which the Netdata Agent is installed, including the - `PATH` and any installation options. Useful for [reinstalling](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/REINSTALL.md) or - [uninstalling](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/UNINSTALL.md) the Agent. - -The Netdata config directory also contains one symlink: - -- `orig` is a symbolic link to the directory `/usr/lib/netdata/conf.d`, which contains stock configuration files. Stock - versions are copied into the config directory when opened with `edit-config`. _Do not edit the files in - `/usr/lib/netdata/conf.d`, as they are overwritten by updates to the Netdata Agent._ - -## Configure a Netdata docker container - -See [configure agent containers](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/docker/README.md#configure-agent-containers). - -## Use `edit-config` to edit configuration files - -The **recommended way to easily and safely edit Netdata's configuration** is with the `edit-config` script. This script -opens existing Netdata configuration files using your system's `$EDITOR`. If the file doesn't yet exist in your config -directory, the script copies the stock version from `/usr/lib/netdata/conf.d` (or wherever the symlink `orig` under the config directory leads to) -to the proper place in the config directory and opens the copy for editing. - -If you have trouble running the script, you can manually copy the file and edit the copy. - -e.g. `cp /usr/lib/netdata/conf.d/go.d/bind.conf /etc/netdata/go.d/bind.conf; vi /etc/netdata/go.d/bind.conf` - -Run `edit-config` without options, to see details on its usage, or `edit-config --list` to see a list of all the configuration -files you can edit. - -```bash -USAGE: - ./edit-config [options] FILENAME - - Copy and edit the stock config file named: FILENAME - if FILENAME is already copied, it will be edited as-is. - - Stock config files at: '/etc/netdata/../../usr/lib/netdata/conf.d' - User config files at: '/etc/netdata' - - The editor to use can be specified either by setting the EDITOR - environment variable, or by using the --editor option. - - The file to edit can also be specified using the --file option. - - For a list of known config files, run './edit-config --list' -``` - -To edit `netdata.conf`, run `./edit-config netdata.conf`. You may need to elevate your privileges with `sudo` or another -method for `edit-config` to write into the config directory. Use your `$EDITOR`, make your changes, and save the file. - -> `edit-config` uses the `EDITOR` environment variable on your system to edit the file. On many systems, that is -> defaulted to `vim` or `nano`. Use `export EDITOR=` to change this temporarily, or edit your shell configuration file -> to change to permanently. - -After you make your changes, you need to [restart the Agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) with `sudo systemctl -restart netdata` or the appropriate method for your system. - -Here's an example of editing the node's hostname, which appears in both the local dashboard and in Netdata Cloud. - - - -### Other configuration files - -You can edit any Netdata configuration file using `edit-config`. A few examples: - -```bash -./edit-config apps_groups.conf -./edit-config ebpf.d.conf -./edit-config health.d/load.conf -./edit-config go.d/prometheus.conf -``` - -The documentation for each of Netdata's components explains which file(s) to edit to achieve the desired behavior. - -## See an Agent's running configuration - -On start, the Netdata Agent daemon attempts to load `netdata.conf`. If that file is missing, incomplete, or contains -invalid settings, the daemon attempts to run sane defaults instead. In other words, the state of `netdata.conf` on your -filesystem may be different from the state of the Netdata Agent itself. - -To see the _running configuration_, navigate to `http://NODE:19999/netdata.conf` in your browser, replacing `NODE` with -the IP address or hostname of your node. The file displayed here is exactly the settings running live in the Netdata -Agent. - -If you're having issues with configuring the Agent, apply the running configuration to `netdata.conf` by downloading the -file to the Netdata config directory. Use `sudo` to elevate privileges. - -```bash -wget -O /etc/netdata/netdata.conf http://localhost:19999/netdata.conf -# or -curl -o /etc/netdata/netdata.conf http://NODE:19999/netdata.conf -``` diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..372f2030b --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ +# Dashboards and Charts + +This guide covers how to access both Agent and Cloud dashboards, along with links to explore specific sections in more detail. + +When you access the Netdata dashboard through the Cloud, you'll always have the latest version available. + +By default, the Agent dashboard shows the latest version (matching Netdata Cloud). However, there are a few exceptions: + +- Without internet access, the Agent can't download the newest dashboards. In this case, it will automatically use the bundled version. +- Users have defined, e.g. through URL bookmark, that they want to see the previous version of the dashboard (accessible `http://NODE:19999/v1`, replacing `NODE` with the IP address or hostname of your Agent). + +## Main sections + +The Netdata dashboard consists of the following main sections: + +- [Home tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/home-tab.md) +- [Nodes tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/nodes-tab.md) +- [Netdata charts](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md) +- [Metrics tab and single node tabs](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md) +- [Top tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/top-tab.md) +- [Logs tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/logs-tab.md) +- [Dashboards tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md) +- [Alerts tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md) +- [Events tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/events-feed.md) + +> **Note** +> +> Some sections of the dashboard, when accessed through the agent, may require the user to be signed in to Netdata Cloud or have the Agent claimed to Netdata Cloud for their full functionality. Examples include saving visualization settings on charts or custom dashboards, claiming the node to Netdata Cloud, or executing functions on an Agent. + +## How to access the dashboards? + +### Netdata Cloud + +You can access the dashboard at <https://app.netdata.cloud/> and [sign-in with an account or sign-up](/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/README.md) if you don't have an account yet. + +### Netdata Agent + +To view your Netdata dashboard, open a web browser and enter the address `http://NODE:19999` - replace `NODE` with your Agent's IP address or hostname. If the Agent is on the same machine, use http://localhost:19999. + +Documentation for previous Agent dashboard can still be found [here](/src/web/gui/README.md). diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..00d3efcb7 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,66 @@ +# Alerts tab + +Netdata comes with hundreds of pre-configured health alerts designed to notify you when an anomaly or performance issue affects your node or its applications. + +## Active tab + +From the Active tab you can see all the active alerts in your Room. You will be presented with a table having information about each alert that is in warning or critical state. + +You can always sort the table by a certain column by clicking on the name of that column, and using the gear icon on the top right to control which columns are visible at any given time. + +### Filter alerts + +From this tab, you can also filter alerts with the right hand bar. More specifically you can filter: + +- Alert status + - Filter based on the status of the alerts (e.g. Warning, Critical) +- Alert class + - Filter based on the class of the alert (e.g. Latency, Utilization, Workload etc.) +- Alert type & component + - Filter based on the alert's type (e.g. System, Web Server) and component (e.g. CPU, Disk, Load) +- Alert role + - Filter by the role that the alert is set to notify (e.g. Sysadmin, Webmaster etc.) +- Host labels + - Filter based on the host labels that are configured for the nodes across the Room (e.g. `_cloud_instance_region` to match `us-east-1`) +- Node status + - Filter by node availability status (e.g. Live or Offline) +- Netdata version + - Filter by Netdata version (e.g. `v1.45.3`) +- Nodes + - Filter the alerts based on the nodes of your Room. + +### View alert details + +By clicking on the name of an entry of the table you can access that alert's details page, providing you with: + +- Latest and Triggered time values +- The alert's description +- A link to the Netdata Advisor's page about this alert +- The chart at the time frame that the alert was triggered +- The alert's information: Node name, chart instance, type, component and class +- Configuration section +- Instance values - Node Instances + +At the bottom of the panel you can click the green button "View alert page" to open a dynamic tab containing all the info for this alert in a tab format, where you can also run correlations and go to the node's chart that raised the particular alert. + +### Silence an alert + +From this tab, the "Silencing" column shows if there is any rule present for each alert, and from the "Actions" column you can create a new [silencing rule](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md#alert-notifications-silencing-rules) for this alert, or get help and information about this alert from the [Netdata Assistant](/docs/netdata-assistant.md). + +## Alert Configurations tab + +From this tab you can view all the configurations for all running alerts in your Room. Each row concerns one alert, and it provides information about it in the rest of the table columns. + +By running alerts we mean alerts that are related to some metric that is or was collected. Netdata may have more alerts pre-configured that aren't applicable to your monitoring use-cases. + +You can control which columns are visible by using the gear icon on the right-hand side. + +Similarly to the previous tab, you can see the silencing status of an alert, while also being able to dig deeper and show the configuration for the alert and ask the [Netdata Assistant](/docs/netdata-assistant.md) for help. + +### See the configuration for an alert + +From the actions column you can explore the alert's configuration, split by the different nodes that have this alert configured. + +From there you can click on any of the rows to get to the individual alert configurations for that node. + +Click on an alert row to see the alert's page, with all the information about when it was last triggered and what it's configuration is. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/anomaly-advisor-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/anomaly-advisor-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..51b58b23a --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/anomaly-advisor-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ +# Anomaly Advisor tab + +The Anomaly Advisor tab lets you focus on potentially anomalous metrics and charts related to a particular highlighted window of interest. In addition to this tab, each chart in the [Metrics tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md) also has an [Anomaly Rate ribbon](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#anomaly-rate-ribbon). + + +More details about configuration can be found in the [ML documentation](/src/ml/README.md#configuration). + +This tab uses our [Anomaly Rate ML feature](/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate---averageanomaly-bit) to score metrics in terms of anomalous behavior. + +- The "Anomaly Rate" chart shows the percentage of anomalous metrics over time per node. + +- The "Count of Anomalous Metrics" chart shows raw counts of anomalous metrics per node so may often be similar to the Anomaly Rate chart, apart from where nodes may have different numbers of metrics. + +- The "Anomaly Events Detected" chart shows whether the anomaly rate per node has increased enough to cause a node-level anomaly. Anomaly events will appear slightly after the anomaly rate starts to increase in the timeline, this is because a significant number of metrics in the node need to be anomalous before an anomaly event is triggered. + +Once you have highlighted a window of interest, you should see an ordered list of charts, with the Anomaly Rate being displayed as a purple ribbon in the chart. + +> **Tip** +> +> You can also use the [node filter](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/node-filter.md) to select which nodes you want to include or exclude. + +The right side of the page displays an anomaly index for the highlighted timeline of interest. The index is sorted from most anomalous (highest level of anomaly) to least (lowest level of anomaly). Clicking on an entry in the index will get you to the corresponding chart for the anomalous metric. + +## Usage Tips + +- If you are interested in a subset of specific nodes then filtering to just those nodes before highlighting is recommended to get better results. When you highlight a timeframe, Netdata will ask the Agents for a ranking across all metrics, so if there is a subset of nodes there will be less "averaging" going on and you'll get a less noisy ranking. +- Ideally try and highlight close to a spike or window of interest so that the resulting ranking can narrow-in more easily on the timeline you are interested in. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..4d7bbc84f --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,96 @@ +# Dashboards tab + +With Netdata Cloud, you can build **custom dashboards** that target your infrastructure's unique needs. Put key metrics from any number of distributed systems in one place for a bird's eye view of your infrastructure. + +Click on the **Dashboards** tab in any Room to get started. + +## Create your first dashboard + +From the Dashboards tab, click on the **+** button. + +In the modal, give your custom dashboard a name, and click **+ Add**. + +- The **Add Chart** button on the top right of the interface adds your first chart card. From the dropdown, select either **All Nodes** or a specific node. + + Next, select the context. You'll see a preview of the chart before you finish adding it. In this modal you can also [interact with the chart](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md), meaning you can configure all the aspects of the [NIDL framework](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#nidl-framework) of the chart and more in detail, you can: + - define which `group by` method to use + - select the aggregation function over the data source + - select nodes + - select instances + - select dimensions + - select labels + - select the aggregation function over time + + After you are done configuring the chart, you can also change the type of the chart from the right hand side of the [Title bar](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#title-bar), and select which of the final dimensions you want to be visible and in what order, from the [Dimensions bar](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#dimensions-bar). + +- The **Add Text** button on the top right of the interface creates a new card with user-defined text, which you can use to describe or document a particular dashboard's meaning and purpose. + +> ### Important +> +> Be sure to click the **Save** button any time you make changes to your dashboard. + +## Using your dashboard + +Dashboards are designed to be interactive and flexible so you can design them to your needs. They are made from any number of charts and cards, which can contain charts or text. + +### Charts + +The charts you add to any dashboard are [fully interactive](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md), just like any other Netdata chart. You can zoom in and out, highlight timeframes, and more. + +Charts also synchronize as you interact with them, even across contexts _or_ nodes. + +### Text cards + +You can use text cards as notes to explain to other members of the [Room](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-rooms) the purpose of the dashboard's arrangement. + +By clicking the `T` icon on the text box, you can switch between font sizes. + +### Move elements + +To move a chart or a card, click and hold on **Drag & drop** at the top right of each element and drag it to a new location. A green placeholder indicates the +new location. Once you release your mouse, other elements re-sort to the grid system automatically. + +### Resize elements + +To resize any element on a dashboard, click on the bottom-right corner and drag it to its new size. Other elements re-sort to the grid system automatically. + +### Go to chart + +Quickly jump to the location of the chart in either the [Metrics tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md) or if the chart refers to a single node, its single node dashboard by clicking the 3-dot icon in the corner of any chart to open a menu. Hit the **Go to Chart** item. + +You'll land directly on that chart of interest, but you can now scroll up and down to correlate your findings with other +charts. Of course, you can continue to zoom, highlight, and pan through time just as you're used to with Netdata Charts. + +### Rename a chart + +Using the 3-dot icon in the corner of any chart, you can rename it to better explain your use case or the visualization settings you've chosen for the chart. + +### Remove an individual element + +Click on the 3-dot icon in the corner of any card to open a menu. Click the **Remove** item to remove the card. + +## Managing your dashboard + +To see dashboards associated with the current Room, click the **Dashboards** tab in any Room. You can select dashboards and delete them using the 🗑️ icon. + +### Update/save a dashboard + +If you've made changes to a dashboard, such as adding or moving elements, the **Save** button is enabled. Click it to save your most recent changes. + +Any other members of the Room will be able to see these changes the next time they load this dashboard. + +If multiple users attempt to make concurrent changes to the same dashboard, the second user who hits Save will be +prompted to either overwrite the dashboard or reload to see the most recent changes. + +### Delete a dashboard + +Delete any dashboard by navigating to it and clicking the **Delete** button. This will remove this entry from the +dropdown for every member of this Room. + +### Minimum browser viewport + +Because of the visual complexity of individual charts, dashboards require a minimum browser viewport of 800px. + +## What's next? + +Once you've designed a dashboard or two, make sure to [invite your team](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team) if you haven't already. You can add these new users to the same Room to let them see the same dashboards without any effort. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/events-feed.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/events-feed.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..a5386e80e --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/events-feed.md @@ -0,0 +1,74 @@ +# Events tab + +The Events tab provides a feed which is a powerful feature that tracks events that happen on your infrastructure, or in your Space. The feed lets you investigate events that occurred in the past, which is invaluable for troubleshooting. Common use cases are ones like when a node goes offline, and you want to understand what events happened before that. A detailed event history can also assist in attributing sudden pattern changes in a time series to specific changes in your environment. + +## What are the available events? + +At a high-level view, these are the domains from which the Events feed will provide visibility into. + +> **Note** +> +> Based on your space's plan, different allowances are defined to query past data. + +| **Domains of events** | **Community** | **Homelab** | **Business** | **Enterprise On-Premise** | +|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:--------------|:------------|:-------------|:--------------------------| +| **[Auditing events](#auditing-events)** <p>Events related to actions done on your Space, e.g. invite user, change user role or change plan.</p> | 4 hours | 90 days | 90 days | User dependent | +| **[Topology events](#topology-events)** <p>Node state transition events, e.g. live or offline.</p> | 4 hours | 14 days | 14 days | User dependent | +| **[Alert events](#alert-events)** <p>Alert state transition events, can be seen as an alert history log.</p> | 4 hours | 90 days | 90 days | User dependent | + +### Auditing events + +| **Event name** | **Description** | **Example** | +|:------------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Space Created | The space was created. | Space `Acme Space` was **created** | +| Room Created | A Room was created on the Space. | Room `DB Servers` was **created** by `John Doe` | +| Room Deleted | A Room was deleted from the Space. | Room `DB servers` was **deleted** by `John Doe` | +| User Invited to Space | A user was invited to join the Space. | User `John Smith` was **invited** to this space by `Alan Doe` | +| User Uninvited from Space | An invitation for a user to join the space was revoked. | User `John Smith` was **uninvited** from this space | +| User Added to Space | A user was added to the Space from an invitation (user accepted the invitation). | User `John Smith` was **added** to this space by invite of `Alan Doe` | +| User Removed from Space | A user was added to the Space from an invitation. | User `John Smith` was **removed** from this space by `Alan Doe` | +| User Added to Room | A user was added to a Room on the Space. | User `John Smith` was **added** to Room `DB servers` | +| User Removed from Room | A user was removed from a Room on the Space. | User `John Smith` was **removed** from Room `DB Servers` by `Alan Doe` | +| User Space Properties Changed | The properties of a user on the Space have changed, e.g. change user role | User role for `John Smith` was **changed** to `troubleshooter` by `Alan Doe` | +| Node Added To Room | The node was added to a Room on the Space. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **added** to Room `DB Servers` by `John Doe` | +| Node Removed To Room | The node was removed from a Room on the Space. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **removed** from Room `DB Servers` by `John Doe` | +| Silencing Rule Created | A new alert notification silencing rule was created on the Space. | Silencing rule `DB Servers schedule silencing` on Rooms `All nodes` and `DB Servers` was **created** by `John Smith` | +| Silencing Rule Changed | An existing alert notification silencing rule was modified on the Space. | Silencing rule `DB Servers schedule silencing` on Rooms `All nodes` and `DB Servers` was **changed** by `John Doe` | +| Silencing Rule Deleted | An existing alert notifications silencing rule was removed from the Space. | Silencing rule `DB Servers schedule silencing` on Rooms `All nodes` and `DB Servers` was **changed** by `Alan Smith` | +| Space Claiming Token Created | A Space Claiming Token was created. | Claiming Token was created by user `John Doe` | +| Space Claiming Token Revoked | A Space Claiming Token was revoked. | Claiming Token `_OtF2ssjrv` was revoked by user `John Doe` | + +### Topology events + +| **Event name** | **Description** | **Example** | +|:--------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Node Became Live | The node is collecting and streaming metrics to Cloud. | Node `netdata-k8s-state-xyz` was **live** | +| Node Became Stale | The node is offline and not streaming metrics to Cloud. It can show historical data from a parent node. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **stale** | +| Node Became Offline | The node is offline, not streaming metrics to Cloud and not available in any parent node. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **offline** | +| Node Created | The node is created but it is still `Unseen` on Cloud, didn't establish a successful connection yet. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **created** | +| Node Removed | The node was removed from the Space, for example by using the `Delete` action on the node. This is a soft delete in that the node gets marked as deleted, but retains the association with this space. If it becomes live again, it will be restored (see `Node Restored` below) and reappear in this space as before. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **deleted (soft)** | +| Node Restored | The node was restored. See `Node Removed` above. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **restored** | +| Node Deleted | The node was deleted from the Space. This is a hard delete and no information on the node is retained. | Node `ip-xyz.ec2.internal` was **deleted (hard)** | +| Agent Connected | The agent connected to the Cloud MQTT server (Agent-Cloud Link established).<br/>These events can only be seen on _All nodes_ Room. | Agent with claim ID `7d87bqs9-cv42-4823-8sd4-3614548850c7` has connected to Cloud. | +| Agent Disconnected | The agent disconnected from the Cloud MQTT server (Agent-Cloud Link severed).<br/>These events can only be seen on _All nodes_ Room. | Agent with claim ID `7d87bqs9-cv42-4823-8sd4-3614548850c7` has disconnected from Cloud: **Connection Timeout**. | +| Space Statistics | Daily snapshot of space node statistics.<br/>These events can only be seen on _All nodes_ Room. | Space statistics. Nodes: **22 live**, **21 stale**, **18 removed**, **61 total**. | + +### Alert events + +| **Event name** | **Description** | **Example** | +|:-------------------------|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Node Alert State Changed | These are node alert state transition events and can be seen as an alert history log. You will be able to see transitions to or from any of these states: Cleared, Warning, Critical, Removed, Error or Unknown | Transition to Cleared:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` recovered with value **8.33%**<br/><br/>Transition from Cleared to Warning or Critical:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` was raised to **WARNING** with value **10%**<br/><br/>Transition from Warning to Critical:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` escalated to **CRITICAL** with value **25%**<br/><br/>Transition from Critical to Warning:<br/>`httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` was demoted to **WARNING** with value **10%**<br/><br/>Transition to Removed:<br/>Alert `httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` for `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` is no longer available, state can't be assessed.<br/><br/>Transition to Error:<br/>For this alert `httpcheck_web_service_bad_status` related to `httpcheck_netdata_cloud.request_status` on `netdata-parent-xyz` we couldn't calculate the current value ⓘ | + +## Who can access the events? + +All users will be able to see events from the Topology and Alerts domain but Auditing events, once these are added, will only be accessible to administrators. For more details check the [Netdata Role-Based Access model](/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md). + +## How to use the events feed + +1. Click on the **Events** tab (located near the top of your screen) +1. You will be presented with a table listing the events that occurred from the timeframe defined on the [date time picker](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md#date-and-time-selector) +1. You can use the filtering capabilities available on right-hand bar to slice through the results provided. See more details on [event types and filters](#event-types-and-filters) + +> **Note** +> +> When you try to query a longer period than what your space allows you will see an error message highlighting that you are querying data outside your plan. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/home-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/home-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..23764815f --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/home-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,60 @@ +# Home tab + +The Home tab allows users to see an overview of their Room. + +## Total nodes + +The total number of nodes is presented and dissected by their state, Live, Offline or Stale. + +## Active alerts + +The number of active alerts is presented in a donut chart, while also having counters for both Critical and Warning alerts. + +## Nodes map + +A map consisting of node entries allows for quick hoverable information about each node, while also presenting node status in a color-coded way. + +The map classification can be altered, allowing the categorization of nodes by: + +- Status (e.g. Live) +- OS (e.g. Ubuntu) +- Technology (e.g. Container) +- Agent version (e.g. v1.45.2) +- Replication factor (e.g. Single, Multi) +- Cloud provider (e.g AWS) +- Cloud region (e.g. us-east-1) +- Instance type (e.g. c6a.xlarge) + +Color-coding can also be configured between: + +- Status (e.g. Live, Offline) +- Connection stability (e.g. Stable, Unstable) +- Replication factor (e.g. None, Single) + +## Data replication + +There are two views about data replication in the Home tab: + +The first bar chart presents the amount of **Parents**, **Children** and **Standalone** nodes. + +The second bar chart presents the number of nodes depending on their Replication factor, **None**, **Single** and **Multi**. + +## Alerts overview over the last 24h + +There are two views that display information about nodes that produced the most alerts and top alerts in the last 24 hours. + +The first bar chart presents the nodes that produced the most alerts in a time window of the last 24 hours. + +The second table contains the top alerts in the last 24 hours, along with their instance, the occurrences and their duration in seconds. + +## Netdata Assistant shortcut + +In the Home tab there is a shortcut button in order to start an instant conversation with the [Netdata Assistant](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/netdata-assistant.md). + +## Space metrics + +There are three key metrics that are displayed in the Home tab, **Metrics collected**, **Charts visualized** and **Alerts configured**. + +## Data retention per Nodes + +This bar chart shows the number of nodes based on their retention period. diff --git a/docs/dashboard/import-export-print-snapshot.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/import-export-print-snapshot.md index 4a5ca499e..80bf514ae 100644 --- a/docs/dashboard/import-export-print-snapshot.md +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/import-export-print-snapshot.md @@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ description: >- they've already happened, and are interoperable with any other node running Netdata." type: "how-to" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/import-export-print-snapshot.md" +custom_edit_url: "/docs/dashboards-and-charts/import-export-print-snapshot.md" sidebar_label: "Import, export, and print a snapshot" learn_status: "Published" learn_topic_type: "Tasks" @@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ learn_rel_path: "Operations" # Import, export, and print a snapshot >❗This feature is only available on v1 dashboards, it hasn't been port-forwarded to v2. -> For more information on accessing dashboards check [this documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md). +> For more information on accessing dashboards check [this documentation](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md). Netdata can export snapshots of the contents of your dashboard at a given time, which you can then import into any other @@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ node running Netdata. Or, you can create a print-ready version of your dashboard paper. Snapshots can be incredibly useful for diagnosing anomalies after they've already happened. Let's say Netdata triggered a warning alert while you were asleep. In the morning, you can [select the -timeframe](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md) when the alert triggered, export a snapshot, and send it to a +timeframe](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md) when the alert triggered, export a snapshot, and send it to a colleague for further analysis. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/kubernetes-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/kubernetes-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..9b5df87d8 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/kubernetes-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,42 @@ +# Kubernetes tab + +The Netdata dashboards feature enhanced visualizations for the resource utilization of Kubernetes (k8s) clusters, embedded in the default [Metrics tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md) dashboard. + +These visualizations include a health map for viewing the status of k8s pods/containers, in addition to [Netdata charts](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md) for viewing per-second CPU, memory, disk, and networking metrics from k8s nodes. + +See our [Kubernetes deployment instructions](/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md) for details on deploying Netdata on your Kubernetes cluster. + +## Available Kubernetes metrics + +Netdata Cloud organizes and visualizes the following metrics from your Kubernetes cluster from every container: + +| Metric | Description | +|------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| `k8s.cgroup.cpu_limit` | CPU utilization as a percentage of the limit defined by the [pod specification `spec.containers[].resources.limits.cpu`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#resource-requests-and-limits-of-pod-and-container) or a [`LimitRange` object](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/manage-resources/cpu-default-namespace/#create-a-limitrange-and-a-pod). | +| `k8s.cgroup.cpu` | CPU utilization of the pod/container. 100% usage equals 1 fully-utilized core, 200% equals 2 fully-utilized cores, and so on. | +| `k8s.cgroup.throttled` | The percentage of runnable periods when tasks in a cgroup have been throttled. | +| `k8s.cgroup.throttled_duration` | The total time duration for which tasks in a cgroup have been throttled. | +| `k8s.cgroup.mem_utilization` | Memory utilization within the configured or system-wide (if not set) limits. | +| `k8s.cgroup.mem_usage_limit` | Memory utilization, without cache, as a percentage of the limit defined by the [pod specification `spec.containers[].resources.limits.memory`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/#resource-requests-and-limits-of-pod-and-container) or a [`LimitRange` object](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/manage-resources/cpu-default-namespace/#create-a-limitrange-and-a-pod). | +| `k8s.cgroup.mem_usage` | Used memory, without cache. | +| `k8s.cgroup.mem` | The sum of `cache` and `rss` (resident set size) memory usage. | +| `k8s.cgroup.writeback` | The size of `dirty` and `writeback` cache. | +| `k8s.cgroup.pgfaults` | Sum of page fault bandwidth, which are raised when the Kubernetes cluster tries accessing a memory page that is mapped into the virtual address space, but not actually loaded into main memory. | +| `k8s.cgroup.throttle_io` | Sum of `read` and `write` per second across all PVs/PVCs attached to the container. | +| `k8s.cgroup.throttle_serviced_ops` | Sum of the `read` and `write` operations per second across all PVs/PVCs attached to the container. | +| `k8s.cgroup.net_net` | Sum of `received` and `sent` bandwidth per second. | +| `k8s.cgroup.net_packets` | Sum of `multicast`, `received`, and `sent` packets. | + + +When viewing the [overview of this dashboard](#kubernetes-containers-overview), Netdata presents the above metrics per container, or aggregated based on +their associated pods. + +## Kubernetes Containers overview + +At the top of the Kubernetes containers section there is a map, that with a given context colorizes the containers in terms of their utilization. + +The filtering of this map is controlled by using the [NIDL framework](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#nidl-framework) from the definition bar of the chart. + +### Detailed information + +Hover over any of the pods/containers in the map to display a modal window, which contains contextual information and real-time metrics from that resource. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/logs-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/logs-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..3851d90da --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/logs-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,16 @@ +# Logs tab + +The Logs tab is using the [`systemd` journal plugin](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md), to present a structured view into your infrastructure's `systemd` logs. + +We have a thorough section explaining how you can [work with logs](/docs/category-overview-pages/working-with-logs.md), detailing how the plugin works, and what other utilities are used under the hood to provide you with the visualizations and the log entries. + +The [`systemd` journal plugin](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md) documentation has information about: + +- [Key features the plugin provides](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md#key-features) +- [Journal sources](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md#journal-sources) +- [Journal fields](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md#journal-fields) +- [Full-text search](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md#full-text-search) +- [Query performance](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md#query-performance) +- [Performance at scale](/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin/README.md#performance-at-scale) + +We recommend you to read through that document, to better understand how the plugin and the visualizations work. diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..bf31b8a71 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md @@ -0,0 +1,25 @@ +# Metrics tab and single node tabs + +The Metrics tab is where all the time series [charts](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md) for all the nodes of a Room are located. + +You can also see single-node dashboards, essentially the same dashboard the Metrics tab offers but only for one node. They are reached from most places in the UI, often by clicking the name of a node. + +From this tab, a user can also reach the Integrations tab and run [Metric Correlations](/docs/metric-correlations.md) + +## Dashboard structure + +The dashboard consists of various charts presented in different chart types. They are categorized based on their [context](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#contexts) and at the beginning of each section, there is a predefined arrangement of charts helping you to get an overview for that particular section. + +## Chart navigation Menu + +On the right-hand side, there is a bar that: + +- Allows for quick navigation through the sections of the dashboard +- Provides a filtering mechanism that can filter charts by: + - Host labels + - Node status + - Netdata version + - Individual nodes +- Presents the active alerts for the Room + +From this bar you can also view the maximum chart anomaly rate on each menu section by clicking the `AR%` button. diff --git a/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md index 57b4c253d..5536f83b2 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md @@ -13,14 +13,14 @@ These charts provide a lot of useful information, so that you can: - View the combined anomaly rate of all underlying data with the [Anomaly Rate ribbon](#anomaly-rate-ribbon) - Explore even more details about a chart's metrics through [hovering over certain elements of it](#hover-over-the-chart) - Use intuitive tooling and shortcuts to pan, zoom or highlight areas of interest in your charts -- On highlight, get easy access to [Metric Correlations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md) to see other metrics with similar patterns +- On highlight, get easy access to [Metric Correlations](/docs/metric-correlations.md) to see other metrics with similar patterns - Have the dimensions sorted based on name or value - View information about the chart, its plugin, context, and type - View individual metric collection status about a chart These charts are available on Netdata Cloud's -[Overview tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md), Single Node tab and -on your [Custom Dashboards](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md). +[Metrics tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md), [single sode tabs](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md) and +on your [Custom Dashboards](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md). ## Overview @@ -42,8 +42,8 @@ With a quick glance you have immediate information available at your disposal: While Netdata's charts require no configuration and are easy to interact with, they have a lot of underlying complexity. To meaningfully organize charts out of the box based on what's happening in your nodes, Netdata uses the concepts of [dimensions](#dimensions), [contexts](#contexts), and [families](#families). Understanding how these work will help you more easily navigate the dashboard, -[write new alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md), or play around -with the [API](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/api/README.md). +[write new alerts](/src/health/REFERENCE.md), or play around +with the [API](/src/web/api/README.md). ### Dimensions @@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ whereas anything after the `.` is specified either by the chart's developer or b By default, a chart's type affects where it fits in the menu, while its family creates submenus. -Netdata also relies on contexts for [alert configuration](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md) (the [`on` line](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-on)). +Netdata also relies on contexts for [alert configuration](/src/health/REFERENCE.md) (the [`on` line](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-on)). ### Families @@ -98,24 +98,29 @@ names: ## Title bar -When you start interacting with a chart, you'll notice valuable information on the top bar: +When you start interacting with a chart, you'll notice valuable information on the Title bar: -<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/70198089/236133832-fad45e65-5bd6-4fd1-8d68-33acf69fff5c.png" width="900"/> +<img src="https://github.com/netdata/netdata/assets/70198089/75d700de-bc7d-4b96-b73d-7b248b83afea" width="900"/> -The elements that you can find on this top bar are: +Title bar elements: -- **Netdata icon**: this indicates that data is continuously being updated, this happens if [Time controls](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md#time-controls) are in Play or Force Play mode. +- **Netdata icon**: this indicates that data is continuously being updated, this happens if [Time controls](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md#time-controls) are in Play or Force Play mode. - **Chart title**: on the chart title you can see the title together with the metric being displayed, as well as the unit of measurement. - **Chart status icon**: possible values are: Loading, Timeout, Error or No data, otherwise this icon is not shown. Along with viewing chart type, context and units, on this bar you have access to immediate actions over the chart: -<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/70198089/236134195-ecb08f79-1355-4bce-8449-e829f4a6b1c0.png" width="200" /> +<img src="https://github.com/netdata/netdata/assets/70198089/d21f326e-065c-4a08-bee9-69ad23736e38" width="200" /> + +- **Manage Alerts**: manage [Alert configurations](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md#alert-configurations-tab) for this chart. - **Chart info**: get more information relevant to the chart you are interacting with. - **Chart type**: change the chart type from **line**, **stacked**, **area**, **stacked bar** and **multi bar**. - **Enter fullscreen mode**: expand the current chart to the full size of your screen. -- **Add chart to dashboard**: add the chart to an existing custom dashboard or directly create a new one that includes the chart. +- **User settings**: save your settings for the chart at hand, so it persists across dashboard reloads. + - Personal has the top priority. + - Room and Space settings for a chart are shared across all users who don't have personal settings for it. +- **Drag and Drop the chart to a Dashboard**: add the chart to an existing custom [Dashboard](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md) or directly create a new one that includes the chart. ## Definition bar @@ -172,7 +177,7 @@ It supports: 1. **Group by Node**, to summarize the data of each node, and provide one dimension on the chart for each of the nodes involved. Filtering nodes is supported at the same time, using the nodes dropdown menu. 2. **Group by Instance**, to summarize the data of each instance and provide one dimension on the chart for each of the instances involved. Filtering instances is supported at the same time, using the instances dropdown menu. -3. **Group by Dimension**, so that each metric in the visualization is the aggregation of a single dimension. This provides a per dimension view of the data from all the nodes in the War Room, taking into account filtering criteria if defined. +3. **Group by Dimension**, so that each metric in the visualization is the aggregation of a single dimension. This provides a per dimension view of the data from all the nodes in the Room, taking into account filtering criteria if defined. 4. **Group by Label**, to summarize the data for each label value. Multiple label keys can be selected at the same time. Using this menu, you can slice and dice the data in any possible way, to quickly get different views of it, without the need to edit a query string and without any need to better understand the format of the underlying data. @@ -262,7 +267,7 @@ By default the aggregation applied is _average_ but the user can choose differen - Delta - Single or Double exponential smoothing -For more details on each, you can refer to our Agent's HTTP API details on [Data Queries - Data Grouping](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/api/queries/README.md#data-grouping). +For more details on each, you can refer to our Agent's HTTP API details on [Data Queries - Data Grouping](/src/web/api/queries/README.md#data-grouping). ### Reset to defaults @@ -318,7 +323,7 @@ All these indicators are also visualized per dimension, in the pop-over that app ## Play, Pause and Reset -Your charts are controlled using the available [Time controls](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md#time-controls). +Your charts are controlled using the available [Time controls](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md#time-controls). Besides these, when interacting with the chart you can also activate these controls by: - Hovering over any chart to temporarily pause it - this momentarily switches time control to Pause, so that you can @@ -363,12 +368,16 @@ it like pushing the current timeframe off the screen to see what came before or Selecting timeframes is useful when you see an interesting spike or change in a chart and want to investigate further by: - Looking at the same period of time on other charts/sections -- Running [metric correlations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md) to filter metrics that also show something different in the selected period, vs the previous one +- Running [metric correlations](/docs/metric-correlations.md) to filter metrics that also show something different in the selected period, vs the previous one | Interaction | Keyboard/mouse | Touchpad/touchscreen | |:-----------------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------|:---------------------| | **Highlight** a specific timeframe | `Alt + mouse selection` or `⌘ + mouse selection` (macOS) | `n/a` | +> **Note** +> +> To clear a highlighted timeframe, simply click on the chart area. + ### Select and zoom You can zoom to a specific timeframe, either horizontally of vertically, by selecting a timeframe. diff --git a/docs/cloud/visualize/node-filter.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/node-filter.md index 1b3979ff4..9f5371fff 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/visualize/node-filter.md +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/node-filter.md @@ -1,12 +1,12 @@ # Node filter -The node filter allows you to quickly filter the nodes visualized in a War Room's views. It appears on all views, except on single-node dashboards. +The node filter allows you to quickly filter the nodes visualized in a Room's views. It appears on all views, except on single-node dashboards. Inside the filter, the nodes get categorized into three groups: | Group | Description | |---------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| Live | Nodes that are currently online, collecting and streaming metrics to Cloud. Live nodes display raised [Alert](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md) counters, [Machine Learning](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md) availability, and [Functions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md) availability | +| Live | Nodes that are currently online, collecting and streaming metrics to Cloud. Live nodes display raised [Alert](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md) counters, [Machine Learning](/src/ml/README.md) availability, and [Functions](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md) availability | | Stale | Nodes that are offline and not streaming metrics to Cloud. Only historical data can be presented from a parent node. For these nodes you can only see their ML status, as they are not online to provide more information | | Offline | Nodes that are offline, not streaming metrics to Cloud and not available in any parent node. Offline nodes are automatically deleted after 30 days and can also be deleted manually. | diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/nodes-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/nodes-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..70d2bca89 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/nodes-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,57 @@ +# Nodes tab + +The nodes tab provides a summarized view of your [Room](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-rooms), allowing you to view quick information per node. + +> **Tip** +> +> Keep in mind that all configurations mentioned below are persistent and visible across all users. + +## Center information view + +The center information view consists of one row per node, and can be configured and filtered by the user. + +### Filtering and adjusting the view + +In the top right-hand corner, you can: + +- Order the nodes per status or per alert status +- Select which charts you want to be displayed as quick reference points + +### Node row + +Each node row allows you to: + +- View the node's status +- Go to a single node dashboard, by clicking the node name +- View information about the node, along with a button to display more in the right-hand sidebar +- View active alerts for the node +- View Machine Learning status +- View Functions capability status +- Add configuration (beta) +- [Add alert silencing rules](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-alert-notification-silencing-rules.md) +- View a set of key attributes collected on your node + +## Right bar + +The bar on the right-hand side provides additional information about the nodes in the Room and allows you to filter what is displayed in the [center information view](#center-information-view). + +### Node hierarchy + +The first tab displays a hierarchy of the nodes displayed, making it easy to find a specific node by name. It follows the ordering that the user has selected. + +### Filters sub-tab + +The second tab allows you to filter which nodes are displayed, you can filter by: + +- Host labels +- Node status +- Netdata version +- Individual nodes + +### Alerts sub-tab + +The third tab displays Room alerts and allows you to see additional information about each alert. + +### Info sub-tab + +The last tab presents information about a node, by clicking the `i` icon from a node's row, right next to its name. diff --git a/docs/cloud/manage/themes.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/themes.md index 0ca7425ae..0ca7425ae 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/manage/themes.md +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/themes.md diff --git a/docs/dashboards-and-charts/top-tab.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/top-tab.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..4edaf32f9 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/top-tab.md @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ +# Top tab + +The Top tab allows you to run [Netdata Functions](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md) on a node where a Netdata Agent is running. These routines are exposed by a given collector. +They can be used to retrieve additional information to help you troubleshoot or to trigger some action to happen on the node itself. + +> **Tip** +> +> You can also execute a Function from the [Nodes tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/nodes-tab.md), by pressing the `f(x)` button. + +> **Note** +> +> If you get an error saying that your node can't execute Functions please check the [prerequisites](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md#prerequisites). + +The main view of this tab provides you with (depending on the Function) two elements: a visualization on the top and a table on the bottom. + +Visualizations vary depending on the Function and most allow for user customization. + +On the top right-hand corner you can: + +- Refresh the results (Given that the dashboard is on `Paused` mode) +- Set the update interval of the results. + +## Functions bar + +The bar on the right-hand side allows you to select which Function to run, on which node, and then depending on the Function, there might be more fine-grained filtering available. + +For example the `Block-devices` Function allows you to filter per Device, Type, ID, Model and Serial number or the Block devices on your node. diff --git a/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md index 99e4c308e..3e2b6dbdc 100644 --- a/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md +++ b/docs/dashboards-and-charts/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md @@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ The date and time selector allows you to change the visible timeframe and change ### Pick timeframes to visualize -While [panning through time and zooming in/out](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) from charts it is helpful when you're looking a recent history, or want to do granular troubleshooting, what if you want to see metrics from 6 hours ago? Or 6 days? +While [panning through time and zooming in/out](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md) from charts it is helpful when you're looking a recent history, or want to do granular troubleshooting, what if you want to see metrics from 6 hours ago? Or 6 days? Netdata's dashboard features a **timeframe selector** to help you visualize specific timeframes in a few helpful ways. By default, it shows a certain number of minutes of historical metrics based on the your browser's viewport to ensure it's always showing per-second granularity. @@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ beyond stored historical metrics, you'll see this message:  -At any time, [configure the internal TSDB's storage capacity](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md) to expand your +At any time, [configure the internal TSDB's storage capacity](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md) to expand your depth of historical metrics. ### Timezone selector diff --git a/docs/deployment-guides/README.md b/docs/deployment-guides/README.md index 18f578857..1b6571b99 100644 --- a/docs/deployment-guides/README.md +++ b/docs/deployment-guides/README.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ # Deployment Guides -Netdata can be used to monitor all kinds of infrastructure, from stand-alone tiny IoT devices to complex hybrid setups combining on-premise and cloud infrastructure, mixing bare-metal servers, virtual machines and containers. +Netdata can be used to monitor all kinds of infrastructure, from tiny stand-alone IoT devices to complex hybrid setups combining on-premise and cloud infrastructure, mixing bare-metal servers, virtual machines and containers. There are 3 components to structure your Netdata ecosystem: @@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ There are 3 components to structure your Netdata ecosystem: 2. **Netdata Parents** - To create [observability centralization points](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md) within your infrastructure, to offload Netdata Agents functions from your production systems, to provide high-availability of your data, increased data retention and isolation of your nodes. + To create [observability centralization points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md) within your infrastructure, to offload Netdata Agents functions from your production systems, to provide high-availability of your data, increased data retention and isolation of your nodes. Netdata Parents are implemented using the Netdata Agent software. Any Netdata Agent can be an Agent for a node and a Parent for other Agents, at the same time. diff --git a/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-strategies.md b/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-strategies.md index 3be2edbcf..1a3c67164 100644 --- a/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-strategies.md +++ b/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-strategies.md @@ -1,64 +1,42 @@ -# Deployment strategies - +# Deployment Examples ## Deployment Options Overview -This section provides a quick overview of a few common deployment options. The next sections go into configuration examples and further reading. - -### Stand-alone Deployment - -To help our users have a complete experience of Netdata when they install it for the first time, a Netdata Agent with default configuration -is a complete monitoring solution out of the box, having all these features enabled and available. - -The Agent will act as a _stand-alone_ Agent by default, and this is great to start out with for small setups and home labs. By [connecting each Agent to Cloud](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md), you can see an overview of all your nodes, with aggregated charts and centralized alerting, without setting up a Parent. - - - -### Parent – Child Deployment - -An Agent connected to a Parent is called a _Child_. It will _stream_ metrics to its Parent. The Parent can then take care of storing metrics on behalf of that node (with longer retention), handle metrics queries for showing dashboards, and provide alerting. - -When using Cloud, it is recommended that just the Parent is connected to Cloud. Child Agents can then be configured to have short retention, in RAM instead of on Disk, and have alerting and other features disabled. Because they don't need to connect to Cloud themselves, those children can then be further secured by not allowing outbound traffic. - - +This section provides a quick overview for a few common deployment options for Netdata. -This setup allows for leaner Child nodes and is good for setups with more than a handful of nodes. Metrics data remains accessible if the Child node is temporarily unavailable or decommissioned, although there is no failover in case the Parent becomes unavailable. +You can read about [Standalone Deployment](/docs/deployment-guides/standalone-deployment.md) and [Deployment with Centralization Points](/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-with-centralization-points.md) in the documentation inside this section. +The sections below go into configuration examples about these deployment concepts. -### Active–Active Parent Deployment +## Deployment Configuration Details -For high availability, Parents can be configured to stream data for their children between them, and keep the data sets in sync. Child Agents are configured with the addresses of both Parent Agents, but will only stream to one of them at a time. When that Parent becomes unavailable, it reconnects to another. When the first Parent becomes available again, that Parent will catch up by receiving the backlog from the second. +### Stand-alone -With both Parent Agents connected to Cloud, Cloud will route queries to either Parent transparently, depending on their availability. Alerts trigger on either Parent will stream to Cloud, and Cloud will deduplicate and debounce state changes to prevent spurious notifications. +The stand-alone setup is configured out of the box with reasonable defaults, but please consult our [configuration documentation](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) for details, including the overview of [common configuration changes](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/common-configuration-changes.md). - +### Parent – Child +For setups involving Parent and Child Agents, they need to be configured for [streaming](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/configuration.md), through the configuration file `stream.conf`. -## Configuration Details +This will instruct the Child to stream data to the Parent and the Parent to accept streaming connections for one or more Child Agents. To secure this connection, both need a shared API key (to replace the string `API_KEY` in the examples below). Additionally, the Child can be configured with one or more addresses of Parent Agents (`PARENT_IP_ADDRESS`). -### Stand-alone Deployment - -The stand-alone setup is configured out of the box with reasonable defaults, but please consult our [configuration documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/cheatsheet.md) for details, including the overview of [common configuration changes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/common-changes.md). - -### Parent – Child Deployment - -For setups involving Child and Parent Agents, the Agents need to be configured for [_streaming_](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/streaming/README.md), through the configuration file `stream.conf`. This will instruct the Child to stream data to the Parent and the Parent to accept streaming connections for one or more Child Agents. To secure this connection, both need set up a shared API key (to replace the string `API_KEY` in the examples below). Additionally, the Child is configured with one or more addresses of Parent Agents (`PARENT_IP_ADDRESS`). - -An API key is a key created with `uuidgen` and is used for authentication and/or customization in the Parent side. I.e. a Child will stream using the API key, and a Parent is configured to accept connections from Child, but can also apply different options for children by using multiple different API keys. The easiest setup uses just one API key for all Child Agents. +An API key is a key created with `uuidgen` and is used for authentication and/or customization on the Parent side. For example, a Child can stream using the API key, and a Parent can be configured to accept connections from the Child, but it can also apply different options for Children by using multiple different API keys. The easiest setup uses just one API key for all Child Agents. #### Child config -As mentioned above, the recommendation is to not claim the Child to Cloud directly during your setup, avoiding establishing an [ACLK](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/aclk/README.md) connection. +As mentioned above, we do not recommend to claim the Child to Cloud directly during your setup. -To reduce the footprint of the Netdata Agent on your production system, some capabilities can be switched OFF on the Child and kept ON on the Parent. In this example, Machine Learning and Alerting are disabled in the Child, so that the Parent can take the load. We also use RAM instead of disk to store metrics with limited retention, covering temporary network issues. +This is done in order to reduce the footprint of the Netdata Agent on your production system, as some capabilities can be switched OFF for the Child and kept ON for the Parent. + +In this example, Machine Learning and Alerting are disabled for the Child, so that the Parent can take the load. We also use RAM instead of disk to store metrics with limited retention, covering temporary network issues. ##### netdata.conf -On the child node, edit `netdata.conf` by using the edit-config script: `/etc/netdata/edit-config netdata.conf` set the following parameters: +On the child node, edit `netdata.conf` by using the [edit-config](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#edit-netdataconf) script and set the following parameters: ```yaml [db] - # https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/agent/database + # https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md # none = no retention, ram = some retention in ram mode = ram # The retention in seconds. @@ -85,9 +63,7 @@ On the child node, edit `netdata.conf` by using the edit-config script: `/etc/ne ##### stream.conf -To edit `stream.conf`, again use the edit-config script: `/etc/netdata/edit-config stream.conf`. - -Set the following parameters: +To edit `stream.conf`, use again the [edit-config](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#edit-netdataconf) script and set the following parameters: ```yaml [stream] @@ -101,7 +77,7 @@ Set the following parameters: #### Parent config -For the Parent, besides setting up streaming, the example will also provide an example configuration of multiple [tiers](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/engine/README.md#tiering) of metrics [storage](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md), for 10 children, with about 2k metrics each. +For the Parent, besides setting up streaming, this example also provides configuration for multiple [tiers of metrics storage](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics), for 10 Children, with about 2k metrics each. This allows for: - 1s granularity at tier 0 for 1 week - 1m granularity at tier 1 for 1 month @@ -114,7 +90,7 @@ Requiring: ##### netdata.conf -On the Parent, edit `netdata.conf` with `/etc/netdata/edit-config netdata.conf` and set the following parameters: +On the Parent, edit `netdata.conf` by using the [edit-config](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#edit-netdataconf) script and set the following parameters: ```yaml [db] @@ -149,7 +125,7 @@ On the Parent, edit `netdata.conf` with `/etc/netdata/edit-config netdata.conf` ##### stream.conf -On the Parent node, edit `stream.conf` with `/etc/netdata/edit-config stream.conf`, and then set the following parameters: +On the Parent node, edit `stream.conf` by using the [edit-config](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#edit-netdataconf) script and set the following parameters: ```yaml [API_KEY] @@ -157,13 +133,13 @@ On the Parent node, edit `stream.conf` with `/etc/netdata/edit-config stream.con enabled = yes ``` -### Active–Active Parent Deployment +### Active–Active Parents -In order to setup active–active streaming between Parent 1 and Parent 2, Parent 1 needs to be instructed to stream data to Parent 2 and Parent 2 to stream data to Parent 1. The Child Agents need to be configured with the addresses of both Parent Agents. The Agent will only connect to one Parent at a time, falling back to the next if the previous failed. These examples use the same API key between Parent Agents as for connections from Child Agents. +In order to setup active–active streaming between Parent 1 and Parent 2, Parent 1 needs to be instructed to stream data to Parent 2 and Parent 2 to stream data to Parent 1. The Child Agents need to be configured with the addresses of both Parent Agents. An Agent will only connect to one Parent at a time, falling back to the next upon failure. These examples use the same API key between Parent Agents and for connections for Child Agents. -On both Netdata Parent and all Child Agents, edit `stream.conf` with `/etc/netdata/edit-config stream.conf`: +On both Netdata Parent and all Child Agents, edit `stream.conf` by using the [edit-config](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#edit-netdataconf) script: -##### stream.conf on Parent 1 +#### stream.conf on Parent 1 ```yaml [stream] @@ -178,7 +154,7 @@ On both Netdata Parent and all Child Agents, edit `stream.conf` with `/etc/netda enabled = yes ``` -##### stream.conf on Parent 2 +#### stream.conf on Parent 2 ```yaml [stream] @@ -192,7 +168,7 @@ On both Netdata Parent and all Child Agents, edit `stream.conf` with `/etc/netda enabled = yes ``` -##### stream.conf on Child Agents +#### stream.conf on Child Agents ```yaml [stream] @@ -208,32 +184,24 @@ On both Netdata Parent and all Child Agents, edit `stream.conf` with `/etc/netda We strongly recommend the following configuration changes for production deployments: -1. Understand Netdata's [security and privacy design](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md) and - [secure your nodes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/secure-nodes.md) +1. Understand Netdata's [security and privacy design](/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md) and [secure your nodes](/docs/netdata-agent/securing-netdata-agents.md) To safeguard your infrastructure and comply with your organization's security policies. -2. Set up [streaming and replication](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/streaming/README.md) to: - - - Offload Netdata Agents running on production systems and free system resources for the production applications running on them. - - Isolate production systems from the rest of the world and improve security. - - Increase data retention. - - Make your data highly available. - -3. [Optimize the Netdata Agents system utilization and performance](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/configure/performance.md) +2. [Optimize the Netdata Agents system utilization and performance](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimize-the-netdata-agents-performance.md) To save valuable system resources, especially when running on weak IoT devices. We also suggest that you: -1. [Use Netdata Cloud to access the dashboards](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md) +1. [Use Netdata Cloud to access the dashboards](/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md) - For increased security, user management and access to our latest tools for advanced dashboarding and troubleshooting. + For increased security, user management and access to our latest features, tools and troubleshooting solutions. -2. [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md) +2. [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md) - To control Netdata's memory use, when you have a lot of ephemeral metrics. + To control Netdata's memory use, when you have a lot of ephemeral metrics. -3. [Use host labels](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/using-host-labels.md) +3. [Use host labels](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/organize-systems-metrics-and-alerts.md) To organize systems, metrics, and alerts. diff --git a/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-with-centralization-points.md b/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-with-centralization-points.md index b3e2b40dc..87fd4a61a 100644 --- a/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-with-centralization-points.md +++ b/docs/deployment-guides/deployment-with-centralization-points.md @@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ When metrics and logs are centralized, the Children are never queried for metric | Unified infrastructure dashboards for logs | All logs are accessible via the same dashboard at Netdata Cloud, although they are unified per Netdata Parent | | Centrally configured alerts | Yes, at Netdata Parents | | Centrally dispatched alert notifications | Yes, at Netdata Cloud | -| Data are exclusively on-prem | Yes, Netdata Cloud queries Netdata Agents to satisfy dashboard queries. | +| Data are exclusively on-prem | Yes, Netdata Cloud queries Netdata Agents to satisfy dashboard queries. | A configuration with 2 observability centralization points, looks like this: @@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ flowchart LR dashboard for all nodes"]] NC(["<b>Netdata Cloud</b> - decides which agents + decides which Agents need to be queried"]) SA1["Netdata at AWS A1"] @@ -93,16 +93,24 @@ flowchart LR SB1 & SB2 & SBN ---|stream| PB ``` -### Configuration steps for deploying Netdata with Observability Centralization Points +## Active–Active Parent Deployment + +For high availability, Parents can be configured to stream data for their Children between them, and keep their data sets in sync. Children are configured with the addresses of both Parents, but will only stream to one of them at a time. When one Parent becomes unavailable, the Child reconnects to the other. When the first Parent becomes available again, that Parent will catch up by receiving the backlog from the second. + +With both Parent Agents connected to Netdata Cloud, it will route queries to either of them transparently, depending on their availability. Alerts trigger on either Parent will stream to Cloud, and Cloud will deduplicate and debounce state changes to prevent spurious notifications. + +## Configuration steps for deploying Netdata with Observability Centralization Points For Metrics: -- Install Netdata agents on all systems and the Netdata Parents. +- Install Netdata Agents on all systems and the Netdata Parents. - Configure `stream.conf` at the Netdata Parents to enable streaming access with an API key. - Configure `stream.conf` at the Netdata Children to enable streaming to the configured Netdata Parents. +Check the [related section in our documentation](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md) for more info + For Logs: - Install `systemd-journal-remote` on all systems and the Netdata Parents. @@ -111,11 +119,4 @@ For Logs: - Configure `systemd-journal-upload` at the Netdata Children to enable transmission of their logs to the Netdata Parents. -Optionally: - -- Disable ML, health checks and dashboard access at Netdata Children to save resources and avoid duplicate notifications. - -When using Netdata Cloud: - -- Optionally: disable dashboard access on all Netdata agents (including Netdata Parents). -- Optionally: disable alert notifications on all Netdata agents (including Netdata Parents). +Check the [related section in our documentation](/docs/observability-centralization-points/logs-centralization-points-with-systemd-journald/README.md) for more info diff --git a/docs/deployment-guides/standalone-deployment.md b/docs/deployment-guides/standalone-deployment.md index 5baef805a..3138141f7 100644 --- a/docs/deployment-guides/standalone-deployment.md +++ b/docs/deployment-guides/standalone-deployment.md @@ -1,22 +1,22 @@ # Standalone Deployment -To help our users have a complete experience of Netdata when they install it for the first time, a Netdata Agent with default configuration is a complete monitoring solution out of the box, having all its features enabled and available. +To help our users have a complete experience of Netdata when they install it for the first time, the Netdata Agent with default configuration is a complete monitoring solution out of the box, with features enabled and available. -So, each Netdata agent acts as a standalone monitoring system by default. +So, each Netdata Agent acts as a standalone monitoring system by default. -## Standalone agents, without Netdata Cloud +## Standalone Agents, without Netdata Cloud | Feature | How it works | |:---------------------------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------------:| -| Unified infrastructure dashboards for metrics | No, each Netdata agent provides its own dashboard | -| Unified infrastructure dashboards for logs | No, each Netdata agent exposes its own logs | +| Unified infrastructure dashboards for metrics | No, each Netdata Agent provides its own dashboard | +| Unified infrastructure dashboards for logs | No, each Netdata Agent exposes its own logs | | Centrally configured alerts | No, each Netdata has its own alerts configuration | -| Centrally dispatched alert notifications | No, each Netdata agent sends notifications by itself | +| Centrally dispatched alert notifications | No, each Netdata Agent sends notifications by itself | | Data are exclusively on-prem | Yes | -When using Standalone Netdata agents, each of them offers an API and a dashboard, at its own unique URL, that looks like `http://agent-ip:19999`. +When using Standalone Netdata Agents, each of them offers an API and a dashboard, at its own unique URL, that looks like `http://agent-ip:19999`. -So, each of the Netdata agents has to be accessed individually and independently of the others: +So, each of the Netdata Agents has to be accessed individually and independently of the others: ```mermaid flowchart LR @@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ flowchart LR WEB -->|URL N| SN ``` -The same is true for alert notifications. Each of the Netdata agents runs its own alerts and sends notifications by itself, according to its configuration: +The same is true for alert notifications. Each of the Netdata Agents runs its own alerts and sends notifications by itself, according to its configuration: ```mermaid flowchart LR @@ -61,23 +61,23 @@ flowchart LR S1 & S2 & SN ==> OTHER ``` -### Configuration steps for standalone Netdata agents without Netdata Cloud +### Configuration steps for standalone Netdata Agents without Netdata Cloud No special configuration needed. -- Install Netdata agents on all your systems, then access each of them via its own unique URL, that looks like `http://agent-ip:19999/`. +- Install Netdata Agents on all your systems, then access each of them via its own unique URL, that looks like `http://agent-ip:19999/`. -## Standalone agents, with Netdata Cloud +## Standalone Agents, with Netdata Cloud | Feature | How it works | |:---------------------------------------------:|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| | Unified infrastructure dashboards for metrics | Yes, via Netdata Cloud, all charts aggregate metrics from all servers. | | Unified infrastructure dashboards for logs | All logs are accessible via the same dashboard at Netdata Cloud, although they are not unified (ie. logs from different servers are not multiplexed into a single view) | -| Centrally configured alerts | No, each Netdata has its own alerts configuration | +| Centrally configured alerts | No, each Netdata has its own alerts configuration | | Centrally dispatched alert notifications | Yes, via Netdata Cloud | | Data are exclusively on-prem | Yes, Netdata Cloud queries Netdata Agents to satisfy dashboard queries. | -By [connecting all Netdata agents to Netdata Cloud](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md), you can have a unified infrastructure view of all your nodes, with aggregated charts, without configuring [observability centralization points](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md). +By [connecting all Netdata Agents to Netdata Cloud](/src/claim/README.md), you can have a unified infrastructure view of all your nodes, with aggregated charts, without configuring [observability centralization points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md). ```mermaid flowchart LR @@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ flowchart LR dashboard for all nodes"]] NC(["<b>Netdata Cloud</b> - decides which agents + decides which Agents need to be queried"]) S1["Standalone Netdata @@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ flowchart LR NC -->|queries| S1 & S2 & SN ``` -Similarly for alerts, Netdata Cloud receives all alert transitions from all agents, decides which notifications should be sent and how, applies silencing rules, maintenance windows and based on each Netdata Cloud space and user settings, dispatches notifications: +Similarly for alerts, Netdata Cloud receives all alert transitions from all Agents, decides which notifications should be sent and how, applies silencing rules, maintenance windows and based on each Netdata Cloud space and user settings, dispatches notifications: ```mermaid flowchart LR @@ -128,12 +128,14 @@ flowchart LR S1 & S2 & SN -->|alert transition| NC ``` -> Note that alerts are still triggered by Netdata agents. Netdata Cloud takes care of the notifications only. +> **Note** +> +> Alerts are still triggered by Netdata Agents. Netdata Cloud only takes care of the notifications. -### Configuration steps for standalone Netdata agents with Netdata Cloud +### Configuration steps for standalone Netdata Agents with Netdata Cloud -- Install Netdata agents using the commands given by Netdata Cloud, so that they will be automatically added to your Netdata Cloud space. Otherwise, install Netdata agents and then claim them via the command line or their dashboard. +- Install Netdata Agents using the commands given by Netdata Cloud, so that they will be automatically connected to your Netdata Cloud space. Otherwise, install Netdata Agents and then claim them via the command line or their dashboard. - Optionally: disable their direct dashboard access to secure them. -- Optionally: disable their alert notifications to avoid receiving email notifications directly from them (email notifications are automatically enabled when a working MTA is found on the systems Netdata agents are installed). +- Optionally: disable their alert notifications to avoid receiving email notifications directly from them (email notifications are automatically enabled when a working MTA is found on the systems Netdata Agents are installed). diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/developer-and-contributor-corner.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/README.md index d4d86382a..d4d86382a 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/developer-and-contributor-corner.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/README.md diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/build-the-netdata-agent-yourself.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/build-the-netdata-agent-yourself.md index 99166ad95..99166ad95 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/build-the-netdata-agent-yourself.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/build-the-netdata-agent-yourself.md diff --git a/docs/guides/collect-apache-nginx-web-logs.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/collect-apache-nginx-web-logs.md index 055219935..55af82fb7 100644 --- a/docs/guides/collect-apache-nginx-web-logs.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/collect-apache-nginx-web-logs.md @@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ You can use the [LTSV log format](http://ltsv.org/), track TLS and cipher usage, ever. In one test on a system with SSD storage, the collector consistently parsed the logs for 200,000 requests in 200ms, using ~30% of a single core. -The [web_log](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/weblog/README.md) collector is currently compatible +The [web_log](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/weblog/README.md) collector is currently compatible with [Nginx](https://nginx.org/en/) and [Apache](https://httpd.apache.org/). This guide will walk you through using the new Go-based web log collector to turn the logs these web servers @@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ jobs: ``` Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. Netdata should pick up your web server's access log and +method](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. Netdata should pick up your web server's access log and begin showing real-time charts! ### Custom log formats and fields @@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ The web log collector is capable of parsing custom Nginx and Apache log formats leave that topic for a separate guide. We do have [extensive -documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/weblog/README.md#custom-log-format) on how +documentation](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/weblog/README.md#custom-log-format) on how to build custom parsing for Nginx and Apache logs. ## Tweak web log collector alerts @@ -109,4 +109,4 @@ You can also edit this file directly with `edit-config`: ``` For more information about editing the defaults or writing new alert entities, see our -[health monitoring documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/README.md). +[health monitoring documentation](/src/health/README.md). diff --git a/docs/guides/collect-unbound-metrics.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/collect-unbound-metrics.md index 5467592a0..ac997b7f9 100644 --- a/docs/guides/collect-unbound-metrics.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/collect-unbound-metrics.md @@ -58,9 +58,7 @@ configuring the collector. You may not need to do any more configuration to have Netdata collect your Unbound metrics. If you followed the steps above to enable `remote-control` and make your Unbound files readable by Netdata, that should -be enough. Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. You should see Unbound metrics in your Netdata -dashboard! +be enough. Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the appropriate method for your system. You should see Unbound metrics in your Netdata dashboard!  @@ -93,7 +91,7 @@ jobs: tls_skip_verify: yes tls_cert: /path/to/unbound_control.pem tls_key: /path/to/unbound_control.key - + - name: local address: 127.0.0.1:8953 cumulative: yes @@ -101,16 +99,15 @@ jobs: ``` Netdata will attempt to read `unbound.conf` to get the appropriate `address`, `cumulative`, `use_tls`, `tls_cert`, and -`tls_key` parameters. +`tls_key` parameters. -Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. +Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the appropriate method for your system. ### Manual setup for a remote Unbound server Collecting metrics from remote Unbound servers requires manual configuration. There are too many possibilities to cover all remote connections here, but the [default `unbound.conf` -file](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/config/go.d/unbound.conf) contains a few useful examples: +file](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/plugin/go.d/config/go.d/unbound.conf) contains a few useful examples: ```yaml jobs: @@ -132,11 +129,11 @@ jobs: ``` To see all the available options, see the default [unbound.conf -file](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/config/go.d/unbound.conf). +file](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/plugin/go.d/config/go.d/unbound.conf). ## What's next? -Now that you're collecting metrics from your Unbound servers, let us know how it's working for you! There's always room +Now that you're collecting metrics from your Unbound servers, let us know how it's working for you! There's always Room for improvement or refinement based on real-world use cases. Feel free to [file an issue](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug%2Cneeds+triage&template=BUG_REPORT.yml) with your thoughts. diff --git a/docs/dashboard/customize.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/customize.md index afcf9216b..03a6a842a 100644 --- a/docs/dashboard/customize.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/customize.md @@ -2,9 +2,9 @@ > ### Disclaimer > -> This document is only applicable to the v1 version of the dashboard and doesn't affect the [Netdata Dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md). +> This document is only applicable to the v1 version of the dashboard and doesn't affect the [Netdata Dashboard](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md). -While the [Netdata dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/gui/README.md) comes preconfigured with hundreds of charts and +While the [Netdata dashboard](/src/web/gui/README.md) comes preconfigured with hundreds of charts and thousands of metrics, you may want to alter your experience based on a particular use case or preferences. ## Dashboard settings @@ -21,8 +21,7 @@ Here are a few popular settings: ### Change chart legend position -Find this setting under the **Visual** tab. By default, Netdata places the -[legend of dimensions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/dimensions-contexts-families.md#dimension) _below_ charts. +Find this setting under the **Visual** tab. By default, Netdata places the legend of dimensions _below_ charts. Click this toggle to move the legend to the _right_ of charts. @@ -65,7 +64,7 @@ Edit the file with customizations to the `title`, `icon`, and `info` fields. Rep icon from [Font Awesome](https://fontawesome.com/cheatsheet) to customize the icons that appear throughout the dashboard. -Save the file, then navigate to your [Netdata config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) to edit `netdata.conf`. Add +Save the file, then navigate to your [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) to edit `netdata.conf`. Add the following line to the `[web]` section to tell Netdata where to find your custom configuration. ```conf diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md index 982c35e79..011aac8da 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/kubernetes-k8s-netdata.md @@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ To follow this tutorial, you need: - A free Netdata Cloud account. [Sign up](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-up?cloudRoute=/spaces) if you don't have one already. - A working cluster running Kubernetes v1.9 or newer, with a Netdata deployment and connected parent/child nodes. See - our [Kubernetes deployment process](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md) for details on deployment and + our [Kubernetes deployment process](/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md) for details on deployment and conneting to Cloud. - The [`kubectl`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/) command line tool, within [one minor version difference](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl/#before-you-begin) of your cluster, on an @@ -93,13 +93,7 @@ The Netdata Helm chart deploys and enables everything you need for monitoring Ku Netdata and connect your cluster's nodes, you're ready to check out the visualizations **with zero configuration**. To get started, [sign in](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=/spaces) to your Netdata Cloud account. Head over -to the War Room you connected your cluster to, if not **General**. - -Netdata Cloud is already visualizing your Kubernetes metrics, streamed in real-time from each node, in the -[Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md): - - +to the Room you connected your cluster to, if not **General**. Let's walk through monitoring each layer of a Kubernetes cluster using the Overview as our framework. @@ -118,9 +112,6 @@ cluster](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1153921/109042169-19c8fa00-76 For example, the chart above shows a spike in the CPU utilization from `rabbitmq` every minute or so, along with a baseline CPU utilization of 10-15% across the cluster. -Read about the [Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md) and some best practices on [viewing -an overview of your infrastructure](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md) for details on using composite charts to -drill down into per-node performance metrics. ## Pod and container metrics @@ -132,7 +123,7 @@ visualizations](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1153921/109049195-349f ### Health map -The first visualization is the [health map](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md#health-map), +The first visualization is the [health map](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/kubernetes-tab.md#health-map), which places each container into its own box, then varies the intensity of their color to visualize the resource utilization. By default, the health map shows the **average CPU utilization as a percentage of the configured limit** for every container in your cluster. @@ -146,7 +137,7 @@ Let's explore the most colorful box by hovering over it. container](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1153921/109049544-a8417980-7695-11eb-80a7-109b4a645a27.png) The **Context** tab shows `rabbitmq-5bb66bb6c9-6xr5b` as the container's image name, which means this container is -running a [RabbitMQ](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/rabbitmq/README.md) workload. +running a [RabbitMQ](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/rabbitmq/README.md) workload. Click the **Metrics** tab to see real-time metrics from that container. Unsurprisingly, it shows a spike in CPU utilization at regular intervals. @@ -165,7 +156,7 @@ different namespaces.  -Each composite chart has a [definition bar](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#definition-bar) +Each composite chart has a [definition bar](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#definition-bar) for complete customization. For example, grouping the top chart by `k8s_container_name` reveals new information.  @@ -175,20 +166,20 @@ for complete customization. For example, grouping the top chart by `k8s_containe Netdata has a [service discovery plugin](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery), which discovers and creates configuration files for [compatible services](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart#service-discovery-and-supported-services) and any endpoints covered by -our [generic Prometheus collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus/README.md). +our [generic Prometheus collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/prometheus/README.md). Netdata uses these files to collect metrics from any compatible application as they run _inside_ of a pod. Service discovery happens without manual intervention as pods are created, destroyed, or moved between nodes. Service metrics show up on the Overview as well, beneath the **Kubernetes** section, and are labeled according to the service in question. For example, the **RabbitMQ** section has numerous charts from the [`rabbitmq` -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/rabbitmq/README.md): +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/rabbitmq/README.md):  > The robot-shop cluster has more supported services, such as MySQL, which are not visible with zero configuration. This > is usually because of services running on non-default ports, using non-default names, or required passwords. Read up -> on [configuring service discovery](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md#configure-service-discovery) to collect +> on [configuring service discovery](/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md#configure-service-discovery) to collect > more service metrics. Service metrics are essential to infrastructure monitoring, as they're the best indicator of the end-user experience, @@ -202,7 +193,7 @@ Netdata also automatically collects metrics from two essential Kubernetes proces The **k8s kubelet** section visualizes metrics from the Kubernetes agent responsible for managing every pod on a given node. This also happens without any configuration thanks to the [kubelet -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubelet/README.md). +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/k8s_kubelet/README.md). Monitoring each node's kubelet can be invaluable when diagnosing issues with your Kubernetes cluster. For example, you can see if the number of running containers/pods has dropped, which could signal a fault or crash in a particular @@ -218,7 +209,7 @@ configuration-related errors, and the actual vs. desired numbers of volumes, plu The **k8s kube-proxy** section displays metrics about the network proxy that runs on each node in your Kubernetes cluster. kube-proxy lets pods communicate with each other and accept sessions from outside your cluster. Its metrics are collected by the [kube-proxy -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubeproxy/README.md). +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/k8s_kubeproxy/README.md). With Netdata, you can monitor how often your k8s proxies are syncing proxy rules between nodes. Dramatic changes in these figures could indicate an anomaly in your cluster that's worthy of further investigation. @@ -238,9 +229,9 @@ clusters of all sizes. - [Netdata Helm chart](https://github.com/netdata/helmchart) - [Netdata service discovery](https://github.com/netdata/agent-service-discovery) - [Netdata Agent · `kubelet` - collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubelet/README.md) + collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/k8s_kubelet/README.md) - [Netdata Agent · `kube-proxy` - collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/k8s_kubeproxy/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · `cgroups.plugin`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md) + collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/k8s_kubeproxy/README.md) +- [Netdata Agent · `cgroups.plugin`](/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md) diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/lamp-stack.md index cc649dba9..2df5a7167 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/lamp-stack.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/lamp-stack.md @@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ To follow this tutorial, you need: ## Install the Netdata Agent If you don't have the free, open-source Netdata monitoring agent installed on your node yet, get started with a [single -kickstart command](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md): +kickstart command](/packaging/installer/README.md): <OneLineInstallWget/> @@ -61,15 +61,15 @@ replacing `NODE` with the hostname or IP address of your system. ## Enable hardware and Linux system monitoring -There's nothing you need to do to enable [system monitoring](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/system-metrics.md) and Linux monitoring with +There's nothing you need to do to enable system monitoring and Linux monitoring with the Netdata Agent, which autodetects metrics from CPUs, memory, disks, networking devices, and Linux processes like systemd without any configuration. If you're using containers, Netdata automatically collects resource utilization -metrics from each using the [cgroups data collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md). +metrics from each using the [cgroups data collector](/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin/README.md). ## Enable Apache monitoring Let's begin by configuring Apache to work with Netdata's [Apache data -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/apache/README.md). +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/apache/README.md). Actually, there's nothing for you to do to enable Apache monitoring with Netdata. @@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ metrics](https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/mod_status.html), which is just _ ## Enable web log monitoring The Netdata Agent also comes with a [web log -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/weblog/README.md), which reads Apache's access +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/weblog/README.md), which reads Apache's access log file, processes each line, and converts them into per-second metrics. On Debian systems, it reads the file at `/var/log/apache2/access.log`. @@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ monitoring. Because your MySQL database is password-protected, you do need to tell MySQL to allow the `netdata` user to connect to without a password. Netdata's [MySQL data -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/mysql/README.md) collects metrics in _read-only_ +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/mysql/README.md) collects metrics in _read-only_ mode, without being able to alter or affect operations in any way. First, log into the MySQL shell. Then, run the following three commands, one at a time: @@ -105,15 +105,15 @@ FLUSH PRIVILEGES; ``` Run `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate alternative for your -system](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation), to collect dozens of metrics every second for robust MySQL monitoring. +system](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation), to collect dozens of metrics every second for robust MySQL monitoring. ## Enable PHP monitoring Unlike Apache or MySQL, PHP isn't a service that you can monitor directly, unless you instrument a PHP-based application -with [StatsD](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/statsd.plugin/README.md). +with [StatsD](/src/collectors/statsd.plugin/README.md). However, if you use [PHP-FPM](https://php-fpm.org/) in your LAMP stack, you can monitor that process with our [PHP-FPM -data collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/phpfpm/README.md). +data collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/phpfpm/README.md). Open your PHP-FPM configuration for editing, replacing `7.4` with your version of PHP: @@ -159,12 +159,12 @@ If the Netdata Agent isn't already open in your browser, open a new tab and navi > If you [signed up](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-up?cloudRoute=/spaces) for Netdata Cloud earlier, you can also view > the exact same LAMP stack metrics there, plus additional features, like drag-and-drop custom dashboards. Be sure to -> [connecting your node](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md) to start streaming metrics to your browser through Netdata Cloud. +> [connecting your node](/src/claim/README.md) to start streaming metrics to your browser through Netdata Cloud. Netdata automatically organizes all metrics and charts onto a single page for easy navigation. Peek at gauges to see overall system performance, then scroll down to see more. Click-and-drag with your mouse to pan _all_ charts back and forth through different time intervals, or hold `SHIFT` and use the scrollwheel (or two-finger scroll) to zoom in and -out. Check out our doc on [interacting with charts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) for all the details. +out. Check out our doc on [interacting with charts](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md) for all the details.  @@ -197,15 +197,15 @@ Here's a quick reference for what charts you might want to focus on after settin The Netdata Agent comes with hundreds of pre-configured alerts to help you keep tabs on your system, including 19 alerts designed for smarter LAMP stack monitoring. -Click the 🔔 icon in the top navigation to [see active alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md). The **Active** tabs +Click the 🔔 icon in the top navigation to [see active alerts](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md). The **Active** tabs shows any alerts currently triggered, while the **All** tab displays a list of _every_ pre-configured alert. The  -[Tweak alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md) based on your infrastructure monitoring needs, and to see these alerts +[Tweak alerts](/src/health/REFERENCE.md) based on your infrastructure monitoring needs, and to see these alerts in other places, like your inbox or a Slack channel, [enable a notification -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md). +method](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/README.md). ## What's next? @@ -215,7 +215,7 @@ services. The per-second metrics granularity means you have the most accurate in any LAMP-related issues. Another powerful way to monitor the availability of a LAMP stack is the [`httpcheck` -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/httpcheck/README.md), which pings a web server at +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/httpcheck/README.md), which pings a web server at a regular interval and tells you whether if and how quickly it's responding. The `response_match` option also lets you monitor when the web server's response isn't what you expect it to be, which might happen if PHP-FPM crashes, for example. @@ -225,14 +225,14 @@ we're not covering it here, but it _does_ work in a single-node setup. Just don' node crashed. If you're planning on managing more than one node, or want to take advantage of advanced features, like finding the -source of issues faster with [Metric Correlations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md), +source of issues faster with [Metric Correlations](/docs/metric-correlations.md), [sign up](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-up?cloudRoute=/spaces) for a free Netdata Cloud account. ### Related reference documentation -- [Netdata Agent · Get started](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · Apache data collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/apache/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · Web log collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/weblog/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · MySQL data collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/mysql/README.md) -- [Netdata Agent · PHP-FPM data collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/phpfpm/README.md) +- [Netdata Agent · Get started](/packaging/installer/README.md) +- [Netdata Agent · Apache data collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/apache/README.md) +- [Netdata Agent · Web log collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/weblog/README.md) +- [Netdata Agent · MySQL data collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/mysql/README.md) +- [Netdata Agent · PHP-FPM data collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/phpfpm/README.md) diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor-cockroachdb.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/monitor-cockroachdb.md index 9d4d3ea03..f0db12cc4 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor-cockroachdb.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/monitor-cockroachdb.md @@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ learn_rel_path: "Miscellaneous" [CockroachDB](https://github.com/cockroachdb/cockroach) is an open-source project that brings SQL databases into scalable, disaster-resilient cloud deployments. Thanks to -a [new CockroachDB collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/cockroachdb/README.md) +a [new CockroachDB collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/cockroachdb/README.md) released in [v1.20](https://blog.netdata.cloud/posts/release-1.20/), you can now monitor any number of CockroachDB databases with maximum granularity using Netdata. Collect more than 50 unique metrics and put them on interactive visualizations @@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ display them on the dashboard. If your CockroachDB instance is accessible through `http://localhost:8080/` or `http://127.0.0.1:8080`, your setup is complete. Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, and refresh your browser. You should see CockroachDB +method](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, and refresh your browser. You should see CockroachDB metrics in your Netdata dashboard! <figure> @@ -115,4 +115,4 @@ cd /etc/netdata/ # Replace with your Netdata configuration directory, if not /et ./edit-config health.d/cockroachdb.conf # You may need to use `sudo` for write privileges ``` -For more information about editing the defaults or writing new alert entities, see our documentation on [configuring health alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md). +For more information about editing the defaults or writing new alert entities, see our documentation on [configuring health alerts](/src/health/REFERENCE.md). diff --git a/docs/guides/troubleshoot/monitor-debug-applications-ebpf.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/monitor-debug-applications-ebpf.md index 728606c83..91d2a2ef2 100644 --- a/docs/guides/troubleshoot/monitor-debug-applications-ebpf.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/monitor-debug-applications-ebpf.md @@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ learn_rel_path: "Operations" When trying to troubleshoot or debug a finicky application, there's no such thing as too much information. At Netdata, we developed programs that connect to the [_extended Berkeley Packet Filter_ (eBPF) virtual -machine](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md) to help you see exactly how specific applications are interacting with the +machine](/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md) to help you see exactly how specific applications are interacting with the Linux kernel. With these charts, you can root out bugs, discover optimizations, diagnose memory leaks, and much more. This means you can see exactly how often, and in what volume, the application creates processes, opens files, writes to @@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ To start troubleshooting an application with eBPF metrics, you need to ensure yo displays those metrics independent from any other process. You can use the `apps_groups.conf` file to configure which applications appear in charts generated by -[`apps.plugin`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md). Once you edit this file and create a new group for the application +[`apps.plugin`](/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md). Once you edit this file and create a new group for the application you want to monitor, you can see how it's interacting with the Linux kernel via real-time eBPF metrics. Let's assume you have an application that runs on the process `custom-app`. To monitor eBPF metrics for that application @@ -61,12 +61,12 @@ dev: custom-app ``` Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to begin seeing metrics for this particular +method](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to begin seeing metrics for this particular group+process. You can also add additional processes to the same group. You can set up `apps_groups.conf` to more show more precise eBPF metrics for any application or service running on your system, even if it's a standard package like Redis, Apache, or any other [application/service Netdata collects -from](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md). +from](/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md). ```conf # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- @@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ to show other charts that will help you debug and troubleshoot how it interacts ## Configure the eBPF collector to monitor errors -The eBPF collector has [two possible modes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md#ebpf-load-mode): `entry` and `return`. The default +The eBPF collector has [two possible modes](/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md#ebpf-load-mode): `entry` and `return`. The default is `entry`, and only monitors calls to kernel functions, but the `return` also monitors and charts _whether these calls return in error_. @@ -110,7 +110,7 @@ Replace `entry` with `return`: ``` Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. +method](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. ## Get familiar with per-application eBPF metrics and charts @@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ Pay particular attention to the charts in the **ebpf file**, **ebpf syscall**, * sub-sections. These charts are populated by low-level Linux kernel metrics thanks to eBPF, and showcase the volume of calls to open/close files, call functions like `do_fork`, IO activity on the VFS, and much more. -See the [eBPF collector documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md#integration-with-appsplugin) for the full list +See the [eBPF collector documentation](/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md#integration-with-appsplugin) for the full list of per-application charts. Let's show some examples of how you can first identify normal eBPF patterns, then use that knowledge to identify @@ -239,16 +239,16 @@ same application on multiple systems and want to correlate how it performs on ea findings with someone else on your team. If you don't already have a Netdata Cloud account, go [sign in](https://app.netdata.cloud) and get started for free. -You can also read how to [monitor your infrastructure with Netdata Cloud](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md) to understand the key features that it has to offer. +You can also read how to [monitor your infrastructure with Netdata Cloud](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md) to understand the key features that it has to offer. -Once you've added one or more nodes to a Space in Netdata Cloud, you can see aggregated eBPF metrics in the [Overview -dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md) under the same **Applications** or **eBPF** sections that you -find on the local Agent dashboard. Or, [create new dashboards](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md) using eBPF metrics +Once you've added one or more nodes to a Space in Netdata Cloud, you can see aggregated eBPF metrics in the Overview +dashboard under the same **Applications** or **eBPF** sections that you +find on the local Agent dashboard. Or, [create new dashboards](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/dashboards-tab.md) using eBPF metrics from any number of distributed nodes to see how your application interacts with multiple Linux kernels on multiple Linux systems. Now that you can see eBPF metrics in Netdata Cloud, you can [invite your -team](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team) and share your findings with others. +team](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team) and share your findings with others. diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor-hadoop-cluster.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/monitor-hadoop-cluster.md index b536e0fa0..98bf3d21f 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor-hadoop-cluster.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/monitor-hadoop-cluster.md @@ -27,8 +27,8 @@ alternative, like the guide available from For more specifics on the collection modules used in this guide, read the respective pages in our documentation: -- [HDFS](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/hdfs/README.md) -- [Zookeeper](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/zookeeper/README.md) +- [HDFS](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/hdfs/README.md) +- [Zookeeper](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/zookeeper/README.md) ## Set up your HDFS and Zookeeper installations @@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ jobs: address : 203.0.113.10:2182 ``` -Finally, [restart Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation). +Finally, [restart Netdata](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation). ```sh sudo systemctl restart netdata @@ -188,4 +188,4 @@ sudo /etc/netdata/edit-config health.d/zookeeper.conf ``` For more information about editing the defaults or writing new alert entities, see our -[health monitoring documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/README.md). +[health monitoring documentation](/src/health/README.md). diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/pi-hole-raspberry-pi.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/pi-hole-raspberry-pi.md index 1e76cc096..df6bb0809 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/pi-hole-raspberry-pi.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/pi-hole-raspberry-pi.md @@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ service](https://discourse.pi-hole.net/t/how-do-i-configure-my-devices-to-use-pi finished setting up Pi-hole at this point. As far as configuring Netdata to monitor Pi-hole metrics, there's nothing you actually need to do. Netdata's [Pi-hole -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/pihole/README.md) will autodetect the new service +collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/pihole/README.md) will autodetect the new service running on your Raspberry Pi and immediately start collecting metrics every second. Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, which will then recognize that Pi-hole is running and start a @@ -100,14 +100,12 @@ part of your system might affect another.  -If you're completely new to Netdata, look at the [Introduction](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/getting-started/introduction.md) section for a walkthrough of all its features. For a more expedited tour, see the [get started documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md). - ### Enable temperature sensor monitoring You need to manually enable Netdata's built-in [temperature sensor -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/charts.d.plugin/sensors/README.md) to start collecting metrics. +collector](/src/collectors/charts.d.plugin/sensors/README.md) to start collecting metrics. -> Netdata uses a few plugins to manage its [collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md), each using a different language: Go, +> Netdata uses a few plugins to manage its [collectors](/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md), each using a different language: Go, > Python, Node.js, and Bash. While our Go collectors are undergoing the most active development, we still support the > other languages. In this case, you need to enable a temperature sensor collector that's written in Bash. @@ -125,7 +123,7 @@ Raspberry Pi temperature sensor monitoring. ### Storing historical metrics on your Raspberry Pi By default, Netdata allocates 256 MiB in disk space to store historical metrics inside the [database -engine](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/engine/README.md). On the Raspberry Pi used for this guide, Netdata collects 1,500 metrics every +engine](/src/database/engine/README.md). On the Raspberry Pi used for this guide, Netdata collects 1,500 metrics every second, which equates to storing 3.5 days worth of historical metrics. You can increase this allocation by editing `netdata.conf` and increasing the `dbengine multihost disk space` setting to @@ -137,6 +135,6 @@ more than 256. ``` Use our [database sizing -calculator](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics) -and the [Database configuration documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md) to help you determine the right +calculator](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics) +and the [Database configuration documentation](/src/database/README.md) to help you determine the right setting for your Raspberry Pi. diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/process.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/process.md index af36aefa1..2902a24f6 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/process.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/process.md @@ -37,16 +37,16 @@ With Netdata's process monitoring, you can: ## Prerequisites -- One or more Linux nodes running [Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md) +- One or more Linux nodes running [Netdata](/packaging/installer/README.md) - A general understanding of how - to [configure the Netdata Agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) + to [configure the Netdata Agent](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) using `edit-config`. - A Netdata Cloud account. [Sign up](https://app.netdata.cloud) if you don't have one already. ## How does Netdata do process monitoring? The Netdata Agent already knows to look for hundreds -of [standard applications that we support via collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md), +of [standard applications that we support via collectors](/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md), and groups them based on their purpose. Let's say you want to monitor a MySQL database using its process. The Netdata Agent already knows to look for processes with the string `mysqld` in their @@ -55,12 +55,12 @@ process-specific charts. The process and groups settings are used by two unique and powerful collectors. -[**`apps.plugin`**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md) looks at the Linux +[**`apps.plugin`**](/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md) looks at the Linux process tree every second, much like `top` or `ps fax`, and collects resource utilization information on every running process. It then automatically adds a layer of meaningful visualization on top of these metrics, and creates per-process/application charts. -[**`ebpf.plugin`**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md): Netdata's extended +[**`ebpf.plugin`**](/src/collectors/ebpf.plugin/README.md): Netdata's extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) collector monitors Linux kernel-level metrics for file descriptors, virtual filesystem IO, and process management, and then hands process-specific metrics over to `apps.plugin` for visualization. The eBPF collector also collects and visualizes @@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ aware of hundreds of processes, and collects metrics from them automatically. But, if you want to change the grouping behavior, add an application that isn't yet supported in the Netdata Agent, or monitor a custom application, you need to edit the `apps_groups.conf` configuration file. -Navigate to your [Netdata config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) and +Navigate to your [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) and use `edit-config` to edit the file. ```bash @@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ others, and groups them into `sql`. That makes sense, since all these processes sql: mysqld* mariad* postgres* postmaster* oracle_* ora_* sqlservr ``` -These groups are then reflected as [dimensions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/README.md#dimensions) +These groups are then reflected as [dimensions](/src/web/README.md#dimensions) within Netdata's charts.  for your system, to start collecting utilization metrics +the [appropriate method](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to start collecting utilization metrics from your application. Time to [visualize your process metrics](#visualize-process-metrics). ### Custom applications @@ -207,7 +207,7 @@ custom-app: custom-app ``` Restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or -the [appropriate method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to start collecting utilization metrics +the [appropriate method](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to start collecting utilization metrics from your application. ## Visualize process metrics diff --git a/docs/guides/python-collector.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/python-collector.md index 4dd6d2c4c..0b7aa96a6 100644 --- a/docs/guides/python-collector.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/python-collector.md @@ -1,8 +1,8 @@ # Develop a custom data collector in Python -The Netdata Agent uses [data collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md) to +The Netdata Agent uses [data collectors](/src/collectors/README.md) to fetch metrics from hundreds of system, container, and service endpoints. While the Netdata team and community has built -[powerful collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md) for most system, container, +[powerful collectors](/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md) for most system, container, and service/application endpoints, some custom applications can't be monitored by default. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to leverage the [Python programming language](https://www.python.org/) to build a @@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ want to make it available for other users, you should create the pull request in ## What you need to get started - A physical or virtual Linux system, which we'll call a _node_. - - A working [installation of Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md) monitoring agent. + - A working [installation of Netdata](/packaging/installer/README.md) monitoring agent. ### Quick start @@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ For a quick start, you can look at the Netdata (as opposed to having to install Netdata from source again with your new changes) you can copy over the relevant file to where Netdata expects it and then either `sudo systemctl restart netdata` to have it be picked up and used by Netdata or you can just run the updated collector in debug mode by following a process like below (this assumes you have -[installed Netdata from a GitHub fork](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/manual.md) you +[installed Netdata from a GitHub fork](/packaging/installer/methods/manual.md) you have made to do your development on). ```bash @@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ The basic elements of a Netdata collector are: - `get_data()`: The basic function of the plugin which will return to Netdata the correct values. **Note**: All names are better explained in the -[External Plugins Documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md). +[External Plugins Documentation](/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md). Parameters like `priority` and `update_every` mentioned in that documentation are handled by the `python.d.plugin`, not by each collection module. @@ -117,7 +117,7 @@ context, charttype]`, where: that is `A.B`, with `A` being the name of the collector, and `B` being the name of the specific metric. - `charttype`: Either `line`, `area`, or `stacked`. If null line is the default value. -You can read more about `family` and `context` in the [web dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/README.md#families) doc. +You can read more about `family` and `context` in the [web dashboard](/src/web/README.md#families) doc. Once the chart has been defined, you should define the dimensions of the chart. Dimensions are basically the metrics to be represented in this chart and each chart can have more than one dimension. In order to define the dimensions, the @@ -410,7 +410,7 @@ ORDER = [ ] ``` -[Restart Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) with `sudo systemctl restart netdata` to see the new humidity +[Restart Netdata](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) with `sudo systemctl restart netdata` to see the new humidity chart:  @@ -467,7 +467,7 @@ ORDER = [ ] ``` -[Restart Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) with `sudo systemctl restart netdata` to see the new +[Restart Netdata](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) with `sudo systemctl restart netdata` to see the new min/max/average temperature chart with multiple dimensions:  @@ -521,7 +521,7 @@ variables and inform the user about the defaults. For example, take a look at th [GitHub](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/example/example.conf). You can read more about the configuration file on the [`python.d.plugin` -documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/README.md). +documentation](/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/README.md). You can find the source code for the above examples on [GitHub](https://github.com/papajohn-uop/netdata). diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/raspberry-pi-anomaly-detection.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/raspberry-pi-anomaly-detection.md index 3c56ac79a..41cf007eb 100644 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/raspberry-pi-anomaly-detection.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/raspberry-pi-anomaly-detection.md @@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ We love IoT and edge at Netdata, we also love machine learning. Even better if w of monitoring increasingly complex systems. We recently explored what might be involved in enabling our Python-based [anomalies -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/anomalies/README.md) on a Raspberry Pi. To our delight, it's actually quite +collector](/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/anomalies/README.md) on a Raspberry Pi. To our delight, it's actually quite straightforward! Read on to learn all the steps and enable unsupervised anomaly detection on your on Raspberry Pi(s). @@ -17,14 +17,14 @@ Read on to learn all the steps and enable unsupervised anomaly detection on your - A Raspberry Pi running Raspbian, which we'll call a _node_. - The [open-source Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata) monitoring agent. If you don't have it installed on your - node yet, [get started now](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md). + node yet, [get started now](/packaging/installer/README.md). ## Install dependencies First make sure Netdata is using Python 3 when it runs Python-based data collectors. -Next, open `netdata.conf` using [`edit-config`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md#use-edit-config-to-edit-configuration-files) -from within the [Netdata config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md#the-netdata-config-directory). Scroll down to the +Next, open `netdata.conf` using [`edit-config`](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#edit-netdataconf) +from within the [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#the-netdata-config-directory). Scroll down to the `[plugin:python.d]` section to pass in the `-ppython3` command option. ```conf @@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ LLVM_CONFIG=llvm-config-9 pip3 install --user llvmlite numpy==1.20.1 netdata-pan ## Enable the anomalies collector -Now you're ready to enable the collector and [restart Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation). +Now you're ready to enable the collector and [restart Netdata](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation). ```bash sudo ./edit-config python.d.conf @@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ centralized cloud somewhere) is the resource utilization impact of running a mon With the default configuration, the anomalies collector uses about 6.5% of CPU at each run. During the retraining step, CPU utilization jumps to between 20-30% for a few seconds, but you can [configure -retraining](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/anomalies/README.md#configuration) to happen less often if you wish. +retraining](/src/collectors/python.d.plugin/anomalies/README.md#configuration) to happen less often if you wish.  diff --git a/docs/running-through-cf-tunnels.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/running-through-cf-tunnels.md index 324ce40e4..3179d5805 100644 --- a/docs/running-through-cf-tunnels.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/running-through-cf-tunnels.md @@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ RestartSec=5s WantedBy=multi-user.target ``` -You can edit the configuration file using the `edit-config` script from the Netdata [config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md#the-netdata-config-directory). +You can edit the configuration file using the `edit-config` script from the Netdata [config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#the-netdata-config-directory). - Edit `netdata.conf` and input: @@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ You can edit the configuration file using the `edit-config` script from the Netd destination = tcp:127.0.0.1:19999 ``` -[Restart the Agents](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation), and you are done! +[Restart the Agents](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation), and you are done! You should now be able to have a Local Dashboard that gets its metrics from Child instances, running through Cloudflare tunnels. diff --git a/docs/contributing/style-guide.md b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/style-guide.md index 2487f2eb1..94656bd76 100644 --- a/docs/contributing/style-guide.md +++ b/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/style-guide.md @@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ The _Netdata style guide_ establishes editorial guidelines for any writing produced by the Netdata team or the Netdata community, including documentation, articles, in-product UX copy, and more. > ### Note -> This document is meant to be accompanied by the [Documentation Guidelines](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guidelines.md). If you want to contribute to Netdata's documentation, please read it too. +> This document is meant to be accompanied by the [Documentation Guidelines](/docs/guidelines.md). If you want to contribute to Netdata's documentation, please read it too. Both internal Netdata teams and external contributors to any of Netdata's open-source projects should reference and adhere to this style guide as much as possible. @@ -25,8 +25,7 @@ One way we write empowering, educational content is by using a consistent voice _Voice_ is like your personality, which doesn't really change day to day. _Tone_ is how you express your personality. Your expression changes based on your attitude or mood, or based on who -you're around. In writing, your reflect tone in your word choice, punctuation, sentence structure, or even the use of -emoji. +you're around. In writing, you reflect tone in your word choice, punctuation, sentence structure, or emoji. The same idea about voice and tone applies to organizations, too. Our voice shouldn't change much between two pieces of content, no matter who wrote each, but the tone might be quite different based on who we think is reading. @@ -239,12 +238,11 @@ reader. | | | |-----------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| Not recommended | To install Netdata, click [here](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md). | -| **Recommended** | To install Netdata, read the [installation instructions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md). | +| Not recommended | To install Netdata, click [here](/packaging/installer/README.md). | +| **Recommended** | To install Netdata, read the [installation instructions](/packaging/installer/README.md). | -Use links as often as required to provide necessary context. Blog posts and guides require less hyperlinks than -documentation. See the section on [linking between documentation](#linking-between-documentation) for guidance on the -Markdown syntax and path structure of inter-documentation links. +Use links as often as required to provide necessary context. Blog posts and guides require fewer hyperlinks than +documentation. ### Contractions @@ -295,17 +293,17 @@ Netdata Agent installation will have commands under the same paths. When applica path, providing a recommendation or instructions on how to view the running configuration, which includes the correct paths. -For example, the [configuration](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) doc first +For example, the [configuration](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) doc first teaches users how to find the Netdata config directory and navigate to it, then runs commands from the `/etc/netdata` path so that the instructions are more universal. Don't include full paths, beginning from the system's root (`/`), as these might not work on certain systems. -| | | -|-----------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| Not recommended | Use `edit-config` to edit Netdata's configuration: `sudo /etc/netdata/edit-config netdata.conf`. | -| **Recommended** | Use `edit-config` to edit Netdata's configuration by first navigating to your [Netdata config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md#the-netdata-config-directory), which is typically at `/etc/netdata`, then running `sudo edit-config netdata.conf`. | +| | | +|-----------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Not recommended | Use `edit-config` to edit Netdata's configuration: `sudo /etc/netdata/edit-config netdata.conf`. | +| **Recommended** | Use `edit-config` to edit Netdata's configuration by first navigating to your [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#the-netdata-config-directory), which is typically at `/etc/netdata`, then running `sudo edit-config netdata.conf`. | ### `sudo` @@ -331,20 +329,6 @@ paragraphs, styled text, lists, tables, and more. The following sections describe situations in which a specific syntax is required. -### Syntax standards (`remark-lint`) - -The Netdata team uses [`remark-lint`](https://github.com/remarkjs/remark-lint) for Markdown code styling. - -- Use a maximum of 120 characters per line. -- Begin headings with hashes, such as `# H1 heading`, `## H2 heading`, and so on. -- Use `_` for italics/emphasis. -- Use `**` for bold. -- Use dashes `-` to begin an unordered list, and put a single space after the dash. -- Tables should be padded so that pipes line up vertically with added whitespace. - -If you want to see all the settings, open the -[`remarkrc.js`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/.remarkrc.js) file in the `netdata/netdata` repository. - ### References to UI elements When referencing a user interface (UI) element in Netdata, reference the label text of the link/button with Markdown's @@ -466,16 +450,16 @@ The following tables describe the standard spelling, capitalization, and usage o | Term | Definition | |-----------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| **claimed node** | A node that you've proved ownership of by completing the [connecting to Cloud process](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md). The claimed node will then appear in your Space and any War Rooms you added it to. | +| **claimed node** | A node that you've proved ownership of by completing the [connecting to Cloud process](/src/claim/README.md). The claimed node will then appear in your Space and any Rooms you added it to. | | **Netdata** | The company behind the open-source Netdata Agent and the Netdata Cloud web application. Never use _netdata_ or _NetData_. <br /><br />In general, focus on the user's goals, actions, and solutions rather than what the company provides. For example, write _Learn more about enabling alert notifications on your preferred platforms_ instead of _Netdata sends alert notifications to your preferred platforms_. | | **Netdata Agent** | The free and open source [monitoring agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata) that you can install on all of your distributed systems, whether they're physical, virtual, containerized, ephemeral, and more. The Agent monitors systems running Linux, Docker, Kubernetes, macOS, FreeBSD, and more, and collects metrics from hundreds of popular services and applications. | | **Netdata Cloud** | The web application hosted at [https://app.netdata.cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud) that helps you monitor an entire infrastructure of distributed systems in real time. <br /><br />Never use _Cloud_ without the preceding _Netdata_ to avoid ambiguity. | | **Netdata community forum** | The Discourse-powered forum for feature requests, Netdata Cloud technical support, and conversations about Netdata's monitoring and troubleshooting products. | | **node** | A system on which the Netdata Agent is installed. The system can be physical, virtual, in a Docker container, and more. Depending on your infrastructure, you may have one, dozens, or hundreds of nodes. Some nodes are _ephemeral_, in that they're created/destroyed automatically by an orchestrator service. | | **Space** | The highest level container within Netdata Cloud for a user to organize their team members and nodes within their infrastructure. A Space likely represents an entire organization or a large team. <br /><br />_Space_ is always capitalized. | -| **unreachable node** | A connected node with a disrupted [Agent-Cloud link](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/aclk/README.md). Unreachable could mean the node no longer exists or is experiencing network connectivity issues with Cloud. | +| **unreachable node** | A connected node with a disrupted [Agent-Cloud link](/src/aclk/README.md). Unreachable could mean the node no longer exists or is experiencing network connectivity issues with Cloud. | | **visited node** | A node which has had its Agent dashboard directly visited by a user. A list of these is maintained on a per-user basis. | -| **War Room** | A smaller grouping of nodes where users can view key metrics in real-time and monitor the health of many nodes with their alert status. War Rooms can be used to organize nodes in any way that makes sense for your infrastructure, such as by a service, purpose, physical location, and more. <br /><br />_War Room_ is always capitalized. | +| **Room** | A smaller grouping of nodes where users can view key metrics in real-time and monitor the health of many nodes with their alert status. Rooms can be used to organize nodes in any way that makes sense for your infrastructure, such as by a service, purpose, physical location, and more. <br /><br />_Room_ is always capitalized. | ### Other technical terms diff --git a/docs/export/enable-connector.md b/docs/export/enable-connector.md deleted file mode 100644 index 346d4553e..000000000 --- a/docs/export/enable-connector.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,105 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Enable an exporting connector" -description: "Learn how to enable and configure any connector using examples to start exporting metrics to external time-series databases in minutes." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/export/enable-connector.md" -sidebar_label: "Enable an exporting connector" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Tasks" -learn_rel_path: "Configuration" ---> - -# Enable an exporting connector - -Now that you found the right connector for your [external time-series -database](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/export/external-databases.md#supported-databases), you can now enable the exporting engine and the -connector itself. We'll walk through the process of enabling the exporting engine itself, followed by two examples using -the OpenTSDB and Graphite connectors. - -> When you enable the exporting engine and a connector, the Netdata Agent exports metrics _beginning from the time you -> restart its process_, not the entire -> [database of long-term metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md). - -Once you understand the process of enabling a connector, you can translate that knowledge to any other connector. - -## Enable the exporting engine - -Use `edit-config` from your -[Netdata config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md#the-netdata-config-directory) -to open `exporting.conf`: - -```bash -sudo ./edit-config exporting.conf -``` - -Enable the exporting engine itself by setting `enabled` to `yes`: - -```conf -[exporting:global] - enabled = yes -``` - -Save the file but keep it open, as you will edit it again to enable specific connectors. - -## Example: Enable the OpenTSDB connector - -Use the following configuration as a starting point. Copy and paste it into `exporting.conf`. - -```conf -[opentsdb:http:my_opentsdb_http_instance] - enabled = yes - destination = localhost:4242 -``` - -Replace `my_opentsdb_http_instance` with an instance name of your choice, and change the `destination` setting to the IP -address or hostname of your OpenTSDB database. - -Restart your Agent with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or -the [appropriate method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to begin exporting to your OpenTSDB -database. The -Netdata Agent exports metrics _beginning from the time the process starts_, and because it exports as metrics are -collected, you should start seeing data in your external database after only a few seconds. - -Any further configuration is optional, based on your needs and the configuration of your OpenTSDB database. See the -[OpenTSDB connector doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md) -and [exporting engine reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md#configuration) for -details. - -## Example: Enable the Graphite connector - -Use the following configuration as a starting point. Copy and paste it into `exporting.conf`. - -```conf -[graphite:my_graphite_instance] - enabled = yes - destination = 203.0.113.0:2003 -``` - -Replace `my_graphite_instance` with an instance name of your choice, and change the `destination` setting to the IP -address or hostname of your Graphite-supported database. - -Restart your Agent with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or -the [appropriate method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to begin exporting to your -Graphite-supported database. -Because the Agent exports metrics as they're collected, you should start seeing data in your external database after -only a few seconds. - -Any further configuration is optional, based on your needs and the configuration of your Graphite-supported database. -See [exporting engine reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md#configuration) for -details. - -## What's next? - -If you want to further configure your exporting connectors, see -the [exporting engine reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md#configuration). - -For a comprehensive example of using the Graphite connector, read our documentation on -[exporting metrics to Graphite providers](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md). Or, start -[using host labels](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/using-host-labels.md) on exported metrics. - -### Related reference documentation - -- [Exporting engine reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md) -- [OpenTSDB connector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md) -- [Graphite connector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md) - - diff --git a/docs/export/external-databases.md b/docs/export/external-databases.md deleted file mode 100644 index 1679947ce..000000000 --- a/docs/export/external-databases.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,77 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Export metrics to external time-series databases" -description: "Use the exporting engine to send Netdata metrics to popular external time series databases for long-term storage or further analysis." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/export/external-databases.md" -sidebar_label: "Export metrics to external time-series databases" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Concepts" ---> - -# Export metrics to external time-series databases - -Netdata allows you to export metrics to external time-series databases with the [exporting -engine](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md). This system uses a number of **connectors** to initiate connections to [more than -thirty](#supported-databases) supported databases, including InfluxDB, Prometheus, Graphite, ElasticSearch, and much -more. - -The exporting engine resamples Netdata's thousands of per-second metrics at a user-configurable interval, and can export -metrics to multiple time-series databases simultaneously. - -Based on your needs and resources you allocated to your external time-series database, you can configure the interval -that metrics are exported or export only certain charts with filtering. You can also choose whether metrics are exported -as-collected, a normalized average, or the sum/volume of metrics values over the configured interval. - -Exporting is an important part of Netdata's effort to be interoperable -with other monitoring software. You can use an external time-series database for long-term metrics retention, further -analysis, or correlation with other tools, such as application tracing. - -## Supported databases - -Netdata supports exporting metrics to the following databases through several -[connectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md#features). Once you find the connector that works for your database, open its -documentation and the [enabling a connector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/export/enable-connector.md) doc for details on enabling it. - -- **AppOptics**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **AWS Kinesis**: [AWS Kinesis Data Streams](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/aws_kinesis/README.md) -- **Azure Data Explorer**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Azure Event Hubs**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Blueflood**: [Graphite](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md) -- **Chronix**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Cortex**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **CrateDB**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **ElasticSearch**: [Graphite](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [Prometheus remote - write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Gnocchi**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Google BigQuery**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Google Cloud Pub/Sub**: [Google Cloud Pub/Sub Service](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/pubsub/README.md) -- **Graphite**: [Graphite](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [Prometheus remote - write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **InfluxDB**: [Graphite](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [Prometheus remote - write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **IRONdb**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **JSON**: [JSON document databases](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/json/README.md) -- **Kafka**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **KairosDB**: [Graphite](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [OpenTSDB](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md) -- **M3DB**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **MetricFire**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **MongoDB**: [MongoDB](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/mongodb/README.md) -- **New Relic**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **OpenTSDB**: [OpenTSDB](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md), [Prometheus remote - write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **PostgreSQL**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) - via [PostgreSQL Prometheus Adapter](https://github.com/CrunchyData/postgresql-prometheus-adapter) -- **Prometheus**: [Prometheus scraper](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/README.md) -- **TimescaleDB**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md), - [netdata-timescale-relay](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/TIMESCALE.md) -- **QuasarDB**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **SignalFx**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Splunk**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **TiKV**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Thanos**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **VictoriaMetrics**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) -- **Wavefront**: [Prometheus remote write](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) - -Can't find your preferred external time-series database? Ask our [community](https://community.netdata.cloud/) for -solutions, or file an [issue on -GitHub](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug%2Cneeds+triage&template=BUG_REPORT.yml). diff --git a/docs/exporting-metrics/README.md b/docs/exporting-metrics/README.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..d667cea15 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/exporting-metrics/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,67 @@ +# Export metrics to external time-series databases + +Netdata allows you to export metrics to external time-series databases with the [exporting +engine](/src/exporting/README.md). This system uses a number of **connectors** to initiate connections to [more than +thirty](#supported-databases) supported databases, including InfluxDB, Prometheus, Graphite, ElasticSearch, and much +more. + +The exporting engine resamples Netdata's thousands of per-second metrics at a user-configurable interval, and can export +metrics to multiple time-series databases simultaneously. + +Based on your needs and resources you allocated to your external time-series database, you can configure the interval +that metrics are exported or export only certain charts with filtering. You can also choose whether metrics are exported +as-collected, a normalized average, or the sum/volume of metrics values over the configured interval. + +Exporting is an important part of Netdata's effort to be interoperable +with other monitoring software. You can use an external time-series database for long-term metrics retention, further +analysis, or correlation with other tools, such as application tracing. + +## Supported databases + +Netdata supports exporting metrics to the following databases through several +[connectors](/src/exporting/README.md#features). Once you find the connector that works for your database, open its +documentation and the [enabling a connector](/docs/exporting-metrics/enable-an-exporting-connector.md) doc for details on enabling it. + +- **AppOptics**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **AWS Kinesis**: [AWS Kinesis Data Streams](/src/exporting/aws_kinesis/README.md) +- **Azure Data Explorer**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Azure Event Hubs**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Blueflood**: [Graphite](/src/exporting/graphite/README.md) +- **Chronix**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Cortex**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **CrateDB**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **ElasticSearch**: [Graphite](/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [Prometheus remote + write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Gnocchi**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Google BigQuery**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Google Cloud Pub/Sub**: [Google Cloud Pub/Sub Service](/src/exporting/pubsub/README.md) +- **Graphite**: [Graphite](/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [Prometheus remote + write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **InfluxDB**: [Graphite](/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [Prometheus remote + write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **IRONdb**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **JSON**: [JSON document databases](/src/exporting/json/README.md) +- **Kafka**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **KairosDB**: [Graphite](/src/exporting/graphite/README.md), [OpenTSDB](/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md) +- **M3DB**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **MetricFire**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **MongoDB**: [MongoDB](/src/exporting/mongodb/README.md) +- **New Relic**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **OpenTSDB**: [OpenTSDB](/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md), [Prometheus remote + write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **PostgreSQL**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) + via [PostgreSQL Prometheus Adapter](https://github.com/CrunchyData/postgresql-prometheus-adapter) +- **Prometheus**: [Prometheus scraper](/src/exporting/prometheus/README.md) +- **TimescaleDB**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md), + [netdata-timescale-relay](/src/exporting/TIMESCALE.md) +- **QuasarDB**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **SignalFx**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Splunk**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **TiKV**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Thanos**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **VictoriaMetrics**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) +- **Wavefront**: [Prometheus remote write](/src/exporting/prometheus/remote_write/README.md) + +Can't find your preferred external time-series database? Ask our [community](https://community.netdata.cloud/) for +solutions, or file an [issue on +GitHub](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug%2Cneeds+triage&template=BUG_REPORT.yml). diff --git a/docs/exporting-metrics/enable-an-exporting-connector.md b/docs/exporting-metrics/enable-an-exporting-connector.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..6a5542fdb --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/exporting-metrics/enable-an-exporting-connector.md @@ -0,0 +1,43 @@ +# Enable an exporting connector + +Now that you found the right connector for your [external time-series +database](/docs/exporting-metrics/README.md#supported-databases), you can now enable the exporting engine and the +connector itself. We'll walk through the process of enabling the exporting engine itself, followed by two examples using +the OpenTSDB and Graphite connectors. + +> **Note** +> +> When you enable the exporting engine and a connector, the Netdata Agent exports metrics _beginning from the time you +> restart its process_, not the entire +> [database of long-term metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md). + +Once you understand how to enable a connector, you can apply that knowledge to any other connector. + +## Enable the exporting engine + +Use `edit-config` from your [Netdata config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md#the-netdata-config-directory) to edit `exporting.conf`. + +Enable the exporting engine itself by setting `enabled` to `yes`: + +```conf +[exporting:global] + enabled = yes +``` + +Save the file but keep it open, as you will edit it again to enable specific connectors. + +## Example: Enable the OpenTSDB connector + +Use the following configuration as a starting point. Copy and paste it into `exporting.conf`. + +```conf +[opentsdb:http:my_opentsdb_http_instance] + enabled = yes + destination = localhost:4242 +``` + +Replace `my_opentsdb_http_instance` with an instance name of your choice, and change the `destination` setting to the IP address or hostname of your OpenTSDB database. + +[Restart your Agent](/docs/netdata-agent/start-stop-restart.md) to initiate exporting to your OpenTSDB database. The Netdata Agent continuously exports metrics collected from the moment it starts. You can expect to see data appear in your OpenTSDB database within seconds of restarting the Agent. + +Any further configuration is optional, based on your needs and the configuration of your OpenTSDB database. See the [OpenTSDB connector doc](/src/exporting/opentsdb/README.md) and [exporting engine reference](/src/exporting/README.md#configuration) for details. diff --git a/docs/getting-started/introduction.md b/docs/getting-started/introduction.md deleted file mode 100644 index 65fd059d0..000000000 --- a/docs/getting-started/introduction.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,192 +0,0 @@ -# Getting started with Netdata - -Learn how Netdata can get you monitoring your infrastructure in minutes. - -## What is Netdata ? - -Netdata is designed by system administrators, DevOps engineers, and developers to collect everything, help you visualize -metrics, troubleshoot complex performance problems, and make data interoperable with the rest of your monitoring stack. - -You can install Netdata on most Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and more), container platforms (Kubernetes -clusters, Docker), and many other operating systems (FreeBSD). - -Netdata is: - -### Simple to deploy - -- **One-line deployment** for Linux distributions, plus support for Kubernetes/Docker infrastructures. -- **Zero configuration and maintenance** required to collect thousands of metrics, every second, from the underlying - OS and running applications. -- **Prebuilt charts and alerts** alert you to common anomalies and performance issues without manual configuration. -- **Distributed storage** to simplify the cost and complexity of storing metrics data from any number of nodes. - -### Powerful and scalable - -- **1% CPU utilization, a few MB of RAM, and minimal disk I/O** to run the monitoring Agent on bare metal, virtual - machines, containers, and even IoT devices. -- **Per-second granularity** for an unlimited number of metrics based on the hardware and applications you're running - on your nodes. -- **Interoperable exporters** let you connect Netdata's per-second metrics with an existing monitoring stack and other - time-series databases. - -### Optimized for troubleshooting - -- **Visual anomaly detection** with a UI/UX that emphasizes the relationships between charts. -- **Customizable dashboards** to pinpoint correlated metrics, respond to incidents, and help you streamline your - workflows. -- **Distributed metrics in a centralized interface** to assist users or teams trace complex issues between distributed - nodes. - -### Secure by design - -- **Distributed data architecture** so fast and efficient, there’s no limit to the number of metrics you can follow. -- Because your data is **stored at the edge**, security is ensured. - -### Comparison with other monitoring solutions - -Netdata offers many benefits over the existing monitoring landscape, whether they're expensive SaaS products or other -open-source tools. - -| Netdata | Others (open-source and commercial) | -|:----------------------------------------------------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------| -| **High resolution metrics** (1s granularity) | Low resolution metrics (10s granularity at best) | -| Collects **thousands of metrics per node** | Collects just a few metrics | -| Fast UI optimized for **anomaly detection** | UI is good for just an abstract view | -| **Long-term, autonomous storage** at one-second granularity | Centralized metrics in an expensive data lake at 10s granularity | -| **Meaningful presentation**, to help you understand the metrics | You have to know the metrics before you start | -| Install and get results **immediately** | Long sales process and complex installation process | -| Use it for **troubleshooting** performance problems | Only gathers _statistics of past performance_ | -| **Kills the console** for tracing performance issues | The console is always required for troubleshooting | -| Requires **zero dedicated resources** | Require large dedicated resources | - -Netdata works with tons of applications, notifications platforms, and other time-series databases: - -- **300+ system, container, and application endpoints**: Collectors autodetect metrics from default endpoints and - immediately visualize them into meaningful charts designed for troubleshooting. See [everything we - support](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md). -- **20+ notification platforms**: Netdata's health watchdog sends warning and critical alerts to your [favorite - platform](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md) to inform you of anomalies just seconds - after they affect your node. -- **30+ external time-series databases**: Export resampled metrics as they're collected to other [local- and - Cloud-based databases](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/export/external-databases.md) for best-in-class - interoperability. - -## How it works - -Netdata is a highly efficient, highly modular, metrics management engine. Its lockless design makes it ideal for concurrent operations on the metrics. - -You can see a high level representation in the following diagram. - - - -And a higher level diagram in this one. - - - -You can even visit this slightly dated [interactive infographic](https://my-netdata.io/infographic.html) and get lost in a rabbit hole. - -But the best way to get under the hood or in the steering wheel of our highly efficient, low-latency system (supporting multiple readers and one writer on each metric) is to read the rest of our docs, or just to jump in and [get started](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md). But here's a good breakdown: - -### Netdata Agent - -Netdata's distributed monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices. - -You can install Netdata on most Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and more), container/microservice platforms (Kubernetes clusters, Docker), and many other operating systems (FreeBSD, macOS), with no sudo required. - -### Netdata Cloud - -Netdata Cloud is a web application that gives you real-time visibility for your entire infrastructure. With Netdata Cloud, you can view key metrics, insightful charts, and active alerts from all your nodes in a single web interface. When an anomaly strikes, seamlessly navigate to any node to troubleshoot and discover the root cause with the familiar Netdata dashboard. - -Netdata Cloud is free! You can add an entire infrastructure of nodes, invite all your colleagues, and visualize any number of metrics, charts, and alerts entirely for free. - -While Netdata Cloud offers a centralized method of monitoring your Agents, your metrics data is not stored or centralized in any way. Metrics data remains with your nodes and is only streamed to your browser, through Cloud, when you're viewing the Netdata Cloud interface. - -## Use Netdata standalone or as part of your monitoring stack - -Netdata is an extremely powerful monitoring, visualization, and troubleshooting platform. While you can use it as an -effective standalone tool, we also designed it to be open and interoperable with other tools you might already be using. - -Netdata helps you collect everything and scales to infrastructure of any size, but it doesn't lock-in data or force you -to use specific tools or methodologies. Each feature is extensible and interoperable so they can work in parallel with -other tools. For example, you can use Netdata to collect metrics, visualize metrics with a second open-source program, -and centralize your metrics in a cloud-based time-series database solution for long-term storage or further analysis. - -You can build a new monitoring stack, including Netdata, or integrate Netdata's metrics with your existing monitoring -stack. No matter which route you take, Netdata helps you monitor infrastructure of any size. - -Here are a few ways to enrich your existing monitoring and troubleshooting stack with Netdata: - -### Collect metrics from Prometheus endpoints - -Netdata automatically detects 600 popular endpoints and collects per-second metrics from them via the [generic -Prometheus collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/go/collectors/go.d.plugin/modules/prometheus/README.md). This even -includes support for Windows 10 via [`windows_exporter`](https://github.com/prometheus-community/windows_exporter). - -This collector is installed and enabled on all Agent installations by default, so you don't need to waste time -configuring Netdata. Netdata will detect these Prometheus metrics endpoints and collect even more granular metrics than -your existing solutions. You can now use all of Netdata's meaningfully-visualized charts to diagnose issues and -troubleshoot anomalies. - -### Export metrics to external time-series databases - -Netdata can send its per-second metrics to external time-series databases, such as InfluxDB, Prometheus, Graphite, -TimescaleDB, ElasticSearch, AWS Kinesis Data Streams, Google Cloud Pub/Sub Service, and many others. - -Once you have Netdata's metrics in a secondary time-series database, you can use them however you'd like, such as -additional visualization/dashboarding tools or aggregation of data from multiple sources. - -### Visualize metrics with Grafana - -One popular monitoring stack is Netdata, Prometheus, and Grafana. Netdata acts as the stack's metrics collection -powerhouse, Prometheus as the time-series database, and Grafana as the visualization platform. You can also use Grafite instead of Prometheus, -or directly use the [Netdata source plugin for Grafana](https://blog.netdata.cloud/introducing-netdata-source-plugin-for-grafana/) - -Of course, just because you export or visualize metrics elsewhere, it doesn't mean Netdata's equivalent features -disappear. You can always build new dashboards in Netdata Cloud, drill down into per-second metrics using Netdata's -charts, or use Netdata's health watchdog to send notifications whenever an anomaly strikes. - -## Community - -Netdata is an inclusive open-source project and community. Please read our [Code of Conduct](https://github.com/netdata/.github/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). - -Find most of the Netdata team in our [community forums](https://community.netdata.cloud). It's the best place to -ask questions, find resources, and engage with passionate professionals. The team is also available and active in our [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/mPZ6WZKKG2) too. - -You can also find Netdata on: - -- [Twitter](https://twitter.com/netdatahq) -- [YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/c/Netdata) -- [Reddit](https://www.reddit.com/r/netdata/) -- [LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/company/netdata-cloud/) -- [StackShare](https://stackshare.io/netdata) -- [Product Hunt](https://www.producthunt.com/posts/netdata-monitoring-agent/) -- [Repology](https://repology.org/metapackage/netdata/versions) -- [Facebook](https://www.facebook.com/linuxnetdata/) - -## Contribute - -Contributions are the lifeblood of open-source projects. While we continue to invest in and improve Netdata, we need help to democratize monitoring! - -- Check our [Security Policy](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/security/policy). -- Found a bug? Open a [GitHub issue](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug%2Cneeds+triage&template=BUG_REPORT.yml&title=%5BBug%5D%3A+). -- Read our [Contributing Guide](https://github.com/netdata/.github/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md), which contains all the information you need to contribute to Netdata, such as improving our documentation, engaging in the community, and developing new features. We've made it as frictionless as possible, but if you need help, just ping us on our community forums! - -Package maintainers should read the guide on [building Netdata from source](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/source.md) for -instructions on building each Netdata component from source and preparing a package. - -## License - -The Netdata Agent is an open source project distributed under [GPLv3+](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/LICENSE). Netdata re-distributes other open-source tools and libraries. Please check the -[third party licenses](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/REDISTRIBUTED.md). - -## Is it any good? - -Yes. - -_When people first hear about a new product, they frequently ask if it is any good. A Hacker News user -[remarked](https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=3067434):_ - -> Note to self: Starting immediately, all raganwald projects will have a “Is it any good?” section in the readme, and -> the answer shall be "yes.". -******************************************************************************* diff --git a/docs/glossary.md b/docs/glossary.md index e25a6e6b3..bcada6030 100644 --- a/docs/glossary.md +++ b/docs/glossary.md @@ -13,152 +13,130 @@ Use the alphabatized list below to find the answer to your single-term questions ## A -- [**Agent** or **Netdata Agent**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md): Netdata's distributed monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices. +- [**Agent** or **Netdata Agent**](/packaging/installer/README.md): Netdata's distributed monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices. -- [**Agent-cloud link** or **ACLK**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/aclk/README.md): The Agent-Cloud link (ACLK) is the mechanism responsible for securely connecting a Netdata Agent to your web browser through Netdata Cloud. +- [**Agent-cloud link** or **ACLK**](/src/aclk/README.md): The Agent-Cloud link (ACLK) is the mechanism responsible for securely connecting a Netdata Agent to your web browser through Netdata Cloud. -- [**Aggregate Function**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#aggregate-functions-over-time): A function applied When the granularity of the data collected is higher than the plotted points on the chart. +- [**Aggregate Function**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#aggregate-functions-over-time): A function applied When the granularity of the data collected is higher than the plotted points on the chart. -- [**Alerts** (formerly **Alarms**)](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md): With the information that appears on Netdata Cloud and the local dashboard about active alerts, you can configure alerts to match your infrastructure's needs or your team's goals. +- [**Alerts** (formerly **Alarms**)](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md): With the information that appears on Netdata Cloud and the local dashboard about active alerts, you can configure alerts to match your infrastructure's needs or your team's goals. -- [**Alarm Entity Type**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#health-entity-reference): Entity types that are attached to specific charts and use the `alarm` label. +- [**Alarm Entity Type**](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#health-entity-reference): Entity types that are attached to specific charts and use the `alarm` label. -- [**Anomaly Advisor**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md): A Netdata feature that lets you quickly surface potentially anomalous metrics and charts related to a particular highlight window of interest. +- [**Anomaly Advisor**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/anomaly-advisor-tab.md): A Netdata feature that lets you focus on potentially anomalous metrics and charts related to a particular highlight window of interest. ## B -- [**Bookmarks**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#manage-spaces): Netdata Cloud's bookmarks put your tools in one accessible place. Bookmarks are shared between all War Rooms in a Space, so any users in your Space will be able to see and use them. +- [**Bookmarks**](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#manage-spaces): Netdata Cloud's bookmarks put your tools in one accessible place. Bookmarks are shared between all Rooms in a Space, so any users in your Space will be able to see and use them. ## C -- [**Child**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md#streaming-basics): A node, running Netdata, that streams metric data to one or more parent. +- [**Child**](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md): A node, running Netdata, that streams metric data to one or more parent. -- [**Cloud** or **Netdata Cloud**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md): Netdata Cloud is a web application that gives you real-time visibility for your entire infrastructure. With Netdata Cloud, you can view key metrics, insightful charts, and active alerts from all your nodes in a single web interface. +- [**Cloud** or **Netdata Cloud**](/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md): Netdata Cloud is a web application that gives you real-time visibility for your entire infrastructure. With Netdata Cloud, you can view key metrics, insightful charts, and active alerts from all your nodes in a single web interface. -- [**Collector**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology): A catch-all term for any Netdata process that gathers metrics from an endpoint. +- [**Collector**](/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology): A catch-all term for any Netdata process that gathers metrics from an endpoint. - [**Community**](https://community.netdata.cloud/): As a company with a passion and genesis in open-source, we are not just very proud of our community, but we consider our users, fans, and chatters to be an imperative part of the Netdata experience and culture. -- [**Composite Charts**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#overview-and-single-node-view): Charts used by the **Overview** tab which aggregate metrics from all the nodes (or a filtered selection) in a given War Room. +- [**Context**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#contexts): A way of grouping charts by the types of metrics collected and dimensions displayed. It's kind of like a machine-readable naming and organization scheme. -- [**Context**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#contexts): A way of grouping charts by the types of metrics collected and dimensions displayed. It's kind of like a machine-readable naming and organization scheme. - -- [**Custom dashboards**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/gui/custom/README.md) A dashboard that you can create using simple HTML (no javascript is required for basic dashboards). +- [**Custom dashboards**](/src/web/gui/custom/README.md) A dashboard that you can create using simple HTML (no javascript is required for basic dashboards). ## D -- [**Dashboards**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md): Out-of-the box visual presentation of metrics that allows you to make sense of your infrastructure and its health and performance. +- [**Dashboard**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md): Out-of-the-box visual representation of metrics to provide insight into your infrastructure, its health and performance. -- [**Definition Bar**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md): Bar within a composite chart that provides important information and options about the metrics within the chart. +- [**Definition Bar**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md): Bar within a composite chart that provides important information and options about the metrics within the chart. -- [**Dimension**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#dimensions): A dimension is a value that gets shown on a chart. +- [**Dimension**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#dimensions): A dimension is a value that gets shown on a chart. ## E -- [**External Plugins**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md): These gather metrics from external processes, such as a webserver or database, and run as independent processes that communicate with the Netdata daemon via pipes. +- [**External Plugins**](/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md): These gather metrics from external processes, such as a webserver or database, and run as independent processes that communicate with the Netdata daemon via pipes. ## F -- [**Family**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#families): 1. What we consider our Netdata community of users and engineers. 2. A single instance of a hardware or software resource that needs to be displayed separately from similar instances. +- [**Family**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#families): 1. What we consider our Netdata community of users and engineers. 2. A single instance of a hardware or software resource that needs to be displayed separately from similar instances. -- [**Flood Protection**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md#flood-protection): If a node has too many state changes like firing too many alerts or going from reachable to unreachable, Netdata Cloud enables flood protection. As long as a node is in flood protection mode, Netdata Cloud does not send notifications about this node +- [**Flood Protection**](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md#flood-protection): If a node has too many state changes like firing too many alerts or going from reachable to unreachable, Netdata Cloud enables flood protection. As long as a node is in flood protection mode, Netdata Cloud does not send notifications about this node -- [**Functions** or **Netdata Functions**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md): Routines exposed by a collector on the Netdata Agent that can bring additional information to support troubleshooting or trigger some action to happen on the node itself. +- [**Functions** or **Netdata Functions**](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md): Routines exposed by a collector on the Netdata Agent that can bring additional information to support troubleshooting or trigger some action to happen on the node itself. ## G -- [**Guided Troubleshooting**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/troubleshooting-overview.md): Troubleshooting with our Machine-Learning-powered tools designed to give you a cutting edge advantage in your troubleshooting battles. - -- [**Group by**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md#group-by-dimension-node-or-chart): The drop-down on the dimension bar of a composite chart that allows you to group metrics by dimension, node, or chart. - -## H - -- [**Headless Collector Streaming**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md#supported-streaming-configurations): Streaming configuration where child `A`, _without_ a database or web dashboard, streams metrics to parent `B`. +- [**Group by**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#group-by-dimension-node-or-chart): The drop-down on the dimension bar of a composite chart that allows you to group metrics by dimension, node, or chart. -- [**Health Configuration Files**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#edit-health-configuration-files): Files that you can edit to configure your Agent's health watchdog service. +- [**Health Configuration Files**](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#edit-health-configuration-files): Files that you can edit to configure your Agent's health watchdog service. -- [**Health Entity Reference**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#health-entity-reference): +- [**Health Entity Reference**](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#health-entity-reference): -- [**Home** tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#home): Tab in Netdata Cloud that provides a predefined dashboard of relevant information about entities in the War Room. +- [**Home** tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/home-tab.md): Tab in Netdata Cloud that provides a predefined dashboard of relevant information about entities in the Room. ## I -- [**Internal plugins**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology): These gather metrics from `/proc`, `/sys`, and other Linux kernel sources. They are written in `C` and run as threads within the Netdata daemon. +- [**Internal plugins**](/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology): These gather metrics from `/proc`, `/sys`, and other Linux kernel sources. They are written in `C` and run as threads within the Netdata daemon. ## K -- [**Kickstart** or **Kickstart Script**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md): An automatic one-line installation script named 'kickstart.sh' that works on all Linux distributions and macOS. +- [**Kickstart** or **Kickstart Script**](/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md): An automatic one-line installation script named 'kickstart.sh' that works on all Linux distributions and macOS. -- [**Kubernetes Dashboard** or **Kubernetes Tab**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md): Netdata Cloud features enhanced visualizations for the resource utilization of Kubernetes (k8s) clusters, embedded in the default Overview dashboard. +- [**Kubernetes Dashboard** or **Kubernetes Tab**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/kubernetes-tab.md): Netdata Cloud features enhanced visualizations for the resource utilization of Kubernetes (k8s) clusters, embedded in the default Overview dashboard. ## M -- [**Metrics Collection**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md): With zero configuration, Netdata auto-detects thousands of data sources upon starting and immediately collects per-second metrics. Netdata can immediately collect metrics from these endpoints thanks to 300+ collectors, which all come pre-installed when you install Netdata. +- [**Metrics Collection**](/src/collectors/README.md): With zero configuration, Netdata auto-detects thousands of data sources upon starting and immediately collects per-second metrics. Netdata can immediately collect metrics from these endpoints thanks to 300+ collectors, which all come pre-installed when you install Netdata. -- [**Metric Correlations**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md): A Netdata feature that lets you quickly find metrics and charts related to a particular window of interest that you want to explore further. +- [**Metric Correlations**](/docs/metric-correlations.md): A Netdata feature that lets you quickly find metrics and charts related to a particular window of interest that you want to explore further. -- [**Metrics Exporting**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/export/external-databases.md): Netdata allows you to export metrics to external time-series databases with the exporting engine. This system uses a number of connectors to initiate connections to more than thirty supported databases, including InfluxDB, Prometheus, Graphite, ElasticSearch, and much more. +- [**Metrics Exporting**](/docs/exporting-metrics/README.md): Netdata allows you to export metrics to external time-series databases with the exporting engine. This system uses a number of connectors to initiate connections to more than thirty supported databases, including InfluxDB, Prometheus, Graphite, ElasticSearch, and much more. -- [**Metrics Storage**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md): Upon collection the collected metrics need to be either forwarded, exported or just stored for further treatment. The Agent is capable to store metrics both short and long-term, with or without the usage of non-volatile storage. +- [**Metrics Storage**](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md): Upon collection the collected metrics need to be either forwarded, exported or just stored for further treatment. The Agent is capable to store metrics both short and long-term, with or without the usage of non-volatile storage. -- [**Metrics Streaming Replication**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md): Each node running Netdata can stream the metrics it collects, in real time, to another node. Metric streaming allows you to replicate metrics data across multiple nodes, or centralize all your metrics data into a single time-series database (TSDB). +- [**Metrics Streaming Replication**](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md): Each node running Netdata can stream the metrics it collects, in real time, to another node. Metric streaming allows you to replicate metrics data across multiple nodes, or centralize all your metrics data into a single time-series database (TSDB). -- [**Module**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md#enable-and-disable-a-specific-collection-module): A type of collector. +- [**Module**](/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md#enable-and-disable-a-specific-collection-module): A type of collector. ## N -- [**Netdata**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/getting-started/introduction.md): Netdata is a monitoring tool designed by system administrators, DevOps engineers, and developers to collect everything, help you visualize +- [**Netdata**](https://www.netdata.cloud/): Netdata is a monitoring tool designed by system administrators, DevOps engineers, and developers to collect everything, help you visualize metrics, troubleshoot complex performance problems, and make data interoperable with the rest of your monitoring stack. -- [**Netdata Agent** or **Agent**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md): Netdata's distributed monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices. - -- [**Netdata Cloud** or **Cloud**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md): Netdata Cloud is a web application that gives you real-time visibility for your entire infrastructure. With Netdata Cloud, you can view key metrics, insightful charts, and active alerts from all your nodes in a single web interface. - -- [**Netdata Functions** or **Functions**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md): Routines exposed by a collector on the Netdata Agent that can bring additional information to support troubleshooting or trigger some action to happen on the node itself. - -<!-- No link for this keyword - **Netdata Logs** https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/tasks/miscellaneous/check-netdata-logs.md: The three log files - `error.log`, `access.log` and `debug.log` - used by Netdata --> +- [**Netdata Agent** or **Agent**](/packaging/installer/README.md): Netdata's distributed monitoring Agent collects thousands of metrics from systems, hardware, and applications with zero configuration. It runs permanently on all your physical/virtual servers, containers, cloud deployments, and edge/IoT devices. -<!-- Here we need to explain Agent notifications and Cloud notifications, not just "notifications" +- [**Netdata Cloud** or **Cloud**](/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md): Netdata Cloud is a web application that gives you real-time visibility for your entire infrastructure. With Netdata Cloud, you can view key metrics, insightful charts, and active alerts from all your nodes in a single web interface. -- **Notifications** https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/concepts/health-monitoring/notifications.md: Netdata can send centralized alert notifications to your team whenever a node enters a warning, critical, or unreachable state. By enabling notifications, you ensure no alert, on any node in your infrastructure, goes unnoticed by you or your team. --> +- [**Netdata Functions** or **Functions**](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md): Routines exposed by a collector on the Netdata Agent that can bring additional information to support troubleshooting or trigger some action to happen on the node itself. ## O -- [**Obsoletion**(of nodes)](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#obsoleting-offline-nodes-from-a-space): Removing nodes from a space. +- [**Obsoletion**(of nodes)](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#obsoleting-offline-nodes-from-a-space): Removing nodes from a space. -- [**Orchestrators**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology): External plugins that run and manage one or more modules. They run as independent processes. - -- [**Overview** tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#overview-and-single-node-view): Tab in Netdata Cloud that uses composite charts. These charts display real-time aggregated metrics from all the nodes (or a filtered selection) in a given War Room. +- [**Orchestrators**](/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology): External plugins that run and manage one or more modules. They run as independent processes. ## P -- [**Parent**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md#streaming-basics): A node, running Netdata, that receives streamed metric data. - -- [**Proxy**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md#streaming-basics): A node, running Netdata, that receives metric data from a child and "forwards" them on to a separate parent node. - -- [**Proxy Streaming**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md#supported-streaming-configurations): Streaming configuration where child `A`, _with or without_ a database, sends metrics to proxy `C`, also _with or without_ a database. `C` sends metrics to parent `B` +- [**Parent**](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md): A node, running Netdata, that receives streamed metric data. ## R -- [**Registry**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/registry/README.md): Registry that allows Netdata to provide unified cross-server dashboards. +- [**Registry**](/src/registry/README.md): Registry that allows Netdata to provide unified cross-server dashboards. -- [**Replication Streaming**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/streaming/README.md): Streaming configuration where child `A`, _with_ a database and web dashboard, streams metrics to parent `B`. +- [**Replication Streaming**](/src/streaming/README.md): Streaming configuration where child `A`, _with_ a database and web dashboard, streams metrics to parent `B`. -- [**Room** or **War Room**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms): War Rooms organize your connected nodes and provide infrastructure-wide dashboards using real-time metrics and visualizations. +- [**Room**](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-rooms): Rooms organize your connected nodes and provide infrastructure-wide dashboards using real-time metrics and visualizations. ## S -- [**Single Node Dashboard**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#overview-and-single-node-view): A dashboard pre-configured with every installation of the Netdata agent, with thousand of metrics and hundreds of interactive charts that requires no set up. +- [**Single Node Dashboard**](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md): A dashboard pre-configured with every installation of the Netdata agent, with thousand of metrics and hundreds of interactive charts that requires no set up. -<!-- No link for this file in current structure. - **Snapshots** https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/tasks/miscellaneous/snapshot-data.md: An image of your dashboard at any given time, whicn can be imiported into any other node running Netdata or used to genereated a PDF file for your records. --> - -- [**Space**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces): A high-level container and virtual collaboration area where you can organize team members, access levels,and the nodes you want to monitor. +- [**Space**](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces): A high-level container and virtual collaboration area where you can organize team members, access levels,and the nodes you want to monitor. ## T -- [**Template Entity Type**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#entity-types): Entity type that defines rules that apply to all charts of a specific context, and use the template label. Templates help you apply one entity to all disks, all network interfaces, all MySQL databases, and so on. +- [**Template Entity Type**](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#entity-types): Entity type that defines rules that apply to all charts of a specific context, and use the template label. Templates help you apply one entity to all disks, all network interfaces, all MySQL databases, and so on. -- [**Tiers**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/engine/README.md#tiers): Tiering is a mechanism of providing multiple tiers of data with different granularity of metrics (the frequency they are collected and stored, i.e. their resolution). +- [**Tiers**](/src/database/engine/README.md#tiers): Tiering is a mechanism of providing multiple tiers of data with different granularity of metrics (the frequency they are collected and stored, i.e. their resolution). ## U @@ -167,12 +145,8 @@ even thousands of nodes. There are no actual bottlenecks especially if you retai ## V -- [**Visualizations**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/visualizations-overview.md): Netdata uses dimensions, contexts, and families to sort your metric data into graphs, charts, and alerts that maximize your understand of your infrastructure and your ability to troubleshoot it, along or on a team. - -## W - -- [**War Room** or **Room**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms): War Rooms organize your connected nodes and provide infrastructure-wide dashboards using real-time metrics and visualizations. +- [**Visualizations**](/docs/category-overview-pages/visualizations-overview.md): Netdata uses dimensions, contexts, and families to sort your metric data into graphs, charts, and alerts that maximize your understand of your infrastructure and your ability to troubleshoot it, along or on a team. ## Z -- [**Zero Configuration**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/getting-started/introduction.md#simple-to-deploy): Netdata is preconfigured and capable to autodetect and monitor any well known application that runs on your system. You just deploy and claim Netdata Agents in your Netdata space, and monitor them in seconds. +- **Zero Configuration**: Netdata is preconfigured and capable to autodetect and monitor any well known application that runs on your system. You just deploy and claim Netdata Agents in your Netdata space, and monitor them in seconds. diff --git a/docs/guidelines.md b/docs/guidelines.md index e8ff98e4e..b0e6759cc 100644 --- a/docs/guidelines.md +++ b/docs/guidelines.md @@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Check out our [blog](https://github.com/netdata/blog#readme) repo! Any blog subm #### Before you get started -Anyone interested in contributing significantly to documentation should first read the [Netdata style guide](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/contributing/style-guide.md) and the [Netdata Community Code of Conduct](https://github.com/netdata/.github/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). +Anyone interested in contributing significantly to documentation should first read the [Netdata style guide](/docs/developer-and-contributor-corner/style-guide.md) and the [Netdata Community Code of Conduct](https://github.com/netdata/.github/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). Netdata's documentation uses Markdown syntax. If you're not familiar with Markdown, read the [Mastering Markdown](https://guides.github.com/features/mastering-markdown/) guide from GitHub for the basics on creating paragraphs, styled text, lists, tables, and more. @@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ Please ensure that any links to a different documentation resource are fully exp e.g. ``` -[Correct link to this document](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guidelines.md) +[Correct link to this document](/docs/guidelines.md) vs [Incorrect link to this document](https://learn.netdata.cloud/XYZ) ``` diff --git a/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md b/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md deleted file mode 100644 index bc19a4f28..000000000 --- a/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,76 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Machine learning (ML) powered anomaly detection" -sidebar_label: "Machine learning (ML) powered anomaly detection" -description: "Detect anomalies in any system, container, or application in your infrastructure with machine learning and the open-source Netdata Agent." -image: /img/seo/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.png -custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/guides/monitor/anomaly-detection.md -learn_status: "Published" -learn_rel_path: "Operations" ---> - -# Machine learning (ML) powered anomaly detection - - -## Overview - -As of [`v1.32.0`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/releases/tag/v1.32.0), Netdata comes with some ML powered [anomaly detection](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anomaly_detection) capabilities built into it and available to use out of the box, with zero configuration required (ML was enabled by default in `v1.35.0-29-nightly` in [this PR](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/pull/13158), previously it required a one line config change). - -This means that in addition to collecting raw value metrics, the Netdata agent will also produce an [`anomaly-bit`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-bit---100--anomalous-0--normal) every second which will be `100` when recent raw metric values are considered anomalous by Netdata and `0` when they look normal. Once we aggregate beyond one second intervals this aggregated `anomaly-bit` becomes an ["anomaly rate"](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate---averageanomaly-bit). - -To be as concrete as possible, the below api call shows how to access the raw anomaly bit of the `system.cpu` chart from the [london.my-netdata.io](https://london.my-netdata.io) Netdata demo server. Passing `options=anomaly-bit` returns the anomaly bit instead of the raw metric value. - -``` -https://london.my-netdata.io/api/v1/data?chart=system.cpu&options=anomaly-bit -``` - -If we aggregate the above to just 1 point by adding `points=1` we get an "[Anomaly Rate](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md#anomaly-rate---averageanomaly-bit)": - -``` -https://london.my-netdata.io/api/v1/data?chart=system.cpu&options=anomaly-bit&points=1 -``` - -The fundamentals of Netdata's anomaly detection approach and implementation are covered in lots more detail in the [agent ML documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md). - -This guide will explain how to get started using these ML based anomaly detection capabilities within Netdata. - -## Anomaly Advisor - -The [Anomaly Advisor](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md) is the flagship anomaly detection feature within Netdata. In the "Anomalies" tab of Netdata you will see an overall "Anomaly Rate" chart that aggregates node level anomaly rate for all nodes in a space. The aim of this chart is to make it easy to quickly spot periods of time where the overall "[node anomaly rate](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md#node-anomaly-rate)" is elevated in some unusual way and for what node or nodes this relates to. - - - -Once an area on the Anomaly Rate chart is highlighted netdata will append a "heatmap" to the bottom of the screen that shows which metrics were more anomalous in the highlighted timeframe. Each row in the heatmap consists of an anomaly rate sparkline graph that can be expanded to reveal the raw underlying metric chart for that dimension. - -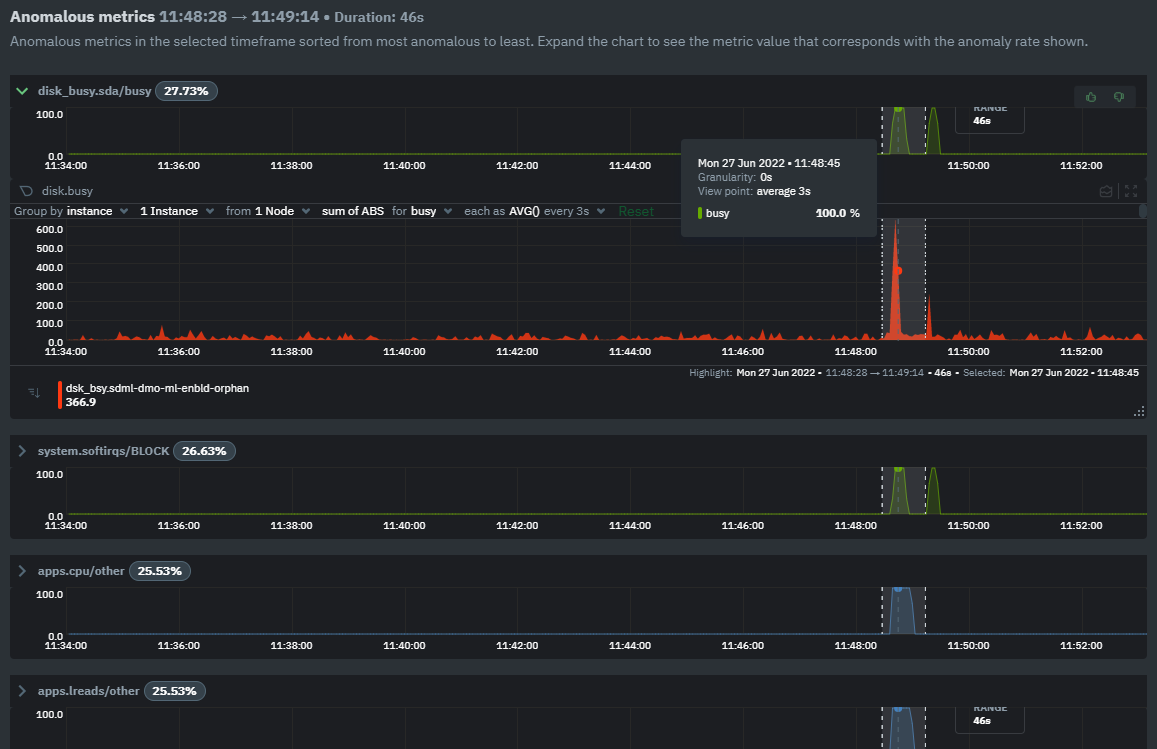 - -## Embedded Anomaly Rate Charts - -Charts in both the [Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md) and [single node dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#jump-to-single-node-dashboards) tabs also expose the underlying anomaly rates for each dimension so users can easily see if the raw metrics are considered anomalous or not by Netdata. - -Pressing the anomalies icon (next to the information icon in the chart header) will expand the anomaly rate chart to make it easy to see how the anomaly rate for any individual dimension corresponds to the raw underlying data. In the example below we can see that the spike in `system.pgpgio|in` corresponded in the anomaly rate for that dimension jumping to 100% for a small period of time until the spike passed. - -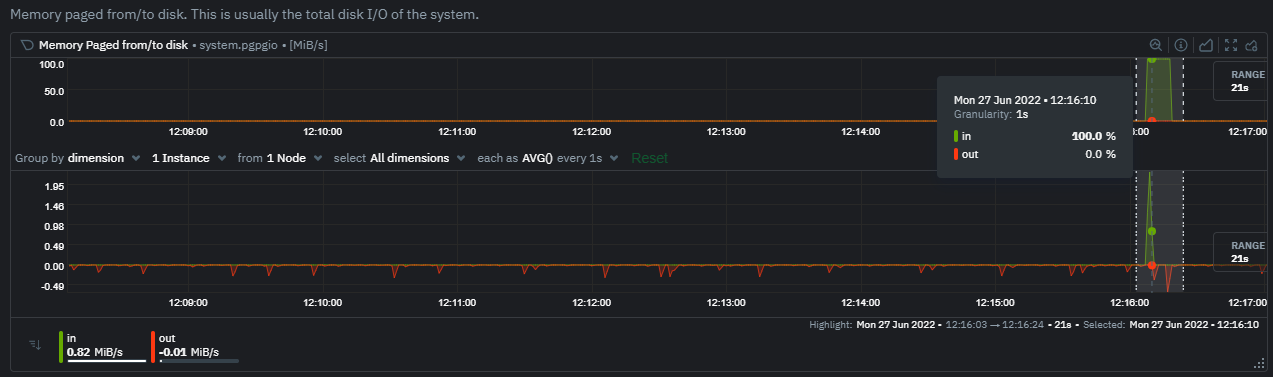 - -## Anomaly Rate Based Alerts - -It is possible to use the `anomaly-bit` when defining traditional Alerts within netdata. The `anomaly-bit` is just another `options` parameter that can be passed as part of an alert line lookup. - -You can see some example ML based alert configurations below: - -- [Anomaly rate based CPU dimensions alert](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#example-8---anomaly-rate-based-cpu-dimensions-alert) -- [Anomaly rate based CPU chart alert](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#example-9---anomaly-rate-based-cpu-chart-alert) -- [Anomaly rate based node level alert](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#example-10---anomaly-rate-based-node-level-alert) -- More examples in the [`/health/health.d/ml.conf`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/health.d/ml.conf) file that ships with the agent. - -## Learn More - -Check out the resources below to learn more about how Netdata is approaching ML: - -- [Agent ML documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md). -- [Anomaly Advisor documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md). -- [Metric Correlations documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md). -- Anomaly Advisor [launch blog post](https://www.netdata.cloud/blog/introducing-anomaly-advisor-unsupervised-anomaly-detection-in-netdata/). -- Netdata Approach to ML [blog post](https://www.netdata.cloud/blog/our-approach-to-machine-learning/). -- `areal/ml` related [GitHub Discussions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/discussions?discussions_q=label%3Aarea%2Fml). -- Netdata Machine Learning Meetup [deck](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1rfSxktg2av2k-eMwMbjN0tXeo76KC33iBaxerYinovs/edit?usp=sharing) and [YouTube recording](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eJGWZHVQdNU). -- Netdata Anomaly Advisor [YouTube Playlist](https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PL-P-gAHfL2KPeUcCKmNHXC-LX-FfdO43j). diff --git a/docs/guides/troubleshoot/troubleshooting-agent-with-cloud-connection.md b/docs/guides/troubleshoot/troubleshooting-agent-with-cloud-connection.md deleted file mode 100644 index 0c9962ba2..000000000 --- a/docs/guides/troubleshoot/troubleshooting-agent-with-cloud-connection.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,147 +0,0 @@ -# Troubleshoot Agent-Cloud connectivity issues - -Learn how to troubleshoot connectivity issues leading to agents not appearing at all in Netdata Cloud, or -appearing with a status other than `live`. - -After installing an agent with the claiming token provided by Netdata Cloud, you should see charts from that node on -Netdata Cloud within seconds. If you don't see charts, check if the node appears in the list of nodes -(Nodes tab, top right Node filter, or Manage Nodes screen). If your node does not appear in the list, or it does appear with a status other than "Live", this guide will help you troubleshoot what's happening. - - The most common explanation for connectivity issues usually falls into one of the following three categories: - -- If the node does not appear at all in Netdata Cloud, [the claiming process was unsuccessful](#the-claiming-process-was-unsuccessful). -- If the node appears as in Netdata Cloud, but is in the "Unseen" state, [the Agent was claimed but can not connect](#the-agent-was-claimed-but-can-not-connect). -- If the node appears as in Netdata Cloud as "Offline" or "Stale", it is a [previously connected agent that can no longer connect](#previously-connected-agent-that-can-no-longer-connect). - -## The claiming process was unsuccessful - -If the claiming process fails, the node will not appear at all in Netdata Cloud. - -First ensure that you: -- Use the newest possible stable or nightly version of the agent (at least v1.32). -- Your node can successfully issue an HTTPS request to https://app.netdata.cloud - -Other possible causes differ between kickstart installations and Docker installations. - -### Verify your node can access Netdata Cloud - -If you run either `curl` or `wget` to do an HTTPS request to https://app.netdata.cloud, you should get -back a 404 response. If you do not, check your network connectivity, domain resolution, -and firewall settings for outbound connections. - -If your firewall is configured to completely prevent outbound connections, you need to whitelist `app.netdata.cloud` and `mqtt.netdata.cloud`. If you can't whitelist domains in your firewall, you can whitelist the IPs that the hostnames resolve to, but keep in mind that they can change without any notice. - -If you use an outbound proxy, you need to [take some extra steps]( https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md#connect-through-a-proxy). - -### Troubleshoot claiming with kickstart.sh - -Claiming is done by executing `netdata-claim.sh`, a script that is usually located under `${INSTALL_PREFIX}/netdata/usr/sbin/netdata-claim.sh`. Possible error conditions we have identified are: -- No script found at all in any of our search paths. -- The path where the claiming script should be does not exist. -- The path exists, but is not a file. -- The path is a file, but is not executable. -Check the output of the kickstart script for any reported errors claiming and verify that the claiming script exists -and can be executed. - -### Troubleshoot claiming with Docker - -First verify that the NETDATA_CLAIM_TOKEN parameter is correctly configured and then check for any errors during -initialization of the container. - -The most common issue we have seen claiming nodes in Docker is [running on older hosts with seccomp enabled](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md#known-issues-on-older-hosts-with-seccomp-enabled). - -## The Agent was claimed but can not connect - -Agents that appear on the cloud with state "Unseen" have successfully been claimed, but have never -been able to successfully establish an ACLK connection. - -Agents that appear with state "Offline" or "Stale" were able to connect at some point, but are currently not -connected. The difference between the two is that "Stale" nodes had some of their data replicated to a -parent node that is still connected. - -### Verify that the agent is running - -#### Troubleshoot connection establishment with kickstart.sh - -The kickstart script will install/update your Agent and then try to claim the node to the Cloud -(if tokens are provided). To complete the second part, the Agent must be running. In some platforms, -the Netdata service cannot be enabled by default and you must do it manually, using the following steps: - -1. Check if the Agent is running: - - ```bash - systemctl status netdata - ``` - - The expected output should contain info like this: - - ```bash - Active: active (running) since Wed 2022-07-06 12:25:02 EEST; 1h 40min ago - ``` - -2. Enable and start the Netdata Service. - - ```bash - systemctl enable netdata - systemctl start netdata - ``` - -3. Retry the kickstart claiming process. - -> ### Note -> -> In some cases a simple restart of the Agent can fix the issue. -> Read more about [Starting, Stopping and Restarting the Agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation). - -#### Troubleshoot connection establishment with Docker - -If a Netdata container exits or is killed before it properly starts, it may be able to complete the claiming -process, but not have enough time to establish the ACLK connection. - -### Verify that your firewall allows websockets - -The agent initiates an SSL connection to `app.netdata.cloud` and then upgrades that connection to use secure -websockets. Some firewalls completely prevent the use of websockets, even for outbound connections. - -## Previously connected agent that can no longer connect - -The states "Offline" and "Stale" suggest that the agent was able to connect at some point in the past, but -that it is currently not connected. - -### Verify that network connectivity is still possible - -Verify that you can still issue HTTPS requests to app.netdata.cloud and that no firewall or proxy changes were made. - -### Verify that the claiming info is persisted - -If you use Docker, verify that the contents of `/var/lib/netdata` are preserved across container restarts, using a persistent volume. - -### Verify that the claiming info is not cloned - -A relatively common case we have seen especially with VMs is two or more nodes sharing the same credentials. -This happens if you claim a node in a VM and then create an image based on that node. Netdata can't properly -work this way, as we have unique node identification information under `/var/lib/netdata`. - -### Verify that your IP is not blocked by Netdata Cloud - -Most of the nodes change IPs dynamically. It is possible that your current IP has been restricted from accessing `app.netdata.cloud` due to security concerns, usually because it was spamming Netdata Coud with too many -failed requests (old versions of the agent). - -To verify this: - -1. Check the Agent's `aclk-state`. - - ```bash - sudo netdatacli aclk-state | grep "Banned By Cloud" - ``` - - The output will contain a line indicating if the IP is banned from `app.netdata.cloud`: - - ```bash - Banned By Cloud: yes - ``` - -2. If your node's IP is banned, you can: - - - Contact our team to whitelist your IP by submitting a ticket in the [Netdata forum](https://community.netdata.cloud/) - - Change your node's IP diff --git a/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md b/docs/metric-correlations.md index 7dc50c59c..0467b8dd0 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md +++ b/docs/metric-correlations.md @@ -1,36 +1,22 @@ -<!-- -title: "Metric Correlations" -description: "Quickly find metrics and charts closely related to a particular timeframe of interest anywhere in your infrastructure to discover the root cause faster." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md" -sidebar_label: "Metric Correlations" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Tasks" -learn_rel_path: "Operations" ---> - # Metric Correlations -The Metric Correlations (MC) feature lets you quickly find metrics and charts related to a particular window of interest that you want to explore further. By displaying the standard Netdata dashboard, filtered to show only charts that are relevant to the window of interest, you can get to the root cause sooner. +The Metric Correlations feature lets you quickly find metrics and charts related to a particular window of interest that you want to explore further. + +By displaying the standard Netdata dashboard, filtered to show only charts that are relevant to the window of interest, you can get to the root cause sooner. Because Metric Correlations uses every available metric from your infrastructure, with as high as 1-second granularity, you get the most accurate insights using every possible metric. ## Using Metric Correlations -When viewing the overview or a single-node dashboard, the **Metric Correlations** button appears in the top right corner of the page. - -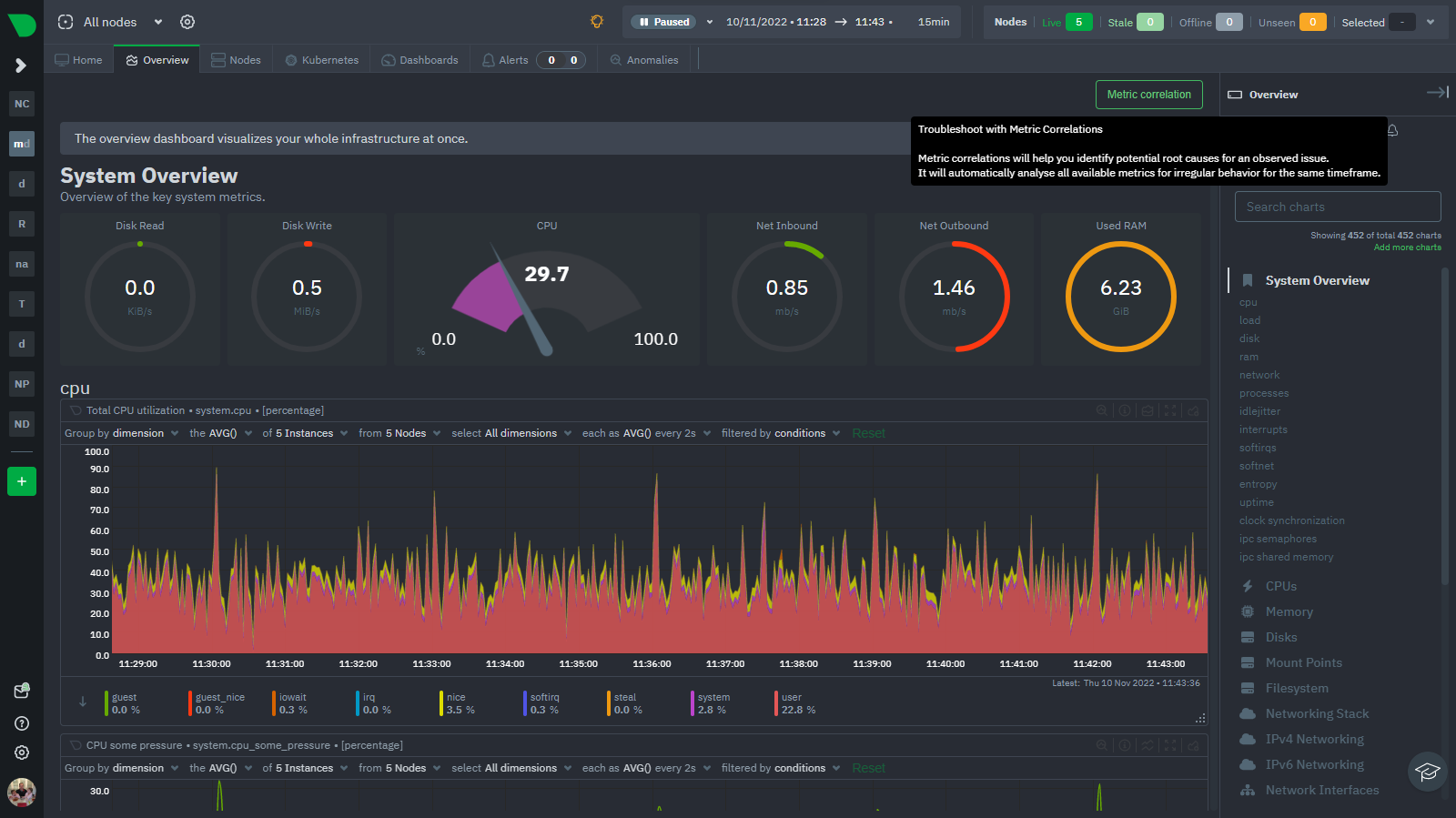 +When viewing the [Metrics tab or a single-node dashboard](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md), the **Metric Correlations** button appears in the top right corner of the page. -To start correlating metrics, click the **Metric Correlations** button, then hold the `Alt` key (or `⌘` on macOS) and click-and-drag a selection of metrics on a single chart. The selected timeframe needs to be at least 15 seconds for Metric Correlation to work. +To start correlating metrics, click the **Metric Correlations** button, [highlight a selection of metrics](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#highlight) on a single chart. The selected timeframe needs at least 15 seconds for Metric Correlation to work. The menu then displays information about the selected area and reference baseline. Metric Correlations uses the reference baseline to discover which additional metrics are most closely connected to the selected metrics. The reference baseline is based upon the period immediately preceding the highlighted window and is the length of 4 times the highlighted window. This is to ensure that the reference baseline is always immediately before the highlighted window of interest and a bit longer so as to ensure it's a more representative short term baseline. -Press the **Find Correlations** button to start up the correlations process, the button is only enabled when a valid timeframe is selected (at least 15 seconds). Once pressed, the process will score all available metrics on your nodes and return a filtered version of the Netdata dashboard. Now, you'll see only those metrics that have changed the most between a baseline window and the highlighted window you have selected. - -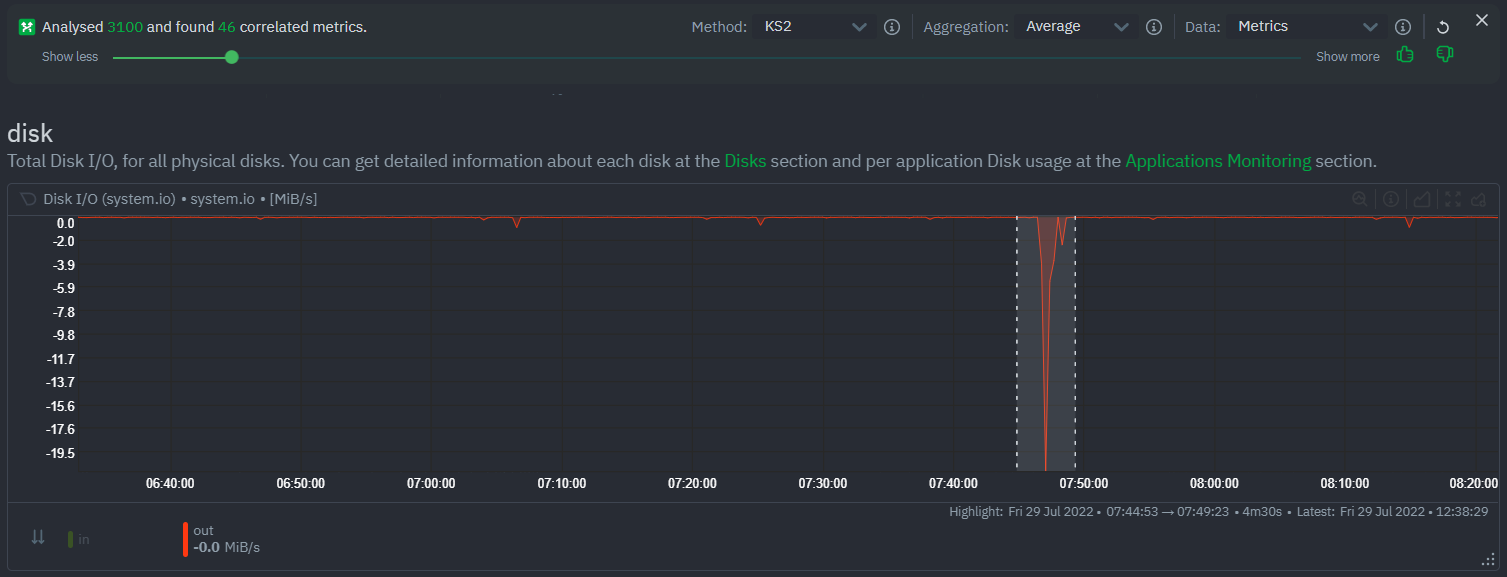 - -These charts are fully interactive, and whenever possible, will only show the _dimensions_ related to the timeline you selected. +Click the **Find Correlations** button to begin the correlation process. This button is only active if a valid timeframe is selected. Once clicked, the process will evaluate all available metrics on your nodes and return a filtered version of the Netdata dashboard. You will now only see the metrics that changed the most between the base window and the highlighted window you selected.. -You can interact with all the scored metrics via the slider. Slide toward **show less** for more nuanced and significant results, or toward **show more** to "loosen" the threshold to explore other charts that may have changed too, but in a less significant manner. +These charts are fully interactive, and whenever possible, will only show the **dimensions** related to the timeline you selected. If you find something else interesting in the results, you can select another window and press **Find Correlations** again to kick the process off again. @@ -53,29 +39,21 @@ Behind the scenes, Netdata will aggregate the raw data as needed such that arbit ### Data -Netdata is different from typical observability agents since, in addition to just collecting raw metric values, it will by default also assign an "[Anomaly Bit](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/ml#anomaly-bit---100--anomalous-0--normal)" related to each collected metric each second. This bit will be 0 for "normal" and 1 for "anomalous". This means that each metric also natively has an "[Anomaly Rate](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/ml#anomaly-rate---averageanomaly-bit)" associated with it and, as such, MC can be run against the raw metric values or their corresponding anomaly rates. +Unlike other observability agents that only collect raw metrics, Netdata also assigns an [Anomaly Bit](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/ml#anomaly-bit) in real-time. This bit flags whether a metric is within normal ranges (0) or deviates significantly (1). This built-in anomaly detection allows for the analysis of both the raw data and the anomaly rates. -**Note**: Read more [here](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/ml/README.md) to learn more about the native anomaly detection features within netdata. +**Note**: Read more [here](/src/ml/README.md) to learn more about the native anomaly detection features within netdata. - `Metrics` - Run MC on the raw metric values. - `Anomaly Rate` - Run MC on the corresponding anomaly rate for each metric. -## Metric Correlations on the agent - -As of `v1.35.0` Netdata is able to run the Metric Correlations algorithm ([Two Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolmogorov%E2%80%93Smirnov_test#Two-sample_Kolmogorov%E2%80%93Smirnov_test)) on the agent itself. This avoids sending the underlying raw data to the original Netdata Cloud based microservice and so typically will be much much faster as no data moves around and the computation happens instead on the agent. +## Metric Correlations on the Agent When a Metric Correlations request is made to Netdata Cloud, if any node instances have MC enabled then the request will be routed to the node instance with the highest hops (e.g. a parent node if one is found or the node itself if not). If no node instances have MC enabled then the request will be routed to the original Netdata Cloud based service which will request input data from the nodes and run the computation within the Netdata Cloud backend. -#### Enabling/Disabling Metric Correlations on the agent - -As of `v1.35.0-22-nightly` Metric Correlation has been enabled by default on all agents. After further optimizations to the implementation, the impact of running the metric correlations algorithm on the agent was less than the impact of preparing all the data to send to cloud for MC to run in the cloud, as such running MC on the agent is less impactful on local resources than running via cloud. - -Should you still want to, disabling nodes for Metric Correlation on the agent is a simple one line config change. Just set `enable metric correlations = no` in the `[global]` section of `netdata.conf` - -## Usage tips! +## Usage tips -- When running Metric Correlations from the [Overview tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#overview-and-single-node-view) across multiple nodes, you might find better results if you iterate on the initial results by grouping by node to then filter to nodes of interest and run the Metric Correlations again. So a typical workflow in this case would be to: - - If unsure which nodes you are interested in then run MC on all nodes. +- When running Metric Correlations from the [Metrics tab](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/metrics-tab-and-single-node-tabs.md) across multiple nodes, you might find better results if you iterate on the initial results by grouping by node to then filter to nodes of interest and rerun the Metric Correlations. So a typical workflow in this case would be to: + - If unsure which nodes you are interested in then run MC on all nodes. - Within the initial results returned group the most interesting chart by node to see if the changes are across all nodes or a subset of nodes. - If you see a subset of nodes clearly jump out when you group by node, then filter for just those nodes of interest and run the MC again. This will result in less aggregation needing to be done by Netdata and so should help give clearer results as you interact with the slider. - Use the `Volume` algorithm for metrics with a lot of gaps (e.g. request latency when there are few requests), otherwise stick with `KS2` diff --git a/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md b/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md deleted file mode 100644 index c8fb76b94..000000000 --- a/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,226 +0,0 @@ -# How metrics streaming works - -Each node running Netdata can stream the metrics it collects, in real time, to another node. Streaming allows you to -replicate metrics data across multiple nodes, or centralize all your metrics data into a single time-series database -(TSDB). - -When one node streams metrics to another, the node receiving metrics can visualize them on the dashboard, run health checks to -[trigger alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md) and -[send notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md), and -[export](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/export/external-databases.md) all metrics to an external TSDB. When Netdata streams metrics to another -Netdata, the receiving one is able to perform everything a Netdata instance is capable of. - -Streaming lets you decide exactly how you want to store and maintain metrics data. While we believe Netdata's distributed architecture is ideal for speed and scale, streaming provides centralization options and high data availability. - -This document will get you started quickly with streaming. More advanced concepts and suggested production deployments -can be found in the [streaming and replication reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/streaming/README.md). - -## Streaming basics - -There are three types of nodes in Netdata's streaming ecosystem. - -- **Parent**: A node, running Netdata, that receives streamed metric data. -- **Child**: A node, running Netdata, that streams metric data to one or more parent. -- **Proxy**: A node, running Netdata, that receives metric data from a child and "forwards" them on to a - separate parent node. - -Netdata uses API keys, which are just random GUIDs, to authorize the communication between child and parent nodes. We -recommend using `uuidgen` for generating API keys, which can then be used across any number of streaming connections. -Or, you can generate unique API keys for each parent-child relationship. - -Once the parent node authorizes the child's API key, the child can start streaming metrics. - -It's important to note that the streaming connection uses TCP, UDP, or Unix sockets, _not HTTP_. To proxy streaming -metrics, you need to use a proxy that tunnels [OSI layer 4-7 -traffic](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model#Layer_4:_Transport_Layer) without interfering with it, such as -[SOCKS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOCKS) or Nginx's -[TCP/UDP load balancing](https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/load-balancer/tcp-udp-load-balancer/). - -## Supported streaming configurations - -Netdata supports any combination of parent, child, and proxy nodes that you can imagine. Any node can act as both a -parent, child, or proxy at the same time, sending or receiving streaming metrics from any number of other nodes. - -Here are a few example streaming configurations: - -- **Headless collector**: - - Child `A`, _without_ a database or web dashboard, streams metrics to parent `B`. - - `A` metrics are only available via the local Agent dashboard for `B`. - - `B` generates alerts for `A`. -- **Replication**: - - Child `A`, _with_ a database and web dashboard, streams metrics to parent `B`. - - `A` metrics are available on both local Agent dashboards, and can be stored with the same or different metrics - retention policies. - - Both `A` and `B` generate alerts. -- **Proxy**: - - Child `A`, _with or without_ a database, sends metrics to proxy `C`, also _with or without_ a database. `C` sends - metrics to parent `B`. - - Any node with a database can generate alerts. - - - -### A basic parent child setup - - - -For a predictable number of non-ephemeral nodes, install a Netdata agent on each node and replicate its data to a -Netdata parent, preferrably on a management/admin node outside your production infrastructure. -There are two variations of the basic setup: - -- When your nodes have sufficient RAM and disk IO the Netdata agents on each node can run with the default - settings for data collection and retention. - -- When your nodes have severe RAM and disk IO limitations (e.g. Raspberry Pis), you should - [optimize the Netdata agent's performance](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/configure/performance.md). - -[Secure your nodes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/secure-nodes.md) to -protect them from the internet by making their UI accessible only via an nginx proxy, with potentially different subdomains -for the parent and even each child, if necessary. - -Both children and the parent are connected to the cloud, to enable infrastructure observability, -[without transferring the collected data](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md). -Requests for data are always serverd by a connected Netdata agent. When both a child and a parent are connected, -the cloud will always select the parent to query the user requested data. - -### An advanced setup - - - -When the nodes are ephemeral, we recommend using two parents in an active-active setup, and having the children not store data at all. - -Both parents are configured on each child, so that if one is not available, they connect to the other. - -The children in this set up are not connected to Netdata Cloud at all, as high availability is achieved with the second parent. - -## Enable streaming between nodes - -The simplest streaming configuration is **replication**, in which a child node streams its metrics in real time to a -parent node, and both nodes retain metrics in their own databases. - -To configure replication, you need two nodes, each running Netdata. First you'll first enable streaming on your parent -node, then enable streaming on your child node. When you're finished, you'll be able to see the child node's metrics in -the parent node's dashboard, quickly switch between the two dashboards, and be able to serve -[alert notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md) from either or both nodes. - -### Enable streaming on the parent node - -First, log onto the node that will act as the parent. - -Run `uuidgen` to create a new API key, which is a randomly-generated machine GUID the Netdata Agent uses to identify -itself while initiating a streaming connection. Copy that into a separate text file for later use. - -> Find out how to [install `uuidgen`](https://command-not-found.com/uuidgen) on your node if you don't already have it. - -Next, open `stream.conf` using [`edit-config`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md#use-edit-config-to-edit-configuration-files) -from within the [Netdata config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md#the-netdata-config-directory). - -```bash -cd /etc/netdata -sudo ./edit-config stream.conf -``` - -Scroll down to the section beginning with `[API_KEY]`. Paste the API key you generated earlier between the brackets, so -that it looks like the following: - -```conf -[11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555] -``` - -Set `enabled` to `yes`, and `default memory mode` to `dbengine`. Leave all the other settings as their defaults. A -simplified version of the configuration, minus the commented lines, looks like the following: - -```conf -[11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555] - enabled = yes - default memory mode = dbengine -``` - -Save the file and close it, then restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. - -### Enable streaming on the child node - -Connect to your child node with SSH. - -Open `stream.conf` again. Scroll down to the `[stream]` section and set `enabled` to `yes`. Paste the IP address of your -parent node at the end of the `destination` line, and paste the API key generated on the parent node onto the `api key` -line. - -Leave all the other settings as their defaults. A simplified version of the configuration, minus the commented lines, -looks like the following: - -```conf -[stream] - enabled = yes - destination = 203.0.113.0 - api key = 11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555 -``` - -Save the file and close it, then restart Netdata with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system. - -### Enable TLS/SSL on streaming (optional) - -While encrypting the connection between your parent and child nodes is recommended for security, it's not required to -get started. If you're not interested in encryption, skip ahead to [view streamed -metrics](#view-streamed-metrics-in-netdatas-dashboard). - -In this example, we'll use self-signed certificates. - -On the **parent** node, use OpenSSL to create the key and certificate, then use `chown` to make the new files readable -by the `netdata` user. - -```bash -sudo openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -sha512 -x509 -days 365 -keyout /etc/netdata/ssl/key.pem -out /etc/netdata/ssl/cert.pem -sudo chown netdata:netdata /etc/netdata/ssl/cert.pem /etc/netdata/ssl/key.pem -``` - -Next, enforce TLS/SSL on the web server. Open `netdata.conf`, scroll down to the `[web]` section, and look for the `bind -to` setting. Add `^SSL=force` to turn on TLS/SSL. See the [web server -reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support) for other TLS/SSL options. - -```conf -[web] - bind to = *=dashboard|registry|badges|management|streaming|netdata.conf^SSL=force -``` - -Next, connect to the **child** node and open `stream.conf`. Add `:SSL` to the end of the existing `destination` setting -to connect to the parent using TLS/SSL. Uncomment the `ssl skip certificate verification` line to allow the use of -self-signed certificates. - -```conf -[stream] - enabled = yes - destination = 203.0.113.0:SSL - ssl skip certificate verification = yes - api key = 11111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555 -``` - -Restart both the parent and child nodes with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or the [appropriate -method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) for your system, to stream encrypted metrics using TLS/SSL. - -### View streamed metrics in Netdata Cloud - -In Netdata Cloud you should now be able to see a new parent showing up in the Home tab under "Nodes by data replication". -The replication factor for the child node has now increased to 2, meaning that its data is now highly available. - -You don't need to do anything else, as the cloud will automatically prefer to fetch data about the child from the parent -and switch to querying the child only when the parent is unavailable, or for some reason doesn't have the requested -data (e.g. the connection between parent and the child is broken). - -### View streamed metrics in Netdata's dashboard - -At this point, the child node is streaming its metrics in real time to its parent. Open the local Agent dashboard for -the parent by navigating to `http://PARENT-NODE:19999` in your browser, replacing `PARENT-NODE` with its IP address or -hostname. - -This dashboard shows parent metrics. To see child metrics, open the left-hand sidebar with the hamburger icon - -in the top panel. Both nodes appear under the **Replicated Nodes** menu. Click on either of the links to switch between -separate parent and child dashboards. - -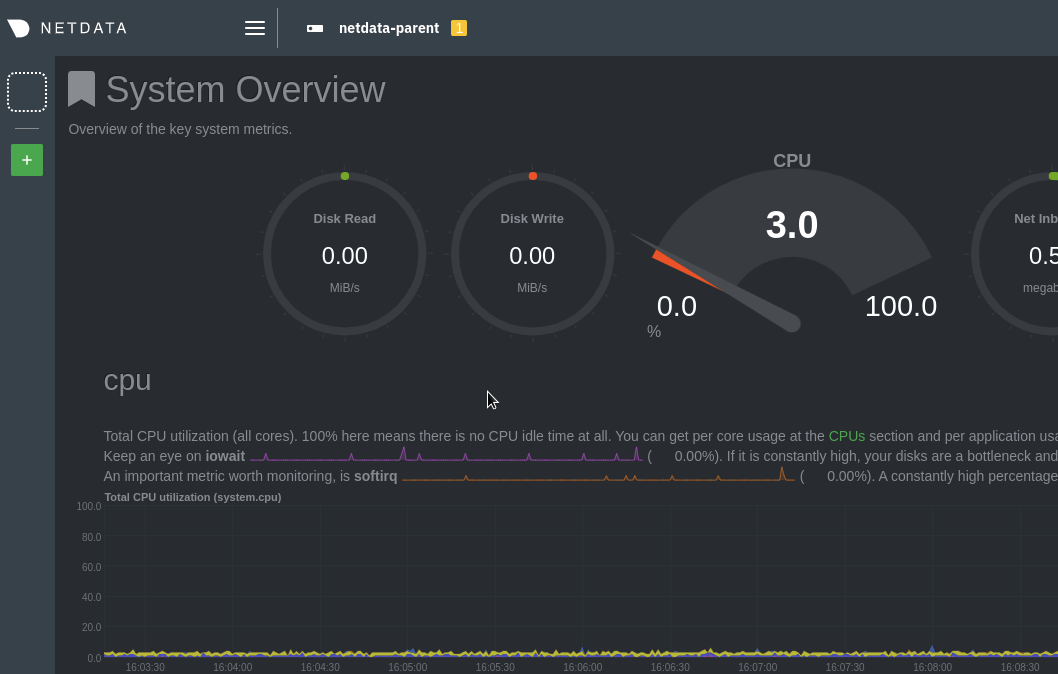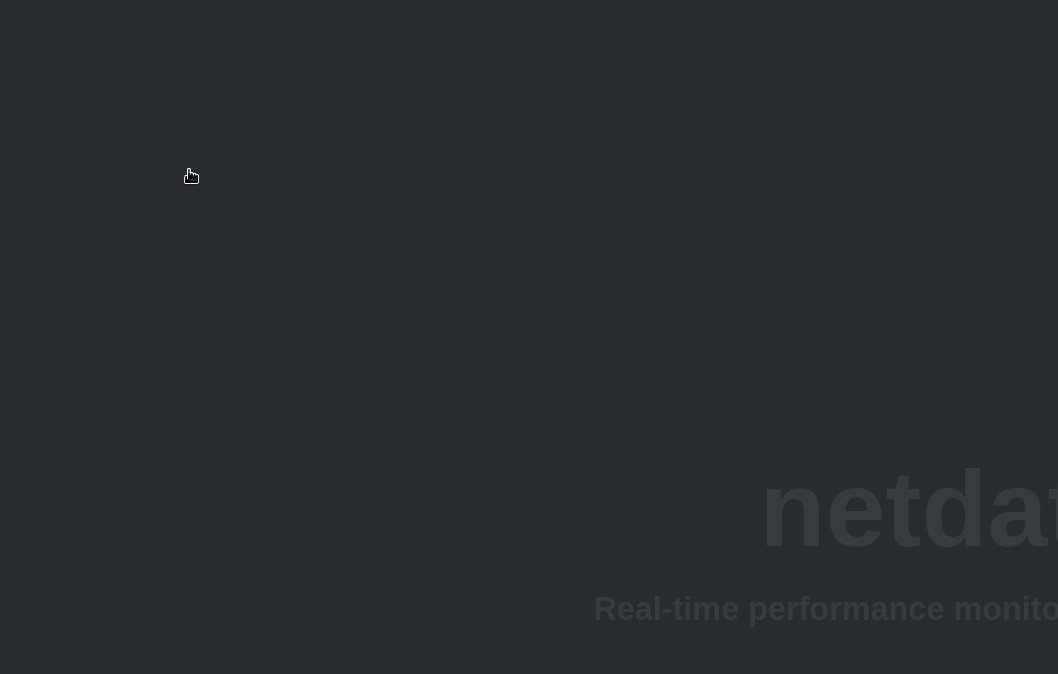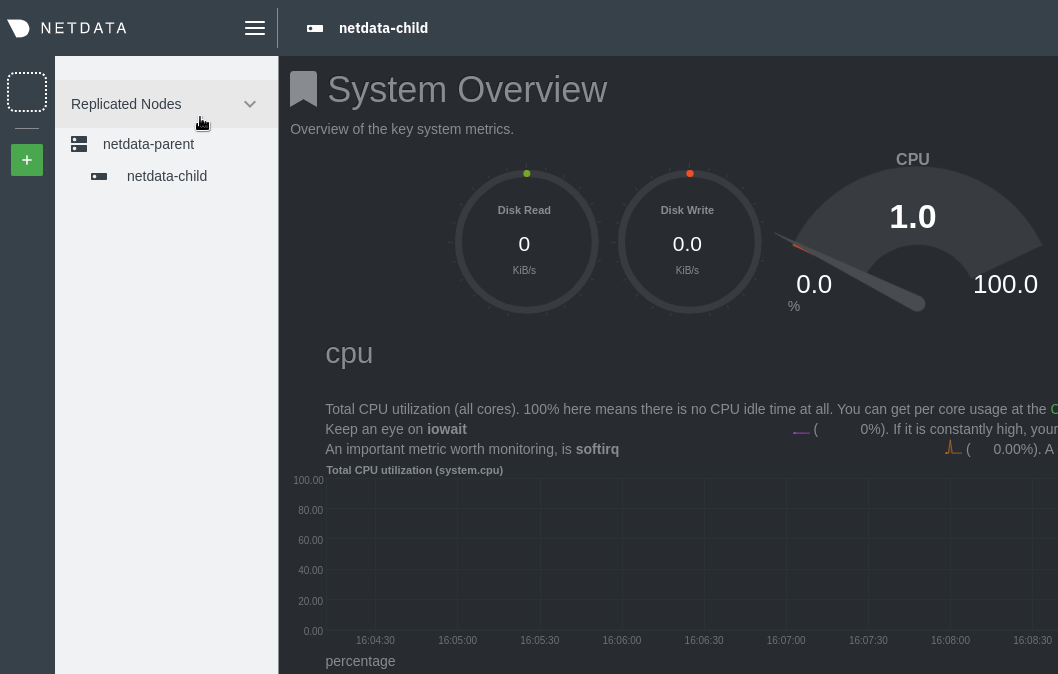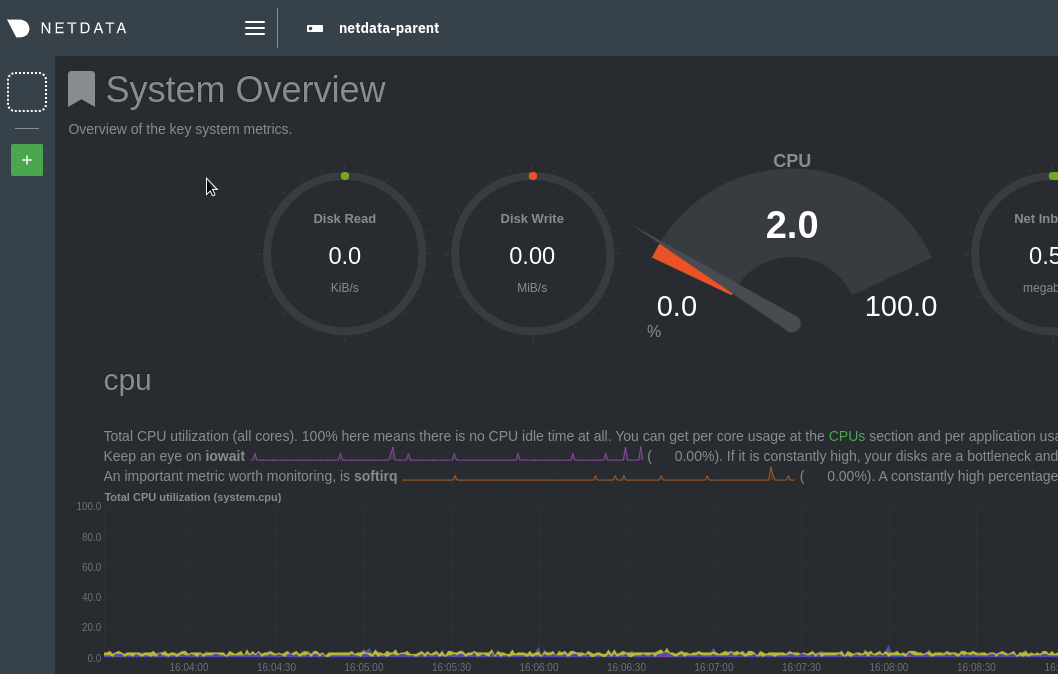 - -The child dashboard is also available directly at `http://PARENT-NODE:19999/host/CHILD-HOSTNAME`, which in this example -is `http://203.0.113.0:19999/host/netdata-child`. - diff --git a/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md b/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md deleted file mode 100644 index 7fec9ed50..000000000 --- a/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,90 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Alert notifications" -description: "Send Netdata alerts from a centralized place with Netdata Cloud, or configure nodes individually, to enable incident response and faster resolution." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md" -sidebar_label: "Notify" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_rel_path: "Integrations/Notify" ---> - -# Alert notifications - -Netdata offers two ways to receive alert notifications on external platforms. These methods work independently _or_ in -parallel, which means you can enable both at the same time to send alert notifications to any number of endpoints. - -Both methods use a node's health alerts to generate the content of alert notifications. Read our documentation on [configuring alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md) to change the preconfigured thresholds or to create tailored alerts for your -infrastructure. - -Netdata Cloud offers [centralized alert notifications](#netdata-cloud) via email, which leverages the health status -information already streamed to Netdata Cloud from connected nodes to send notifications to those who have enabled them. - -The Netdata Agent has a [notification system](#netdata-agent) that supports more than a dozen services, such as email, -Slack, PagerDuty, Twilio, Amazon SNS, Discord, and much more. - -For example, use centralized alert notifications in Netdata Cloud for immediate, zero-configuration alert notifications -for your team, then configure individual nodes send notifications to a PagerDuty endpoint for an automated incident -response process. - -## Netdata Cloud - -Netdata Cloud's [centralized alert -notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md) is a zero-configuration way to -get notified when an anomaly or incident strikes any node or application in your infrastructure. The advantage of using -centralized alert notifications from Netdata Cloud is that you don't have to worry about configuring each node in your -infrastructure. - -To enable centralized alert notifications for a Space, click on **Manage Space** in the left-hand menu, then click on -the **Notifications** tab. Click the toggle switch next to **E-mail** to enable this notification method. - -Next, enable notifications on a user level by clicking on your profile icon, then **Profile** in the dropdown. The -**Notifications** tab reveals rich management settings, including the ability to enable/disable methods entirely or -choose what types of notifications to receive from each War Room. - - - -See the [centralized alert notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md) -reference doc for further details about what information is conveyed in an email notification, flood protection, and -more. - -## Netdata Agent - -The Netdata Agent's [notification system](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/README.md) runs on every node and dispatches -notifications based on configured endpoints and roles. You can enable multiple endpoints on any one node _and_ use Agent -notifications in parallel with centralized alert notifications in Netdata Cloud. - -> ❗ If you want to enable notifications from multiple nodes in your infrastructure, each running the Netdata Agent, you -> must configure each node individually. - -Below, we'll use [Slack notifications](#enable-slack-notifications) as an example of the process of enabling any -notification platform. - -### Supported notification endpoints - -- [**alerta.io**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/alerta/README.md) -- [**Amazon SNS**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/awssns/README.md) -- [**Custom endpoint**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/custom/README.md) -- [**Discord**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/discord/README.md) -- [**Dynatrace**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/dynatrace/README.md) -- [**Email**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/email/README.md) -- [**Flock**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/flock/README.md) -- [**Gotify**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/gotify/README.md) -- [**IRC**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/irc/README.md) -- [**Kavenegar**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/kavenegar/README.md) -- [**Matrix**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/matrix/README.md) -- [**Messagebird**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/messagebird/README.md) -- [**Microsoft Teams**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/msteams/README.md) -- [**Netdata Agent dashboard**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/web/README.md) -- [**Opsgenie**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/opsgenie/README.md) -- [**PagerDuty**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/pagerduty/README.md) -- [**Prowl**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/prowl/README.md) -- [**PushBullet**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/pushbullet/README.md) -- [**PushOver**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/pushover/README.md) -- [**Rocket.Chat**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/rocketchat/README.md) -- [**Slack**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/slack/README.md) -- [**SMS Server Tools 3**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/smstools3/README.md) -- [**Syslog**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/syslog/README.md) -- [**Telegram**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/telegram/README.md) -- [**Twilio**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/notifications/twilio/README.md) - - diff --git a/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md b/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md deleted file mode 100644 index 02eed0a84..000000000 --- a/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,70 +0,0 @@ -# View active alerts - -Netdata comes with hundreds of pre-configured health alerts designed to notify you when an anomaly or performance issue affects your node or its applications. - -From the Alerts tab you can see all the active alerts in your War Room. You will be presented with a table having information about each alert that is in warning and critical state. -You can always sort the table by a certain column by clicking on the name of that column, and use the gear icon on the top right to control which columns are visible at any given time. - -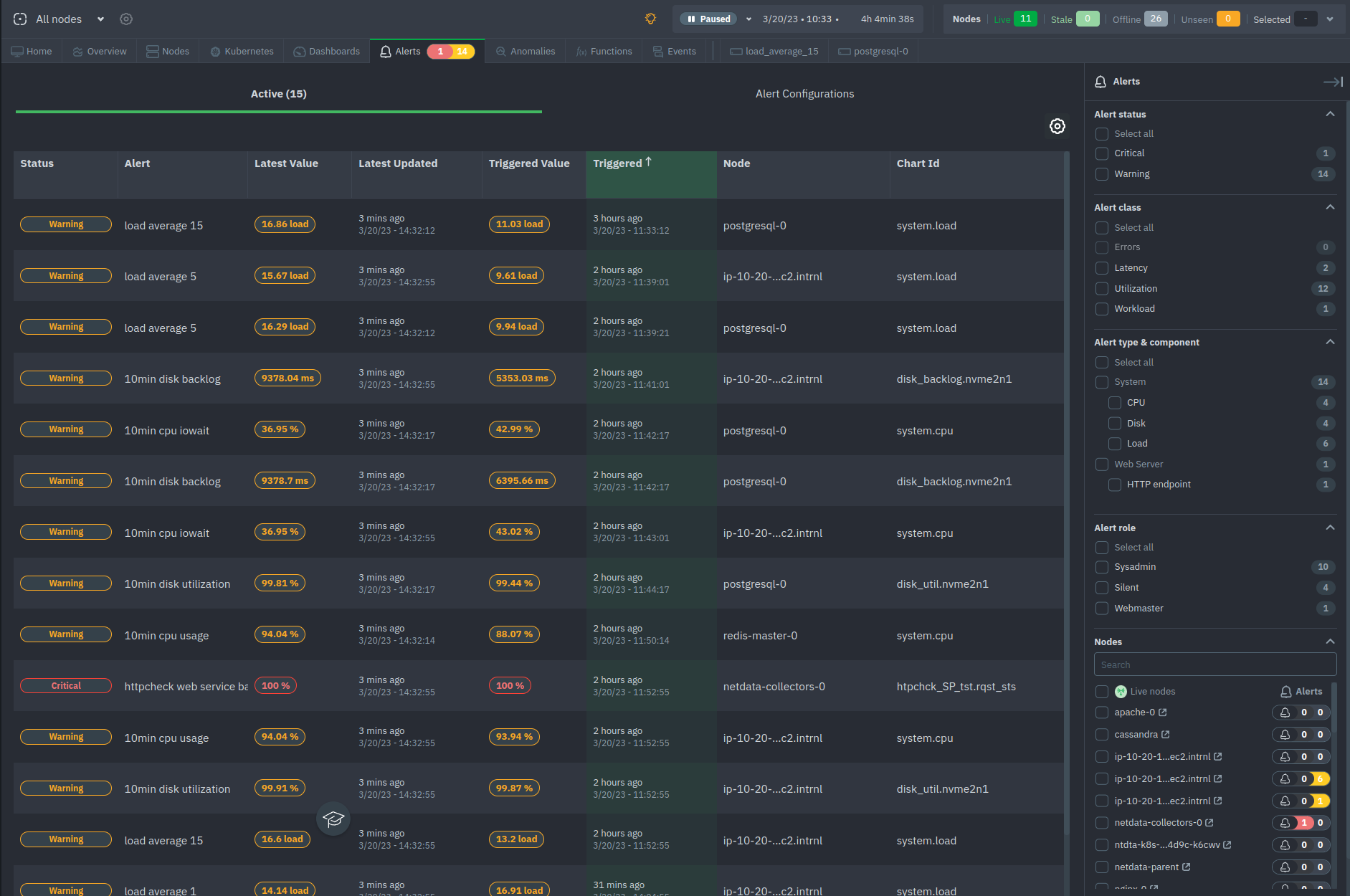 - -## Filter alerts - -From this tab, you can also filter alerts with the right hand bar. More specifically you can filter: - -- Alert status - - Filter based on the status of the alerts (e.g. Warning, Critical) -- Alert class - - Filter based on the class of the alert (e.g. Latency, Utilization, Workload etc.) -- Alert type & component - - Filter based on the alert's type (e.g. System, Web Server) and component (e.g. CPU, Disk, Load) -- Alert role - - Filter by the role that the alert is set to notify (e.g. Sysadmin, Webmaster etc.) -- Nodes - - Filter the alerts based on the nodes that are online, next to each node's name you can see how many alerts the node has, "critical" colored in red and "warning" colored in yellow - -## View alert details - -By clicking on the name of an entry of the table you can access that alert's details page, providing you with: - -- Latest and Triggered time values -- The alert's description -- A link to the Community forum's alert page -- The chart at the time frame that the alert was triggered -- The alert's information: Node name, chart ID, type, component and class -- Configuration section -- Instance values - Node Instances - -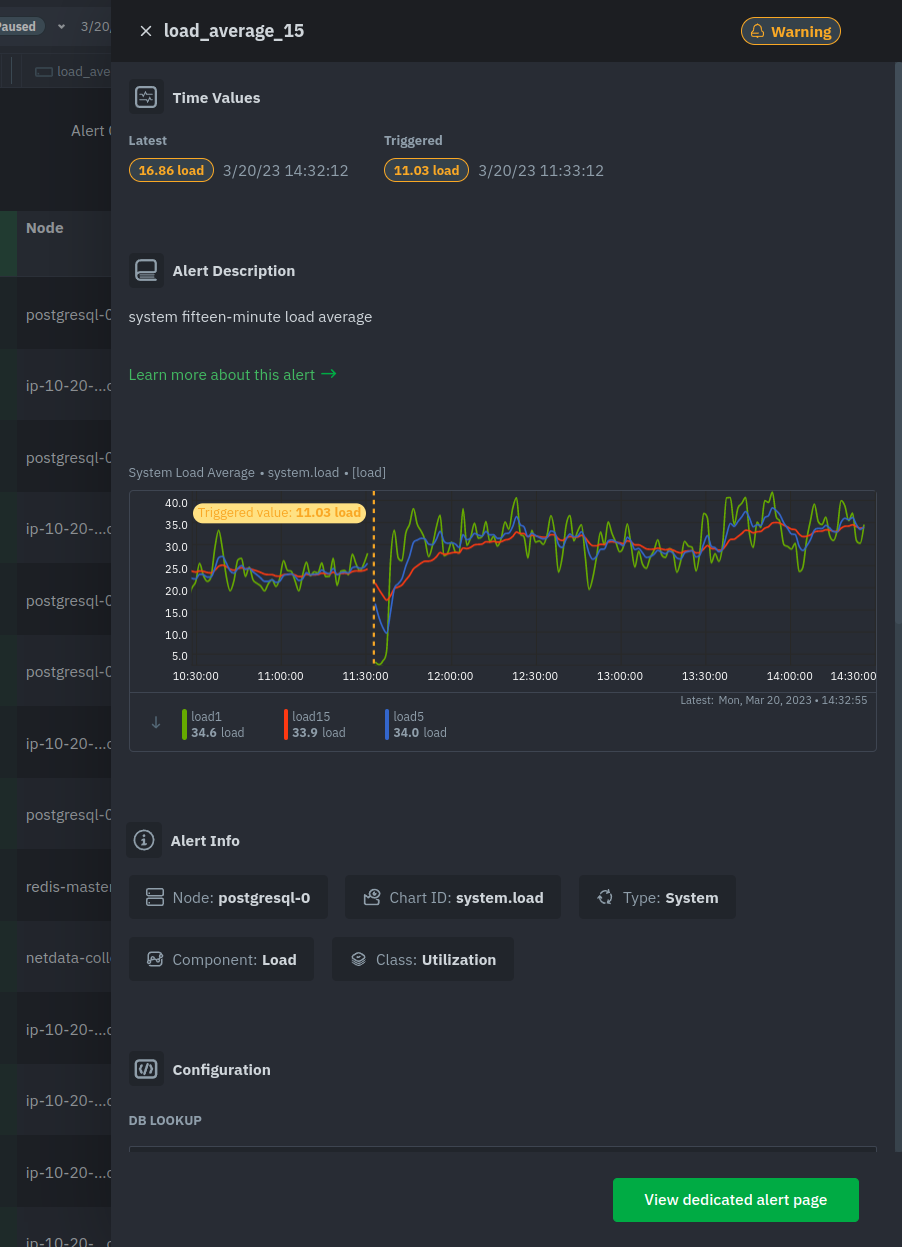 - -At the bottom of the panel you can click the green button "View dedicated alert page" to open a [dynamic tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md#dynamic-tabs) containing all the info for this alert in a tab format, where you can also run correlations and go to the node's chart that raised the particular alert. - -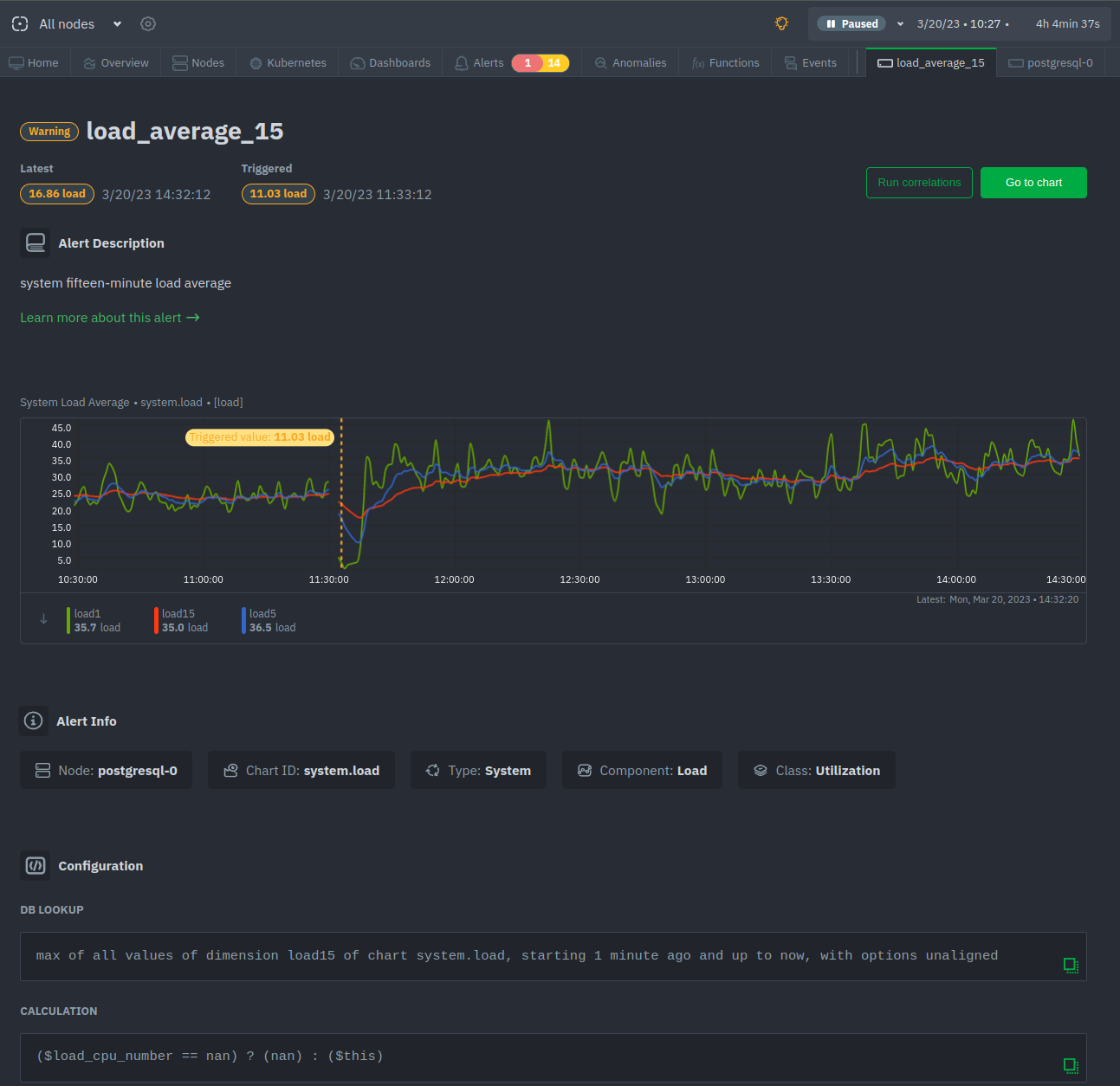 - -<!-- -## Local Netdata Agent dashboard - -Find the alerts icon  -in the top navigation to bring up a modal that shows currently raised alerts, all running alerts, and the alerts log. -Here is an example of a raised `system.cpu` alert, followed by the full list and alert log: - -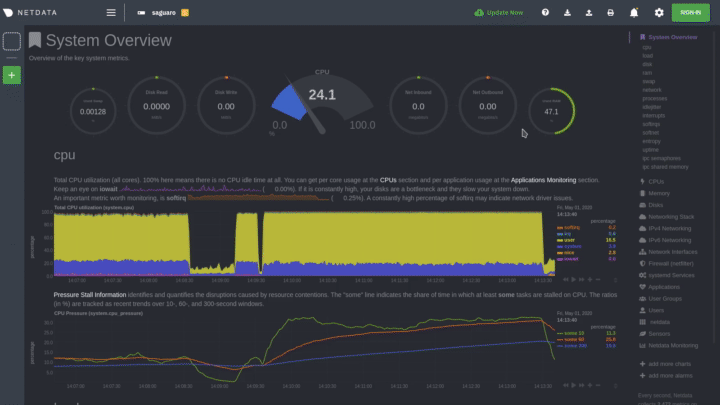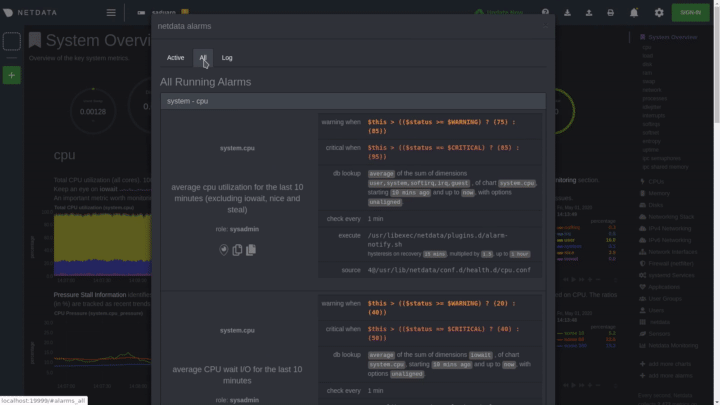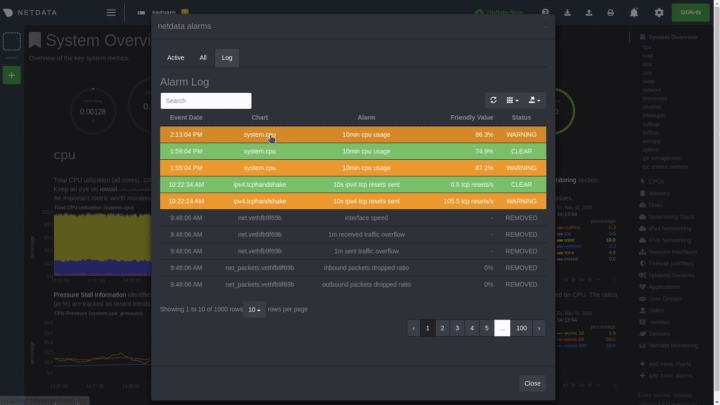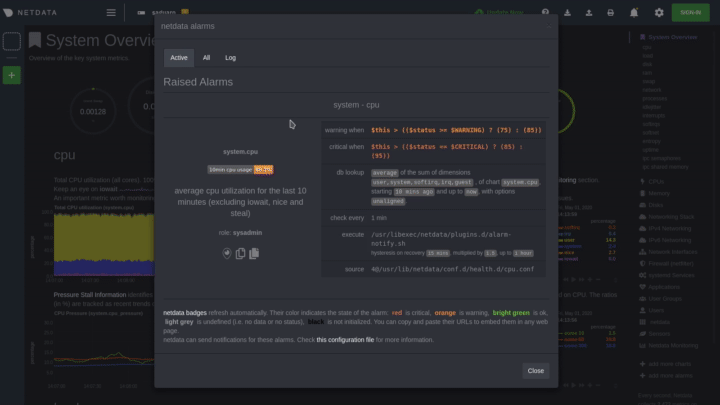 - -And a static screenshot of the raised CPU alert: - -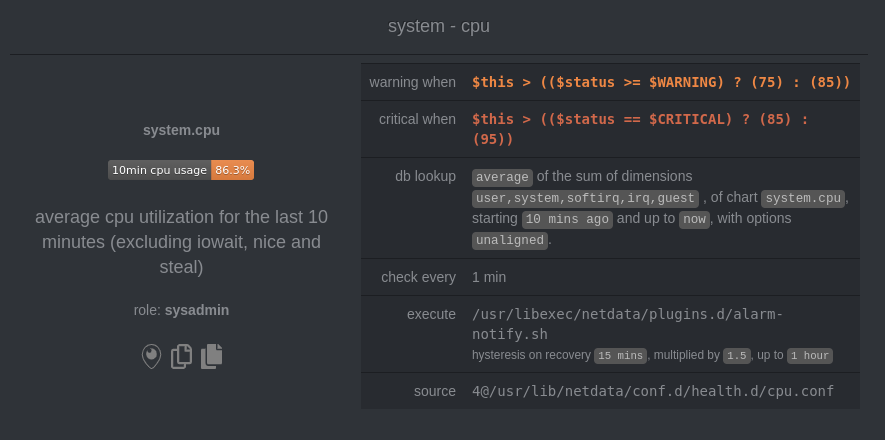 - -The alert itself is named **system - cpu**, and its context is `system.cpu`. Beneath that is an auto-updating badge that -shows the latest value of the chart that triggered the alert. - -With the three icons beneath that and the **role** designation, you can: - -1. Scroll to the chart associated with this raised alert. -2. Copy a link to the badge to your clipboard. -3. Copy the code to embed the badge onto another web page using an `<embed>` element. - -The table on the right-hand side displays information about the health entity that triggered the alert, which you can -use as a reference to [configure alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md). - --> diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/README.md b/docs/netdata-agent/README.md index faf262fd4..75bd4898e 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-agent/README.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/README.md @@ -65,11 +65,11 @@ stateDiagram-v2 ## Comparison to other observability solutions -1. **One moving part**: Other monitoring solution require maintaining metrics exporters, time-series databases, visualization engines. Netdata has everything integrated into one package, even when [Metrics Centralization Points](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md) are required, making deployment and maintenance a lot simpler. +1. **One moving part**: Other monitoring solution require maintaining metrics exporters, time-series databases, visualization engines. Netdata has everything integrated into one package, even when [Metrics Centralization Points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md) are required, making deployment and maintenance a lot simpler. 2. **Automation**: Netdata is designed to automate most of the process of setting up and running an observability solution. It is designed to instantly provide comprehensive dashboards and fully automated alerts, with zero configuration. -3. **High Fidelity Monitoring**: Netdata was born from our need to kill the console for observability. So, it provides metrics and logs in the same granularity and fidelity console tools do, but also comes with tools that go beyond metrics and logs, to provide a holistic view of the monitored infrastructure (e.g. check [Top Monitoring](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md)). +3. **High Fidelity Monitoring**: Netdata was born from our need to kill the console for observability. So, it provides metrics and logs in the same granularity and fidelity console tools do, but also comes with tools that go beyond metrics and logs, to provide a holistic view of the monitored infrastructure (e.g. check [Top Monitoring](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md)). 4. **Minimal impact on monitored systems and applications**: Netdata has been designed to have a minimal impact on the monitored systems and their applications. There are [independent studies](https://www.ivanomalavolta.com/files/papers/ICSOC_2023.pdf) reporting that Netdata excels in CPU usage, RAM utilization, Execution Time and the impact Netdata has on monitored applications and containers. @@ -79,6 +79,6 @@ stateDiagram-v2 The Netdata agents (Standalone, Children and Parents) **share the dashboard** of Netdata Cloud. However, when the user is logged-in and the Netdata agent is connected to Netdata Cloud, the following are enabled (which are otherwise disabled): -1. **Access to Sensitive Data**: Some data, like systemd-journal logs and several [Top Monitoring](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md) features expose sensitive data, like IPs, ports, process command lines and more. To access all these when the dashboard is served directly from a Netdata agent, Netdata Cloud is required to verify that the user accessing the dashboard has the required permissions. +1. **Access to Sensitive Data**: Some data, like systemd-journal logs and several [Top Monitoring](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md) features expose sensitive data, like IPs, ports, process command lines and more. To access all these when the dashboard is served directly from a Netdata agent, Netdata Cloud is required to verify that the user accessing the dashboard has the required permissions. 2. **Dynamic Configuration**: Netdata agents are configured via configuration files, manually or through some provisioning system. The latest Netdata includes a feature to allow users change some of the configuration (collectors, alerts) via the dashboard. This feature is only available to users of paid Netdata Cloud plan. diff --git a/docs/maintenance/backup-restore.md b/docs/netdata-agent/backup-and-restore-an-agent.md index 7e603d21c..d17cad604 100644 --- a/docs/maintenance/backup-restore.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/backup-and-restore-an-agent.md @@ -1,12 +1,16 @@ # Backing up a Netdata Agent +> **Note** +> +> Users are responsible for backing up, recovering, and ensuring their data's availability because Netdata stores data locally on each system due to its decentralized architecture. + ## Introduction When preparing to backup a Netdata Agent it is worth considering that there are different kinds of data that you may wish to backup independently or all together: | Data type | Description | Location | |---------------------|------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| Agent configuration | Files controlling configuration of the Netdata Agent | [config directory](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md) | +| Agent configuration | Files controlling configuration of the Netdata Agent | [config directory](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) | | Metrics | Database files | /var/cache/netdata | | Identity | Claim token, API key and some other files | /var/lib/netdata | @@ -22,7 +26,7 @@ In this standard scenario, you are backing up your Netdata Agent in case of a no > **Note** > The specific paths may vary depending on installation method, Operating System, and whether it is a Docker/Kubernetes deployment. -2. It is recommended that you [stop the Netdata Agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/start-stop-restart.md) when backing up the Metrics/database files. +2. It is recommended that you [stop the Netdata Agent](/docs/netdata-agent/start-stop-restart.md) when backing up the Metrics/database files. Backing up the Agent configuration and Identity folders is straightforward as they should not be changing very frequently. 3. Using a backup tool such as `tar` you will need to run the backup as _root_ or as the _netdata_ user to access all the files in the directories. @@ -42,9 +46,9 @@ If you want to minimize the gap in metrics caused by stopping the Netdata Agent, ### Restoring Netdata -1. Ensure that the Netdata agent is installed and is [stopped](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) +1. Ensure that the Netdata agent is installed and is [stopped](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) - If you plan to deploy the Agent and restore a backup on top of it, then you might find it helpful to use the [`--dont-start-it`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md#other-options) option upon installation. + If you plan to deploy the Agent and restore a backup on top of it, then you might find it helpful to use the [`--dont-start-it`](/packaging/installer/methods/kickstart.md#other-options) option upon installation. ``` wget -O /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh https://get.netdata.cloud/kickstart.sh && sh /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh --dont-start-it @@ -63,4 +67,4 @@ If you want to minimize the gap in metrics caused by stopping the Netdata Agent, sudo tar -xvpzf /path/to/netdata_backup.tar.gz -C / ``` -3. [Start the Netdata agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) +3. [Start the Netdata agent](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md index 853199843..097fb9310 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md @@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ The main Netdata agent configuration is `netdata.conf`. ## The Netdata config directory -On most Linux systems, by using our [recommended one-line installation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#install-on-linux-with-one-line-installer), the **Netdata config +On most Linux systems, by using our [recommended one-line installation](/packaging/installer/README.md#install-on-linux-with-one-line-installer), the **Netdata config directory** will be `/etc/netdata/`. The config directory contains several configuration files with the `.conf` extension, a few directories, and a shell script named `edit-config`. diff --git a/docs/anonymous-statistics.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/anonymous-telemetry-events.md index 0db002f7c..b943ea9a3 100644 --- a/docs/anonymous-statistics.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/anonymous-telemetry-events.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ <!-- title: "Anonymous telemetry events" -custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/anonymous-statistics.md +custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/anonymous-telemetry-events.md sidebar_label: "Anonymous telemetry events" learn_status: "Published" learn_rel_path: "Configuration" @@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ We use the statistics gathered from this information for two purposes: Netdata collects usage information via two different channels: -- **Agent dashboard**: We use the [PostHog JavaScript integration](https://posthog.com/docs/integrations/js-integration) (with sensitive event attributes overwritten to be anonymized) to send product usage events when you access an [Agent's dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md). +- **Agent dashboard**: We use the [PostHog JavaScript integration](https://posthog.com/docs/integrations/js-integration) (with sensitive event attributes overwritten to be anonymized) to send product usage events when you access an [Agent's dashboard](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md). - **Agent backend**: The `netdata` daemon executes the [`anonymous-statistics.sh`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/6469cf92724644f5facf343e4bdd76ac0551a418/daemon/anonymous-statistics.sh.in) script when Netdata starts, stops cleanly, or fails. You can opt-out from sending anonymous statistics to Netdata through three different [opt-out mechanisms](#opt-out). @@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ Starting with v1.21, we additionally collect information about: - Failures to build the dependencies required to use Cloud features. - Unavailability of Cloud features in an agent. -- Failures to connect to the Cloud in case the [connection process](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/claim/README.md) has been completed. This includes error codes +- Failures to connect to the Cloud in case the [connection process](/src/claim/README.md) has been completed. This includes error codes to inform the Netdata team about the reason why the connection failed. To see exactly what and how is collected, you can review the script template `daemon/anonymous-statistics.sh.in`. The @@ -85,13 +85,13 @@ installation, including manual, offline, and macOS installations. Create the fil .opt-out-from-anonymous-statistics` from your Netdata configuration directory. **Pass the option `--disable-telemetry` to any of the installer scripts in the [installation -docs](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md).** You can append this option during the initial installation or a manual +docs](/packaging/installer/README.md).** You can append this option during the initial installation or a manual update. You can also export the environment variable `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` with a non-zero or non-empty value (e.g: `export DISABLE_TELEMETRY=1`). When using Docker, **set your `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` environment variable to `1`.** You can set this variable with the following command: `export DISABLE_TELEMETRY=1`. When creating a container using Netdata's [Docker -image](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/docker/README.md#create-a-new-netdata-agent-container) for the first time, this variable will disable +image](/packaging/docker/README.md#create-a-new-netdata-agent-container) for the first time, this variable will disable the anonymous statistics script inside of the container. Each of these opt-out processes does the following: diff --git a/docs/cloud/cheatsheet.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/cheatsheet.md index 460b03ea0..3e1428694 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/cheatsheet.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/cheatsheet.md @@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ You are expected to use this method in all following configuration changes. ## Metrics collection & retention You can tweak your settings in the netdata.conf file. -📄 [Find your netdata.conf file](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/config/README.md) +📄 [Find your netdata.conf file](/src/daemon/config/README.md) Open a new terminal and navigate to the netdata.conf file. Use the edit-config script to make changes: `sudo ./edit-config netdata.conf` diff --git a/docs/configure/common-changes.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/common-configuration-changes.md index 2d1757fe9..e9d8abadc 100644 --- a/docs/configure/common-changes.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/common-configuration-changes.md @@ -1,13 +1,3 @@ -<!-- -title: "Common configuration changes" -description: "See the most popular configuration changes to make to the Netdata Agent, including longer metrics retention, reduce sampling, and more." -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/configure/common-changes.md" -sidebar_label: "Common configuration changes" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Tasks" -learn_rel_path: "Configuration" ---> - # Common configuration changes The Netdata Agent requires no configuration upon installation to collect thousands of per-second metrics from most @@ -15,14 +5,14 @@ systems, containers, and applications, but there are hundreds of settings to twe over your monitoring platform. This document assumes familiarity with -using [`edit-config`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) from the Netdata config +using [`edit-config`](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) from the Netdata config directory. ## Change dashboards and visualizations -The Netdata Agent's [local dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/accessing-netdata-dashboards.md), accessible +The Netdata Agent's [local dashboard](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/README.md), accessible at `http://NODE:19999` is highly configurable. If -you use [Netdata Cloud](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md) +you use [Netdata Cloud](/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md) for infrastructure monitoring, you will see many of these changes reflected in those visualizations due to the way Netdata Cloud proxies metric data and metadata to your browser. @@ -30,15 +20,15 @@ changes reflected in those visualizations due to the way Netdata Cloud proxies m ### Increase the long-term metrics retention period Read our doc -on [increasing long-term metrics storage](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md) +on [increasing long-term metrics storage](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md) for details, including a -[calculator](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics) +[calculator](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md#calculate-the-system-resources-ram-disk-space-needed-to-store-metrics) to help you determine the exact settings for your desired retention period. ### Reduce the data collection frequency Change `update every` in -the [`[global]` section](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/config/README.md#global-section-options) +the [`[global]` section](/src/daemon/config/README.md#global-section-options) of `netdata.conf` so that it is greater than `1`. An `update every` of `5` means the Netdata Agent enforces a _minimum_ collection frequency of 5 seconds. @@ -51,13 +41,13 @@ of 5 seconds. Every collector and plugin has its own `update every` setting, which you can also change in the `go.d.conf`, `python.d.conf` or `charts.d.conf` files, or in individual collector configuration files. If the `update every` for an individual collector is less than the global, the Netdata Agent uses the global setting. See -the [enable or configure a collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md#enable-and-disable-a-specific-collection-module) +the [enable or configure a collector](/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md#enable-and-disable-a-specific-collection-module) doc for details. ### Disable a collector or plugin Turn off entire plugins in -the [`[plugins]` section](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/config/README.md#plugins-section-options) +the [`[plugins]` section](/src/daemon/config/README.md#plugins-section-options) of `netdata.conf`. @@ -83,9 +73,9 @@ sudo ./edit-config health.d/example-alert.conf Or, append your new alert to an existing file by editing a relevant existing file in the `health.d/` directory. -Read more about [configuring alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md) to +Read more about [configuring alerts](/src/health/REFERENCE.md) to get started, and see -the [health monitoring reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md) for a full listing +the [health monitoring reference](/src/health/REFERENCE.md) for a full listing of options available in health entities. ### Configure a specific alert @@ -94,7 +84,7 @@ Tweak existing alerts by editing files in the `health.d/` directory. For example the Agent responds to anomalies related to CPU utilization. To see which configuration file you need to edit to configure a specific -alert, [view your active alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md) in +alert, [view your active alerts](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/alerts-tab.md) in Netdata Cloud or the local Agent dashboard and look for the **source** line. For example, it might read `source 4@/usr/lib/netdata/conf.d/health.d/cpu.conf`. @@ -116,13 +106,12 @@ template: disk_fill_rate ### Turn of all alerts and notifications Set `enabled` to `no` in -the [`[health]`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/config/README.md#health-section-options) +the [`[health]`](/src/daemon/config/README.md#health-section-options) section of `netdata.conf`. ### Enable alert notifications -Open `health_alarm_notify.conf` for editing. First, read the [enabling -notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/enable-notifications.md#netdata-agent) doc +Open `health_alarm_notify.conf` for editing. First, read the [enabling notifications](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/README.md#netdata-agent) doc for an example of the process using Slack, then click on the link to your preferred notification method to find documentation for that specific endpoint. @@ -131,12 +120,12 @@ click on the link to your preferred notification method to find documentation fo While the Netdata Agent is both [open and secure by design](https://www.netdata.cloud/blog/netdata-agent-dashboard/), we recommend every user take some action to administer and secure their nodes. -Learn more about the available options in the [security design documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md). +Learn more about the available options in the [security design documentation](/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md). ## Reduce resource usage Read -our [performance optimization guide](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/configure/performance.md) +our [performance optimization guide](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimize-the-netdata-agents-performance.md) for a long list of specific changes that can reduce the Netdata Agent's CPU/memory footprint and IO requirements. @@ -147,7 +136,7 @@ and as metadata to Netdata Cloud, and help you organize the metrics coming from defined in the section `[host labels]`. For a quick introduction, read -the [host label guide](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/using-host-labels.md). +the [host label guide](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/organize-systems-metrics-and-alerts.md). The following restrictions apply to host label names: diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/dynamic-configuration.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/dynamic-configuration.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..7064abf9a --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/dynamic-configuration.md @@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ +# Dynamic Configuration Manager + +**Netdata Cloud paid subscription required.** + +The Dynamic Configuration Manager allows direct configuration of collectors and alerts through the Netdata UI. This feature allows users to: + +- **Create, test, and deploy configurations** for one or more nodes directly within the UI. +- **Eliminate the need for manual command-line edits and node access**, enhancing workflow efficiency. + +**Cloud Connection and Security**: Nodes using Dynamic Configuration Manager require a connection to Netdata Cloud. This ensures proper permission handling and data security. + +> **Info** +> +> To understand what actions users can perform based on their role, refer to the [Role Based Access documentation](/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md#dynamic-configuration-manager). + +## Collectors + +### Module + +A module represents a specific data collector, such as Apache, MySQL, or Redis. Think of modules as templates for data collection. + +Each module can have multiple jobs, which are unique configurations of that template tailored to your specific needs. + +You can manage individual modules using the following actions: + +| Action | Description | +|--------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| **Add job** | Create new configuration instances (jobs) for a particular module. | +| **Enable/Disable** | Disabling a module deactivates all currently running jobs and prevents any future jobs from being created for that module | + +### Job + +A job represents a running instance of a module with a specific configuration. Think of it as a customized data collection task based on a module template. + +Every job has a designated "source type" indicating its origin: + +- **Stock**: Pre-installed with Netdata and provides basic data collection for common services. +- **User**: Originates from user-created files on the node. +- **Discovered**: Automatically generated by Netdata upon discovering a service running on the node. +- **Dynamic Configuration**: Created and managed using the Dynamic Configuration Manager. + +You can manage individual jobs using the following actions: + +| Action | Description | +|--------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| **Restart** | This restarts a job's data collection, useful if a job encounters a "Failed" state. Upon restart, a notification with the failure message will be displayed. | +| **Remove** | Delete a job configuration entirely. Note that only jobs created through Dynamic Configuration can be removed. Other job types originate from files on the node and cannot be deleted here. | +| **Enable/Disable** | Control the job's activity. Disabling a running job stops data collection. | +| **Edit** | Modify an existing job's configuration. | +| **Test** | Validate newly created or edited configurations before applying them permanently. | + +## Health + +Each entry in the Health tab contains an Alert template, that then is used to create Alerts. + +The functionality in the main view is the same as with the [Collectors tab](#collectors). + +### Health entry configuration + +You can create new configurations both for templates or individual Alerts. + +Each template can have multiple items which resemble Alerts that either apply to a certain [instance](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#instances-dropdown), or all instances under a specific [context](/docs/dashboards-and-charts/netdata-charts.md#contexts) diff --git a/docs/guides/configure/performance.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimize-the-netdata-agents-performance.md index e1b32778e..6acbd4977 100644 --- a/docs/guides/configure/performance.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimize-the-netdata-agents-performance.md @@ -22,8 +22,8 @@ The following table summarizes the effect of each optimization on the CPU, RAM a | [Use streaming and replication](#use-streaming-and-replication) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | [Disable unneeded plugins or collectors](#disable-unneeded-plugins-or-collectors) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | [Reduce data collection frequency](#reduce-collection-frequency) | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | -| [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md) | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | -| [Use a different metric storage database](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md) | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md) | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| [Use a different metric storage database](/src/database/README.md) | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | [Disable machine learning](#disable-machine-learning) | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | [Use a reverse proxy](#run-netdata-behind-a-proxy) | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | [Disable/lower gzip compression for the agent dashboard](#disablelower-gzip-compression-for-the-dashboard) | :heavy_check_mark: | | | @@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ including all its components, should be below 5 - 15% of a single core. For exam 0.6% - 1.8% of a total CPU capacity, depending on the CPU characteristics. The Netdata Agent runs with the lowest -possible [process scheduling policy](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/README.md#netdata-process-scheduling-policy), +possible [process scheduling policy](/src/daemon/README.md#netdata-process-scheduling-policy), which is `nice 19`, and uses the `idle` process scheduler. Together, these settings ensure that the Agent only gets CPU resources when the node has CPU resources to space. If the node reaches 100% CPU utilization, the Agent is stopped first to ensure your applications get any available resources. @@ -72,8 +72,8 @@ The memory footprint of Netdata is mainly influenced by the number of metrics co To estimate and control memory consumption, you can (either one or a combination of the following actions): 1. [Disable unneeded plugins or collectors](#disable-unneeded-plugins-or-collectors) -2. [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md) -3. [Use a different metric storage database](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md). +2. [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md) +3. [Use a different metric storage database](/src/database/README.md). ### Disk footprint and I/O @@ -91,11 +91,11 @@ To optimize your disk footprint in any aspect described below you can: To configure retention, you can: -1. [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md). +1. [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md). To control disk I/O: -1. [Use a different metric storage database](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md), +1. [Use a different metric storage database](/src/database/README.md), Minimize deployment impact on the production system by optimizing disk footprint: @@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ Minimize deployment impact on the production system by optimizing disk footprint For all production environments, parent Netdata nodes outside the production infrastructure should be receiving all collected data from children Netdata nodes running on the production infrastructure, -using [streaming and replication](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md). +using [streaming and replication](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md). ### Disable health checks on the child nodes @@ -125,12 +125,12 @@ in `stream.conf`). On the child nodes you should add to `netdata.conf` the follo ### Use memory mode ram for the child nodes -See [using a different metric storage database](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md). +See [using a different metric storage database](/src/database/README.md). ## Disable unneeded plugins or collectors If you know that you don't need an [entire plugin or a specific -collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology), +collector](/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology), you can disable any of them. Keep in mind that if a plugin/collector has nothing to do, it simply shuts down and does not consume system resources. You will only improve the Agent's performance by disabling plugins/collectors that are actively collecting metrics. @@ -171,7 +171,7 @@ The fastest way to improve the Agent's resource utilization is to reduce how oft ### Global If you don't need per-second metrics, or if the Netdata Agent uses a lot of CPU even when no one is viewing that node's -dashboard, [configure the Agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) to collect +dashboard, [configure the Agent](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) to collect metrics less often. Open `netdata.conf` and edit the `update every` setting. The default is `1`, meaning that the Agent collects metrics @@ -191,11 +191,11 @@ seconds, respectively. Every collector and plugin has its own `update every` setting, which you can also change in the `go.d.conf`, `python.d.conf`, or `charts.d.conf` files, or in individual collector configuration files. If the `update every` for an individual collector is less than the global, the Netdata Agent uses the global setting. See -the [collectors configuration reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) for +the [collectors configuration reference](/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) for details. To reduce the frequency of -an [internal_plugin/collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology), +an [internal_plugin/collector](/src/collectors/README.md#collector-architecture-and-terminology), open `netdata.conf` and find the appropriate section. For example, to reduce the frequency of the `apps` plugin, which collects and visualizes metrics on application resource utilization: @@ -204,7 +204,7 @@ collects and visualizes metrics on application resource utilization: update every = 5 ``` -To [configure an individual collector](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md#configure-a-collector), +To [configure an individual collector](/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md#configure-a-collector), open its specific configuration file with `edit-config` and look for the `update_every` setting. For example, to reduce the frequency of the `nginx` collector, run `sudo ./edit-config go.d/nginx.conf`: @@ -216,13 +216,13 @@ update_every: 10 ## Lower memory usage for metrics retention See how -to [change how long Netdata stores metrics](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md). +to [change how long Netdata stores metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md). ## Use a different metric storage database -Consider [using a different metric storage database](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/README.md) +Consider [using a different metric storage database](/src/database/README.md) when running Netdata on IoT devices, and for children in a parent-child set up based -on [streaming and replication](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md). +on [streaming and replication](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md). ## Disable machine learning @@ -237,11 +237,11 @@ outside your production infrastructure, or if you have cpu and memory to spare. ## Run Netdata behind a proxy A dedicated web server like nginx provides more robustness than the Agent's -internal [web server](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/README.md). +internal [web server](/src/web/README.md). Nginx can handle more concurrent connections, reuse idle connections, and use fast gzip compression to reduce payloads. For details on installing another web server as a proxy for the local Agent dashboard, -see [reverse proxies](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/reverse-proxies.md). +see [reverse proxies](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/README.md). ## Disable/lower gzip compression for the dashboard diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/optimizing-metrics-database.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/README.md index fdbd3b690..fdbd3b690 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/optimizing-metrics-database.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/README.md diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..8a8659eff --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md @@ -0,0 +1,124 @@ +# Change how long Netdata stores metrics + +Netdata offers a granular approach to data retention, allowing you to manage storage based on both **time** and **disk +space**. This provides greater control and helps you optimize storage usage for your specific needs. + +**Default Retention Limits**: + +| Tier | Resolution | Time Limit | Size Limit (min 256 MB) | +|:----:|:-------------------:|:----------:|:-----------------------:| +| 0 | high (per second) | 14 days | 1 GiB | +| 1 | middle (per minute) | 3 months | 1 GiB | +| 2 | low (per hour) | 2 years | 1 GiB | + +> **Note**: If a user sets a disk space size less than 256 MB for a tier, Netdata will automatically adjust it to 256 MB. + +With these defaults, Netdata requires approximately 4 GiB of storage space (including metadata). + +## Retention Settings + +> **In a parent-child setup**, these settings manage the shared storage space utilized by the Netdata parent agent for +> storing metrics collected by both the parent and its child nodes. + +You can fine-tune retention for each tier by setting a time limit or size limit. Setting a limit to 0 disables it, +allowing for no time-based deletion for that tier or using all available space, respectively. This enables various +retention strategies as shown in the table below: + +| Setting | Retention Behavior | +|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| Size Limit = 0, Time Limit > 0 | **Time-based only:** data is stored for a specific duration regardless of disk usage. | +| Time Limit = 0, Size Limit > 0 | **Space-based only:** data is stored until it reaches a certain amount of disk space, regardless of time. | +| Time Limit > 0, Size Limit > 0 | **Combined time and space limits:** data is deleted once it reaches either the time limit or the disk space limit, whichever comes first. | + +You can change these limits in `netdata.conf`: + +``` +[db] + mode = dbengine + storage tiers = 3 + + # Tier 0, per second data. Set to 0 for no limit. + dbengine tier 0 disk space MB = 1024 + dbengine tier 0 retention days = 14 + + # Tier 1, per minute data. Set to 0 for no limit. + dbengine tier 1 disk space MB = 1024 + dbengine tier 1 retention days = 90 + + # Tier 2, per hour data. Set to 0 for no limit. + dbengine tier 2 disk space MB = 1024 + dbengine tier 2 retention days = 730 +``` + +## Monitoring Retention Utilization + +Netdata provides a visual representation of storage utilization for both time and space limits across all tiers within +the 'dbengine retention' subsection of the 'Netdata Monitoring' section on the dashboard. This chart shows exactly how +your storage space (disk space limits) and time (time limits) are used for metric retention. + +## Legacy configuration + +### v1.45.6 and prior + +Netdata versions prior to v1.46.0 relied on a disk space-based retention. + +**Default Retention Limits**: + +| Tier | Resolution | Size Limit | +|:----:|:-------------------:|:----------:| +| 0 | high (per second) | 256 MB | +| 1 | middle (per minute) | 128 MB | +| 2 | low (per hour) | 64 GiB | + +You can change these limits in `netdata.conf`: + +``` +[db] + mode = dbengine + storage tiers = 3 + + # Tier 0, per second data + dbengine multihost disk space MB = 256 + + # Tier 1, per minute data + dbengine tier 1 multihost disk space MB = 1024 + + # Tier 2, per hour data + dbengine tier 2 multihost disk space MB = 1024 +``` + +### v1.35.1 and prior + +These versions of the Agent do not support tiers. You could change the metric retention for the parent and +all of its children only with the `dbengine multihost disk space MB` setting. This setting accounts the space allocation +for the parent node and all of its children. + +To configure the database engine, look for the `page cache size MB` and `dbengine multihost disk space MB` settings in +the `[db]` section of your `netdata.conf`. + +```conf +[db] + dbengine page cache size MB = 32 + dbengine multihost disk space MB = 256 +``` + +### v1.23.2 and prior + +_For Netdata Agents earlier than v1.23.2_, the Agent on the parent node uses one dbengine instance for itself, and +another instance for every child node it receives metrics from. If you had four streaming nodes, you would have five +instances in total (`1 parent + 4 child nodes = 5 instances`). + +The Agent allocates resources for each instance separately using the `dbengine disk space MB` (**deprecated**) setting. +If `dbengine disk space MB`(**deprecated**) is set to the default `256`, each instance is given 256 MiB in disk space, +which means the total disk space required to store all instances is, +roughly, `256 MiB * 1 parent * 4 child nodes = 1280 MiB`. + +#### Backward compatibility + +All existing metrics belonging to child nodes are automatically converted to legacy dbengine instances and the localhost +metrics are transferred to the multihost dbengine instance. + +All new child nodes are automatically transferred to the multihost dbengine instance and share its page cache and disk +space. If you want to migrate a child node from its legacy dbengine instance to the multihost dbengine instance, you +must delete the instance's directory, which is located in `/var/cache/netdata/MACHINE_GUID/dbengine`, after stopping the +Agent. diff --git a/docs/guides/using-host-labels.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/organize-systems-metrics-and-alerts.md index 961f4b2d7..b0094a60f 100644 --- a/docs/guides/using-host-labels.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/organize-systems-metrics-and-alerts.md @@ -1,16 +1,16 @@ # Organize systems, metrics, and alerts When you use Netdata to monitor and troubleshoot an entire infrastructure, you need sophisticated ways of keeping everything organized. -Netdata allows to organize your observability infrastructure with spaces, war rooms, virtual nodes, host labels, and metric labels. +Netdata allows to organize your observability infrastructure with Spaces, Rooms, virtual nodes, host labels, and metric labels. -## Spaces and war rooms +## Spaces and Rooms -[Spaces](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces) are used for organization-level or infrastructure-level +[Spaces](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces) are used for organization-level or infrastructure-level grouping of nodes and people. A node can only appear in a single space, while people can have access to multiple spaces. -The [war rooms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/cloud/war-rooms.md) in a space bring together nodes and people in -collaboration areas. War rooms can also be used for fine-tuned -[role based access control](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md). +The [Rooms](/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-rooms) in a space bring together nodes and people in +collaboration areas. Rooms can also be used for fine-tuned +[role based access control](/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md). ## Virtual nodes @@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ sudo ./edit-config netdata.conf ``` Create a new `[host labels]` section defining a new host label and its value for the system in question. Make sure not -to violate any of the [host label naming rules](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/common-changes.md#organize-nodes-with-host-labels). +to violate any of the [host label naming rules](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/common-configuration-changes.md#organize-nodes-with-host-labels). ```conf [host labels] @@ -139,9 +139,9 @@ child system. It's a vastly simplified way of accessing critical information abo > ⚠️ Because automatic labels for child nodes are accessible via API calls, and contain sensitive information like > kernel and operating system versions, you should secure streaming connections with SSL. See the [streaming -> documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/streaming/README.md#securing-streaming-communications) for details. You may also want to use -> [access lists](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#access-lists) or [expose the API only to LAN/localhost -> connections](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/category-overview-pages/secure-nodes.md#expose-netdata-only-in-a-private-lan). +> documentation](/src/streaming/README.md#securing-streaming-communications) for details. You may also want to use +> [access lists](/src/web/server/README.md#access-lists) or [expose the API only to LAN/localhost +> connections](/docs/netdata-agent/securing-netdata-agents.md#expose-netdata-only-in-a-private-lan). You can also use `_is_parent`, `_is_child`, and any other host labels in both health entities and metrics exporting. Speaking of which... @@ -192,11 +192,11 @@ Or when ephemeral Docker nodes are involved: ``` Of course, there are many more possibilities for intuitively organizing your systems with host labels. See the [health -documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-host-labels) for more details, and then get creative! +documentation](/src/health/REFERENCE.md#alert-line-host-labels) for more details, and then get creative! ### Host labels in metrics exporting -If you have enabled any metrics exporting via our experimental [exporters](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md), any new host +If you have enabled any metrics exporting via our experimental [exporters](/src/exporting/README.md), any new host labels you created manually are sent to the destination database alongside metrics. You can change this behavior by editing `exporting.conf`, and you can even send automatically-generated labels on with exported metrics. @@ -221,7 +221,7 @@ send automatic labels = yes ``` By applying labels to exported metrics, you can more easily parse historical metrics with the labels applied. To learn -more about exporting, read the [documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/exporting/README.md). +more about exporting, read the [documentation](/src/exporting/README.md). ## Metric labels diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/reverse-proxies.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/README.md index 1b4d935a3..00fe63af1 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/reverse-proxies.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/README.md @@ -1,17 +1,17 @@ -# Running Netdata behind a reverse proxy +# Running the Netdata Agent behind a reverse proxy If you need to access a Netdata agent's user interface or API in a production environment we recommend you put Netdata behind another web server and secure access to the dashboard via SSL, user authentication and firewall rules. -A dedicated web server also provides more robustness and capabilities than the Agent's [internal web server](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/README.md). +A dedicated web server also provides more robustness and capabilities than the Agent's [internal web server](/src/web/README.md). We have documented running behind -[nginx](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-nginx.md), -[Apache](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-apache.md), -[HAProxy](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-haproxy.md), -[Lighttpd](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-lighttpd.md), -[Caddy](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-caddy.md), -and [H2O](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-h2o.md). +[nginx](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-nginx.md), +[Apache](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-apache.md), +[HAProxy](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-haproxy.md), +[Lighttpd](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-lighttpd.md), +[Caddy](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-caddy.md), +and [H2O](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-h2o.md). If you prefer a different web server, we suggest you follow the documentation for nginx and tell us how you did it by adding your own "Running behind webserverX" document. diff --git a/docs/Running-behind-apache.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-apache.md index 6fa119c67..1f7274d5c 100644 --- a/docs/Running-behind-apache.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-apache.md @@ -342,15 +342,15 @@ If your apache server is not on localhost, you can set: *note: Netdata v1.9+ support `allow connections from`* -`allow connections from` accepts [Netdata simple patterns](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) to match against the connection IP address. +`allow connections from` accepts [Netdata simple patterns](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) to match against the connection IP address. ## Prevent the double access.log apache logs accesses and Netdata logs them too. You can prevent Netdata from generating its access log, by setting this in `/etc/netdata/netdata.conf`: ``` -[global] - access log = none +[logs] + access = off ``` ## Troubleshooting mod_proxy diff --git a/docs/Running-behind-caddy.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-caddy.md index b7608b309..b7608b309 100644 --- a/docs/Running-behind-caddy.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-caddy.md diff --git a/docs/Running-behind-h2o.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-h2o.md index 7e4601ae8..276b72e8b 100644 --- a/docs/Running-behind-h2o.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-h2o.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ <!-- title: "Running Netdata behind H2O" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/Running-behind-h2o.md" +custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-h2o.md" sidebar_label: "Running Netdata behind H2O" learn_status: "Published" learn_topic_type: "Tasks" @@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ Using the above, you access Netdata on the backend servers, like this: ### Encrypt the communication between H2O and Netdata -In case Netdata's web server has been [configured to use TLS](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support), it is +In case Netdata's web server has been [configured to use TLS](/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support), it is necessary to specify inside the H2O configuration that the final destination is using TLS. To do this, change the `http://` on the `proxy.reverse.url` line in your H2O configuration with `https://` @@ -173,7 +173,7 @@ If your H2O server is not on localhost, you can set: *note: Netdata v1.9+ support `allow connections from`* -`allow connections from` accepts [Netdata simple patterns](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) to match against +`allow connections from` accepts [Netdata simple patterns](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) to match against the connection IP address. ## Prevent the double access.log @@ -182,6 +182,6 @@ H2O logs accesses and Netdata logs them too. You can prevent Netdata from genera this in `/etc/netdata/netdata.conf`: ``` -[global] - access log = none +[logs] + access = off ``` diff --git a/docs/Running-behind-haproxy.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-haproxy.md index 4c9c32cc4..9d2aff670 100644 --- a/docs/Running-behind-haproxy.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-haproxy.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ <!-- title: "Netdata via HAProxy" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/Running-behind-haproxy.md" +custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-haproxy.md" sidebar_label: "Netdata via HAProxy" learn_status: "Published" learn_topic_type: "Tasks" diff --git a/docs/Running-behind-lighttpd.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-lighttpd.md index d1d9acc3e..637bc0642 100644 --- a/docs/Running-behind-lighttpd.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-lighttpd.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ <!-- title: "Netdata via lighttpd v1.4.x" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/Running-behind-lighttpd.md" +custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-lighttpd.md" sidebar_label: "Netdata via lighttpd v1.4.x" learn_status: "Published" learn_topic_type: "Tasks" diff --git a/docs/Running-behind-nginx.md b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-nginx.md index 2cda4ab2a..f2dd137dd 100644 --- a/docs/Running-behind-nginx.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-nginx.md @@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ Using the above, you access Netdata on the backend servers, like this: ### Encrypt the communication between Nginx and Netdata -In case Netdata's web server has been [configured to use TLS](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support), it is +In case Netdata's web server has been [configured to use TLS](/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support), it is necessary to specify inside the Nginx configuration that the final destination is using TLS. To do this, please, append the following parameters in your `nginx.conf` @@ -236,7 +236,7 @@ If your Nginx server is not on localhost, you can set: *note: Netdata v1.9+ support `allow connections from`* -`allow connections from` accepts [Netdata simple patterns](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) to match against the +`allow connections from` accepts [Netdata simple patterns](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md) to match against the connection IP address. ## Prevent the double access.log @@ -244,8 +244,8 @@ connection IP address. Nginx logs accesses and Netdata logs them too. You can prevent Netdata from generating its access log, by setting this in `/etc/netdata/netdata.conf`: ``` -[global] - access log = none +[logs] + access = off ``` ## Use gzip compression diff --git a/docs/category-overview-pages/secure-nodes.md b/docs/netdata-agent/securing-netdata-agents.md index 99e273920..5232173fb 100644 --- a/docs/category-overview-pages/secure-nodes.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/securing-netdata-agents.md @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ -# Secure your nodes
+# Securing Netdata Agents
Netdata is a monitoring system. It should be protected, the same way you protect all your admin apps. We assume Netdata
will be installed privately, for your eyes only.
@@ -44,10 +44,10 @@ that align with your goals and your organization's standards. ## Disable the local dashboard
This is the _recommended method for those who have connected their nodes to Netdata Cloud_ and prefer viewing real-time
-metrics using the War Room Overview, Nodes tab, and Cloud dashboards.
+metrics using the Room Overview, Nodes tab, and Cloud dashboards.
You can disable the local dashboard (and API) but retain the encrypted Agent-Cloud link
-([ACLK](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/aclk/README.md)) that
+([ACLK](/src/aclk/README.md)) that
allows you to stream metrics on demand from your nodes via the Netdata Cloud interface. This change mitigates all
concerns about revealing metrics and system design to the internet at large, while keeping all the functionality you
need to view metrics and troubleshoot issues with Netdata Cloud.
@@ -60,15 +60,18 @@ static-threaded` setting, and change it to `none`. mode = none
```
-Save and close the editor, then [restart your Agent](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation)
+Save and close the editor, then [restart your Agent](/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation)
using `sudo systemctl
restart netdata`. If you try to visit the local dashboard to `http://NODE:19999` again, the connection will fail because
that node no longer serves its local dashboard.
-> See the [configuration basics doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) for details on how to find
+> See the [configuration basics doc](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md) for details on how to find
`netdata.conf` and use
> `edit-config`.
+If you are using Netdata with Docker, make sure to set the `NETDATA_HEALTHCHECK_TARGET` environment variable to `cli`.
+
+
## Expose Netdata only in a private LAN
If your organisation has a private administration and management LAN, you can bind Netdata on this network interface on all your servers.
@@ -98,7 +101,7 @@ the internet using multiple hosting providers). ## Fine-grained access control
If you want to keep using the local dashboard, but don't want it exposed to the internet, you can restrict access with
-[access lists](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#access-lists). This method also fully
+[access lists](/src/web/server/README.md#access-lists). This method also fully
retains the ability to stream metrics
on-demand through Netdata Cloud.
@@ -107,7 +110,7 @@ static IP, only `localhost`, or connections from behind a management LAN. By default, this setting is `localhost *`. This setting allows connections from `localhost` in addition to _all_
connections, using the `*` wildcard. You can change this setting using Netdata's [simple
-patterns](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md).
+patterns](/src/libnetdata/simple_pattern/README.md).
```conf
[web]
@@ -134,9 +137,9 @@ The `allow connections from` setting is global and restricts access to the dashb allow management from = localhost
```
-See the [web server](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#access-lists) docs for additional details
+See the [web server](/src/web/server/README.md#access-lists) docs for additional details
about access lists. You can take
-access lists one step further by [enabling SSL](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support) to encrypt data from local
+access lists one step further by [enabling SSL](/src/web/server/README.md#enabling-tls-support) to encrypt data from local
dashboard in transit. The connection to Netdata Cloud is always secured with TLS.
## Use an authenticating web server in proxy mode
@@ -144,12 +147,12 @@ dashboard in transit. The connection to Netdata Cloud is always secured with TLS Use one web server to provide authentication in front of **all your Netdata servers**. So, you will be accessing all your Netdata with
URLs like `http://{HOST}/netdata/{NETDATA_HOSTNAME}/` and authentication will be shared among all of them (you will sign-in once for all your servers).
Instructions are provided on how to set the proxy configuration to have Netdata run behind
-[nginx](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-nginx.md),
-[HAproxy](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-haproxy.md),
-[Apache](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-apache.md),
-[lighthttpd](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-lighttpd.md),
-[caddy](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-caddy.md), and
-[H2O](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/Running-behind-h2o.md).
+[nginx](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-nginx.md),
+[HAproxy](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-haproxy.md),
+[Apache](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-apache.md),
+[lighthttpd](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-lighttpd.md),
+[caddy](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-caddy.md), and
+[H2O](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/running-the-netdata-agent-behind-a-reverse-proxy/Running-behind-h2o.md).
## Use Netdata parents as Web Application Firewalls
@@ -159,7 +162,7 @@ your production systems from the rest of the world. Netdata Parents receive metric data from Netdata Agents or other Netdata Parents on one side, and serve most queries using their own
copy of the data to satisfy dashboard requests on the other side.
-For more information see [Streaming and replication](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/metrics-storage-management/enable-streaming.md).
+For more information see [Streaming and replication](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md).
## Other methods
diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/README.md b/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/README.md index b945dc56c..3ba346f7a 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/README.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/README.md @@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ The following guides provide instructions on how to do this. Netdata Parents automatically size resource utilization based on the workload they receive. The only possible option for improving query performance is to dedicate more RAM to them, by increasing their caches efficiency. -Check [RAM Requirements](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/ram-requirements.md) for more information. +Check [RAM Requirements](/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/ram-requirements.md) for more information. ## Innovations Netdata has for optimal performance and scalability diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/disk-requirements-and-retention.md b/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/disk-requirements-and-retention.md index d9e879cb6..7cd9a527d 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/disk-requirements-and-retention.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/disk-requirements-and-retention.md @@ -2,41 +2,17 @@ ## Database Modes and Tiers -Netdata comes with 3 database modes: +Netdata offers two database modes to suit your needs for performance and data persistence: -1. `dbengine`: the default high-performance multi-tier database of Netdata. Metric samples are cached in memory and are saved to disk in multiple tiers, with compression. -2. `ram`: metric samples are stored in ring buffers in memory, with increments of 1024 samples. Metric samples are not committed to disk. Kernel-Same-Page (KSM) can be used to deduplicate Netdata's memory. -3. `alloc`: metric samples are stored in ring buffers in memory, with flexible increments. Metric samples are not committed to disk. - -## `ram` and `alloc` - -Modes `ram` and `alloc` can help when Netdata should not introduce any disk I/O at all. In both of these modes, metric samples exist only in memory, and only while they are collected. - -When Netdata is configured to stream its metrics to a Metrics Observability Centralization Point (a Netdata Parent), metric samples are forwarded in real-time to that Netdata Parent. The ring buffers available in these modes is used to cache the collected samples for some time, in case there are network issues, or the Netdata Parent is restarted for maintenance. - -The memory required per sample in these modes, is 4 bytes: - -- `ram` mode uses `mmap()` behind the scene, and can be incremented in steps of 1024 samples (4KiB). Mode `ram` allows the use of the Linux kernel memory dedupper (Kernel-Same-Page or KSM) to deduplicate Netdata ring buffers and save memory. -- `alloc` mode can be sized for any number of samples per metric. KSM cannot be used in this mode. - -To configure database mode `ram` or `alloc`, in `netdata.conf`, set the following: - -- `[db].mode` to either `ram` or `alloc`. -- `[db].retention` to the number of samples the ring buffers should maintain. For `ram` if the value set is not a multiple of 1024, the next multiple of 1024 will be used. +| Mode | Description | +|:------------------:|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| dbengine (default) | High-performance, multi-tier storage with compression. Metric samples are cached in memory and then written to disk in multiple tiers for efficient retrieval and long-term storage. | +| ram | In-memory storage. Metric samples are stored in memory only, and older data is overwritten as new data arrives. This mode prioritizes speed, making it ideal for Netdata Child instances that stream data to a central Netdata parent. | ## `dbengine` -`dbengine` supports up to 5 tiers. By default, 3 tiers are used, like this: - -| Tier | Resolution | Uncompressed Sample Size | Usually On Disk | -|:--------:|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:------------------------:|:---------------:| -| `tier0` | native resolution (metrics collected per-second as stored per-second) | 4 bytes | 0.6 bytes | -| `tier1` | 60 iterations of `tier0`, so when metrics are collected per-second, this tier is per-minute. | 16 bytes | 6 bytes | -| `tier2` | 60 iterations of `tier1`, so when metrics are collected per second, this tier is per-hour. | 16 bytes | 18 bytes | - -Data are saved to disk compressed, so the actual size on disk varies depending on compression efficiency. - -`dbegnine` tiers are overlapping, so higher tiers include a down-sampled version of the samples in lower tiers: +Netdata's `dbengine` mode efficiently stores data on disk using compression. The actual disk space used depends on how well the data compresses. +This mode utilizes a tiered storage approach: data is saved in multiple tiers on disk. Each tier retains data at a different resolution (detail level). Higher tiers store a down-sampled (less detailed) version of the data found in lower tiers. ```mermaid gantt @@ -49,83 +25,28 @@ gantt tier2, 365d :a3, 2023-11-02, 59d ``` -## Disk Space and Metrics Retention - -You can find information about the current disk utilization of a Netdata Parent, at <http://agent-ip:19999/api/v2/info>. The output of this endpoint is like this: - -```json -{ - // more information about the agent - // then, near the end: - "db_size": [ - { - "tier": 0, - "metrics": 43070, - "samples": 88078162001, - "disk_used": 41156409552, - "disk_max": 41943040000, - "disk_percent": 98.1245269, - "from": 1705033983, - "to": 1708856640, - "retention": 3822657, - "expected_retention": 3895720, - "currently_collected_metrics": 27424 - }, - { - "tier": 1, - "metrics": 72987, - "samples": 5155155269, - "disk_used": 20585157180, - "disk_max": 20971520000, - "disk_percent": 98.1576785, - "from": 1698287340, - "to": 1708856640, - "retention": 10569300, - "expected_retention": 10767675, - "currently_collected_metrics": 27424 - }, - { - "tier": 2, - "metrics": 148234, - "samples": 314919121, - "disk_used": 5957346684, - "disk_max": 10485760000, - "disk_percent": 56.8136853, - "from": 1667808000, - "to": 1708856640, - "retention": 41048640, - "expected_retention": 72251324, - "currently_collected_metrics": 27424 - } - ] -} -``` +`dbengine` supports up to 5 tiers. By default, 3 tiers are used: + +| Tier | Resolution | Uncompressed Sample Size | Usually On Disk | +|:-------:|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:------------------------:|:---------------:| +| `tier0` | native resolution (metrics collected per-second as stored per-second) | 4 bytes | 0.6 bytes | +| `tier1` | 60 iterations of `tier0`, so when metrics are collected per-second, this tier is per-minute. | 16 bytes | 6 bytes | +| `tier2` | 60 iterations of `tier1`, so when metrics are collected per second, this tier is per-hour. | 16 bytes | 18 bytes | + +**Configuring dbengine mode and retention**: + +- Enable dbengine mode: The dbengine mode is already the default, so no configuration change is necessary. For reference, the dbengine mode can be configured by setting `[db].mode` to `dbengine` in `netdata.conf`. +- Adjust retention (optional): see [Change how long Netdata stores metrics](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/optimizing-metrics-database/change-metrics-storage.md). + +## `ram` + +`ram` mode can help when Netdata should not introduce any disk I/O at all. In both of these modes, metric samples exist only in memory, and only while they are collected. + +When Netdata is configured to stream its metrics to a Metrics Observability Centralization Point (a Netdata Parent), metric samples are forwarded in real-time to that Netdata Parent. The ring buffers available in these modes is used to cache the collected samples for some time, in case there are network issues, or the Netdata Parent is restarted for maintenance. + +The memory required per sample in these modes, is 4 bytes: `ram` mode uses `mmap()` behind the scene, and can be incremented in steps of 1024 samples (4KiB). Mode `ram` allows the use of the Linux kernel memory dedupper (Kernel-Same-Page or KSM) to deduplicate Netdata ring buffers and save memory. + +**Configuring ram mode and retention**: -In this example: - -- `tier` is the database tier. -- `metrics` is the number of unique time-series in the database. -- `samples` is the number of samples in the database. -- `disk_used` is the currently used disk space in bytes. -- `disk_max` is the configured max disk space in bytes. -- `disk_percent` is the current disk space utilization for this tier. -- `from` is the first (oldest) timestamp in the database for this tier. -- `to` is the latest (newest) timestamp in the database for this tier. -- `retention` is the current retention of the database for this tier, in seconds (divide by 3600 for hours, divide by 86400 for days). -- `expected_retention` is the expected retention in seconds when `disk_percent` will be 100 (divide by 3600 for hours, divide by 86400 for days). -- `currently_collected_metrics` is the number of unique time-series currently being collected for this tier. - -So, for our example above: - -| Tier | # Of Metrics | # Of Samples | Disk Used | Disk Free | Current Retention | Expected Retention | Sample Size | -|-----:|-------------:|--------------:|----------:|----------:|------------------:|-------------------:|------------:| -| 0 | 43.1K | 88.1 billion | 38.4Gi | 1.88% | 44.2 days | 45.0 days | 0.46 B | -| 1 | 73.0K | 5.2 billion | 19.2Gi | 1.84% | 122.3 days | 124.6 days | 3.99 B | -| 2 | 148.3K | 315.0 million | 5.6Gi | 43.19% | 475.1 days | 836.2 days | 18.91 B | - -To configure retention, in `netdata.conf`, set the following: - -- `[db].mode` to `dbengine`. -- `[db].dbengine multihost disk space MB`, this is the max disk size for `tier0`. The default is 256MiB. -- `[db].dbengine tier 1 multihost disk space MB`, this is the max disk space for `tier1`. The default is 50% of `tier0`. -- `[db].dbengine tier 2 multihost disk space MB`, this is the max disk space for `tier2`. The default is 50% of `tier1`. +- Enable ram mode: To use in-memory storage, set `[db].mode` to ram in your `netdata.conf` file. Remember, this mode won't retain historical data after restarts. +- Adjust retention (optional): While ram mode focuses on real-time data, you can optionally control the number of samples stored in memory. Set `[db].retention` in `netdata.conf` to the desired number in seconds. Note: If the value you choose isn't a multiple of 1024, Netdata will automatically round it up to the nearest multiple. diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/ram-requirements.md b/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/ram-requirements.md index 159c979a9..8d8522517 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/ram-requirements.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/ram-requirements.md @@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ Netdata supports memory ballooning and automatically sizes and limits the memory With default settings, Netdata should run with 100MB to 200MB of RAM, depending on the number of metrics being collected. -This number can be lowered by limiting the number of database tier or switching database modes. For more information check [Disk Requirements and Retention](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/disk-requirements-and-retention.md). +This number can be lowered by limiting the number of database tier or switching database modes. For more information check [Disk Requirements and Retention](/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/disk-requirements-and-retention.md). ## On Metrics Centralization Points, Netdata Parents diff --git a/docs/maintenance/start-stop-restart.md b/docs/netdata-agent/start-stop-restart.md index 2effe8863..6fbe18d31 100644 --- a/docs/maintenance/start-stop-restart.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/start-stop-restart.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ # Start, stop, or restart the Netdata Agent -When you install the Netdata Agent, the [daemon](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/daemon/README.md) is +When you install the Netdata Agent, the [daemon](/src/daemon/README.md) is configured to start at boot and stop and restart/shutdown. You will most often need to _restart_ the Agent to load new or editing configuration files. @@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ If you start the daemon this way, close it with `sudo killall netdata`. ## Using `netdatacli` -The Netdata Agent also comes with a [CLI tool](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/cli/README.md) capable of performing shutdowns. Start the Agent back up +The Netdata Agent also comes with a [CLI tool](/src/cli/README.md) capable of performing shutdowns. Start the Agent back up using your preferred method listed above. ```bash diff --git a/docs/netdata-agent/versions-and-platforms.md b/docs/netdata-agent/versions-and-platforms.md index 787874d6e..14dc393b5 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-agent/versions-and-platforms.md +++ b/docs/netdata-agent/versions-and-platforms.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ # Netdata Agent Versions & Platforms -Netdata is evolving rapidly and new features are added at a constant pace. Therefore we have frequent release cadence to deliver all these features to use as soon as possible. +Netdata is evolving rapidly and new features are added at a constant pace. Therefore we have a frequent release cadence to deliver all these features to use as soon as possible. Netdata Agents are available in 2 versions: @@ -28,11 +28,11 @@ Binary distribution packages are provided by Netdata, via CI integration, for th | Oracle Linux | 8.x, 9.x | `x86_64`, `AArch64` | RPM | | Redhat Enterprise Linux | 7.x | `x86_64` | RPM | | Redhat Enterprise Linux | 8.x, 9.x | `x86_64`, `AArch64` | RPM | -| Ubuntu | 20.04, 22.04, 23.10 | `x86_64`, `i386`, `ARMv7` | DEB | +| Ubuntu | 20.04, 22.04, 23.10 | `x86_64`, `i386`, `ARMv7`, `AArch64` | DEB | -> IMPORTANT: Linux distributions frequently provide binary packages of Netdata. However, the packages you will find at the distributions' repositories may be outdated, incomplete, missing significant features or completely broken. We recommend to use the packages we provide. +> IMPORTANT: Linux distributions frequently provide binary packages of Netdata. However, the packages you will find in the distributions' repositories may be outdated, incomplete, missing significant features or completely broken. We recommend using the packages we provide. -## Third party Supported Binary Packages +## Third-party Supported Binary Packages The following distributions always provide the latest stable version of Netdata: @@ -67,4 +67,4 @@ Static builds usually miss certain features that require operating-system suppor - systemd-journal features - eBPF related features -When platforms are removed from the [Binary Distribution Packages](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/makeself/README.md) list, they default to install or update Netdata to a static build. This may mean that after platforms become EOL, Netdata on them may lose some of its features. We recommend to upgrade the operating system before it becomes EOL, to continue using all the features of Netdata. +When platforms are removed from the [Binary Distribution Packages](/packaging/makeself/README.md) list, they default to install or update Netdata to a static build. This may mean that after platforms become EOL, Netdata on them may lose some of its features. We recommend upgrading the operating system before it becomes EOL, to continue using all the features of Netdata. diff --git a/docs/cloud/netdata-assistant.md b/docs/netdata-assistant.md index afa13f6e9..afa13f6e9 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/netdata-assistant.md +++ b/docs/netdata-assistant.md diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/getting-started-light-poc.md b/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/getting-started-light-poc.md deleted file mode 100644 index 7e78638e3..000000000 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/getting-started-light-poc.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,60 +0,0 @@ -# Getting started with Netdata Cloud On-Prem Light PoC -Due to the high demand, we designed a very light and easy-to-install version of netdata for clients who do not have Kubernetes cluster installed. Please keep in mind that this is (for now) only designed to be used as a PoC with no built-in resiliency on failures of any kind. - -Requirements: - - Ubuntu 22.04 (clean installation will work best). - - 10 CPU Cores and 24 GiB of memory. - - Access to shell as a sudo. - - TLS certificate for Netdata Cloud On-Prem PoC. A single endpoint is required. The certificate must be trusted by all entities connecting to the On-Prem installation by any means. - - AWS ID and Key - contact Netdata Product Team - info@netdata.cloud - - License Key - contact Netdata Product Team - info@netdata.cloud - -To install the whole environment, log in to the designated host and run: -```shell -curl https://netdata-cloud-netdata-static-content.s3.amazonaws.com/provision.sh -o provision.sh -chmod +x provision.sh -sudo ./provision.sh install \ - -key-id "" \ - -access-key "" \ - -onprem-license-key "" \ - -onprem-license-subject "" \ - -onprem-url "" \ - -certificate-path "" \ - -private-key-path "" -``` - -What does the script do during installation? -1. Prompts for user to provide: - - `-key-id` - AWS ECR access key ID. - - `-access-key` - AWS ECR Access Key. - - `-onprem-license-key` - Netdata Cloud On-Prem license key. - - `-onprem-license-subject` - Netdata Cloud On-Prem license subject. - - `-onprem-url` - URL for the On-prem (without http(s) protocol). - - `-certificate-path` - path to your PEM encoded certificate. - - `-private-key-path` - path to your PEM encoded key. -2. After getting all of the information installation is starting. The script will install: - - Helm - - Kubectl - - AWS CLI - - K3s cluster (single node) -3. When all the required software is installed script starts to provision the K3s cluster with gathered data. - -After cluster provisioning netdata is ready to be used. - -##### How to log in? -Because this is a PoC with 0 configurations required, only log in by mail can work. What's more every mail that Netdata Cloud On-Prem sends will appear on the mailcatcher, which acts as the SMTP server with a simple GUI to read the mails. Steps: -1. Open Netdata Cloud On-Prem PoC in the web browser on URL you specified -2. Provide email and use the button to confirm -3. Mailcatcher will catch all the emails so go to `<URL from point 1.>/mailcatcher`. Find yours and click the link. -4. You are now logged into the netdata. Add your first nodes! - -##### How to remove Netdata Cloud On-Prem PoC? -To uninstall the whole PoC, use the same script that installed it, with the `uninstall` switch. - -```shell -cd <script dir> -sudo ./provision.sh uninstall -``` - -#### WARNING -This script will automatically expose not only netdata but also a mailcatcher under `<URL from point 1.>/mailcatcher`. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/getting-started.md b/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/getting-started.md deleted file mode 100644 index 9d2eea66f..000000000 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/getting-started.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,200 +0,0 @@ -# Getting started with Netdata Cloud On-Prem -Helm charts are designed for Kubernetes to run as the local equivalent of the Netdata Cloud public offering. This means that no data is sent outside of your cluster. By default, On-Prem installation is trying to reach outside resources only when pulling the container images. -There are 2 helm charts in total: -- netdata-cloud-onprem - installs onprem itself. -- netdata-cloud-dependency - installs all necessary dependency applications. Not for production use, PoC only. - -## Requirements -#### Install host: -- [AWS CLI](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html) -- [Helm](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/) version 3.12+ with OCI Configuration (explained in the installation section) -- [Kubectl](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/) - -#### Kubernetes requirements: -- Kubernetes cluster version 1.23+ -- Kubernetes metrics server (For autoscaling) -- TLS certificate for Netdata Cloud On-Prem. A single endpoint is required but there is an option to split the frontend, api, and mqtt endpoints. The certificate must be trusted by all entities connecting to the On-Prem installation by any means. -- Ingress controller to support HTTPS `*` -- PostgreSQL version 13.7 `*` (Main persistent data app) -- EMQX version 5.11 `*` (MQTT Broker that allows Agents to send messages to the On-Prem Cloud) -- Apache Pulsar version 2.10+ `*` (Central communication hub. Applications exchange messages through Pulsar) -- Traefik version 2.7.x `*` (Internal communication - API Gateway) -- Elasticsearch version 8.8.x `*` (Holds Feed) -- Redis version 6.2 `*` (Cache) -- Some form of generating imagePullSecret `*` (Our ECR repos are secured) -- Default storage class configured and working (Persistent volumes based on SSDs are preferred) -`*` - available in dependencies helm chart for PoC applications. - -#### Hardware requirements: -##### How we tested it: -- Several VMs on the AWS EC2, the size of the instance was c6a.32xlarge (128CPUs / 256GiB memory). -- Host system - Ubuntu 22.04. -- Each VM hosts 200 Agent nodes as docker containers. -- Agents are connected directly to the Netdata Cloud On-Prem (no Parent-Child relationships). This is the worst option for the cloud. -- Cloud hosted on 1 Kubernetes node c6a.8xlarge (32CPUs / 64GiB memory). -- Dependencies were also installed on the same node. -The maximum of nodes connected was ~2000. - -##### Results -There was no point in trying to connect more nodes as we are covering the PoC purposes. -- In a peak connection phase - All nodes startup were triggered in ~15 minutes: - - Up to 60% (20 cores) CPU usage of the Kubernetes node. Top usage came from: - - Ingress controller (we used haproxy ingress controller) - - Postgres - - Pulsar - - EMQX - Combined they were responsible for ~30-35% of CPU usage of the node. -- When all nodes connected and synchronized their state CPU usage floated between 30% and 40% - depending on what we did on the Cloud. Here top offenders were: - - Pulsar - - Postgres - Combined they were responsible for ~15-20% of CPU usage of the node. -- Memory usage - 45GiB in a peak. Most of it (~20GiB) was consumed by: - - Postgres - - Elasticsearch - - Pulsar - -For a comparison - Netdata Cloud On-prem installation with just 100 nodes connected, without dependencies is going to consume ~2CPUs and ~2GiB of memory (REAL usage, not requests on a Kubernetes). - -## Pulling the helm chart -The helm chart for the Netdata Cloud On-Prem installation on Kubernetes is available in the ECR registry. -The ECR registry is private, so you need to log in first. Credentials are sent by our Product Team. If you do not have them, please contact our Product Team - info@netdata.cloud. - -#### Configure AWS CLI -The machine used for helm chart installation will also need [AWS CLI installed](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html). -There are 2 options for configuring `aws cli` to work with the provided credentials. The first one is to set the environment variables: -```bash -export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your_secret_id> -export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your_secret_key> -``` - -The second one is to use an interactive shell: -```bash -aws configure -``` - -#### Configure helm to use secured ECR repository -Using `aws` command we will generate a token for helm to access the secured ECR repository: -```bash -aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | helm registry login --username AWS --password-stdin 362923047827.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/netdata-cloud-onprem -``` - -After this step you should be able to add the repository to your helm or just pull the helm chart: -```bash -helm pull oci://362923047827.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/netdata-cloud-dependency --untar #optional -helm pull oci://362923047827.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/netdata-cloud-onprem --untar -``` - -Local folders with the newest versions of helm charts should appear on your working dir. - -## Installation - -Netdata provides access to two helm charts: -1. netdata-cloud-dependency - required applications for netdata-cloud-onprem. Not for production use. -2. netdata-cloud-onprem - the application itself + provisioning - -### netdata-cloud-dependency -The entire helm chart is designed around the idea that it allows the installation of the necessary applications: -- Redis -- Elasticsearch -- EMQX -- Apache Pulsar -- PostgreSQL -- Traefik -- Mailcatcher -- k8s-ecr-login-renew -- kubernetes-ingress - -Every configuration option is available through `values.yaml` in the folder that contains your netdata-cloud-dependency helm chart. All configuration options are described in README.md which is a part of the helm chart. It is enough to mention here that each component can be enabled/disabled individually. It is done by true/false switches in `values.yaml`. In this way, it is easier for the user to migrate to production-grade components gradually. - -Unless you prefer a different solution to the problem, `k8s-ecr-login-renew` is responsible for calling out the `AWS API` for token regeneration. This token is then injected into the secret that every node is using for authentication with secured ECR when pulling the images. -The default setting in `values.yaml` of `netdata-cloud-onprem` - `.global.imagePullSecrets` is configured to work out of the box with the dependency helm chart. - -For helm chart installation - save your changes in `values.yaml` and execute: -```shell -cd [your helm chart location] -helm upgrade --wait --install netdata-cloud-dependency -n netdata-cloud --create-namespace -f values.yaml . -``` - -### netdata-cloud-onprem - -Every configuration option is available through `values.yaml` in the folder that contains your netdata-cloud-onprem helm chart. All configuration options are described in README.md which is a part of the helm chart. - -#### Installing Netdata Cloud On-Prem -```shell -cd [your helm chart location] -helm upgrade --wait --install netdata-cloud-onprem -n netdata-cloud --create-namespace -f values.yaml . -``` - -##### Important notes -1. Installation takes care of provisioning the resources with migration services. -1. During the first installation, a secret called the `netdata-cloud-common` is created. It contains several randomly generated entries. Deleting helm chart is not going to delete this secret, nor reinstalling the whole On-Prem, unless manually deleted by kubernetes administrator. The content of this secret is extremely relevant - strings that are contained there are essential parts of encryption. Losing or changing the data that it contains will result in data loss. - -## Short description of services -#### cloud-accounts-service -Responsible for user registration & authentication. Manages user account information. -#### cloud-agent-data-ctrl-service -Forwards request from the cloud to the relevant agents. -The requests include: -* Fetching chart metadata from the agent -* Fetching chart data from the agent -* Fetching function data from the agent -#### cloud-agent-mqtt-input-service -Forwards MQTT messages emitted by the agent related to the agent entities to the internal Pulsar broker. These include agent connection state updates. -#### cloud-agent-mqtt-output-service -Forwards Pulsar messages emitted in the cloud related to the agent entities to the MQTT broker. From there, the messages reach the relevant agent. -#### cloud-alarm-config-mqtt-input-service -Forwards MQTT messages emitted by the agent related to the alarm-config entities to the internal Pulsar broker. These include the data for the alarm configuration as seen by the agent. -#### cloud-alarm-log-mqtt-input-service -Forwards MQTT messages emitted by the agent related to the alarm-log entities to the internal Pulsar broker. These contain data about the alarm transitions that occurred in an agent. -#### cloud-alarm-mqtt-output-service -Forwards Pulsar messages emitted in the cloud related to the alarm entities to the MQTT broker. From there, the messages reach the relevant agent. -#### cloud-alarm-processor-service -Persists latest alert statuses received from the agent in the cloud. -Aggregates alert statuses from relevant node instances. -Exposes API endpoints to fetch alert data for visualization on the cloud. -Determines if notifications need to be sent when alert statuses change and emits relevant messages to Pulsar. -Exposes API endpoints to store and return notification-silencing data. -#### cloud-alarm-streaming-service -Responsible for starting the alert stream between the agent and the cloud. -Ensures that messages are processed in the correct order, and starts a reconciliation process between the cloud and the agent if out-of-order processing occurs. -#### cloud-charts-mqtt-input-service -Forwards MQTT messages emitted by the agent related to the chart entities to the internal Pulsar broker. These include the chart metadata that is used to display relevant charts on the cloud. -#### cloud-charts-mqtt-output-service -Forwards Pulsar messages emitted in the cloud related to the charts entities to the MQTT broker. From there, the messages reach the relevant agent. -#### cloud-charts-service -Exposes API endpoints to fetch the chart metadata. -Forwards data requests via the `cloud-agent-data-ctrl-service` to the relevant agents to fetch chart data points. -Exposes API endpoints to call various other endpoints on the agent, for instance, functions. -#### cloud-custom-dashboard-service -Exposes API endpoints to fetch and store custom dashboard data. -#### cloud-environment-service -Serves as the first contact point between the agent and the cloud. -Returns authentication and MQTT endpoints to connecting agents. -#### cloud-feed-service -Processes incoming feed events and stores them in Elasticsearch. -Exposes API endpoints to fetch feed events from Elasticsearch. -#### cloud-frontend -Contains the on-prem cloud website. Serves static content. -#### cloud-iam-user-service -Acts as a middleware for authentication on most of the API endpoints. Validates incoming token headers, injects the relevant ones, and forwards the requests. -#### cloud-metrics-exporter -Exports various metrics from an On-Prem Cloud installation. Uses the Prometheus metric exposition format. -#### cloud-netdata-assistant -Exposes API endpoints to fetch a human-friendly explanation of various netdata configuration options, namely the alerts. -#### cloud-node-mqtt-input-service -Forwards MQTT messages emitted by the agent related to the node entities to the internal Pulsar broker. These include the node metadata as well as their connectivity state, either direct or via parents. -#### cloud-node-mqtt-output-service -Forwards Pulsar messages emitted in the cloud related to the charts entities to the MQTT broker. From there, the messages reach the relevant agent. -#### cloud-notifications-dispatcher-service -Exposes API endpoints to handle integrations. -Handles incoming notification messages and uses the relevant channels(email, slack...) to notify relevant users. -#### cloud-spaceroom-service -Exposes API endpoints to fetch and store relations between agents, nodes, spaces, users, and rooms. -Acts as a provider of authorization for other cloud endpoints. -Exposes API endpoints to authenticate agents connecting to the cloud. - -## Infrastructure Diagram - - - -### If you have any questions or suggestions please contact the Netdata team. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/troubleshooting-onprem.md b/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/troubleshooting-onprem.md deleted file mode 100644 index 4f449c965..000000000 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud-onprem/troubleshooting-onprem.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,21 +0,0 @@ -# Basic troubleshooting -We cannot predict how your particular installation of Netdata Cloud On-prem is going to work. It is a mixture of underlying infrastructure, the number of agents, and their topology. -You can always contact the Netdata team for recommendations! - -#### Loading charts takes a long time or ends with an error -Charts service is trying to collect the data from all of the agents in question. If we are talking about the overview screen, all of the nodes in space are going to be queried (`All nodes` room). If it takes a long time, there are a few things that should be checked: -1. How many nodes are you querying directly? - There is a big difference between having 100 nodes connected directly to the cloud compared to them being connected through a few parents. Netdata always prioritizes querying nodes through parents. This way, we can reduce some of the load by pushing the responsibility to query the data to the parent. The parent is then responsible for passing accumulated data from nodes connected to it to the cloud. -1. If you are missing data from endpoints all the time. - Netdata Cloud always queries nodes themselves for the metrics. The cloud only holds information about metadata, such as information about what charts can be pulled from any node, but not the data points themselves for any metric. This means that if a node is throttled by the network connection or under high resource pressure, the information exchange between the agent and cloud through the MQTT broker might take a long time. In addition to checking resource usage and networking, we advise using a parent node for such endpoints. Parents can hold the data from nodes that are connected to the cloud through them, eliminating the need to query those endpoints. -1. Errors on the cloud when trying to load charts. - If the entire data query is crashing and no data is displayed on the UI, it could indicate problems with the `cloud-charts-service`. The query you are performing might simply exceed the CPU and/or memory limits set on the deployment. We advise increasing those resources. -It takes a long time to load anything on the Cloud UI -When experiencing sluggishness and slow responsiveness, the following factors should be checked regarding the Postgres database: - 1. CPU: Monitor the CPU usage to ensure it is not reaching its maximum capacity. High and sustained CPU usage can lead to sluggish performance. - 1. Memory: Check if the database server has sufficient memory allocated. Inadequate memory could cause excessive disk I/O and slow down the database. - 1. Disk Queue / IOPS: Analyze the disk queue length and disk I/O operations per second (IOPS). A high disk queue length or limited IOPS can indicate a bottleneck and negatively impact database performance. -By examining these factors and ensuring that CPU, memory, and disk IOPS are within acceptable ranges, you can mitigate potential performance issues with the Postgres database. - -#### Nodes are not updated quickly on the Cloud UI -If you're experiencing delays with information exchange between the Cloud UI and the Agent, and you've already checked the networking and resource usage on the agent side, the problem may be related to Apache Pulsar or the database. Slow alerts on node alerts or slow updates on node status (online/offline) could indicate issues with message processing or database performance. You may want to investigate the performance of Apache Pulsar, ensure it is properly configured, and consider scaling or optimizing the database to handle the volume of data being processed or written to it. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md index acf8e42fa..6a2406aeb 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/README.md @@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ Netdata Cloud provides the following features, on top of what the Netdata agents Netdata Cloud is a fundamental component for achieving an optimal cost structure and flexibility, in structuring observability the way that is best suited for each case. -2. **Role Based Access Control (RBAC)**: Netdata Cloud has all the mechanisms for user-management and access control. It allows assigning all users a role, segmenting the infrastructure into rooms, and associating rooms with roles and users. +2. **Role Based Access Control (RBAC)**: Netdata Cloud has all the mechanisms for user-management and access control. It allows assigning all users a role, segmenting the infrastructure into rooms, and associating Rooms with roles and users. 3. **Access from anywhere**: Netdata agents are installed on-prem and this is where all your data are always stored. Netdata Cloud allows querying all the Netdata agents (Standalone, Children and Parents) in real-time when dashboards are accessed via Netdata Cloud. @@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Netdata Cloud provides the following features, on top of what the Netdata agents Custom dashboards are created directly from the UI, without the need for learning a query language. Netdata Cloud provides all the APIs to the Netdata dashboards to store, browse and retrieve custom dashboards created by all users. -6. **Advanced Customization**: Netdata Cloud provides all the APIs for the dashboard to have different default settings per space, per room and per user, allowing administrators and users to customize the Netdata dashboards and charts the way they see fit. +6. **Advanced Customization**: Netdata Cloud provides all the APIs for the dashboard to have different default settings per space, per Room and per user, allowing administrators and users to customize the Netdata dashboards and charts the way they see fit. ## Data Exposed to Netdata Cloud @@ -113,9 +113,9 @@ However, when there are multiple Netdata agents involved, the queries will be fa No. Any or all Netdata agents can be connected to Netdata Cloud. -We recommend to create [observability centralization points](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md), as required for operational efficiency (ephemeral nodes, teams or services isolation, central control of alerts, production systems performance), security policies (internet isolation), or cost optimization (use existing capacities before allocating new ones). +We recommend to create [observability centralization points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/README.md), as required for operational efficiency (ephemeral nodes, teams or services isolation, central control of alerts, production systems performance), security policies (internet isolation), or cost optimization (use existing capacities before allocating new ones). -We suggest to review the [Best Practices for Observability Centralization Points](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/best-practices.md). +We suggest to review the [Best Practices for Observability Centralization Points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/best-practices.md). ## When I have Netdata Parents, do I need to connect Netdata Children to Netdata Cloud too? @@ -129,6 +129,6 @@ Netdata Cloud prefers: - The most distant (from the Child) Parent available, when doing metrics visualization queries (since usually these Parents have been added for this purpose). -- The closest (to the Child) Parent available, for [Top Monitoring](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md) (since top-monitoring provides live data, like the processes running, the list of sockets open, etc). The streaming protocol of Netdata Parents and Children is able to forward such requests to the right child, via the Parents, to respond with live and accurate data. +- The closest (to the Child) Parent available, for [Top Monitoring](/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md) (since top-monitoring provides live data, like the processes running, the list of sockets open, etc). The streaming protocol of Netdata Parents and Children is able to forward such requests to the right child, via the Parents, to respond with live and accurate data. Netdata Children may be connected to Netdata Cloud for high-availability, in case the Netdata Parents are unreachable. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/README.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/README.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..5eb7acf24 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/README.md @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ +# Authentication & Authorization + +This section contains documentation about how Netdata allows users to Authenticate with Netdata Cloud, as well as the Authorization flows that control the access and actions of their teammates in Netdata Cloud. + +## Authentication + +### Email + +To sign in/sign up using email, visit [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=spaces?utm_source=docs&utm_content=sign_in_button_email_section), enter your email address, and click the **Sign in by email** button. + +Click the **Verify** button in the email you received to start using Netdata Cloud. + +### Google and GitHub OAuth + +When you use Google/GitHub OAuth, your Netdata Cloud account is associated with the email address that Netdata Cloud receives through OAuth. + +To sign in/sign up using Google or GitHub OAuth, visit [Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud/sign-in?cloudRoute=spaces?utm_source=docs&utm_content=sign_in_button_google_github_section) select the method you want to use. After the verification steps, you will be signed in to Netdata Cloud. + +### Enterprise SSO Authentication + +Netdata integrates with SSO tools, allowing you to control how your team connects and authenticates to Netdata Cloud. + +For more information, see [Enterprise SSO Authentication](/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/enterprise-sso-authentication.md). + +## Authorization + +Once logged in, you can manage role-based access in your space to give each team member the appropriate role. For more information, see [Role-Based Access model](/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md). diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/api-tokens.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/api-tokens.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..88b73ee68 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/api-tokens.md @@ -0,0 +1,34 @@ +# API Tokens + +## Overview + +Every single user can get access to the Netdata resource programmatically. It is done through the API Token which +can be also called as Bearer Token. This token is used for authentication and authorization, it can be issued +in the Netdata UI under the user Settings: + +<img width="316" alt="image" src="https://github.com/netdata/netdata/assets/14999928/b0846076-afae-47ab-92df-c24967305ab9"/> + +The API Tokens are not going to expire and can be limited to a few scopes: + +* `scope:all` + + this token is given the same level of action as the user has, the use-case for it is Netdata terraform provider + +* `scope:agent-ui` + + this token is mainly used by the local Netdata agent accessing the Cloud UI + +* `scope:grafana-plugin` + + this token is used for the [Netdata Grafana plugin](https://github.com/netdata/netdata-grafana-datasource-plugin/blob/master/README.md) + to access Netdata charts + +Currently, the Netdata Cloud is not exposing stable API. + +## Example usage + +* get the cloud space list + +```console +$ curl -H 'Accept: application/json' -H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" https://app.netdata.cloud/api/v2/spaces +``` diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/enterprise-sso-authentication.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/enterprise-sso-authentication.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..7657e8bcf --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/enterprise-sso-authentication.md @@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ +# Enterprise SSO Authentication + +Netdata provides you with means to streamline and control how your team connects and authenticates to Netdata Cloud. We provide + diferent Single Sign-On (SSO) integrations that allow you to connect with the tool that your organization is using to manage your + user accounts. + + > ❗ This feature focus is on the Authentication flow, it doesn't support the Authorization with managing Users and Roles. + + +## How to set it up? + +If you want to setup your Netdata Space to allow user Authentication through an Enterprise SSO tool you need to: +* Confirm the integration to the tool you want is available ([Authentication integations](https://learn.netdata.cloud/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-&-authorization/cloud-authentication-&-authorization-integrations)) +* Have a Netdata Cloud account +* Have Access to the Space as an administrator +* Your Space needs to be on the Business plan or higher + +Once you ensure the above prerequisites you need to: +1. Click on the Space settings cog (located above your profile icon) +2. Click on the Authentication tab +3. Select the card for the integration you are looking for, click on Configure +4. Fill the required attributes need to establish the integration with the tool + + +## How to authenticate to Netdata? + +### From Netdata Sign-up page + +If you're starting your flow from Netdata sign-in page you need to: +1. Click on the link `Sign-in with an Enterprise Signle Sign-On (SSO)` +2. Enter your email address +3. Go to your mailbox and check the `Sign In to Nedata` email that you have received +4. Click on the **Sign In** button + +Note: If you're not authenticated on the Enterprise SSO tool you'll be prompted to authenticate there +first before being allowed to proceed to Netdata Cloud. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..d2a3ea4f2 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/authentication-and-authorization/role-based-access-model.md @@ -0,0 +1,156 @@ +# Role-Based Access model + +Netdata Cloud's role-based-access mechanism allows you to control what functionalities in the app users can access. Each user can be assigned only one role, which fully specifies all the capabilities they are afforded. + +## What roles are available? + +With the advent of the paid plans we revamped the roles to cover needs expressed by Netdata users, like providing more limited access to their customers, or +being able to join any Room. We also aligned the offered roles to the target audience of each plan. The end result is the following: + +| **Role** | **Community** | **Homelab** | **Business** | **Enterprise On-Premise** | +|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------------------|:-------------------|:-------------------|:--------------------------| +| **Admins**<p>Users with this role can control Spaces, Rooms, Nodes, Users and Billing.</p><p>They can also access any Room in the Space.</p> | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| **Managers**<p>Users with this role can manage Rooms and Users.</p><p>They can access any Room in the Space.</p> | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| **Troubleshooters**<p>Users with this role can use Netdata to troubleshoot, not manage entities.</p><p>They need to be assigned to Rooms in the Space.</p> | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| **Observers**<p>Users with this role can only view data in specific Rooms.</p>💡 Ideal for restricting your customer's access to their own dedicated rooms.<p></p> | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| **Billing**<p>Users with this role can handle billing options and invoices.</p> | - | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| **Member** ⚠️ Legacy role<p>Users with this role you can create Rooms and invite other Members.</p><p>They can only see the Rooms they belong to and all Nodes in the All Nodes Room.</p> | - | - | - | - | + +## Which functionalities are available for each role? + +In more detail, you can find on the following tables which functionalities are available for each role on each domain. + +### Space Management + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | +|:-----------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:| +| See Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Leave Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Delete Space | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | +| Change name | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | +| Change description | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | +| Change slug | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | +| Change preferred nodes | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | + +### Node Management + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:------------------------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:|:-------------------------------------------| +| See all Nodes in Space (_All Nodes_ Room) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | Members are always on the _All Nodes_ Room | +| Connect Node to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | - | +| Delete Node from Space | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | - | + +### User Management + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:-----------------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| See all Users in Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Invite new User to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | You can't invite a user with a role you don't have permissions to appoint to (see below) | +| Delete Pending Invitation to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Delete User from Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | You can't delete a user if he has a role you don't have permissions to appoint to (see below) | +| Appoint Administrators | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | +| Appoint Billing user | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | +| Appoint Managers | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Appoint Troubleshooters | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Appoint Observer | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Appoint Member | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | Only available on Early Bird plans | +| See all Users in a Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Invite existing user to Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | User already invited to the Space | +| Remove user from Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | + +### Room Management + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:-----------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| See all Rooms in a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Join any Room in a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | By joining a Room you will be enabled to get notifications from nodes on that Room | +| Leave Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Create a new Room in a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Delete Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Change Room name | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | If not the _All Nodes_ Room | +| Change Room description | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Add existing Nodes to Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | Node already connected to the Space | +| Remove Nodes from Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | + +### Notifications Management + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| See all configured notifications on a Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Add new configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | +| Enable/Disable configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | +| Edit configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | Some exceptions apply depending on [service level](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#available-actions-per-notification-method-based-on-service-level) | +| Delete configuration | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | | +| Edit personal level notification settings | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | [Manage user notification settings](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/manage-notification-methods.md#manage-user-notification-settings) | +| See space alert notification silencing rules | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | | +| Add new space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Enable/Disable space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Edit space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| Delete space alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | | +| See, add, edit or delete personal level alert notification silencing rule | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | | + +> **Note** +> +> Enable, Edit and Add actions over specific notification methods will only be allowed if your plan has access to those ([service classification](/docs/alerts-and-notifications/notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications/centralized-cloud-notifications-reference.md#service-classification)) + +### Dashboards + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | +|:-----------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:| +| See all dashboards in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Add new dashboard to Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Edit any dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Edit own dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Delete any dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Delete own dashboard in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | + +### Functions + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:-------------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------| +| See all functions in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Run any function in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| Run read-only function in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| Run sensitive function in Room | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | There isn't any function on this category yet, so subject to change. | + +### Events feed + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:-----------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:|:-----------------------------------------------| +| See Alert or Topology events | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | | +| See Auditing events | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | These are coming soon, not currently available | + +### Billing + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | Notes | +|:---------------------------|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:|:------------:|:------------------:|:----------:|:----------------------------------------------------------------| +| See Plan & Billing details | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | Current plan and usage figures | +| Update plans | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | - | This includes cancelling current plan (going to Community plan) | +| See invoices | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | | +| Manage payment methods | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | | +| Update billing email | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | - | | + +### Dynamic Configuration Manager + +Netdata Cloud paid subscription required for all action except "List All". + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | +|:--------------------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:| +| List All (see all configurable items) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Enable/Disable | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| Add | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| Update | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| Remove | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| Test | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| View | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | +| View File Format | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | - | - | + +### Other permissions + +| **Functionality** | **Admin** | **Manager** | **Troubleshooter** | **Observer** | **Billing** | **Member** | +|:---------------------------|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:------------------:|:-----------:|:------------------:| +| See Bookmarks in Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Add Bookmark to Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Delete Bookmark from Space | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| See Visited Nodes | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | +| Update Visited Nodes | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | - | :heavy_check_mark: | diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md index 29601686d..49373c454 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md @@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ flowchart TD users --> ingress agents --> ingress ingress --> traefik - traefik ==>|agents<br/>websockets| emqx + ingress ==>|agents<br/>websockets| emqx traefik -.- auth traefik ==>|http| spaceroom traefik ==>|http| frontend diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/installation.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/installation.md index a02033c24..259ddb5ce 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/installation.md +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/installation.md @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ # Netdata Cloud On-Prem Installation -This installation guide assumes the prerequisites for installing Netdata Cloud On-Prem as satisfied. For more information please refer to the [requirements documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md#requirements). +This installation guide assumes the prerequisites for installing Netdata Cloud On-Prem as satisfied. For more information please refer to the [requirements documentation](/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md#requirements). ## Installation Requirements @@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ aws configure Using `aws` command we will generate a token for helm to access the secured ECR repository: ```bash -aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | helm registry login --username AWS --password-stdin 362923047827.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/netdata-cloud-onprem +aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | helm registry login --username AWS --password-stdin 362923047827.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com ``` After this step you should be able to add the repository to your helm or just pull the helm chart: diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/troubleshooting.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/troubleshooting.md index c330984ae..ac8bdf6f8 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/troubleshooting.md +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/troubleshooting.md @@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ The following are questions that are usually asked by Netdata Cloud On-Prem oper ## Loading charts takes a long time or ends with an error -The charts service is trying to collect data from the agents involved in the query. In most of the cases, this microservice queries many agents (depending on the room), and all of them have to reply for the query to be satisfied. +The charts service is trying to collect data from the agents involved in the query. In most of the cases, this microservice queries many agents (depending on the Room), and all of them have to reply for the query to be satisfied. One or more of the following may be the cause: diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..05538a916 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/organize-your-infrastructure-invite-your-team.md @@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ +# Organize Your Infrastructure and Invite your Team + +Netdata Cloud works with [Spaces](#netdata-cloud-spaces) and [Rooms](#netdata-cloud-rooms). They allow you to better organize your infrastructure and provide the right access to your team. + +## Netdata Cloud Spaces + +A Space is a high-level container. It's a collaboration environment where you can organize team members, access levels and the nodes you want to monitor. + +### How to organize your Netdata Cloud Environment + +You can use any number of Spaces you want, but as you organize your Cloud experience, keep in mind that you can only add any given node to a **single** Space. + +We recommend sticking to a single Space so that you can keep all your nodes and their respective metrics in one place. You can then use multiple [Rooms](#netdata-cloud-rooms) to further organize your infrastructure monitoring. + +### Navigate between Spaces + +You can navigate through your different Spaces by using the left-most bar of the interface. From there you can also create a new Space by clicking the plus **+** icon. + + + +### Manage Spaces + +Manage your spaces by selecting a particular space and clicking on the gear icon in the lower left-hand corner. This will open the Space's settings view, where you can take a multitude of actions regarding the Space's Rooms, nodes, integrations, configurations, and more. + +## Netdata Cloud Rooms + +Spaces use Rooms to organize your connected nodes and provide infrastructure-wide dashboards using real-time metrics and visualizations. + +**A node can be in N Rooms.** + +Once you add nodes to a Space, all of your nodes will be visible in the **All nodes** Room. It gives you an overview of all of your nodes in this particular Space. Then you can create functional separations of your nodes into more Rooms. Every Room has its own dashboards, navigation, indicators, and management tools. + +### Room organization + +We recommend a few strategies for organizing your Rooms. + +- **Service, purpose, location, etc.** + You can group Rooms by a service (Nginx, MySQL, Pulsar, and so on), their purpose (webserver, database, application), their physical location, whether they're "bare metal" or a Docker container, the PaaS/cloud provider it runs on, and much more. This allows you to see entire slices of your infrastructure by moving from one Room to another. + +- **End-to-end apps/services** + If you have a user-facing SaaS product, or an internal service that this said product relies on, you may want to monitor that entire stack in a single Room. This might include Kubernetes clusters, Docker containers, proxies, databases, web servers, brokers, and more. End-to-end Rooms are valuable tools for ensuring the health and performance of your organization's essential services. + +- **Incident response** + You can also create new Rooms as one of the first steps in your incident response process. For example, you have a user-facing web app that relies on Apache Pulsar for a message queue, and one of your nodes using the [Pulsar collector](/src/go/plugin/go.d/modules/pulsar/README.md) begins reporting a suspiciously low messages rate. You can create a Room called `$year-$month-$day-pulsar-rate`, add all your Pulsar nodes in addition to nodes they connect to, and begin diagnosing the root cause in a Room optimized for getting to resolution as fast as possible. + +### Add Rooms + +To add new Rooms to any Space, click on the green plus icon **+** next to the **Rooms** heading on the Room's sidebar. + +### Manage Rooms + +All the users and nodes involved in a particular Space can be part of a Room. + +Click on the gear icon next to the Room's name in the top of the page to do that. This will open the Rooms settings view, where you can take the same actions as with the Spaces settings, but now catered towards the specific Room. + +## Invite your team + +Invite your entire SRE, DevOPs, or ITOps team to your Space, to give everyone access into your infrastructure from a single pane of glass. + +To do so, click on **Invite Users** in the [Space](#netdata-cloud-spaces) management area or any other such prompt around the UI. + +Follow the instructions on screen, to provide the right access and role to the users you want to invite. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/versions.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/versions.md index 1031aa76a..06a8f706a 100644 --- a/docs/netdata-cloud/versions.md +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/versions.md @@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ For more information check our [Pricing](https://www.netdata.cloud/pricing/) pag ## On-Prem Version -To deploy Netdata Cloud On-premises, take a look at the [related section](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md) on our Documentation. +To deploy Netdata Cloud On-premises, take a look at the [related section](/docs/netdata-cloud/netdata-cloud-on-prem/README.md) on our Documentation. diff --git a/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md b/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..2b1a34225 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md @@ -0,0 +1,121 @@ +# Netdata Plans & Billing + +Netdata offers a **Community plan**, a free SaaS and Open Source Agent, and paid subscriptions — **Homelab**, **Business**, and **Enterprise On-Premise** — providing key business features and unlimited access to your dashboards. + +For more info visit the [Netdata Cloud Pricing](https://netdata.cloud/pricing) page. + +## Plans + +Plans define the features and customization options available within a Space. Different Spaces can have different plans, giving you flexibility based on your needs. + +Netdata Cloud plans (excluding Community) involve: + +- A yearly flat fee for [committed nodes](#committed-nodes) +- An on-demand metered component based on the [number of running nodes](#running-nodes-and-billing) + +Billing options include monthly (pay-as-you-go) and yearly (annual prepayment). + +### Technical Details + +#### Running Nodes and Billing + +Billing is based solely on active nodes, excluding offline or stale instances. Daily and P90 metrics ensure fair pricing by mitigating transient increases in node activity. + +#### Committed Nodes + +Yearly plans offer a discounted rate for a pre-defined number of committed nodes. Any usage exceeding this commitment will be billed at the standard rate. + +#### Plan Changes and Credit Balance + +You can change your plan, billing frequency, or committed nodes at any time. For guidance, see [updating your plan](#update-a-subscription-plan). + +> **Note** +> +> - Changes like downgrades or cancellations keep notification configurations active for 24 hours. After that, any methods not supported by the new plan are disabled. +> - Changes may restrict user access in your Space. Review role availability under [each plan](https://netdata.cloud/pricing). +> - Any credits are valid until the end of the following year. + +#### Areas That Change Upon Subscription + +Please refer to the [Netdata Cloud Pricing](https://netdata.cloud/pricing) page for more information on what each plan provides. + +## View Plan and Billing Information + +### Prerequisites + +- A Netdata Cloud account +- Admin or Billing user access to the Space + +### Steps + +#### View Current Plan, Billing Options, and Invoices + +1. Navigate to **Space settings** (the cog above your profile icon). +2. Select the **Plan & Billing** tab. +3. You'll see: + - **Credit** amount, if applicable, usable for future invoices or subscription changes. More on this at [Plan changes and credit balance](/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md#plan-changes-and-credit-balance). + - **Billing email** linked to your subscription, where all related notifications are sent. + - A link to the **Billing options and Invoices** in our billing provider's Customer Portal, where you can: + - Manage subscriptions and payment methods. + - Update billing information such as email, address, phone number, and Tax ID. + - View invoice history. + - The **Change plan** button, showing details of your current plan with options to upgrade or cancel. + - Your **Usage chart**, displaying daily and period counts of live nodes and how they relate to your billing. + +#### Update a Subscription Plan + +1. In the **Plan & Billing** tab, click **Change plan** to see: + - Billing frequency and committed nodes (if applicable). + - Current billing information, which must be updated through our billing provider's Customer Portal via **Change billing info and payment method** link. + - Options to enter a promotion code and a breakdown of charges, including subscription total, applicable discounts, credit usage, tax details, and total payable amount. + +> **Note** +> +> - Checkout is performed directly if there's an active plan. +> - Plan changes, including downgrades or cancellations, may impact notification settings or user access. More details at [Plan changes and credit balance](/docs/netdata-cloud/view-plan-and-billing.md#plan-changes-and-credit-balance). + +## FAQ + +### What Payment Methods are Accepted? + +Netdata accepts most major Credit/Debit Cards and Bank payments through Stripe and AWS, with more options coming soon. + +### What Happens if a Renewal Payment Fails? + +If payment fails, attempts will be made weekly for 15 days. After three unsuccessful attempts, your Space will switch to the **Community** plan. Notification methods not supported by the Community plan will be disabled after 24 hours. + +### Which Currencies Do You Support? + +Currently, we accept US Dollars (USD). Plans to accept Euros (EUR) are in the works but without a set timeline. + +### Can I Get a Refund? + +Refunds are available if you cancel your subscription within 14 days of purchase. Request a refund via [billing@netdata.cloud](mailto:billing@netdata.cloud). + +### How Do I Cancel My Paid Plan? + +Cancel your plan anytime from the **Plan & Billing** section by selecting 'Cancel Plan' or switching to the **Community** plan. + +### How Can I Access My Invoices/Receipts? + +Find all your invoicing history under _Billing Options & Invoices_ in the **Plan & Billing** section. + +### Why Do I See Two Separate Invoices? + +Two invoices are generated per plan purchase or renewal: + +- One for recurring fees of the chosen plan. +- Another for monthly "On-Demand - Usage" based on actual usage. + +### How is the **Total Before Tax** Value Calculated on Plan Changes? + +The total before tax is calculated by: + +1. Calculating the residual value from unused time on your current plan. +2. Deducting any applicable discounts. +3. Subtracting credit from your balance, if necessary. +4. Applying tax to the final amount, if positive. Negative results adjust your customer credit balance. + +> **Note** +> +> A move to single-invoice billing is expected in the future, although a specific timeline is not set. diff --git a/docs/netdata-for-IoT.md b/docs/netdata-for-IoT.md deleted file mode 100644 index 8dfed21eb..000000000 --- a/docs/netdata-for-IoT.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,78 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "Netdata for IoT" -custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/netdata-for-IoT.md -sidebar_label: "Netdata for IoT" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_rel_path: "Miscellaneous" ---> - -# Netdata for IoT - - - -> New to Netdata? Check its demo: **<https://my-netdata.io/>** -> ->[](https://registry.my-netdata.io/#netdata_registry) -> [](https://registry.my-netdata.io/#netdata_registry) -> [](https://registry.my-netdata.io/#netdata_registry) -> ->[](https://registry.my-netdata.io/#netdata_registry) -> [](https://registry.my-netdata.io/#netdata_registry) -> [](https://registry.my-netdata.io/#netdata_registry) - ---- - -Netdata is a [very efficient](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/configure/performance.md) -server performance monitoring solution. When running in server hardware, it can collect -thousands of system and application metrics **per second** with just 1% CPU utilization of a single core. Its web server -responds to most data requests in about **half a millisecond** making its web dashboards spontaneous, amazingly fast! - -Netdata can also be a very efficient real-time monitoring solution for **IoT devices** (RPIs, routers, media players, -wifi access points, industrial controllers and sensors of all kinds). Netdata will generally run everywhere a Linux -kernel runs (and it is glibc and [musl-libc](https://www.musl-libc.org/) friendly). - -You can use it as both a data collection agent (where you pull data using its API), for embedding its charts on other -web pages / consoles, but also for accessing it directly with your browser to view its dashboard. - -The Netdata web API already provides **reduce** functions allowing it to report **average** and **max** for any -timeframe. It can also respond in many formats including JSON, JSONP, CSV, HTML. Its API is also a **google charts** -provider so it can directly be used by google sheets, google charts, google widgets. - - - -Although Netdata has been significantly optimized to lower the CPU and RAM resources it consumes, the plethora of data -collection plugins may be inappropriate for weak IoT devices. Please follow -the [Netdata Agent performance guide](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/guides/configure/performance.md) - -## Monitoring RPi temperature - -The python version of the sensors plugin uses `lm-sensors`. Unfortunately the temperature reading of RPi are not -supported by `lm-sensors`. - -Netdata also has a bash version of the sensors plugin that can read RPi temperatures. It is disabled by default to avoid -the conflicts with the python version. - -To enable it, run: - -```bash -cd /etc/netdata # Replace this path with your Netdata config directory -sudo ./edit-config charts.d.conf -``` - -and uncomment this line: - -```sh -sensors=force -``` - -Then restart Netdata. You will get this: - - - - diff --git a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md index 0efdacd41..812b493d7 100644 --- a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md +++ b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/README.md @@ -45,4 +45,4 @@ A Cluster is configured as a number of circular **Proxies**, ie. each of the nod ## Best Practices -Refer to [Best Practices for Observability Centralization Points](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/best-practices.md). +Refer to [Best Practices for Observability Centralization Points](/docs/observability-centralization-points/best-practices.md). diff --git a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/clustering-and-high-availability-of-netdata-parents.md b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/clustering-and-high-availability-of-netdata-parents.md index d2202960f..17a10b02e 100644 --- a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/clustering-and-high-availability-of-netdata-parents.md +++ b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/clustering-and-high-availability-of-netdata-parents.md @@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ Netdata Children need to maintain a retention only for the time required to swit ## Restoring a Netdata Parent after maintenance -Given the [replication limitations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/replication-of-past-samples.md#replication-limitations), special care is needed when restoring a Netdata Parent after some long maintenance work on it. +Given the [replication limitations](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/replication-of-past-samples.md#replication-limitations), special care is needed when restoring a Netdata Parent after some long maintenance work on it. If the Netdata Children do not have enough retention to replicate the missing data on this Netdata Parent, it is preferable to block access to this Netdata Parent from the Netdata Children, until it replicates the missing data from the other Netdata Parents. diff --git a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/configuration.md b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/configuration.md index e52f7309f..bf2aa98db 100644 --- a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/configuration.md +++ b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/configuration.md @@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ To enable the reception of metrics from Netdata Children, generate a random API uuidgen ``` -Then, copy the UUID generated, [edit `stream.conf`](#edit-stream.conf), find the section that reads like the following and replace `API_KEY` with the UUID you generated: +Then, copy the UUID generated, [edit `stream.conf`](#edit-streamconf), find the section that reads like the following and replace `API_KEY` with the UUID you generated: ```ini [API_KEY] @@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Save the file and restart Netdata. ## Configuring Netdata Children -To enable streaming metrics to a Netdata Parent, [edit `stream.conf`](#edit-stream.conf), and at the `[stream]` section at the top, set: +To enable streaming metrics to a Netdata Parent, [edit `stream.conf`](#edit-streamconf), and at the `[stream]` section at the top, set: ```ini [stream] @@ -61,11 +61,11 @@ While encrypting the connection between your parent and child nodes is recommend This example uses self-signed certificates. > **Note** -> This section assumes you have read the documentation on [how to edit the Netdata configuration files](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/configuration.md). +> This section assumes you have read the documentation on [how to edit the Netdata configuration files](/docs/netdata-agent/configuration/README.md). <!-- here we need link to the section that will contain the restarting instructions --> 1. **Parent node** - To generate an SSL key and certificate using `openssl`, take a look at the related section around [Securing Netdata Agents](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/web/server/README.md#enable-httpstls-support) in our Documentation. + To generate an SSL key and certificate using `openssl`, take a look at the related section around [Securing Netdata Agents](/src/web/server/README.md#enable-httpstls-support) in our Documentation. 2. **Child node** Update `stream.conf` to enable SSL/TLS and allow self-signed certificates. Append ':SSL' to the destination and uncomment 'ssl skip certificate verification'. diff --git a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/faq.md b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/faq.md index 3c019108c..027dfc748 100644 --- a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/faq.md +++ b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/faq.md @@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ Netdata Parents generally scale well. According [to our tests](https://blog.netdata.cloud/netdata-vs-prometheus-performance-analysis/) Netdata Parents scale better than Prometheus for the same workload: -35% CPU utilization, -49% Memory Consumption, -12% Network Bandwidth, -98% Disk I/O, -75% Disk footprint. -For more information, Check [Sizing Netdata Parents](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/sizing-netdata-parents.md). +For more information, Check [Sizing Netdata Parents](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/sizing-netdata-parents.md). ## If I set up a parents cluster, will I be able to have more Child nodes stream to them? @@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ Yes. Function requests will be received by the Parents and forwarded to the Chil ## If I have a cluster of parents and get one out for maintenance for a few hours, will it have missing data when it returns back online? -Check [Restoring a Netdata Parent after maintenance](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/clustering-and-high-availability-of-netdata-parents.md). +Check [Restoring a Netdata Parent after maintenance](/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/clustering-and-high-availability-of-netdata-parents.md). ## I have a cluster of parents. Which one is used by Netdata Cloud? diff --git a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/sizing-netdata-parents.md b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/sizing-netdata-parents.md index 79b223348..edfbabe93 100644 --- a/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/sizing-netdata-parents.md +++ b/docs/observability-centralization-points/metrics-centralization-points/sizing-netdata-parents.md @@ -1,3 +1,3 @@ # Sizing Netdata Parents -To estimate CPU, RAM, and disk requirements for your Netdata Parents, check [sizing Netdata agents](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/README.md). +To estimate CPU, RAM, and disk requirements for your Netdata Parents, check [sizing Netdata agents](/docs/netdata-agent/sizing-netdata-agents/README.md). diff --git a/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md b/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md deleted file mode 100644 index 267122832..000000000 --- a/docs/quickstart/infrastructure.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,226 +0,0 @@ -import { Grid, Box, BoxList, BoxListItemRegexLink } from '@site/src/components/Grid/' -import { RiExternalLinkLine } from 'react-icons/ri' - -# Monitor your infrastructure - -Learn how to view key metrics, insightful charts, and active alerts from all your nodes, with Netdata Cloud's real-time infrastructure monitoring. - -[Netdata Cloud](https://app.netdata.cloud) provides scalable infrastructure monitoring for any number of distributed -nodes running the Netdata Agent. A node is any system in your infrastructure that you want to monitor, whether it's a -physical or virtual machine (VM), container, cloud deployment, or edge/IoT device. - -The Netdata Agent uses zero-configuration collectors to gather metrics from every application and container instantly, -and uses Netdata's distributed data architecture to store metrics -locally. Without a slow and troublesome centralized data lake for your infrastructure's metrics, you reduce the -resources you need to invest in, and the complexity of, monitoring your infrastructure. - -Netdata Cloud unifies infrastructure monitoring by _centralizing the interface_ you use to query and visualize your -nodes' metrics, not the data. By streaming metrics values to your browser, with Netdata Cloud acting as the secure proxy -between them, you can monitor your infrastructure using customizable, interactive, and real-time visualizations from any -number of distributed nodes. - -In this quickstart guide, you'll learn the basics of using Netdata Cloud to monitor an infrastructure with dashboards, -composite charts, and alert viewing. You'll then learn about the most critical ways to configure the Agent on each of -your nodes to maximize the value you get from Netdata. - -This quickstart assumes you've [installed Netdata](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/packaging/installer/README.md) -on more than one node in your infrastructure, and connected those nodes to your Space in Netdata Cloud. - -## Set up your Netdata Cloud experience - -Start your infrastructure monitoring experience by setting up your Netdata Cloud account. - -### Organize Spaces and War Rooms - -Spaces are high-level containers to help you organize your team members and the nodes they can view in each War Room. -You already have at least one Space in your Netdata Cloud account. - -A single Space puts all your metrics in one easily-accessible place, while multiple Spaces creates logical division -between different users and different pieces of a large infrastructure. For example, a large organization might have one -SRE team for the user-facing SaaS application, and a second IT team for managing employees' hardware. Since these teams -don't monitor the same nodes, they can work in separate Spaces and then further organize their nodes into War Rooms. - -Next, set up War Rooms. Netdata Cloud creates dashboards and visualizations based on the nodes added to a given War -Room. You can [organize War Rooms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#war-room-organization) in any way -you want, such as by the application type, for end-to-end application monitoring, or as an incident response tool. - -Learn more about [Spaces](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces) and [War -Rooms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms), including how to manage each, in their respective reference -documentation. - -### Invite your team - -Netdata Cloud makes an infrastructure's real-time metrics available and actionable to all organization members. By -inviting others, you can better synchronize with your team or colleagues to understand your infrastructure's heartbeat. -When something goes wrong, you'll be ready to collaboratively troubleshoot complex performance problems from a single -pane of glass. - -To [invite new users](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team), click on **Invite Users** in the -Space management Area. Choose which War Rooms to add this user to, then click **Send**. - -If your team members have trouble signing in, direct them to the [Netdata Cloud sign -in](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md) doc. - -### See an overview of your infrastructure - -Netdata Cloud utilizes "tabs" in order to provide you with informative sections based on your infrastructure. -These tabs can be separated into "static", meaning they are by default presented, and "non-static" which are tabs that get presented by user action (e.g clicking on a custom dashboard) - -#### Static tabs - -- The default tab for any War Room is the [Home tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#home), which gives you an overview of this Space. - Here you can see the number of Nodes claimed, data retention statics, users by role, alerts and more. - -- The second and most important tab is the [Overview tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#overview-and-single-node-view) which uses composite charts to display real-time metrics from every available node in a given War Room. - -- The [Nodes tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md) gives you the ability to see the status (offline or online), host details, alert status and also a short overview of some key metrics from all your nodes at a glance. - -- [Kubernetes tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md) is a logical grouping of charts regarding your Kubernetes clusters. It contains a subset of the charts available in the **Overview tab**. - -- The [Dashboards tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md) gives you the ability to have tailored made views of specific/targeted interfaces for your infrastructure using any number of charts from any number of nodes. - -- The [Alerts tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md) provides you with an overview for all the active alerts you receive for the nodes in this War Room, you can also see all the alerts that are configured to be triggered in any given moment. - -- The [Anomalies tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md) is dedicated to the Anomaly Advisor tool. - -- The [Functions tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md) gives you the ability to visualize functions that the Netdata Agent collectors are able to expose. - -- The [Feed & events](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md) tab lets you investigate events that occurred in the past, which is invaluable for troubleshooting. - -#### Dynamic tabs - -If you open a [new dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md), jump to a single-node dashboard, or navigate to a dedicated alert page, a new tab will open in War Room bar. - -Tabs can be rearranged with drag-and-drop or closed with the **X** button. Open tabs persist between sessions, so you can always come right back to your preferred setup. - -### Drill down to specific nodes - -Both the Overview and the Nodes tab offer easy access to **single-node dashboards** for targeted analysis. You can use -single-node dashboards in Netdata Cloud to drill down on specific issues, scrub backward in time to investigate -historical data, and see like metrics presented meaningfully to help you troubleshoot performance problems. - -Read about the process in the [infrastructure -overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md#drill-down-with-single-node-dashboards) doc, then learn about [interacting with -dashboards and charts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) to get the most from all of Netdata's real-time -metrics. - -### Create new dashboards - -You can use Netdata Cloud to create new dashboards that match your infrastructure's topology or help you diagnose -complex issues by aggregating correlated charts from any number of nodes. For example, you could monitor the system CPU -from every node in your infrastructure on a single dashboard. - - - -Read more about [creating new dashboards](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md) for more details about the process and -additional tips on best leveraging the feature to help you troubleshoot complex performance problems. - -## Set up your nodes - -You get the most value out of Netdata Cloud's infrastructure monitoring capabilities if each node collects every -possible metric. For example, if a node in your infrastructure is responsible for serving a MySQL database, you should -ensure that the Netdata Agent on that node is properly collecting and streaming all MySQL-related metrics. - -In most cases, collectors autodetect their data source and require no configuration, but you may need to configure -certain behaviors based on your infrastructure. Or, you may want to enable/configure advanced functionality, such as -longer metrics retention or streaming. - -### Configure the Netdata Agent on your nodes - -You can configure any node in your infrastructure if you need to, although most users will find the default settings -work extremely well for monitoring their infrastructures. - -Each node has a configuration file called `netdata.conf`, which is typically at `/etc/netdata/netdata.conf`. The best -way to edit this file is using the `edit-config` script, which ensures updates to the Netdata Agent do not overwrite -your changes. For example: - -```bash -cd /etc/netdata -sudo ./edit-config netdata.conf -``` - -Our [configuration basics doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md) contains more information about `netdata.conf`, `edit-config`, -along with simple examples to get you familiar with editing your node's configuration. - -After you've learned the basics, you should [secure your infrastructure's nodes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md) using -one of our recommended methods. These security best practices ensure no untrusted parties gain access to the metrics -collected on any of your nodes. - -### Collect metrics from systems and applications - -Netdata has [300+ pre-installed collectors](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/COLLECTORS.md) that gather thousands of metrics with zero -configuration. Collectors search each of your nodes in default locations and ports to find running applications and -gather as many metrics as they can without you having to configure them individually. - -Most collectors work without configuration, should you want more info, you can read more on [how Netdata's metrics collectors work](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/README.md) and the [Collectors configuration reference](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/REFERENCE.md) documentation. - -In addition, find detailed information about which [system](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/system-metrics.md), -[container](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/container-metrics.md), and [application](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/collect/application-metrics.md) metrics you can -collect from across your infrastructure with Netdata. - -## Netdata Cloud features - -<Grid columns="2"> - <Box - title="Spaces and War Rooms"> - <BoxList> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces)" title="Spaces" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms)" title="War Rooms" /> - </BoxList> - </Box> - <Box - title="Dashboards"> - <BoxList> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md)" title="Overview" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md)" title="Nodes tab" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md)" title="Kubernetes" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md)" title="Create new dashboards" /> - </BoxList> - </Box> - <Box - title="Alerts and notifications"> - <BoxList> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md#netdata-cloud)" title="View active alerts" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md)" title="Alert notifications" /> - </BoxList> - </Box> - <Box - title="Troubleshooting with Netdata Cloud"> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md)" title="Metric Correlations" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md)" title="Anomaly Advisor" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md)" title="Events Feed" /> - </Box> - <Box - title="Management and settings"> - <BoxList> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md)" title="Sign in with email, Google, or GitHub" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team)" title="Invite your team" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/themes.md)" title="Choose your Netdata Cloud theme" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md)" title="Role-Based Access" /> - <BoxListItemRegexLink to="[](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md)" title="Paid Plans" /> - </BoxList> - </Box> -</Grid> - -- Spaces and War Rooms - - [Spaces](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-spaces) - - [War Rooms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms) -- Dashboards - - [Overview](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md) - - [Nodes tab](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md) - - [Kubernetes](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/kubernetes.md) - - [Create new dashboards](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md) -- Alerts and notifications - - [View active alerts](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/monitor/view-active-alerts.md#netdata-cloud) - - [Alert notifications](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/alerts-notifications/notifications.md) -- Troubleshooting with Netdata Cloud - - [Metric Correlations](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/metric-correlations.md) - - [Anomaly Advisor](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/anomaly-advisor.md) - - [Events Feed](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/insights/events-feed.md) -- Management and settings - - [Sign in with email, Google, or GitHub](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/sign-in.md) - - [Invite your team](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#invite-your-team) - - [Choose your Netdata Cloud theme](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/themes.md) - - [Role-Based Access](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/role-based-access.md) - - [Paid Plans](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/plans.md) diff --git a/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md b/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md index 2fc6b1263..c6bfd699e 100644 --- a/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md +++ b/docs/security-and-privacy-design/README.md @@ -211,6 +211,36 @@ Business Associate Agreement (BAA), it is ultimately the responsibility of the h compliance across all of their operations. Entities should always consult with a legal expert or a HIPAA compliance consultant to ensure that their use of any product, including Netdata, aligns with HIPAA regulations. +## SOC 2 Compliance + +Service Organization Control 2 (SOC 2) is a framework for managing data to ensure the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data. Developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), SOC 2 is specifically designed for service providers storing customer data in the cloud. It requires companies to establish and follow strict information security policies and procedures. + +While Netdata is not currently SOC 2 certified, our commitment to security and privacy aligns closely with the principles of SOC 2. Here’s how Netdata's practices resonate with the key components of SOC 2 compliance: + +### Security + +Netdata has implemented robust security measures, including infrastructure as code, TLS termination, DDoS protection, and a security-focused development process. These measures echo the SOC 2 principle of ensuring the security of customer data against unauthorized access and potential threats. + +### Availability + +Netdata's commitment to system monitoring and troubleshooting ensures the availability of our service, consistent with the availability principle of SOC 2. Our infrastructure is designed to be resilient and reliable, providing users with continuous access to our services. + +### Processing Integrity + +Although Netdata primarily focuses on system monitoring and does not typically process customer data in a way that alters it, our commitment to accurate, timely, and valid delivery of services aligns with the processing integrity principle of SOC 2. + +### Confidentiality + +Netdata's measures to protect data—such as data encryption, strict access controls, and data isolation—demonstrate our commitment to confidentiality, ensuring that customer data is accessed only by authorized personnel and for authorized reasons. + +### Privacy + +Aligning with the privacy principle of SOC 2, Netdata adheres to GDPR and CCPA regulations, ensuring the protection and proper handling of personal data. Our privacy policies and practices are transparent, giving users control over their data. + +### Continuous Improvement and Future Considerations + +Netdata is committed to continuous improvement in security and privacy. While we are not currently SOC 2 certified, we understand the importance of this framework and are continuously evaluating our processes and controls against industry best practices. As Netdata grows and evolves, we remain open to pursuing SOC 2 certification or other similar standards to further demonstrate our dedication to data security and privacy. + ## Conclusion In conclusion, Netdata Cloud's commitment to data security and user privacy is paramount. From the careful design of the diff --git a/docs/security-and-privacy-design/netdata-agent-security.md b/docs/security-and-privacy-design/netdata-agent-security.md index 8cb6a9aa2..f441fe850 100644 --- a/docs/security-and-privacy-design/netdata-agent-security.md +++ b/docs/security-and-privacy-design/netdata-agent-security.md @@ -10,6 +10,11 @@ databases, sent to upstream Netdata servers, or archived to external time-series ## User Data Protection +> **Note** +> +> Users are responsible for backing up, recovering, and ensuring their data's availability because Netdata stores data locally on each system due to its decentralized architecture. + + The Netdata Agent is programmed to safeguard user data. When collecting data, the raw data does not leave the host. All plugins, even those running with escalated capabilities or privileges, perform a hard-coded data collection job. They do not accept commands from Netdata, and the original application data collected do not leave the process they are diff --git a/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md b/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md deleted file mode 100644 index 133d6ca26..000000000 --- a/docs/store/change-metrics-storage.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,207 +0,0 @@ -# Change how long Netdata stores metrics - -The Netdata Agent uses a custom made time-series database (TSDB), named the -[`dbengine`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/engine/README.md), to store metrics. - -To see the number of metrics stored and the retention in days per tier, use the `/api/v1/dbengine_stats` endpoint. - -To increase or decrease the metric retention time, you just [configure](#configure-metric-retention) -the number of storage tiers and the space allocated to each one. The effect of these two parameters -on the maximum retention and the memory used by Netdata is described in detail, below. - -## Calculate the system resources (RAM, disk space) needed to store metrics - -### Effect of storage tiers and disk space on retention - -3 tiers are enabled by default in Netdata, with the following configuration: - -``` -[db] - mode = dbengine - - # per second data collection - update every = 1 - - # number of tiers used (1 to 5, 3 being default) - storage tiers = 3 - - # Tier 0, per second data - dbengine multihost disk space MB = 256 - - # Tier 1, per minute data - dbengine tier 1 multihost disk space MB = 128 - dbengine tier 1 update every iterations = 60 - - # Tier 2, per hour data - dbengine tier 2 multihost disk space MB = 64 - dbengine tier 2 update every iterations = 60 -``` - -The default "update every iterations" of 60 means that if a metric is collected per second in Tier 0, then -we will have a data point every minute in tier 1 and every hour in tier 2. - -Up to 5 tiers are supported. You may add, or remove tiers and/or modify these multipliers, as long as the -product of all the "update every iterations" does not exceed 65535 (number of points for each tier0 point). - -e.g. If you simply add a fourth tier by setting `storage tiers = 4` and define the disk space for the new tier, -the product of the "update every iterations" will be 60 \* 60 \* 60 = 216,000, which is > 65535. So you'd need to reduce -the `update every iterations` of the tiers, to stay under the limit. - -The exact retention that can be achieved by each tier depends on the number of metrics collected. The more -the metrics, the smaller the retention that will fit in a given size. The general rule is that Netdata needs -about **1 byte per data point on disk for tier 0**, and **4 bytes per data point on disk for tier 1 and above**. - -So, for 1000 metrics collected per second and 256 MB for tier 0, Netdata will store about: - -``` -256MB on disk / 1 byte per point / 1000 metrics => 256k points per metric / 86400 sec per day ~= 3 days -``` - -At tier 1 (per minute): - -``` -128MB on disk / 4 bytes per point / 1000 metrics => 32k points per metric / (24 hr * 60 min) ~= 22 days -``` - -At tier 2 (per hour): - -``` -64MB on disk / 4 bytes per point / 1000 metrics => 16k points per metric / 24 hr per day ~= 2 years -``` - -Of course double the metrics, half the retention. There are more factors that affect retention. The number -of ephemeral metrics (i.e. metrics that are collected for part of the time). The number of metrics that are -usually constant over time (affecting compression efficiency). The number of restarts a Netdata Agents gets -through time (because it has to break pages prematurely, increasing the metadata overhead). But the actual -numbers should not deviate significantly from the above. - -To see the number of metrics stored and the retention in days per tier, use the `/api/v1/dbengine_stats` endpoint. - -### Effect of storage tiers and retention on memory usage - -The total memory Netdata uses is heavily influenced by the memory consumed by the DBENGINE. -The DBENGINE memory is related to the number of metrics concurrently being collected, the retention of the metrics -on disk in relation with the queries running, and the number of metrics for which retention is maintained. - -The precise analysis of how much memory will be used by the DBENGINE itself is described in -[DBENGINE memory requirements](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/database/engine/README.md#memory-requirements). - -In addition to the DBENGINE, Netdata uses memory for contexts, metric labels (e.g. in a Kubernetes setup), -other Netdata structures/processes (e.g. Health) and system overhead. - -The quick rule of thumb, for a high level estimation is - -``` -DBENGINE memory in MiB = METRICS x (TIERS - 1) x 8 / 1024 MiB -Total Netdata memory in MiB = Metric ephemerality factor x DBENGINE memory in MiB + "dbengine page cache size MB" from netdata.conf -``` - -You can get the currently collected **METRICS** from the "dbengine metrics" chart of the Netdata dashboard. You just need to divide the -value of the "collected" dimension with the number of tiers. For example, at the specific point highlighted in the chart below, 608k metrics -were being collected across all 3 tiers, which means that `METRICS = 608k / 3 = 203667`. - -<img width="988" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/43294513/225335899-a9216ba7-a09e-469e-89f6-4690aada69a4.png" /> - - -The **ephemerality factor** is usually between 3 or 4 and depends on how frequently the identifiers of the collected metrics change, increasing their -cardinality. The more ephemeral the infrastructure, the more short-lived metrics you have, increasing the ephemerality factor. If the metric cardinality is -extremely high due for example to a lot of extremely short lived containers (hundreds started every minute), the ephemerality factor can be much higher than 4. -In such cases, we recommend splitting the load across multiple Netdata parents, until we can provide a way to lower the metric cardinality, -by aggregating similar metrics. - -#### Small agent RAM usage - -For 2000 metrics (dimensions) in 3 storage tiers and the default cache size: - -``` -DBENGINE memory for 2k metrics = 2000 x (3 - 1) x 8 / 1024 MiB = 32 MiB -dbengine page cache size MB = 32 MiB -Total Netdata memory in MiB = 3*32 + 32 = 128 MiB (low ephemerality) -``` - -#### Large parent RAM usage - -The Netdata parent in our production infrastructure at the time of writing: - - Collects 206k metrics per second, most from children streaming data - - The metrics include moderately ephemeral Kubernetes containers, leading to an ephemerality factor of about 4 - - 3 tiers are used for retention - - The `dbengine page cache size MB` in `netdata.conf` is configured to be 4GB - -Netdata parents can end up collecting millions of metrics per second. See also [scaling dedicated parent nodes](#scaling-dedicated-parent-nodes). - -The rule of thumb calculation for this set up gives us -``` -DBENGINE memory = 206,000 x 16 / 1024 MiB = 3,217 MiB = about 3 GiB -Extra cache = 4 GiB -Metric ephemerality factor = 4 -Estimated total Netdata memory = 3 * 4 + 4 = 16 GiB -``` - -The actual measurement during a low usage time was the following: - -Purpose|RAM|Note -:--- | ---: | :--- -DBENGINE usage | 5.9 GiB | Out of 7GB max -Cardinality/ephemerality related memory (k8s contexts, labels, strings) | 3.4 GiB -Buffer for queries | 0 GiB | Out of 0.5 GiB max, when heavily queried -Other | 0.5 GiB | -System overhead | 4.4 GiB | Calculated by subtracting all of the above from the total -**Total Netdata memory usage** | 14.2 GiB | - -All the figures above except for the system memory management overhead were retrieved from Netdata itself. -The overhead can't be directly calculated, so we subtracted all the other figures from the total Netdata memory usage to get it. -This overhead is usually around 50% of the memory actually useable by Netdata, but could range from 20% in small -setups, all the way to 100% in some edge cases. - -## Configure metric retention - -Once you have decided how to size each tier, open `netdata.conf` with -[`edit-config`](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/configure/nodes.md#use-edit-config-to-edit-configuration-files) -and make your changes in the `[db]` subsection. - -Save the file and restart the Agent with `sudo systemctl restart netdata`, or -the [appropriate method](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/README.md#maintaining-a-netdata-agent-installation) -for your system, to change the database engine's size. - -## Scaling dedicated parent nodes - -When you use streaming in medium to large infrastructures, you can have potentially millions of metrics per second reaching each parent node. -In the lab we have reliably collected 1 million metrics/sec with 16cores and 32GB RAM. - -Our suggestion for scaling parents is to have them running on dedicated VMs, using a maximum of 50% of cpu, and ensuring you have enough RAM -for the desired retention. When your infrastructure can lead a parent to exceed these characteristics, split the load to multiple parents that -do not communicate with each other. With each child sending data to only one of the parents, you can still have replication, high availability, -and infrastructure level observability via the Netdata Cloud UI. - -## Legacy configuration - -### v1.35.1 and prior - -These versions of the Agent do not support tiers. You could change the metric retention for the parent and -all of its children only with the `dbengine multihost disk space MB` setting. This setting accounts the space allocation -for the parent node and all of its children. - -To configure the database engine, look for the `page cache size MB` and `dbengine multihost disk space MB` settings in -the `[db]` section of your `netdata.conf`. - -```conf -[db] - dbengine page cache size MB = 32 - dbengine multihost disk space MB = 256 -``` - -### v1.23.2 and prior - -_For Netdata Agents earlier than v1.23.2_, the Agent on the parent node uses one dbengine instance for itself, and another instance for every child node it receives metrics from. If you had four streaming nodes, you would have five instances in total (`1 parent + 4 child nodes = 5 instances`). - -The Agent allocates resources for each instance separately using the `dbengine disk space MB` (**deprecated**) setting. If `dbengine disk space MB`(**deprecated**) is set to the default `256`, each instance is given 256 MiB in disk space, which means the total disk space required to store all instances is, roughly, `256 MiB * 1 parent * 4 child nodes = 1280 MiB`. - -#### Backward compatibility - -All existing metrics belonging to child nodes are automatically converted to legacy dbengine instances and the localhost -metrics are transferred to the multihost dbengine instance. - -All new child nodes are automatically transferred to the multihost dbengine instance and share its page cache and disk -space. If you want to migrate a child node from its legacy dbengine instance to the multihost dbengine instance, you -must delete the instance's directory, which is located in `/var/cache/netdata/MACHINE_GUID/dbengine`, after stopping the -Agent. diff --git a/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md b/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md index f86096d45..ee76d40ff 100644 --- a/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md +++ b/docs/top-monitoring-netdata-functions.md @@ -1,78 +1,51 @@ -<!-- -title: "Netdata Functions" -sidebar_label: "Netdata Functions" -custom_edit_url: "https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/netdata-functions.md" -sidebar_position: "2800" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Concepts" -learn_rel_path: "Concepts" -learn_docs_purpose: "Present the Netdata Functions what these are and why they should be used." ---> - -# Netdata Functions +# Top Monitoring (Netdata Functions) Netdata Agent collectors are able to expose functions that can be executed in run-time and on-demand. These will be -executed on the node - host where the function is made -available. +executed on the node/host where the function is made available. -#### What is a function? +## What is a function? -Collectors besides the metric collection, storing, and/or streaming work are capable of executing specific routines on -request. These routines will bring additional information -to help you troubleshoot or even trigger some action to happen on the node itself. +Collectors besides the metric collection, storing, and/or streaming work are capable of executing specific routines on request. These routines will bring additional information to help you troubleshoot or even trigger some action to happen on the node itself. -A function is a `key` - `value` pair. The `key` uniquely identifies the function within a node. The `value` is a -function (i.e. code) to be run by a data collector when -the function is invoked. +For more details please check out documentation on how we use our internal collector to get this from the first collector that exposes functions - [plugins.d](/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md#function). -For more details please check out documentation on how we use our internal collector to get this from the first collector that exposes -functions - [plugins.d](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md#function). +## Prerequisites -#### What functions are currently available? +The following is required to be able to run Functions from Netdata Cloud. -| Function | Description | Alternative to CLI tools | Require Cloud | plugin - module | -|:-------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------|:--------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +- At least one of the nodes claimed to your Space should be on a Netdata agent version higher than `v1.37.1` +- Ensure that the node has the collector that exposes the function you want enabled + +## What functions are currently available? + +| Function | Description | Alternative to CLI tools | Require Cloud | plugin - module | +|:-------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------|:--------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | Block-devices | Disk I/O activity for all block devices, offering insights into both data transfer volume and operation performance. | `iostat` | no | [proc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/proc.plugin#readme) | | Containers-vms | Insights into the resource utilization of containers and QEMU virtual machines: CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network traffic. | `docker stats`, `systemd-cgtop` | no | [cgroups](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin#readme) | | Ipmi-sensors | Readings and status of IPMI sensors. | `ipmi-sensors` | no | [freeipmi](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/freeipmi.plugin#readme) | | Mount-points | Disk usage for each mount point, including used and available space, both in terms of percentage and actual bytes, as well as used and available inode counts. | `df` | no | [diskspace](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/diskspace.plugin#readme) | | Network-interfaces | Network traffic, packet drop rates, interface states, MTU, speed, and duplex mode for all network interfaces. | `bmon`, `bwm-ng` | no | [proc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/proc.plugin#readme) | -| Processes | Real-time information about the system's resource usage, including CPU utilization, memory consumption, and disk IO for every running process. | `top`, `htop` | yes | [apps](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md) | +| Processes | Real-time information about the system's resource usage, including CPU utilization, memory consumption, and disk IO for every running process. | `top`, `htop` | yes | [apps](/src/collectors/apps.plugin/README.md) | | Systemd-journal | Viewing, exploring and analyzing systemd journal logs. | `journalctl` | yes | [systemd-journal](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin#readme) | | Systemd-list-units | Information about all systemd units, including their active state, description, whether or not they are enabled, and more. | `systemctl list-units` | yes | [systemd-journal](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/systemd-journal.plugin#readme) | | Systemd-services | System resource utilization for all running systemd services: CPU, memory, and disk IO. | `systemd-cgtop` | no | [cgroups](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/tree/master/src/collectors/cgroups.plugin#readme) | -| Streaming | Comprehensive overview of all Netdata children instances, offering detailed information about their status, replication completion time, and many more. | | yes | | - - -If you have ideas or requests for other functions: -* Participate in the relevant [GitHub discussion](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/discussions/14412) -* Open a [feature request](https://github.com/netdata/netdata-cloud/issues/new?assignees=&labels=feature+request%2Cneeds+triage&template=FEAT_REQUEST.yml&title=%5BFeat%5D%3A+) on Netdata Cloud repo -* Join the Netdata community on [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/mPZ6WZKKG2) and let us know. +| Streaming | Comprehensive overview of all Netdata children instances, offering detailed information about their status, replication completion time, and many more. | | yes | | +| Netdata-api-calls | Real-time tracing of API calls made to the Netdata Agent. It provides information on query, source, status, elapsed time, and more. | | yes | | -#### How do functions work with streaming? +## How do functions work with streaming? -Via streaming, the definitions of functions are transmitted to a parent node, so it knows all the functions available on -any children connected to it. +Via streaming, the definitions of functions are transmitted to a parent node, so it knows all the functions available on any children connected to it. If the parent node is the one connected to Netdata Cloud it is capable of triggering the call to the respective children node to run the function. -If the parent node is the one connected to Netdata Cloud it is capable of triggering the call to the respective children -node to run the function. +## Why are some functions only available on Netdata Cloud? -#### Why are some functions only available on Netdata Cloud? +Since these functions are able to execute routines on the node and due to the potential use cases that they can cover, our concern is to ensure no sensitive information or disruptive actions are exposed through the Agent's API. -Since these functions are able to execute routines on the node and due to the potential use cases that they can cover, our -concern is to ensure no sensitive information or disruptive actions are exposed through the Agent's API. +With the communication between the Netdata Agent and Netdata Cloud being through [ACLK](/src/aclk/README.md) this concern is addressed. -With the communication between the Netdata Agent and Netdata Cloud being -through [ACLK](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/aclk/README.md) this -concern is addressed. +## Feedback -## Related Topics - -### **Related Concepts** - -- [ACLK](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/aclk/README.md) -- [plugins.d](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/src/collectors/plugins.d/README.md) - -### Related Tasks +If you have ideas or requests for other functions: -- [Run-time troubleshooting with Functions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/runtime-troubleshooting-with-functions.md) +- Participate in the relevant [GitHub discussion](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/discussions/14412) +- Open a [feature request](https://github.com/netdata/netdata-cloud/issues/new?assignees=&labels=feature+request%2Cneeds+triage&template=FEAT_REQUEST.yml&title=%5BFeat%5D%3A+) on Netdata Cloud repo +- Join the Netdata community on [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/2mEmfW735j) and let us know. diff --git a/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md b/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md deleted file mode 100644 index 3b1f7fcc5..000000000 --- a/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md +++ /dev/null @@ -1,95 +0,0 @@ -<!-- -title: "See an overview of your infrastructure" -description: "With Netdata Cloud's War Rooms, you can see real-time metrics, from any number of nodes in your infrastructure, in composite charts." -custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/docs/visualize/overview-infrastructure.md -sidebar_label: "See an overview of your infrastructure" -learn_status: "Published" -learn_topic_type: "Tasks" -learn_rel_path: "Operations/Netdata Cloud Visualizations" ---> - -# See an overview of your infrastructure - -In Netdata Cloud, your nodes are organized into War Rooms. One of the two available views for a War Room is the -[**Overview**](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md), which uses composite charts to display -real-time, aggregated metrics from all the nodes (or a filtered selection) in a given War Room. - -With Overview's composite charts, you can see your infrastructure from a single pane of glass, discover trends or -anomalies, then drill down with filtering or single-node dashboards to see more. In the screenshot below, -each chart visualizes average or sum metrics values from across 5 distributed nodes. - -Netdata also supports robust Kubernetes monitoring using the Overview. Read our [deployment -doc](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/packaging/installer/methods/kubernetes.md) for details on visualizing Kubernetes metrics in Netdata Cloud. - - - -## Using the Overview - -The Overview uses roughly the same interface as local Agent dashboards or single-node dashboards in Netdata Cloud. By -showing all available metrics from all your nodes in a single interface, Netdata Cloud helps you visualize the overall -health of your infrastructure. Best of all, you don't have to worry about creating your own dashboards just to get -started with infrastructure monitoring. - -Let's walk through some examples of using the Overview to monitor and troubleshoot your infrastructure. - -### Filter nodes and pick relevant times - -While not exclusive to Overview, you can use two important features, [node -filtering](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/node-filter.md) and the [time & date -picker](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/dashboard/visualization-date-and-time-controls.md), to widen or narrow your infrastructure -monitoring focus. - -By default, the Overview shows composite charts aggregated from every node in the War Room, but you can change that -behavior on an ad-hoc basis. The node filter allows you to create complex queries against your infrastructure based on -the name, OS, or services running on nodes. For example, use `(name contains aws AND os contains ubuntu) OR services == -apache` to show only nodes that have `aws` in the hostname and are Ubuntu-based, or any nodes that have an Apache -webserver running on them. - -The time & date picker helps you visualize both small and large timeframes depending on your goals, whether that's -establishing a baseline of infrastructure performance or targeted root cause analysis of a specific anomaly. - -For example, use the **Quick Selector** options to pick the 12-hour option first thing in the morning to check your -infrastructure for any odd behavior overnight. Use the 7-day option to observe trends between various days of the week. - -See the [War Rooms](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/manage/organize-your-infrastrucutre-invite-your-team.md#netdata-cloud-war-rooms) docs for more details on both features. - -### Configure composite charts to identify problems - -Let's say you notice a sharp decrease in available RAM for applications, as seen in the example screenshot below. In -this situation, you can see when the anomalous behavior began and that it affects the average available and committed -RAM across your infrastructure. However, when _grouped by dimension_, composite charts cannot show whether an anomaly -affects a single node, a subset of nodes, or an entire infrastructure. - -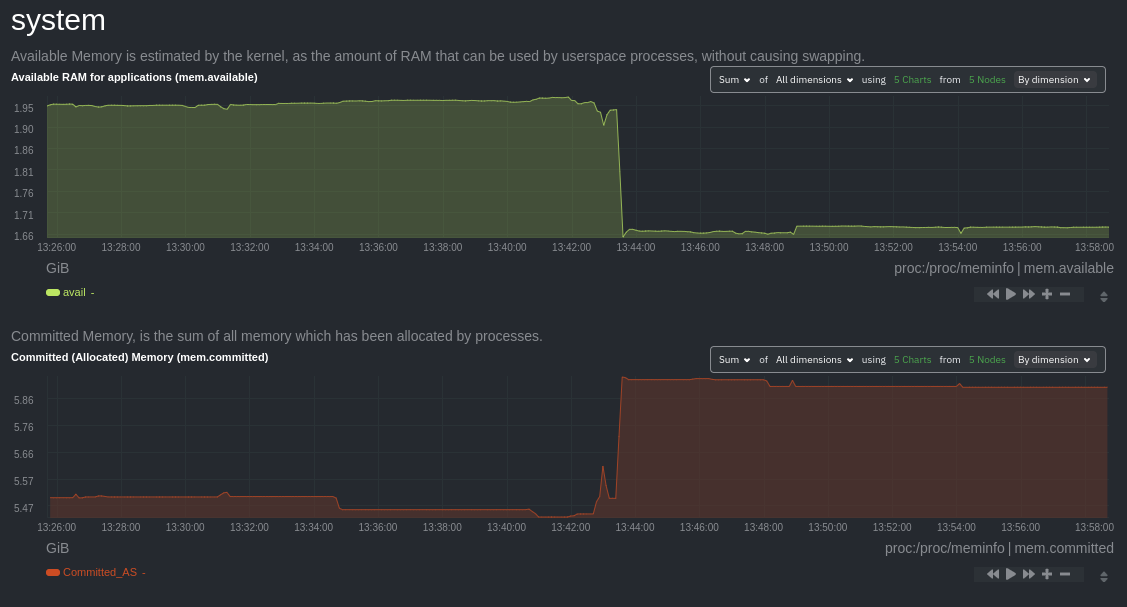 - -Use [_group by node_](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/overview.md#group-by-dimension-or-node) to visualize -a single metric across all contributing nodes. If the composite chart has 5 contributing nodes, there will be 5 -lines/areas, one for the most relevant dimension from each node. - -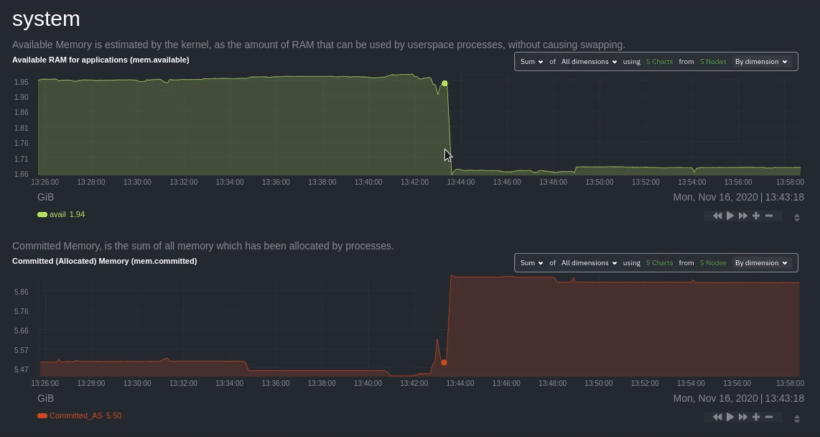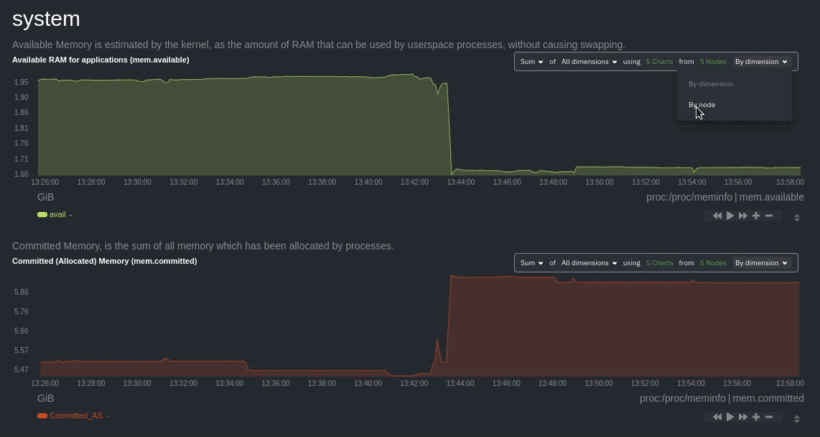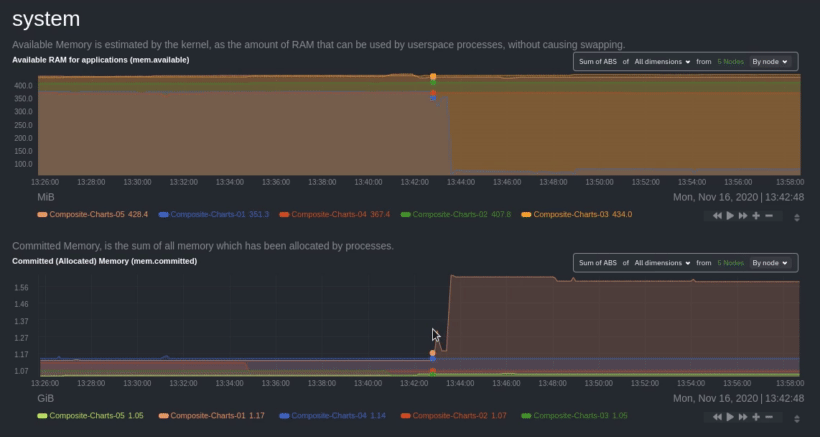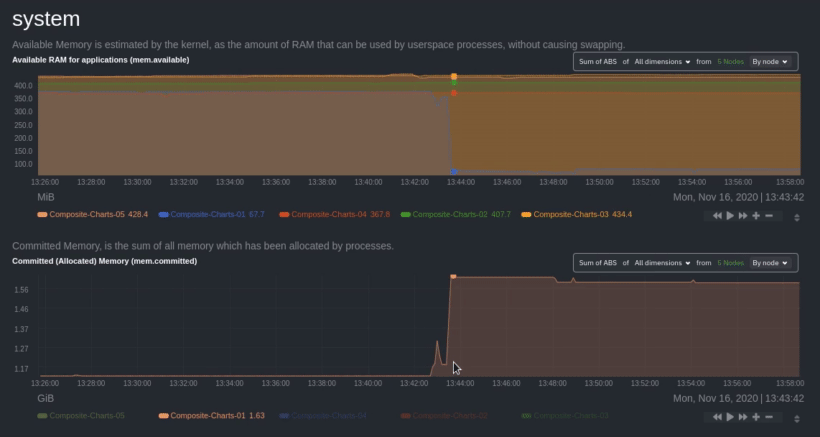 - -After grouping by node, it's clear that the `Composite-Charts-01` node is experiencing anomalous behavior and should be -investigated further by jumping to its [single-node dashboard](#drill-down-with-single-node-dashboards) in Netdata -Cloud. - -### Drill down with single-node dashboards - -Click on **X Charts** of any composite chart's definition bar to display a dropdown of contributing contexts and nodes -contributing. Click on the link icon <img class="img__inline img__inline--link" -src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1153921/95762109-1d219300-0c62-11eb-8daa-9ba509a8e71c.png" /> next to a -given node to quickly _jump to the same chart in that node's single-node dashboard_ in Netdata Cloud. - -You can use single-node dashboards in Netdata Cloud to drill down on specific issues, scrub backward in time to -investigate historical data, and see like metrics presented meaningfully to help you troubleshoot performance problems. -All of the familiar [interactions](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/interact-new-charts.md) are available, as is adding any chart -to a [new dashboard](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/dashboards.md). - -## Nodes tab - -You can also use the **Nodes tab** to monitor the health status and user-configurable key metrics from multiple nodes -in a War Room. Read the [Nodes tab documentation](https://github.com/netdata/netdata/blob/master/docs/cloud/visualize/nodes.md) for details. - - |
